Mastopathy is the most common breast disease that is diagnosed in women of different ages.
But the peak of the disease occurs after 40 years of age.
Of the total percentage of breast diseases, mastopathy in young women makes up 40%, but in women with a history of gynecological diseases, pathology is diagnosed in 90% of cases.
This is why doctors so strongly advise all women to undergo a preventive examination with a mammologist once a year.
And women after 40 years of age are recommended to do this twice a year.
Mastopathy - what is it?
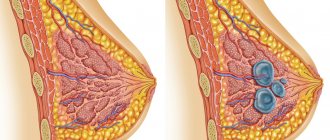
The term “mastopathy” means a pathological condition of the female glands, in which these tissues begin to grow. As a result, compactions form in the form of single or multiple fine-grained nodules and cysts. Often these neoplasms are considered benign tumors and can occur only in one breast, sometimes in both. They are often localized in the upper outer part of the chest.
The pathology occurs in the female half of reproductive age (18-45 years), and the peak of the disease occurs at 30-45 years. But recently, cases of detection of benign neoplasms have become noticeably more frequent. The disease becomes more active not only in women of childbearing age, but also during menopause or the menstrual cycle.
Types of focal formations in mastopathy
Each foreign formation of benign etiology that develops in breast tissue belongs to a specific type. When determining whether a woman has focal mastopathy, the mammologist simultaneously diagnoses the type of benign lump. The following types of focal mastopathy are distinguished:
Fibroadenoma
A foreign neoplasm of the mammary gland, which is formed from one’s own breast tissue. It is characterized by high density and pain. Especially during palpation. A distinctive feature of focal mastopathy fibroadenoma over other tumors is the presence of stromal connective tissue, which forms above the breast parenchyma.
The reasons why young women develop breast fibroadenoma are not completely known. The main peak incidence occurs at the age of 20-30 years. Most of the patients are women who are in the prime of life and lead a healthy lifestyle. Breast doctors associate the occurrence of breast fibroadenoma with hormonal imbalance and inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system.
Lipoma
A benign neoplasm that forms between the connective tissue of the gland. In some cases, it penetrates deep into the muscle fibers. During palpation it does not cause pain and is characterized by high mobility. The structure of breast lipoma is adipose tissue. Therefore, tumors of this kind extremely rarely degenerate into malignant formations. The only exception is liposarcoma.
Lipoma is a benign neoplasm that forms between the connective tissue of the gland
The main causes of breast lipoma in women are metabolic disorders, when fats that enter the body with food are not properly absorbed and are deposited in the mammary gland. Also at risk of developing focal mastopathy of this type are women suffering from excess body weight.
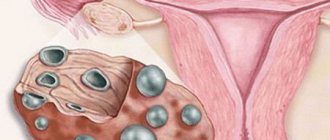
Cyst
Focal fibrocystic mastopathy is a single or simultaneously multiple formation in the ducts of the mammary gland. The cyst is characterized by the presence of a capsule form and liquid contents inside. It is painful, and when squeezing or palpating the breast, the woman experiences a burning sensation. Focal cystic mastopathy develops over a long period of time and makes itself felt only after reaching a certain size.
Without proper treatment, this type of breast pathology provokes inflammatory processes in the breast and suppuration of varying degrees of severity. The main causes of focal cystic mastopathy are an imbalance of sex hormones, the use of oral contraceptives, and inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system that were not treated in a timely manner.
Avascular formation
A type of focal mastopathy, in which an inflammatory process first occurs in the tissues of the mammary gland. Then some of the cells die and the glandular tissue as a whole decomposes. In this regard, exudate accumulates inside the breast, which over time becomes denser and forms a single tumor body. Large varieties of avascular mastopathy can change the shape of the breast, give it a rich red or purple color, and retract the nipple. These types of neoplasms are extremely painful. They can disturb a woman both during palpation of the breast and during periods of physical rest.
Let's delve into the essence of what is happening
To understand the features of the pathological condition of the breast, let’s first consider a photo of mastopathy of the mammary gland, where you can see how the breast is structured. The structure of the gland is somewhat similar to an orange, since inside there are also small segments (from 15 to 25 pieces), which are located radially relative to the nipple. They are separated from each other by fatty tissue. Due to this, the shape of the breast is formed.
