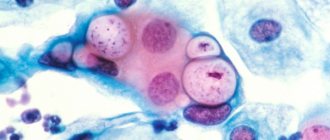
What are coccobacilli
Coccobacilli are bacteria that are similar in appearance to both cocci and bacilli. Cocci look like round microorganisms, and bacilli look like rods. The composition of bacteria is diverse, as they contain many harmful organisms that cause serious diseases.
The most dangerous of them are considered to be Haemophilus influenzae with chlamydia and Gardnerella.
When coccobacillary flora is detected in the analysis, this becomes the reason for diagnosing bacterial vaginitis. In addition, the result data may indicate an STD or vaginal dysbiosis.
Why do coccobacilli appear?
There are many factors influencing the development of this microbial environment. Despite the fact that most often these microorganisms enter the body through lack of hygiene, in some cases, women have become infected with this type of bacteria through the use of antimicrobial drugs.
Their frequent use leads to the development of dysbiosis, which is an excellent opportunity for the development of these microorganisms. Another common reason for their entry into the female body is the development of infections that are transmitted during sexual intercourse.
The main factors that cause the appearance of coccobacilli:
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- wearing synthetic underwear that fits tightly to the body;
- poor hygiene;
- use of panty liners;
- the onset of menopause;
- thyroid diseases;
- the onset of pregnancy;
- use of oral contraceptives;
- supplied spiral;
- when treating any illness, long-term use of antibiotics.
The presented factors at the first stage can be expressed through the development of bacterial vaginitis, but later the lesion occurs in a more serious form, which results in intractable sexually transmitted diseases.
In addition, microbial organisms present from the genitals can enter the woman’s bladder, which causes an inflammatory process. If left untreated, the patient risks developing an inflammatory process in the kidneys.
Coccobacilli can also enter the genital tract due to gastrointestinal disorders. Lack of timely hygiene leads to their entry and reproduction in a beneficial environment.
A little about women's issues
Considering the reasons why the flora norm goes astray, it is worth noting that women have many of them. The first line is usually taken by an active sexual life, which is characterized by changing sexual partners on an ongoing basis, especially if you love sexual intercourse without barrier contraception. All this creates a very high risk of acquiring a disease that is transmitted through unprotected sex.
The norm is also violated when performing vaginal douching. This inevitably disrupts the ratio of healthy microflora. We are talking about the presence of coccobacilli, the appearance of which is responsible for internal factors. Contraceptives can also affect the flora ratio. We are talking about an intrauterine device. If bacterial vaginosis is formed, then usually an abundant flora consisting of coccobacilli is not present, everything is very moderate. Other contraceptives cannot be excluded as risk factors.
We are talking about their oral form. With any hormonal imbalance, pathogenic microflora begins to grow in the female body. Therefore, women taking contraceptive medications need to pay special attention to any discharge and do not forget about how to properly care for their intimate parts.
Treatment of a bacterial infection with antibiotics can also provoke bacterial vaginosis. This risk increases with long-term use of drugs. In this case, special medications are prescribed that help maintain a normal amount of lactobacilli in the body.
Problems affecting the gastrointestinal tract can also affect the condition of the internal genital organs in the female population. The disturbed norm in the intestines affects the pH level of the vagina, and if this is accompanied by immunity, which is weak, and the genital organs of women become noticeably more susceptible to foreign agents.
What does the presence of coccobacilli in a smear mean?
Coccobacillary flora in a smear in women is a factor that makes you think about your own health. If a test test reveals these bacteria, it is necessary to take immediate action, as failure to act will lead to complications.
The microflora of the female body changes, but 90% of it should be occupied by lactobacilli, which protect the body from the penetration of pathogens. The rest, almost 10%, should be occupied by bifidobacteria. The presence of 0.5 or 1% of harmful microorganisms is also allowed. But since their ratio is quite small, they do not threaten women's health.
The presence of coccobacilli in large quantities in the body indicates that the immune system cannot cope with the influx of pathogenic bacteria.
