Gardnerellosis (bacterial vaginosis) is an infectious non-inflammatory disease caused by the anaerobic bacterium gardnerella vaginalis.
Gardnerella vaginalis is an anaerobic bacterium that lives in the human genitourinary system and causes unpleasant symptoms.
Previously, there was an opinion that only women were susceptible to gardnerellosis. But today it is known that both sexes can suffer from gardnerellosis (in men this disease is called bacterial balanoposthitis).
Let's take a closer look at what it is, the symptoms and treatment of gardnerellosis later in the article.
Causes of gardnerellosis
As mentioned above, the disease occurs due to the bacterium gardnerella vaginalis, if their concentration reaches 109-1011 CFU/ml GE/ml in the hollow tract.
Infection of a healthy person in the vast majority of cases occurs for the following reasons:
- unprotected sexual contact, while the bacteria can be introduced into the body not only during vaginal contact, but also in the case of anal or oral sexual intercourse.
- infection is also possible through household means, but this occurs extremely rarely - when sharing some of the patient’s things (underwear, towels, hygiene products).
- There are also cases of transmission of pathogenic flora from mother to fetus during pregnancy and childbirth.
Provoking factors for the development of the disease
Gardnerella infection can remain in the body for a long time without manifesting itself in any way. Inflammation occurs under certain circumstances.
In particular, gardnerella infection actively manifests itself under the following provoking factors:
- promiscuous sex life and frequent changes of partners;
- ignoring the use of condoms;
- presence of chronic diseases;
- weakened immunity (due to HIV infection of a woman or man, tumors, diabetes mellitus);
- wearing tight and synthetic underwear;
- use of intimate hygiene products and towels for the patient;
- violation of basic rules of personal hygiene;
- improper and irregular nutrition;
- douching with chlorine-containing antiseptics (Gibitan, Miramistin);
- taking certain contraceptives;
- hormonal imbalances;
- taking broad-spectrum antibiotics for a long period of time, and others.
Thus, gardnerellosis is a disease that manifests itself under certain provoking factors.
Features of the course of the disease in pregnant women
If a woman is promiscuous while pregnant, she may become infected with gardnerellosis. The incubation period of the disease is 6-10 days. It is worth considering that a woman’s immunity is weakened at this time, which allows bacteria to multiply quickly, and accordingly, the disease progresses.
A situation is possible when the pathology manifests itself only during pregnancy, although the woman did not have promiscuity. This means that she was infected earlier, and against the background of a weakened immune system or strong experiences and constant stress, the bacterium was activated.
Symptoms of gardnerellosis
As mentioned above, gardnerella in women can easily remain in the vaginal microflora in small quantities for many years and not manifest itself in any way. Approximately 25% of healthy girls and women are carriers of Gardnerella vaginalis.
And only under certain circumstances the concentration of bacteria in the vagina becomes greater than the permissible norm and characteristic symptoms arise.
Gardenellosis in women often leads to the development of nonspecific vaginosis. Girls complain of the following obsessive symptoms:
- the appearance of atypical discharge (slight, watery, grayish-white);
- “rotten fish” smell from the vagina;
- mild itching in the genital area;
- painful sensations during sexual intercourse, and sometimes even at rest.
Detection of gardnerellosis
Gardnerella vaginalis is diagnosed quite simply. In order to detect the disease, a woman needs to see a gynecologist.
The doctor will examine the patient and, based on the nature of the discharge and the fishy smell, will be able to suggest a pathology. But since there are cases of asymptomatic disease, you need to undergo certain tests.
To confirm gardnerellosis, a regular smear is taken and then examined under a microscope. The doctor can measure the pH of the vagina (if the environment is normally acidic, then when affected by bacteria it becomes alkaline).
Among the additional diagnostic methods, the doctor prescribes an isonitrile test (confirmation of the disease by the smell of rotten fish) and a general blood test, which will reveal an increase in the number of leukocytes.
More expensive research methods are usually not used, since they only confirm the presence of a particular microorganism in the vagina. And normally, as is already known, even in an absolutely healthy woman, Gardnerella vaginalis can be present in the vagina, but in small quantities.
