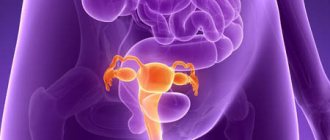
Cold appendages (adnexitis) is a pathological condition of ovarian tissue, which is accompanied by acute or chronic inflammation. In women, this disease manifests itself as the most common symptom in the form of attacks of spasmodic pain, which is localized in the lower abdomen.
The main danger of this disease is the high probability of developing dangerous complications. The most severe consequence of hypothermia of the appendages is a destructive change in the tissue structure of the ovaries, as well as loss of the possibility of childbearing.
Symptoms of cold appendages in women have a local manifestation, when a feeling of discomfort, pain, affects only that part of the body where the diseased ovaries are located. Advanced forms of adnexitis are characterized by the presence of a large number of signs of a pathological condition of the organs of the reproductive system.
In this case, the pain syndrome extends not only to the lower abdomen, but also affects the lumbar spine and is felt in the central part of the abdominal cavity. In addition to the discomfort, various menstrual cycle disorders occur.
What are these appendages in women?
In gynecology, several organs and tissues are considered appendages: ovaries, tubes and ligaments. They are small in size, but can cause many problems with the health of the reproductive system. This can happen if the inflammatory processes affecting these tissues are not treated in time. Since they belong to the organs of the reproductive system, they are located close to the uterus.
Where are they located?
The epididymis is located between the ovary and the end of the fallopian tube. It is possible to determine their location even more precisely: between the peritoneum of the uterus (its widest part) and the ovary, the end of the tube. This wide part of the uterus with its adjacent organs is susceptible to various diseases. Most often this is inflammation of the appendages in women. We will consider the symptoms and treatment of this disease below. The appendage tubes are on average 10-12 cm, physiologically the right one is longer than the left one. These organs are also divided into specific departments, each of which performs its own functions.
What functions do appendages perform?
The fallopian tubes have several sections that help transport the ovulated egg. This process occurs due to the physiological characteristics of this organ - the presence of fimbriae. These are irregularly shaped processes that constantly work like sweeping, they never stop, carrying the egg into the next part of the pipe - the funnel. The fallopian tubes “see off” not only the fertilized egg, this process occurs monthly. On this way, she can meet a sperm and become fertilized. Not only do the fimbriae help push the egg, but the muscular layer of the tubes also does this. If these appendages are damaged despite the muscles working, an ectopic pregnancy can occur. It occurs during a long-term inflammatory process of the tubes. Therefore, as soon as the first symptoms of inflammation of the female appendages appear, it is necessary to immediately contact a specialist. Prolonged illness can subsequently lead to pipe rupture.
The next component organ of the appendages is the ovaries. This is a paired organ of a woman, which is located on the surface of the posterior layer of the broad ligament of the uterus. Thanks to this arrangement, the ovaries perform the functions of the sex gland. They are connected to the uterus by special ligaments, which are also called “appendages”. In women, the ovaries play a very important role for the full functioning of the body. They relate to both the endocrine organs and the reproductive system. They are vital for reproduction, since it is in them that the eggs begin their life and then mature to a certain point. They take part in the work of the endocrine system by producing sex hormones.
If there is a disruption in the functioning of the ovaries, they are able to produce hormones, but not in the required quantity and ratio. Such a pathological process can be caused by many disorders, but also by inflammation. Therefore, if inflammation of the appendages occurs in women, immediate treatment is required. After all, a serious hormonal imbalance in the body can occur.
Causes of inflammation of the tubes and ovaries
The appendages in women are the ovaries, tubes and ligaments. Inflammation can be caused by various pathogens, including those that cause sexually transmitted diseases. The Latin name for the disease is “adnexitis”, and in Greek it sounds like “salpingoophoritis”.
- The infection can enter the appendages through the vagina. And from there they penetrate into the cervical canal, then into the uterus itself, after which they end up in the tubes and ovaries. This is an ascending route of infection.