Each such “lobule” contains mammary glands, consisting of branching tubes called milk ducts. At their ends there are small alveoli (vesicles) where special cells (lactocytes) produce milk.
Every month, the female body undergoes cyclic changes under the influence of progesterone and estrogen. Thanks to them, not only the two-phase menstrual cycle is regulated, but also has some effect on the female glands.
Under normal conditions, during the first phase of the cycle (before ovulation), due to estrogen in the glands, cell multiplication begins (proliferative process). When the second phase of the cycle begins (after ovulation, but before menstruation), progesterone is activated, which delays cell reproduction provoked by estrogen. At this moment, the breasts begin to increase in size, although only slightly.
If fertilization of the egg does not occur, the amount of estrogen increases, due to which the female glands undergo reverse changes and the breasts decrease in size. However, during pregnancy there is an increase in the concentration of prolactin in the blood. Subsequently, it begins to affect milk production.
If you pay attention to the reviews about mastopathy of the mammary gland, we can conclude that this problem worries many women of different ages.
Causes of the disease
A decisive role in the pathogenesis of localized mastopathy belongs to conditions characterized by a decrease in progesterone, as well as functional disorders of the ovaries with the development of hyperestrogenemia (increased estrogen content). The latter position is confirmed by several circumstances:
· Increased proliferative processes in the epithelium under the influence of estrogens;
· Increased activity of fibroblasts and associated proliferation of connective tissue;
· Frequent detection of mastopathy in patients with dysfunctional bleeding from the uterus, fibroids and endometriosis, follicular ovarian cysts, anovulatory form of infertility. In all these conditions, there is an excess of estrogen in the body.
However, the presence of a normal menstrual cycle does not at all exclude the possibility of developing localized mastopathy. This confirms that in the development of this disease, the greatest role is played not by the level of hormones in the blood plasma, but by the state of the receptors, which can be much higher than normal.
What about deviations?
As for deviations from the norm described above, under the influence of a number of negative factors, the hormonal balance is disrupted. This leads to the fact that the amount of estrogen is formed in excess, while there is clearly not enough progesterone in the body. For this reason, too many cells are formed in the female breast, against which mastopathy occurs.
Sometimes the disease occurs against the background of an excess amount of prolactin, the production of which is responsible for the pituitary gland. During pregnancy and lactation, this phenomenon is within normal limits, as milk is produced to feed the baby. However, in the absence of pregnancy, this is considered a pathology and can also lead to the development of mastopathy.
Fibrofatty mastopathy in men
It is interesting to know that overgrowth of the mammary glands also occurs in representatives of the stronger sex. If their glands are enlarged due to the growth of fatty and fibrous tissue, this condition is called false gynecomastia. In some periods of life it is physiological:
· in newborn boys (develops due to female hormones obtained from the mother’s blood);
· in the puberty period (puberty) as a result of the processes of formation of hormonal balance;
· in old age with decreased sexual function, especially in obese men.
The rest of the time, male fibrofatty mastopathy (lipomastia) appears as a result of metabolic disorders. Her reasons:
1. Obesity.
2. Heart failure with symptoms of stagnation.
3. Diabetes mellitus.
4. Abrupt cessation of active training in former athletes, especially those who previously took steroids to stimulate muscle growth.
To correct the situation in men, it is often enough to adjust their habits and diet: eliminate alcohol (including beer, rich in natural estrogens), dietary supplements, carbohydrates and fatty spicy foods.
Cystic form of pathology
Cystic mastopathy of the mammary glands is considered a benign disease, which affects up to 30% of young girls. In medical language it is referred to as fibroadenomatosis or fibrocystic disease. It is characterized by impaired blood supply to the female glands due to an imbalance of sinewy components and connective tissues. Periodically, pain appears in the chest.
But if pathology is not given importance, then a neoplasm subsequently forms. At first it will be benign in nature, but then it will turn into a malignant tumor.