Diagnostics
Before examining a patient, the health care provider must:
- listen carefully to all complaints,
- conduct a visual examination of the patient;
- take biological material for laboratory research.
Based on all the information received, a diagnosis can be made.
Gardnerella is determined by the results of an analysis of a general smear of the vaginal microflora. A more thorough examination to detect Gardnerella (culture, PCR) is not necessary, since this bacterium can be a “resident” of healthy vaginal microflora.
During bacterioscopy, the following picture is observed in patient smears:
- there are no leukocytes, but there are squamous epithelial cells “paired” with gram-variable coccobacteria;
- reduced acidity level of the natural vaginal environment to pH>4.5;
- the amine test gives a positive result;
- no lactic acid bacteria;
- the number of anaerobes exceeds the number of aerobes.
In modern clinics, along with bacterioscopic examinations, microbiological methods, a smear for DNA gardnerella vaginalis, RIF and PCR are used to determine gardnerellosis.
Treatment of gardnerellosis
Of course, patients who are faced with the problem of gardnerella vagina need qualified help. In the absence of complete treatment for gardnerellosis in women, the infection quickly spreads further through the genitourinary organs, contributing to their damage. It is important not to wait for complications, but to regularly see your doctor and follow his recommendations.
Drug treatment (medicines)
Many people are interested in the question: how to treat this disease? The answer to this question can be given by the attending physician, based on the individual characteristics of the patient. But often the procedure comes down to the methods described below.
Therapy should be comprehensive and consist of the following medications:
- antibacterial agents (the most effective in this case is Metronidazole );
- external use products, among which vaginal suppositories or gels ( Flagyl , Metrogyl ) have proven themselves to be excellent.
After taking antibiotics, it is important to restore healthy vaginal microflora. Sometimes immunotherapy is additionally required.
Note! Gardnerella is resistant to groups of antibacterial drugs such as tetracyclines, sulfonamides, aminoglycosides and cephalosporins.
Consequences and possible complications
Previously, doctors were sure that gardenellosis was not dangerous. Nowadays, pathology is considered a risk factor for the inflammatory process in the uterine appendages, infertility in women, early labor, complications of the process of bearing a baby and the birth process itself. It is necessary to cure her. If left untreated, the disease can lead to:
- inflammatory process in organs located in the pelvic area;
- urethral syndrome;
- post-abortion and postpartum endometritis;
- infertility;
- intraepithelial cervical neoplasia;
- Bartholinitis or abscess of the Bartholin gland.
Complementary and alternative treatments at home
Treatment for such a disease should be prescribed by a doctor. Traditional medicine offers a lot of treatment options at home. Such methods are best used as disease prevention or as an additional treatment method.
- Doctors recommend making warm baths of potassium permanganate and salt. The solution helps reduce the number of harmful bacteria in the vaginal microflora without disturbing the balance of beneficial microorganisms. If it is not possible to do such procedures every day, you can use this solution to make tampons, which are inserted into the vagina for 15-20 minutes in the morning and evening.
- You can also make tampons soaked in a mixture of carrot juice and apple cider vinegar. Take 10 ml of fresh carrot juice and 5 ml of vinegar onto a thin swab. The product soaked in liquid must be carefully inserted into the vagina after daily evening hygiene procedures and left there for approximately 15-20 minutes.
Preventive actions
Preventive measures to prevent gardnerellosis include the following:
- Normalization of hormonal levels.
- Therapy with antibiotic medications only after they have been prescribed by a doctor. When taking medications uncontrolled, the hormonal balance is disrupted.
- Maintaining personal hygiene. Frequent douching should be discontinued.
- Refusal of intimate relationships with many lovers.
- Timely treatment for the appearance of intestinal dysbiosis and infection in the genitourinary system.
Gardnerellosis is an insidious disease. It can worsen the patient's quality of life and undermine her health. Timely detection of infection and proper treatment will help preserve a woman’s health for many years.
Prevention
Women who periodically encounter diseases such as bacterial vaginosis should pay attention to the state of the immune system. Indeed, in most cases, it is the decrease in immunity that becomes the main cause of disruption of the vaginal microflora and leads to frequent hormonal disruptions in women.