- Sometimes pathogens can enter from the urinary tract and rectum. This route of entry of pathogens is called secondary.
- The descending path of inflammatory processes in the appendages is rare. With such an infection, pathogenic bacteria have already affected some tissues of the internal organs (for example, the appendix), then spreading to healthy tissues below - the fallopian tubes, ovaries, ligaments.
- In very rare cases, the source of infection can be spread by body fluids - blood and lymph. These liquids themselves are sterile, and normally they cannot contain pathogenic microbes. If they get there, then this most often indicates blood poisoning, that is, sepsis.
Medical abortions can lead to inflammatory processes, including in the appendages. They disrupt hormonal levels in the body, weaken the immune system and can lead to infection of the genital tract.
As for hypothermia, they, of course, should be avoided, although they themselves cannot cause illness. But they significantly weaken the immune system and can activate infectious agents “dormant” in our body. Therefore, you need to dress according to the weather and strengthen your immune system, because treating appendages in women is a difficult and lengthy process.
In addition to physiological causes of the disease, a large percentage are psychological. This is nervous overstrain in a chronic form. After all, a modern woman is busy with work, career, financial support for children, compliance with social status, relationships with her husband and other problems. Experiences weaken the immune system, and any stress factor can already lead to inflammation of the appendages.
Unclaimed sexuality can lead to a disease that will require immediate treatment for inflammation of the appendages in women. During sexual intercourse, among other things, massage of the internal genital organs occurs. Blood flow and nutrition of tissues and cells improves. Therefore, sexual intercourse is useful not only for emotional relief, but also for the prevention of inflammation of the appendages.
Also, pathological processes in the tubes and ovaries can cause hormonal disorders in a woman’s body. Such disruptions lead to changes in the menstrual cycle. As a result, excess fluid accumulates in the appendages and cysts form. This naturally affects the woman’s condition, and can even lead to surgery.
Causes
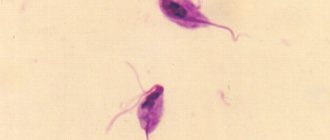
In most cases, the causative agents of the pathological process are such dangerous microorganisms as:
- coli;
- streptococci (group B);
- gonococci;
- Trichomonas;
- Staphylococcus aureus.
In addition, predisposing factors for the disease are:
- infectious diseases of the urinary and reproductive system;
- hypothermia;
- weakened immune system;
- surgical intervention (curettage of the uterine cavity or abdominal surgery);
- varicose veins in this area, causing blood stagnation and the spread of infection;
- the use of medications that have a strong effect on the immune system and flora of the female body;
- long-term use of an intrauterine contraceptive without replacement.
Inflammation of the appendages can be one or two-sided. Symptoms rarely disappear on their own, and in order to avoid the occurrence of even more serious processes, it is recommended not to delay visiting a doctor.
If local pathology is accompanied by tissue infiltration and extensive edema, there is a risk of progression of peritonitis or abscesses.
When the fallopian tube is destroyed, the peritoneum is involved in the process.
What diseases cause pain in the appendage area?
Discomfort in the area where the fallopian tubes and ovaries are located, pain and severe sensations may indicate pathological processes not only in them, but also in nearby organs. This is dangerous because such diseases can lead to infertility and damage to the entire reproductive system.
So, if you feel pain in the appendages, this may indicate the development of the following diseases:
- Adnexitis is inflammation of the uterus and ovaries. This disease is dangerous because it cannot be detected immediately. In most cases it occurs without specific symptoms. Over time, the disease progresses, leading to infertility.
- Various difficult living conditions can also cause pain in the appendage area. These are obesity, diabetes, constant stress, colds. In themselves, these phenomena do not relate to the reproductive system, especially to the ovaries or fallopian tubes. But they can provoke a sharp decrease in immunity, which entails the occurrence of pathologies in a woman’s reproductive function.