Coccobacillary flora in a smear indicates a weak immune system that cannot cope with bacteria.
Coccobacilli consist of coccal and bacillary floras. The first flora belongs to the opportunistic category. This list includes many microorganisms, some of which are quite dangerous. They can cause damage to the brain, intestines and other organs. These include meningococci and staphylococci.
Less dangerous, but still dangerous, are streptococci and gonococci. Regarding gonococci, it is worth saying that they are causative agents of sexually transmitted diseases. The peculiarity of these microorganisms is their resistance to heat and antibiotics.
The bacillary category of microorganisms contains pathogenic and beneficial microorganisms for the human body. If Dederline rods were detected in the analysis, this is normal. These bacteria contribute to the development of lactic acid, which is necessary for the female body.
This acid allows you to maintain the protective function at a high level, preventing pathogens from entering the genitals.
Small bacillary flora is dangerous, as they may include gram-positive bacteria. These microorganisms prevent a rapid healing process, reduce local immunity and lead to vaginal dysbiosis.
Decoding the results
A smear analysis is usually done over several days, and the results are assessed by a quantitative indicator, that is, by the number of bacilli in the sample.
Single coccobacilli indicate the predominance of beneficial bacteria over pathogenic flora. There is no threat to women's health, everything is fine. The likelihood of developing inflammation or dysbiosis is minimal.
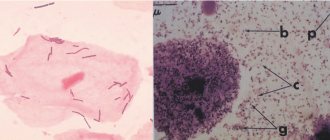
Key cells are squamous epithelial cells containing bacteria from the categories of pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms.
Moderate means that the sample contains from 2 to 8% coccobacilli. It is necessary to take preventive measures to prevent the transition of a moderate number of bacteria to a large number, otherwise the balance of the microflora may be disrupted.
A large number - 50% of the sample and above - are pathogenic microorganisms that suppress “good” bacteria. If their number exceeds half, then there may be no beneficial lactobacilli at all.
Squamous epithelial cells in a smear
With a large number of coccobacilli, there will most likely be characteristic symptoms. The main one is allocation:
- thin and copious;
- white or grayish;
- homogeneous;
- with a pungent unpleasant odor reminiscent of rotten fish.
The amount of discharge may increase before menstruation, after sex or a change of partner. Their character also sometimes changes, and the discharge becomes viscous and viscous, foaming, with a yellow-green tint.
Undifferentiated coccobacilli are unrecognized bacteria whose type has not been reliably determined. In this case, the analysis is performed again.
Gram-variable bacteria are those that combine the properties of gram-positive and gram-negative. Such microflora can be represented by Haemophilus influenzae, Gardnerella, and chlamydia.
Attention! If no pathogenic bacteria are identified, then it is too early to draw conclusions. This result is most likely incorrect and is due to a violation of the smear collection technique. That's why they take him again. But this applies only to women; in men, a complete absence of harmful flora is allowed.
Symptoms of the disease
You need to think about the presence of harmful bacteria and visit a gynecologist when a woman exhibits the following signs:
- feeling of discomfort and constant itching in the genital area;
- pain when urinating;
- the presence of discharge that has a tint of yellow, green or brown;
- the presented discharge is accompanied by an odor reminiscent of rotten fish or sour milk;
- Painful sensations occur during sexual intercourse;
- the external part of the genitals is covered with a whitish coating.
All signs together appear only when an advanced case of the disease is observed. Most often, a patient comes to the doctor with two or three symptoms.
But even if you have one of the presented signs, you should not delay visiting a specialist, since pathogenic microflora has the ability to weaken the immune system. In this case, the body will be more likely to develop diseases.
Is it transmitted sexually?
Sexual transmission of coccobacilli is one of the options for their infection. Those who are sexually promiscuous are more susceptible to infection by bacteria. During sexual intercourse, the entry of sperm into the female body provokes the development of coccobacilli.