Among the most important methods for preventing gardnerellosis are the following:
- active lifestyle;
- proper nutrition;
- healthy sleep about 8 hours a day;
- maintaining intimate hygiene;
- timely visit to the gynecologist;
- having a permanent sexual partner;
- positive attitude.
Thus, in order to prevent the development of a large number of Gardnerella vaginalis in the vaginal microflora, you should try to eat a large amount of fresh vegetables and fruits, drink a lot of water, and include daily walks in the fresh air in your daily schedule. To strengthen the immune system, it is also important to engage in some kind of sport, to toughen up, to have a good mood and a positive attitude. It is also important to wear loose underwear made of natural fabric and prevent hypothermia.
If you have casual sex, you should not forget about condoms. In addition, it is advisable to treat the external genitalia with antiseptic drugs within two hours after intercourse.
Experts do not recommend that women douche during treatment for the disease. The fact is that in this way the natural lubricant is washed out of the vagina and the acidity changes. It is also not advisable to use soap. All this leads to drying out of the mucous membrane and gives impetus to the development of pathogenic microorganisms. Therefore, it is better to use a regular shower and special products for intimate hygiene as hygiene procedures.
To maintain the health of the female genital organs, it is imperative to monitor the state of the intestinal microflora. In case of any gastrointestinal disorders, it is necessary not to delay treatment. The fact is that opportunistic microorganisms living in the intestines can easily penetrate directly into the vagina through a thin wall. Some experts agree that treatment of gardnerellosis is most difficult in patients with intestinal dysbiosis.
Description of the disease
Gardnerellosis, or bacterial vaginosis, is one of the most common gynecological pathologies. According to statistics, every fifth woman develops it at least once.
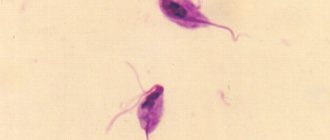
This is interesting. The disease was named after the American scientist Herman Gardner, who discovered its causative agent - a bacterium of the species Gardnerella vaginalis - in 1950.
The pathogenesis of infection is based on vaginal dysbiosis. At the same time, the proportion of normal microflora represented by lactobacilli (Dederlein's bacilli) quickly decreases, and active reproduction of UPM (bacteria that are commonly called conditionally pathogenic), including Gardnerella, occurs.
These microorganisms actively attach to epithelial structures, increasing their granularity and promoting destruction. In microbiology, such altered cells are called key cells.
Photo c shows the main microscopic sign of the disease.
Forecast
Some people do not consider gardnerellosis a disease and wait until it disappears on its own without the use of medications. Yes, an imbalance in the vaginal microflora can recover over time without treatment, but this happens extremely rarely and with very good immunity and other factors. In particular, self-healing occurs with the disappearance of the causes that caused the disease (for example, a woman stopped using an intrauterine device or condoms with various lubricants). In any case, it takes a lot of time to restore the microflora on its own, and no one wants to endure the symptoms of a gardnerella infection for a long time.
Gardnerella vag in women can be successfully treated with timely consultation with a doctor. Recovery occurs quickly if you follow all the recommendations of an experienced gynecologist, so the prognosis is definitely favorable. To prevent infection again, both partners should undergo treatment at once. And after recovery, it is important to take preventive measures.
Thus, now we know what gardnerella is, the causes, symptoms and treatment of gardnerella in women.
How does gardnerella manifest?
Photo of gardnerella
Very often gynecologists hear such questions as gardnerella, what is it and what are the causes of its occurrence. It is worth noting that a representative of the fair sex cannot monitor how the flora of her body changes, which is why quite often one has to face the fact that as a result of the tests, gardnerella can be detected in an acute form. Typically, early in the disease, there is no evidence that gardnerella is present. As soon as the disease becomes serious, far from pleasant sensations begin to arise in the vaginal area, and itching also develops, a burning sensation and even pain may be present.
It is, in principle, impossible to identify a disease by such symptoms, since most infectious diseases manifest themselves in this way. Gardnerella also means a large amount of discharge, as well as the appearance of a pungent odor of a dark shade and even a change in consistency.
Only a doctor can determine how to treat gardnerellosis after passing certain tests. It is worth noting that representatives of the fair sex are often susceptible to this disease during pregnancy.