Full symptoms
Speaking about the symptoms of breast mastopathy, you should turn to its varieties. Each variety has its own signs and manifestations of mastopathy.
- Involutive . Increase in subcutaneous fat masses inside the mammary gland in nulliparous women after 35 years. Not visually identifiable; mammography required.
- Glandular . Various lumps inside the mammary glands. Not the entire breast suffers, but only individual parts. This type of mastopathy is characterized by pain throughout the entire menstrual cycle. At the initial stage they are defined as aching, at a later stage they begin to radiate to the neck and shoulders. Breast size increases. Glandular cystic mastopathy is also characterized by small sacs inside the breast filled with fluid - cysts. In a quarter of cases, they begin to harden and transform into malignant tumors.
- Diffuse . The main symptom of mastopathy is the presence of pain, over time it becomes stronger and radiates to other parts of the body, for example, to the back or shoulder, and takes on a girdling character. At the beginning of menstruation, the pain subsides. There is general malaise and loss of strength, the skin becomes dry, hair breaks, and menstrual irregularities occur.
- Cystic . Painful sensations are observed exclusively in the area of cyst formation. Since with this type of mastopathy the lateral and upper lobes of the breast are at risk, upon examination it is possible to identify enlarged axillary lymph nodes with swelling around them. Purulent discharge from the nipples is observed. There is a risk of cyst rupture and subsequent death of glandular tissue.
- Nodal . The lumps inside the breast are isolated and not connected to other parts. Very often they can be identified by independent palpation of the chest. The symptoms of nodular mastopathy are as follows: pain in the area of the lump appears before the menstrual period, while the breasts become enlarged, and when you press, you can see discharge.
- Fibrocystic . It may not show up at all. Diagnosed during breast examination by a specialist. It consists of many small lumps in the mammary gland. There may be no pain, but in the opposite cases it can be observed even at rest. The disease can simultaneously affect both breasts. You can read more about the symptoms of fibrocystic mastopathy in this article.
We have prepared useful materials for you about the traditional treatment of mastopathy using:
- cabbage leaves;
- burdock;
- red brush;
- salt;
- essential oils.
There are other ways to use folk remedies, more details here.
Diffuse disease
With diffuse mastopathy, the changes that begin affect the entire gland. In some cases, the proliferation of glandular tissue takes on a wider spectrum. Then the diagnosis will be made as follows - diffuse mastopathy with a predominance of the glandular component. This form of pathology mainly occurs only in young girls.
In addition, the disease is characterized by the formation of various types of neoplasms (cords, millet-like nodules). The diffuse form of pathology, in turn, is also divided into several types:
- adenosis;
- sclerosing adenosis;
- fibroadenosis;
- fibrocystic disease
There is also a mixed form of diffuse mastopathy of the mammary gland, and, unfortunately, in our time this phenomenon occurs very often. The affected glands swell, cysts and lumps form. The disease should not be ignored, otherwise it will begin to worsen, manifesting itself in the form of greenish discharge from the nipples.
Diagnosis and treatment of the disease
Initially, the doctor examines the woman and determines whether there are symptoms of menopausal hypoestrogenism. Very often mastopathy develops against the background of this condition. Dryness of the mucous membranes of the genital organs is an indirect sign of mastopathy after 50 years, characteristic of the initial stage.
To clarify the diagnosis, the following procedures are prescribed:
- MRI;
- CT;
- dopplerography;
- biopsy;
- mammography;
- general urine analysis;
- biochemical and general blood tests;
- examination of breast discharge;
- Ultrasound of the mammary glands.
Nodular mastopathy
In this case, the changes are benign in nature and are characterized by the formation of cysts and nodules. From the point of view of most mammologists, this form of the disease is considered a precancerous stage, after which a cancerous tumor will form if treatment is not carried out in a timely manner.
The nodes can be single or multiple in nature, appearing on one breast or in both at once. Typically, this mastopathy also has its own classification:
- Fibrous-nodular.
- Diffuse nodular.
- Cystic nodular.