Male seminal fluid inhibits the development of beneficial lactobacilli, which prevent the entry of harmful microbes. Coccobacillary flora in a smear means that the body is weaker than bacteria. Therefore, it is necessary to take measures to slow down the process of their further development.
The procedure for preparing for a smear test
If the gynecologist suspects that a woman has coccobacilli, she is prescribed a smear to confirm or refute this fact. But for this you need to prepare, since the coccobacillary flora in the smear is a type of harmful microorganisms that require compliance with certain rules for the purity of the result.
Such preparation includes the following steps:
- before going to the hospital, you should wash your genitals with water without gels for intimate hygiene, as well as soap, as they can disrupt the microflora;
- refrain from having sex for 2-3 days before taking tests;
- stop douching for a while;
- do not go to the sauna or bathhouse the day before going to the doctor;
- stop taking medications.
If all conditions are met, then the result will be more accurate. If the rules are violated, a woman may receive an incorrect diagnosis and incorrect treatment, which will lead nowhere.
Reasons for violations
Changes in vaginal microbiocenosis can occur under the influence of various factors. The main reasons are:
- excessive use of intimate hygiene products, douching without a doctor’s prescription;
- violation of the rules of sexual hygiene, improper alternation of different types of sex within one sexual act;
- unfavorable social and living conditions;
- antibiotic treatment;
- immunosuppressive or hormonal therapy;
- intrauterine contraceptives;
- neuroendocrine diseases and ovarian dysfunction;
- extragenital infections;
- surgical interventions;
- condition after radiation therapy.
Bacterial vaginosis is regarded as an imbalance of microflora (dysbiosis) and is not considered an infection. However, against this background, there is a significant decrease in the number of lactobacilli and their replacement by other microorganisms.
Among the large number of factors that provoke bacterial vaginosis, the first place is still occupied by hormonal disorders. The connection with diseases of the digestive tract and urinary system is not denied. Sometimes the exact cause of such violations cannot be determined.
How is a smear taken?
Taking an analysis to check for the presence of microorganisms involves scraping mucus from the wall of the internal genital organs. This happens in a gynecological chair, using a special spatula or cotton swab. The results taken are ground on a small piece of sterile glass.
To ensure the reliability of the result, or to suspect other bacterial developments, a smear is taken not only from the vagina, but also from the urethra, as well as the cervix. If a woman is completely healthy, she should not have coccobacilli. If coccobacillary flora is suspected, an analysis is also taken in men, but it happens differently.
Coccobacillary flora in men
Most often, coccobacilli are found in women, but men can also have such health problems. The microflora of male genital organs differs from female ones, therefore tests are taken in a different way. The smear is taken using a swab that penetrates the urethra to a depth of approximately 3 cm.
The procedure, unlike the female one, is quite unpleasant and, for some, painful.
After it is carried out, the man does not lose the feeling of burning, pain and stinging in the urethra for some time. Coccobacillary flora in a smear always indicates the presence of harmful bacteria in the body. According to the results of the analysis, a representative of the stronger sex may be found to have gonococci with streptococci, as well as other harmful bacteria.
Before getting tested, men should adhere to the following recommendations:
- do not have intimacy for 2-3 days;
- wash well the day before the procedure;
- do not wash before taking tests;
- going to the toilet before taking a smear is prohibited;
- stop taking antibacterial drugs.
Features of delivery
To determine such gram-variable microflora, it is recommended not to neglect the smear. Deviations can be detected through examination under a microscope or of a bacteriological nature. Proper preparation for the analysis is important for real results to be demonstrated. All recommendations are not difficult.
The flora norm may change due to sexual intercourse. Therefore, two days before the expected delivery, it is important to exclude sex. A smear test is recommended for women in the middle of their cycle. Douching should be avoided at least a week before the proposed test.
Any procedures that involve warming up the body should be excluded. We are talking about a hot bath, steam bath and sauna. To prevent false results from flora tests, it is important to refrain from using any vaginal products aimed at treating a particular problem. If cancellation is not possible or was recently carried out, it is important to inform the doctor who is treating you.