The first sign indicating a malfunction in the appendages is a malfunction and disruption of the menstrual cycle. In this case, it is better to consult a specialist for advice.
Kinds
The species classification of the painful condition of the appendages, which were cold as a result of severe hypothermia of the body, is carried out according to the form of the disease.
Acute adnexitis
The acute form of adnexitis is characterized by the presence of intense symptoms, which manifest themselves in the first 2-3 days after the appendages have become cold. The first signs of this type of disease are attacks of severe pain in the lower abdomen, a rapid increase in body temperature, and the presence of atypical discharge from the vaginal cavity.
Women with signs of acute adnexitis should be immediately hospitalized in the gynecological department. Self-treatment is unacceptable, as it risks the disease passing into a latent state with repeated exacerbation after the slightest decrease in immunity.
Chronic adnexitis
This form of painful condition of the appendages is characterized by low-grade inflammation of the ovaries. Over a long period of time, a woman may not feel any signs of pathology, or the symptoms present are insignificant. During the off-season, during an acute respiratory viral infection, as well as another hypothermia of the body, another exacerbation of adnexitis occurs.
Symptoms in women when she has a cold in her appendages are always accompanied by pain
Chronic inflammation of cold appendages is much more dangerous than the acute form of this disease. This is due to the fact that the latent course of the disease leads to atrophic changes in ovarian tissue with further loss of their reproductive function. The most striking sign of chronic adnexitis is an unstable menstrual cycle.
Signs of inflammation of the appendages in a woman
The disease begins acutely. A woman is primarily concerned about sharp pain in the lower abdomen. The most common symptoms of inflammation of the appendages in women are discharge from the genital tract, most often yellow or greenish, mucous, and profuse.
The pain may radiate to the rectum and intensify with urination and defecation. The temperature remains at 37.2-37.8 degrees Celsius.
If you do not go to a medical facility and do not undergo adequate treatment for inflammation of the appendages, women's temperature can reach 39-40 degrees Celsius. There may also be stool disorders, vomiting, and nausea, which occur due to intoxication. At high temperatures, the patient may shiver.
What complications of inflammation can occur?
Basically, the disease is complicated by a chronic course. If the disease develops into such a form, which occurs when inflammation is not treated, the doctor’s prescriptions are not followed, or the individual characteristics of the body, then periods of exacerbations are replaced by remissions. Exacerbations can take place in an erased form, when a serious deterioration of the condition does not occur.
Hormonal imbalances are also often observed, which lead to decreased libido, mastopathy, menstrual irregularities and the occurrence of tumors.
Suppuration may occur in the fallopian tubes, which sometimes leads to inflammation of the peritoneum or peritonitis. This requires surgical intervention. Conservative medical treatments will no longer help here.
Against the background of frequent inflammation, adhesions of the appendages can form, leading to infertility. And if pregnancy does occur, there may be early miscarriages and infection of the fetus. Therefore, as soon as the first signs of inflammation of the appendages appear in a woman, she needs to go to a medical institution and receive serious treatment. There may be spontaneous miscarriages, and even with a normal pregnancy, births occur prematurely.
But don't panic in advance. If you seek help from a specialist in time, you can avoid all the above problems and carry and give birth to a healthy baby.
Medicines
If you have been diagnosed with inflammation of the appendages, then treatment should begin immediately, plus adhere to complex therapy. Most often, specialists prescribe medications, physiotherapy, gynecological massage and osteopathy.
Antibiotics play a fairly important role in treatment. There are a huge number of them in the modern world, but the correct selection is made taking into account the widest possible range of actions and at the same time with a fairly fast half-life.
Do not under any circumstances start the disease, as in a short period of time it can become chronic, which can subsequently lead to infertility. Among the most common antibiotics, it is worth highlighting the following: Amoxiclav, Ceftriaxone, Erythromycin, Metronizadol and others.
There are cases when two drugs are prescribed at the same time. To obtain maximum effectiveness, the antibiotic should be administered as an injection for the first few days, and then you can switch to taking tablets.
We recommend reading: Causes of varicocele in men and boys - all treatment methods
In order to reduce pain, reduce body temperature and swelling, anti-inflammatory suppositories can be prescribed. In addition, they can help the body get rid of harmful substances.
Diagnosis of inflammation of the appendages
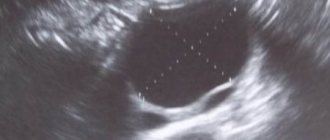
It is not always easy to diagnose “inflammation of the appendages.” In women, the symptoms and treatment of this disease are certainly interrelated. But signs alone are not enough. Your doctor may order a blood test. A woman with symptoms of inflammation of the appendages is prescribed microscopy of vaginal smears. This is a regular gynecological smear and bacteriological examination of biomaterial from the vagina to determine sensitivity to antibiotics. In addition, ultrasound is informative for specialists. Based on all this data, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
But other diseases can have similar symptoms. For example, adnexal cyst. In women, the disease should also be differentiated from appendicitis, renal colic, ectopic pregnancy, and malignant processes in the pelvis.
Hysterosalpygography
In modern conditions, the method of hysterosalpygography allows identifying inflammation of the appendages. This method, used to establish the diagnosis of chronic andexitis, is an x-ray of the appendages and the uterus itself, and involves the introduction of a contrast agent.
Hysterosalpygorrhaphy is necessary to determine the degree of patency and pathological changes in the fallopian tubes.
The doctor is able to establish a correct diagnosis only after a comprehensive examination of the patient has been carried out. After this, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment.
Treatment of inflammation
The appendages in women are very sensitive to various changes in the external environment. It has been proven that in an unfavorable environmental situation, the reproductive system is the first to suffer.
Any inflammatory processes in the vagina or urinary tract can lead to inflammation of the internal genital organs. Therefore, at the first signs of colpitis or cystitis, you need to go to an appointment with an appropriate specialist.
If you are worried about the appendages in women, photos of these organs will help you understand how the pathological process develops in them. Most often, such images are used to determine the extent of the pathological process for medical students. From photographs where women's appendages are clearly visible, it can be determined that the infection can actually be stopped at the vaginal level if local treatment is started in time, which will not cause such harm to the body as general treatment, when antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and hormones are prescribed.
The following methods are used to treat this disease:
- physiotherapy;
- antibiotics;
- drugs for pain relief and inflammation;
- drugs to strengthen the immune system;
- medical products that prevent poisoning of the body by intoxication products;
- temporary absence of sexual intercourse;
- if necessary, treatment of the sexual partner.
How to prevent this pathological process?
Who would want to get to the point where they have to treat such a disease? The first symptoms of inflammation of the appendages in women make them think about preventing this disease. After all, it is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it. It is necessary to avoid hypothermia and stress, which can provoke the development of pathological processes in the ovaries and tubes. For casual sexual relations, use a condom, as pathogens of sexually transmitted infections can lead to serious pathologies in the internal genital organs.
To prevent inflammation of the appendages, it is important to strengthen your body as a whole. A proper, balanced diet and strengthening the immune system with the use of vitamins will help with this. These measures will help fight infections. Protection from unwanted pregnancy will protect you from abortions, which play an important role in the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the tubes and ovaries.
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is performed only if the doctor suspects adnexitis. By examining the surface of the ovaries and fallopian tubes using a laparoscope, the doctor can confirm or refute the preliminary diagnosis.
Diagnostic laparoscopy is performed using an invasive method (by piercing the skin, the equipment penetrates into the patient’s body).
Having a clear view of the whole picture on the monitor screen, the doctor has the opportunity to collect material for studies such as:
- microbiological;
- histological;
- cytological.
It is diagnostic laparoscopy that allows the doctor to find out everything about the condition of the patient’s body in order to correctly establish a diagnosis.