The fibronodular appearance is characterized by a benign course. A dense nodular structure is formed due to the proliferation of connective tissue, and the glands become asymmetrical. Pain can appear either constantly or periodically.
With diffuse nodular mastopathy, cysts form in the breasts, inside of which there is fluid. Their sizes vary, but often the oblong or round shape predominates. In this case, the pain radiates to the shoulder, arm or armpit.
Cystic nodular mastopathy is characterized by the presence of nodes of different sizes with clear boundaries. Gradually, the compactions increase and affect nearby tissues. They are easy to notice as the menstrual cycle approaches. Due to the proliferation of cysts, the gland ducts are compressed, which leads to venous stagnation and edema. Breast sensitivity increases and pain becomes more intense.
Forms of localized mastopathy and morphological structure
From a practical point of view, it is customary to distinguish between two types of localized mastopathy:
1. Proliferating
2. Non-proliferating
Proliferation leads to the appearance of papillomas. If they are localized inside the milk ducts, they are called intraductal, and if inside a cystic formation, they are called cystadenopapillomas. The danger of these changes is that sometimes they can be accompanied by the phenomena of atypia and malignancy. Thus, proliferating mastopathy is considered as a background condition for the development of cancer.
Localized mastopathy can be characterized by a predominant proliferation of either connective or glandular tissue. But in practice, combinations of options are most common. In contrast to diffuse mastopathy, with localized fibroadenomatosis, the formation of 1-2 areas with characteristic pathological changes is observed, the rest of the breast tissue is intact, i.e. has a normal structure. Clinically, this leads to symptoms such as:
· Formation of focal compactions that do not have clear boundaries and are not fused to the skin (unlike cancer);
· Formations are dynamically changing - on the eve of menstruation they increase, and after its end their size decreases;
· Pain (in comparison with diffuse mastopathy in this form it is more severe). The pain often radiates (spreads) to the shoulder blade or shoulder;
· Sometimes there is an increase in axillary lymph nodes. In this case, a careful differential diagnosis with breast cancer is required.
Symptoms of breast mastopathy in women
Typically, signs that indicate the onset of mastopathy cannot be detected and the pathology can be determined by chance. But the further you go, the clearer the clinical picture becomes. The connective tissue grows and small compactions form.
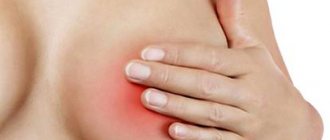
But the disease will not be able to hide for long, and over time, pain in the chest appears, which is the first sign of an upcoming pathological change. With the onset of the premenstrual period, the pain intensifies. In addition, women may feel the heaviness of the mammary glands, and palpation can reveal a lump.
In addition, another sign may be gray-white discharge with a liquid or mucous consistency. If blood is present, this is an alarming sign, since this does not happen with benign neoplasms.
In this article, we will consider not only the symptoms of breast mastopathy (photos of the disease are presented in the article), but also various methods of treating the pathology.
About the disease
What is mastopathy and how does it manifest? Mastopathy refers to benign formations in the breast caused by hormonal imbalances, which are accompanied by tissue growths inside the mammary gland.
Traditionally, the disease is divided into two main subtypes: nodular and diffuse mastopathy, but experts identify a much larger number of varieties:
- involutive;
- glandular forms of the disease;
- diffuse;
- cystic;
- nodal;
- fibrocystic.
Each type of mastopathy is accompanied by certain symptoms. Next, we will look at the signs and symptoms of mastopathy in women.
Palpation of the glands
It is advisable to carry out this procedure while standing or lying down. To begin with, the surface of the chest is palpated with the fingertips in a clockwise direction. Then you need to press on the nipples to check for discharge. At the same time, you should check the lymph nodes that are located in the armpit.
According to experts, such diagnostics should be carried out regularly during the period from the 5th to the 10th day of the menstrual cycle. While palpating your chest, you should try to remember the tactile sensations, and then compare them during the next procedure.
If you know the symptoms and signs of breast mastopathy, treatment will be most successful. And self-diagnosis is the first step in making a diagnosis. What should you pay attention to? The presence of lumps, pain when palpating, and a feeling of lumpiness should alert you. These signs may indicate a diffuse form of the disease. Moreover, the seals are sometimes not located throughout the entire breast, but only in its upper part.
If cystic mastopathy develops, then nodes of different sizes can be detected. During the second period of menstruation, neoplasms become more pronounced.
Prevention of mastopathy
To avoid mastopathy, follow the rules:
- have regular sex life;
- give birth to 2-3 children and breastfeed them;
- plan your pregnancy (avoid abortion);
- regularly monitor hormonal levels; promptly identify and treat gynecological and hormonal diseases, menstrual irregularities;
- treat chronic diseases and infections in a timely manner;
- avoid scandals in the family, stress, neuroses, depression; lead a healthy lifestyle; do not smoke or abuse alcohol;
- strengthen your immune system, take vitamin therapy courses in spring and autumn;
- Perform a breast self-examination every 3 months.
Ultrasonography
During an ultrasound, you can get an image of the structure of the female glands. That is, the doctor can identify heterogeneity in the structure of the glands, the presence of neoplasms in the form of cysts or nodes. This procedure has significant advantages:
- An absolutely safe procedure.
- High degree of information content.
- The condition of blood vessels and tissues can be assessed, which allows you to see the full clinical picture.
In addition, this study can determine not only the size of breast tumors, but also their location. And before the procedure there is no need for special preparation. It is better to perform an ultrasound during the first days of the menstrual cycle.
Diagnostics
There are several options for diagnosing fibroadenomatosis of the mammary gland. The choice of a particular option is influenced by the patient’s general health, the clinical picture of the disease and its first signs, as well as individual factors.
The examination may be:
- Standard examination methods:
- Ultrasound (examination aimed at the mammary gland);
- mammography (mandatory stage of diagnosis).
- Special methods:
- ductography (study of the condition of the mammary ducts of the glands);
- aspiration biopsy (cellular examination);
- stereotactic biopsy (examination of material taken from non-palpable formations);
- trucat biopsy (tissue examination).
- Additional diagnostics:
- laboratory tests for hormone levels;
- X-ray;
- MRI;
- thermography;
- examination of the condition of the lymph nodes.
Mammography
With this study, an X-ray of the glands is taken, as a result of which even small compactions that cannot be detected by palpation can be detected. For all women over 40 years of age, this procedure is mandatory to undergo annually.
During mammography, X-rays of the breast are taken in two planes: (direct and lateral), which makes it easy to detect lumps and the extent of their spread, if any.
By combining radiography with ultrasound, pathology can be more likely to be determined. Just remember that this type of research is not carried out for women who are under 30 years old. In addition, the procedure is done no more than once a year.
Folk remedies
All folk recipes must be treated with caution. Use without consultation with a doctor may result in progression of the pathology. The fact is that not all medications are combined with certain medicinal herbs. In some cases, combining different treatment methods requires reducing the dosage of the main medications. Herbal remedies are used as an adjunct to drug treatment.
Effective folk recipes for the treatment of benign breast tumors:
- Propolis tincture. Sold ready-made. Application: 1 tbsp. l. diluted in 100 ml of boiled (not hot) water. Take 3 times a day.
- Tincture of cinquefoil. Can be bought at a pharmacy. Drink a tablespoon in the morning, lunch and evening, diluting the medicine in 120 ml of water.
It is also allowed to use decoctions and mixtures that contain the following herbs:
- series;
- hawthorn flowers;
- knotweed;
- walnuts;
- hog uterus;
- burdock root;
- yarrow;
- aloe;
- potato flowers;
- flax-seed;
- caraway;
- fennel;
- motherwort.
Features of treatment
Treatment of mastopathy is based on restoring hormonal levels or eliminating the imbalance of sex hormones in the blood. It is carried out only under the strict supervision of a specialist, and always on an outpatient basis.
The diffuse form of the disease is easily treated with conservative treatment. The necessary medications are taken only after visiting a mammologist.
In the case of nodular or fibrocystic mastopathy of the mammary glands, treatment is also carried out conservatively, but there may be a need for radical measures (surgery).
In addition to taking medications, the conservative method includes the following:
- Dieting. To do this, you should include foods rich in fiber in your diet and consume at least 2 liters of water per day. In food, preference should be given to sea fish, vegetable oils, dairy products, cereals, vegetables, fruits, lean meats, mushrooms, and nuts.
- Choosing comfortable underwear. With the right choice of bra, you can reduce pain and, in addition, this leads to a speedy recovery. The fabric should be natural, it is advisable to select models without foam rubber, with wide and comfortable straps. You should also sleep without a bra and not wear it for more than 12 hours.
- The right way of life. If you have bad habits, you need to give them up. As for smoking, this is the main reason for most women's problems.
Who is at risk?
It is worth noting that not every woman has a physiological tendency to develop the inclinations to develop dense cysts of fibrocystic mastopathy. There is a separate category of potential patients of a mammologist. These are women who have the following pathological conditions of the reproductive system:
- girls whose first menstruation began before they reached the age of 11, and the menstrual cycle itself acquired stability in condensed lines;
- mature women who experienced menopause well over 50 years of age;
- women in labor whose first pregnancy was only after 30 years of age and was accompanied by a number of complications;
- refusal of a young mother to breastfeed her child despite the fact that milk continues to be actively produced in the glandular tissue of the breast;
- women leading an immoral lifestyle with promiscuity and abusing bad habits.
About 65% of women who seek medical help from a mammologist with signs of localized focal mastopathy have these risk factors in their lives.
Hormone therapy
How is cystic mastopathy of the mammary glands treated? In this case, different groups of drugs are used.
- Antiestrogens. Reduce the concentration of estrogen in the blood and reduce chest pain. In addition, the menstrual cycle is normalized, the risk of lumps turning into a malignant tumor is significantly reduced. But when taking these drugs there may be side effects: nausea, wave-like attacks of fever, sweating, depression, skin rash, which is a consequence of a decrease in estrogen. The treatment course lasts 3-6 months and is often prescribed “Fareston”, “Tamoxifen”.
- Gestagens. This group not only suppresses the production of estrogen, but also delays the gonadotropic function of the pituitary gland. As a result, hormonal balance is restored. The effectiveness of this treatment is 80%. Only here there are a number of contraindications: pregnancy, cancer and others. The main drugs in this group are “Orgametril”, “Norkolut”, “Progestogel”, “Pregnil”.
- Androgens. Such drugs also help suppress the production of estrogen. Only they have a wider range of side effects. This group is represented by Danazol.
- Prolactin inhibitors. Due to this hormone, cysts are reduced, pain becomes less intense, and the balance between estrogen and progesterone is restored. However, in the presence of malignant tumors, taking such drugs is contraindicated. They can be “Parlodel”, “Bromocriptine”.
However, in some cases, conservative treatment of fibrous mastopathy of the mammary gland and taking hormonal drugs may not be enough. And then all that remains is to resort to a radical method of treatment.
Taking medications
Conservative treatment of mastopathy can be carried out with or without hormones.
Hormonal treatment with oral contraceptives can be prescribed during the initial menopause, when the menstrual cycle is still present.
Most often prescribed:
- Regulon;
- Femoston;
- Janine;
- Novinet.
When menopause has already occurred, the following are prescribed:
- Duphaston;
- Utrozhestan;
- Progesterone.
To suppress estrogen synthesis, the following are used:
- Danazol;
- Norgestel;
- Linestrinol;
- Tamoxifen;
- Toremifene.
If prolactin levels are elevated, the following is prescribed:
- Bromocriptine;
- Abergeen;
- Parlodel.
Livial is also indicated for postmenopausal women, which affects sex hormones and androgens.
Non-hormonal treatment consists of taking homeopathic remedies, for example:
- Mastodinon;
- Klimadinon.
They stabilize hormonal levels and relieve menopausal symptoms.
IMPORTANT!
These drugs do not have a pathological effect on tissue growth.
Taking vitamins is a mandatory component of the course of therapy for mastopathy.
Appointed:
- Retinol;
- Ascorbic acid;
- Aevit;
- Tocopherol;
- Folic acid;
- Triovit;
- Pyridoxine.
Vitamins stimulate metabolic processes, normalize hormonal levels and have an antitumor effect.
Radical measures
Radical treatment includes surgery, which does not eliminate the cause of mastopathy, so the risk of remission remains after seemingly successful treatment. This type of treatment is usually carried out when diagnosing a nodular form of the disease, or when a conservative technique has not given the desired result.
Elimination of mastopathy is carried out through sectoral resection of the gland. To begin with, the planned dimensions are marked, after which they proceed to the operation under general anesthesia and using ultrasound. The cosmetic defect is minimal.
Treatment of mastopathy
Depends on the form of mastopathy (diffuse or nodular), the woman’s age, her hormonal status and concomitant, primarily gynecological diseases.
Diffuse mastopathy is usually treated conservatively. In 90% of cases, hormonal drugs (low-dose oral contraceptives and sex hormone analogues), as well as their antagonists, are used. Treatment lasts for years.
Small nodes (up to 8 mm) are treated conservatively for several months, but if unsuccessful, surgical removal is suggested so as not to miss the development of a malignant tumor. Large nodes are removed without delay. Modern surgical organ-preserving intervention includes sectoral resection of the mammary gland or “husking” of the tumor. After surgical treatment, hormonal therapy is prescribed in half of the cases.
Which doctor should I contact?
At the first suspicion of mastopathy, consult a gynecologist or mammologist. Contact the doctors of the Botkin.pro medical video consultation service. See how our doctors answer patient questions. service doctors for free, without leaving this page, or here. Consult your favorite doctor.
Questions from patients - answers from Botkin.pro doctors:
Mastopathy – increased prolactin
Since 07/02/16 prolactin has been increased. Not pregnant, no children, 37 years old. Diffuse. mastopathy, right mammary cyst. glands. Tests were taken (prolactin, estradiol, FSH, LH, cortisol, 17-one, DHEA-s - 2-3 days of cycle) Everything is normal, except prolactin - 740 (ref. 102 - 496 mIU/l), DHEA-S – 10.25 (ref. 2.68 – 9.23 µmol/l). Kaberlin 0.5 was prescribed (½ tablet X 1 time per week; after 2 months - 1/2 tablet X 1 time every 2 weeks; after 6 months - 1/2 tablet X 1 time per month) During therapy, prolactin 09/24 .16 -315 mIU/l, 11/15/16- 227, 4 mIU/l, ; 01/04/17 - 262.8 mIU/l, DHEA-S decreased (8.29; 7.923 µmol/l). From 01/04/17, 17-one was increased: 1.35 (ref. 0.3 -1.00 ng/ml), then monthly (from 4.4 to 4.6 nmol/l (ref. 0.2-2.4 nmol/l). Prolactin after discontinuation of Caberlin (11.04.17 - 702 mIU/l, 12.05.17 - 466 mIU/l, 8.06.17 - 1142, 7.07.17 - 1374 (ref. 60-600 mIU/l) A CT scan of the adrenal glands was performed (without contrast agent) no abnormalities were detected. Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (2 times per year) - no pathology was detected. MRI of the fetus was recommended. No other medications that increase prolactin were taken. What could have caused the sharp increase in prolactin according to the results of the latest tests? Mastopathy, cyst? Is it worth monitoring in the future, the level of prolactin during the month, regardless of the days of the cycle?
Petrova Galina AndreevnaObstetrician-gynecologist (Gynecologist)
Sign up for a video consultation
Write to the doctor
The level of prolactin correlates with the level of TSH, a hormone that regulates the functioning of the thyroid gland. It is necessary to do a TSH test. And also big-prolactin and big-big-prolactin. Increased prolactitis may be a consequence of a hormonally active tumor of the pituitary gland - you need to take an x-ray of the sella turcica in two projections.
Mastopathy
Is it possible to take radon mud in Azov with mastopathy?
Gnilorybov Andrey MikhailovichTherapistSign up for a video consultation
Write to the doctor
Only one thing can be said for sure: radon baths or any mud for mastopathy should be prescribed only by a mammologist or gynecologist. Firstly, the doctor must be confident in the diagnosis and the absence of contraindications, and secondly, he must assess the effect of the procedures on the body and cancel them in time (if necessary).
Is there a mass in my daughter’s breast – mastopathy?
My 10-year-old daughter's left breast became swollen in the evening.
I felt the ball under the skin. Does not hurt. The swelling is gone. What could it be? Mastopathy? And is it worth going to a surgeon? German Natalya AndreevnaCardiologist (Gynecologist)Sign up for a video consultation
Write to the doctor
Hello. Try to find out if there was any injury to the mammary gland.... It’s also a good idea to visit a mammologist.
Full breasts - I'm afraid of mastopathy!
Good afternoon.
Before your period, your breasts become engorged and ache a little. This month, my period passed, but my breasts remained engorged, hurt when touched, and hardening was palpable. Three days have passed, the chest hardly hurts when you touch it, but hardening can be felt. There is no temperature and there are no external changes. Is this mastopathy? What should I do about it? Should I address it somewhere? Or will it go away on its own? Stetsenko Alexander PavlovichSurgeonSign up for a video consultation
Write to the doctor
Do an ultrasound of the mammary glands, if necessary, a mammogram and, of course, a consultation with a mammologist
Inflamed axillary lymph nodes
Sometimes the lymph node under the left armpit becomes inflamed, after a while it disappears, as if it were the size of a pea, but it’s not visible on the surface, you can only feel it, what could it be?
Mastopathy or breast cancer? Thanks in advance Korol Pavel AlexandrovichRadiologistSign up for a video consultation
Write to the doctor
The axillary lymph nodes are “sentinel” lymph nodes (i.e., the lymph nodes that first receive lymph from the organ) for the mammary glands. Therefore, to begin with, I recommend performing a mammogram or ultrasound of the mammary glands to exclude focal pathology of the mammary gland, followed by consultation with a mammologist
Breast pain in a child
My daughter has pain in her left chest.
The child is 13 years old. I haven't had my period yet. We are afraid that it is mastopathy. Medvedchuk Elina Leonidovna Obstetrician-gynecologist (Gynecologist)Sign up for a video consultation
Write to the doctor
With the onset of puberty, there may be pain in the mammary glands. Try to limit everything in your diet that makes you want to drink (chips, crackers, sweets). There is no need to limit fluid intake. Just in case, you can go for an ultrasound of the mammary glands, but it is unlikely that mastopathy or other pathology will be detected
Mastopathy
Diagnosis: fibrocystic mastopathy (5 mm), nodular leiomyoma of the uterus.
Thyroid hormones are normal, its size is not increased. Doctors do not prescribe treatment, they say that you just need to be constantly monitored and take vitamins. Tell me what other hormone tests need to be done in order to understand the cause of hormonal imbalances and prescribe treatment? 37 years old, has 1 child, do not take birth control pills Shamray Dmitry Viktorovich OncologistSign up for a video consultation
Write to the doctor
There are many tests, including hormone tests. In case of mastopathy, it may be advisable to know the level of prolactic acid, FSH, and LH. To recommend examination tactics to you, it is necessary
1) see the results of a breast ultrasound
2) know your family and obstetric history, life history
3) how long have you been observing 5 mm mastopathy? Are the sizes stable?
Breast
What is this on breast ultrasound: “a few hyperechoic fibrous structures”?
Uzhviy Mikhail NikolaevichNeurologist (Neurologist)Sign up for a video consultation
Write to the doctor
This is mastopathy. Pay attention to your hormonal levels! You need to be examined by a mammologist or gynecologist-endocrinologist. Good luck. Be healthy!
Breast
Good evening!
10 days ago I got caught in good rain. I’m treating mastopathy and my temperature has been 37.5 for two days now! Could my breasts have caught a cold? Could it have given such symptoms just now? Thanks in advance Alekseenko Elena Aleksandrovna Obstetrician-gynecologist (Gynecologist)Sign up for a video consultation
Write to the doctor
If you do not find redness, lumps or local pain in your chest, then most likely you are simply frozen and have a cold!