Types of infection in a smear
Coccobacillary flora in a smear is a rather broad concept that implies the presence of various bacteria related to cocci and bacilli.
For example:
- streptococci detected during testing may not plunge the owner into shock, since a small amount of them in the body is acceptable, and their excess can cause vaginal dysbiosis or inflammation;
- the found enterococci indicate an insufficient level of hygiene, since they multiply to a greater extent in the intestinal system;
- gonococci lead to cervicitis and salpingitis, as well as to STDs;
- diplococci are more serious bacteria, the reproduction of which can lead to meningococcal infections and pneumococci;
- Staphylococcus most often does not manifest itself in any way and does not cause any inconvenience, but their active development causes disorders of the genitourinary organs.
In addition, chlamydia, Haemophilus influenzae, and Gardenerella can be detected in the body.
Norm and deviations - indicators
Harmful bacteria in a woman’s body can be in different quantities.
The pH value determines how many pathogenic organisms are in the female reproductive system:
- pH 5;
- pH from 5 to 7;
- pH 7 to 7.5.
The first indicator indicates an acidic environment, the second is neutral, and the third indicates an alkaline environment, which is not normal for the female body. The higher the alkalinity, the higher the level of harmful bacteria.
In normal conditions, the environment is acidic, which is created by lactobacilli. Their level decreases when the development of coccobacillary flora is observed in the body.
A high alkalinity indicator indicates an incipient inflammatory process or vaginal dysbiosis. A long-term inflammatory process can result in erosion or endometritis, which can lead to further infertility.
Vaginal dysbiosis in pregnant women
Carrying a baby can be overshadowed by the active reproduction of coccobacillary flora. Hormonal changes and a weakened immune system can lead to this, because pregnancy is a strong burden for the female body.
If coccobacilli are found in the analysis of the microflora of a pregnant woman, urgent measures must be taken. After all, this is not only discomfort for the expectant mother, but also possible quite serious complications for her and the unborn baby. Vaginosis, for example, can lead to a uterine infection. It can result in premature birth, infection of the newborn while passing through the birth canal, as well as his low birth weight. Therefore, the gynecologist tries to quickly prescribe treatment that is not contraindicated for the fetus.
Additional diagnostic methods
In addition to a smear, which is taken from the vagina and cervix, there are additional diagnostic methods that help confirm or refute the assumption.
They are as follows:
- one of the methods includes colposcopy, which is used for a detailed examination of the inside of the genital organs, to assess the condition of the mucous membrane;
- the next option is ultrasound of organs related to the pelvis;
- PCR diagnostics, through which it is possible to determine who is the causative agent of the patient’s illness;
After all analysis methods have been carried out, the specialist will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Chlamydia and its symptoms
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted disease that occurs in women with virtually no symptoms. However, it is precisely this that can cause infertility and ectopic pregnancy, since the activity of chlamydia provokes inflammation and adhesions in the fallopian tubes. But the greatest danger threatens the fetus if a woman becomes infected during gestation.
Chlamydia occupies a leading position in the list of sexually transmitted infections
With chlamydia, the fertilized egg cannot attach to the uterus, despite conception having occurred. But even if this is successful, the egg develops incorrectly and spontaneous abortion occurs.
An even greater danger is posed by chlamydia, which worsens at the beginning of the first trimester of pregnancy. In this case, the child may have neural tube defects. After 20 weeks, the infection is fraught with intrauterine infection of the fetus, the birth of a premature baby, and acute endometritis in the mother.
Chlamydia is transmitted primarily through sexual contact, and can also pass from mother to fetus during natural childbirth. Presumably, infection is possible through household contact, since these microbes remain viable on different surfaces for about 2 days. However, this has not yet been clinically proven.
Chlamydia is usually not a problem, and its symptoms often go unnoticed. It can manifest as scanty discharge mixed with mucus and pus. There is no pain, burning or itching.
Help: The inflammatory process develops in the cervix and cervical canal, which the gynecologist will immediately see during examination.
Drug treatment of infection
The most effective and common treatment option for coccobacillary flora is drug intervention.
Treatment occurs in 3 stages, and at each of them, the specialist prescribes his own medications:
- Destroying harmful bacteria. Antibiotics and antiseptics are prescribed.
- Colonization with the necessary microflora by taking medications with lactobacilli.
- Restoration and strengthening of local immunity and the immune system as a whole.
Metronidazole, Ceftriaxone, Terzhinal with Amoxiclav are prescribed at the first stage. The course of drug treatment is 7-10 days, the dosage is prescribed by the attending physician, depending on the situation. Cetriaxone in the form of intramuscular injections is prescribed when gonococci and chlamydia are detected. Terzhinan is produced in the form of suppositories, and they are used for dysbacteriosis.
The second stage is aimed at restoring normal acidic microflora with the help of Vagilac, Acylact, and Vaginorm-S. In addition to tablets, tampons are prescribed, which must be soaked in Lactobacterin and Bifidumbacterin. This stage lasts two weeks.
The third stage lasts 10-14 days and its goal is to renew the immune system. For this purpose, Wobenzym is prescribed in the form of tablets, Interferon in the form of injections, as well as Viferon with Genferon.
Treatment of coccobacillary flora during pregnancy
An equally common situation is the detection of coccobacillary flora in a pregnant woman. The reason is that during pregnancy, a woman’s body is more weakened and therefore there is a risk of various types of infectious diseases. If you ignore the infection, it can spread to the child, and also lead to serious diseases of the female reproductive system.
Treatment of a pregnant woman also occurs in 3 stages, only in this case other, more gentle drugs are used.
The course of treatment begins with taking antimicrobial drugs. More often these are preparations for external use, such as gels or suppositories (Klacid, Metronidazole). The second stage includes saturation with lactic acid bacteria, which restore the microflora. These may be tampons with Lactobactorin.
The third stage includes taking medications that help the immune system recover after the infection develops. This includes Complivit mom with Elevit, as well as Bifiform with Linex.
Interpretation of the study
If the tests mention the presence of coccal flora, this may be a signal of the presence of sexually transmitted diseases in the body. In addition, other diseases that are not associated with sexually transmitted diseases cannot be ruled out.
An option could be an endocrine disorder, a weakened immune system due to allergies or due to the use of antibiotics, which have a strong effect on the entire body as a whole. Against the background of such factors, the coccal flora begins to develop very quickly.
It is worth emphasizing right away that the presence of cocci in itself in the flora in a man’s analysis is not a sign of pathology if their number is minimal. In this case, there is no threat to health. This is a kind of variant of the flora norm. However, sometimes in this case, if a man neglects personal hygiene or his immunity is weakened, intensive growth of the corresponding microorganisms can be provoked. The result of their extensive activity will be inflammatory processes that negatively affect well-being and flora.
The danger of cocci as a flora for men and women lies in the fact that diseases often occur latently, that is, without manifesting themselves in any way, this creates situations where a person does not suspect that he is a carrier, and, accordingly, a carrier of various kinds of diseases .
Diet
During treatment, to obtain more effective results, it is worth adjusting your own diet. It is worth excluding spicy foods and pickles, and dishes with a high fat content. Alcohol must be completely excluded, especially since medications cannot be combined with alcoholic beverages.
Instead of these products, the diet is filled with compotes of fruits and berries, natural juices, and dairy products.
In another, there are no restrictions on food consumption. It is better to practice the presented diet option after completing the course to avoid the risk of relapse of the disease.
Coccobacillary flora in a smear is a rather unpleasant discovery not only for a woman, but also for a man. The reason is that it is quite easy to become infected with these bacteria, but you have to undergo treatment for at least a month. Moreover, relapses are possible in people with weakened immune systems. Therefore, if you observe even single symptoms, you should consult a specialist.
Author of the article: Svetlana Zabula
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky