Blood from the nipple can occur in both women and men. Moreover, the weaker sex is susceptible to this trouble much more often.
The problem is quite common among breastfeeding women.
Bloody discharge may not always indicate some serious pathology, so there is no need to panic, but you should immediately contact a mammologist for a thorough breast examination.
Pathological causes of breast discharge
The main causes of pathological discharge are:
- Chest injury (blows, bruises). If this happens without violating the integrity of the skin, then within two days the bloody fluid can be easily squeezed out of the nipple.
- Ductectasia is a disease characterized by pathological dilatation of ducts called subareolar canals. The disease is typical for women after 40, since its main cause is age-related changes. The disease does not pose a health hazard, but only if treated in a timely manner. Otherwise, serious consequences cannot be ruled out.
- Mastitis and abscess. Ailments either occur during lactation, or are a consequence of penetration of an infected object. With mastitis, the area of the gland becomes inflamed. The cause is a bacterial infection, in most cases Staphylococcus aureus. With an abscess, pus accumulates in the breast tissue, the affected area is limited from the healthy area.
- Intraductal papilloma is a papillary benign tumor. It appears in the duct near the nipple. Due to the development of the tumor, a thick fluid is released, which sometimes contains blood impurities.
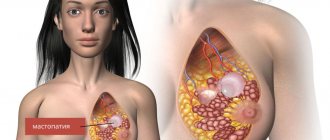
- Fibrocystic mastopathy is the appearance of dense areas of tissue in the mammary gland. The condition is dangerous because it can develop into cancer.
- Malignant neoplasm (breast cancer) is a tumor that forms unnoticed due to uncontrolled cell division. Discharge appears when pressure is applied from both mammary glands or only from one.
- Galactorrhea is a disease in which pressure from the nipple causes milk to leak, but this does not apply to breastfeeding. The main cause of galactorrhea is hormonal imbalance, excess prolactin. The disease sometimes accompanies diseases of the brain or thyroid gland.
- Paget's disease is a malignant tumor that involves the nipple or areola. The disease is extremely dangerous and requires prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Signs of pathology
The appearance of discharge from the mammary glands in the absence of pregnancy and in non-lactating women indicates the development of pathology. Signs such as the color of the discharge, smell, abundance, and thickness are important.
Chest injury
If the mammary gland is injured (bruise, sharp compression), fluid may leak from the nipple when pressed, sometimes mixed with blood. The consequence of injury can be the formation of an abscess - an accumulation of purulent contents.
With the onset of menopause, the ratio of fat and connective tissue in the mammary gland changes, the ducts can expand and become deformed. Ectasia (ductectasia) of the milk duct develops, which is also called plasmacytic mastitis. The discharge is mucous and green or mixed with black. There may be no painful sensations.
The development can also be caused by previous purulent mastitis or post-traumatic inflammation. Excessive milk production during lactation can lead to dilation of the milk duct. Despite the fact that ectasia itself is not a serious disease, it may indicate the onset of an oncological process and requires careful examination and treatment.
Diagnosis of ectasia, in addition to conventional mammography and ultrasound, involves cytological examination of discharge for malignant degeneration.
Treatment of ectasia in most cases is therapeutic: prescribing a course of antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, immunomodulators, correcting hormonal levels, applying compresses. If the condition does not improve, sectoral resection is prescribed - the affected duct is surgically removed.
For various reasons (due to injury, hormonal imbalance), a mushroom-shaped growth - papilloma - can form inside the milk duct. This is a benign tumor that produces a liquid secretion, which is released from the duct.
Non-inflammatory papilloma does not cause pain; its obvious signs are viscous bloody discharge from the mammary gland. When infection penetrates, inflammation is possible - the tumor becomes hard to the touch, can be easily felt, and the characteristic discharge is yellow, mixed with pus.
Cystadenopapilloma is a precancerous disease; when it is detected, it requires not only general examinations - mammography and ductography, but also taking a puncture from the tumor in order to determine its possible malignancy. Treatment is only surgical - a sectoral resection is performed, the tumor and part of the milk duct are removed. The chest is preserved.
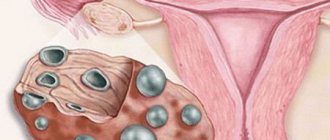
Caused by hormonal fluctuations. Fluid-filled cysts form in the breast tissue. With this condition, nipple discharge is usually brown or greenish. In addition to discharge, symptoms of mastopathy include swelling, thickening of the glands, and a feeling of fullness, especially before menstruation.
Fibrocystic disease requires therapeutic treatment and constant monitoring. With a favorable course of mastopathy, the cystic tissue gradually resolves, malignant degeneration is rare.
Mastitis
This inflammation of the breast tissue is caused by a penetrating staphylococcal infection and is purulent in nature, most often developing in nursing mothers. In this case, purulent foci are formed inside the gland - abscesses, their contents are released through the nipples. General health may deteriorate and the temperature may rise. Antibiotics are used to treat mastitis. In severe cases, if the discharge from the chest is profuse, an operation is performed to remove the purulent contents.
Galactorrhea
In this condition, colostrum is released from the nipples - a thick or thin white secretion that resembles milk. It occurs in non-pregnant, nulliparous women, men and even children. Galactorrhea is not an independent disease - it is a symptom of increased production of prolactin (milk hormone).
The pathology is treated by eliminating the causes: after excluding possible pregnancy, a blood test is performed for the presence of thyroid hormones, sex hormones, magnetic resonance imaging of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus, and a course of hormonal therapy is prescribed. If brain or thyroid tumors are detected, surgery may be required.
Breast cancer
With a malignant tumor in the mammary gland, discharge is quite rare and is possible in two cases:
- intraductal cancer - located in the milk duct;
- in late advanced stages of cancer;
- discharge comes from only one gland affected by the tumor.
The discharged fluid is bloody, yellow or mixed with pus. With cancer, there is a change in the shape and color of the nipple, its retraction, a possible change in the size and shape of the gland, the axillary lymph node enlarges, and a hard lump can be felt in the breast.
Breast cancer is diagnosed in most cases during a self-examination or an appointment with a mammologist. The detected compaction is examined using mammography, ultrasound, MRI, and biopsy.
A malignant tumor that does not have metastases can be removed using sectoral resection, in which case it is possible to save the breast. If the tumor is large, a mastectomy is performed - the entire gland and adjacent affected tissue are removed.
Discharge from the breast during pregnancy
Around the 16th week of pregnancy, many women begin to notice a slight discharge from the breasts. The color of the discharge and its volume may vary. In this article we will try to talk about which discharges are the physiological norm during pregnancy, and which require a visit to the doctor. In addition, we will give some recommendations on how to look after your breasts during pregnancy.
Natural discharge from the breast in a pregnant woman
From the very beginning to the end of pregnancy, a woman’s body undergoes a lot of changes, this can especially be seen in the example of the breasts - the mammary glands become very sensitive, increase in size, the areola of the nipples darkens and sometimes becomes covered with “tubercles”, the nipples themselves increase in size. Around week 16, discharge begins to appear from the breasts. Transparent discharge from the breast is considered a physiological norm for any woman, not just pregnant women. The fact is that inside the glandular tissue there are milk ducts, within which a small amount of liquid is secreted throughout life in order to prevent these ducts from sticking together and becoming overgrown. During pregnancy, due to hormonal changes, the amount of this fluid increases.
Discharge from the breasts in the early stages of pregnancy is also possible for several reasons - any stimulation of the nipples, be it a shower or massage, slight excitement and stress.
In the second half of pregnancy, colostrum may appear - a small discharge of white or yellow color. The release of colostrum from the breast means that the uterus is preparing for the upcoming birth - small “training” contractions, which, as a rule, do not bother the woman much, provoke the release of colostrum.
Small amounts of yellowish and white discharge from the breast, as well as clear discharge, are a physiological norm, and there is no need to worry about this. If you feel a slight itching on the skin, you shouldn’t worry either - it’s just the skin stretching from the expanding mammary glands. To relieve the condition and prevent stretch marks, moisturize your skin throughout your pregnancy.
Pathological discharge from the breast during pregnancy
Unfortunately, breast discharge is not always the norm. Sometimes they may talk about health problems that require medical attention.
Below is a list of symptoms that should prompt you to see a doctor:
discharge of fluid from only one breast;
spotting that does not go away for several days;
discharge accompanied by fever, poor health and aching chest pain;
discharge accompanied by uneven breast growth (one larger, the other smaller) and the appearance of unnatural bumps and depressions;
pronounced yellow color of discharge.
If you find at least one of the above symptoms, be sure to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist or mammologist.
Breast hygiene
Since a pregnant woman's hormonal levels change and her breasts grow, cracks may appear on and around the nipples, which are open gates for infectious pathogens
Therefore, it is very important to maintain breast hygiene during this period. Under no circumstances try to press on the nipples to look at the nature of the discharge, as this may injure the skin. Buy special breast pads at the pharmacy and use them as needed
However, remember that they should be changed every hour!
Buy special breast pads at the pharmacy and use them as needed. However, remember that they should be changed every hour!
Do not leave traces of colostrum on your breasts, as this is an ideal breeding ground for bacteria. Use a gentle blotting motion to dry your nipples.
Try to wash your breasts twice a day in the shower, but do not use regular soap. Soap for intimate hygiene is more suitable here.
From the very beginning of pregnancy, purchase a special bra that will not put pressure on the mammary glands - it does not have rigid elements, but it will accommodate your growing breasts well, support them and protect the skin from overextension. In addition, it is very comfortable to sleep in such a bra, because discharge from the breasts actively appears at night.
Malignant formations
The most dangerous for the body is breast cancer. The most alarming signal for a woman will be the appearance of bloody fluid from only one breast. Intraductal tumor most often becomes a consequence of the diseases described above. At risk are women who have never given birth, as well as those who gave birth at a late age. Alcohol addiction and poor diet are another factor leading to invasive cancer.
One type of cancer is Paget's disease; it occurs in only 4% of breast cancers. Symptoms of the disease are characterized by redness, burning and itching, the skin of the nipples and areolas peels off.
The nipple is sometimes pulled inward and bloody discharge is noticed. To make a diagnosis, it is necessary to perform a biopsy of the areolas. Treatment is by removing the tumor or the entire breast (myastectomy).
It is necessary to see a doctor, and at the first symptoms, make a diagnosis to eliminate the possibility of this disease.
Breast bleeding during feeding
Primiparous women may have complaints that milk comes from the breast with blood. The reasons for blood getting into a nursing mother's milk can be different. Only a doctor can say with certainty which of the reasons led to this. Often, cracks that appear from the baby’s diligent sucking can lead to the blood released from them getting into the milk. This is traumatic blood.
It is necessary to properly care for the juices during feeding and gradually the bleeding will go away. The delicate skin of the nipples of women, especially those who have given birth for the first time, is injured by the baby's sucking, and then it may be observed that blood bleeds during breastfeeding. If you regularly lubricate your nipples with lanolin ointment after feeding, you can prevent cracks and bleeding from the breasts during feeding.
Caution should be exercised when feeding a child older than one year. Its strong squeezing and rubbing of the mother's nipples can also lead to bleeding cracks
The same applies to using a breast pump. When there is excess milk, many express it using this device. But it must be used correctly, otherwise the capillaries under the skin of the nipples may rupture and, as a result, blood may leak.
Breast injury from a breast pump
Diagnostics
What needs to be examined?
The mammary gland of a man or woman is subject to examination. In addition, the patient will need to undergo a blood test to determine the level of white blood cells and measure hemoglobin levels.
A biochemical blood test is also used, which clearly shows the presence of tumor markers (proteins and antigens).
During the growth of a cancer cell, the process of their formation is most active. Using spectral analysis, the doctor can accurately determine the cause of the pathology.
A genetic blood test is also useful, which reveals a predisposition to breast cancer at the genetic level.
How to examine?
Examination of the mammary glands is carried out using instrumental methods.
The following diagnostic tests are used:
- Mammography. The patient is exposed to a small dose of radiation in the chest area. Using this method, developing pathologies can be detected already at the first stage of the disease. The method is very old, but widespread.
- Digital mammography. Some mammologists prefer to use a newer and improved diagnostic method in their practice, which uses semiconductor detectors. They ionize radiation and convert it into an electrical signal.
- Ultrasound. Fast, painless and safest way of examination. Ultrasound examination helps to detect breast lumps and cysts at the very initial stages of their formation. Ultrasound allows early detection of malignant tumors.
- Ductography. It is carried out by injecting a contrast liquid into the ducts of the mammary gland, which allows you to see any pathological processes in the mammary gland. A fast and modern method of ductography most accurately determines the location of a benign or malignant tumor, and also gives a specific idea of its size.
Methods for diagnosing breast cancer at an early stage are described in the video:
What to do
If the cause of blood from the chest is hormonal disorders, then they can be easily corrected by resorting to medications and without delaying the solution of the problem for a long time. A mammologist will determine the root cause of the pathology, referring you to the right specialist or prescribing the necessary diagnostics, which include:
- CT or MRI of the breast;
- mammography (for women after 45 years);
- ultrasonography;
- puncture taken from the mammary gland;
- blood test for cancer cells.
Depending on the results obtained, when a pathological process in the mammary glands is identified, the necessary therapeutic measures are prescribed. For bleeding during breastfeeding and the appearance of microcracks, various ointments and gels are prescribed. If the cause is injury or bruise, then an urgent visit to a doctor can prevent tissue malignancy, i.e., their possible degeneration into a cancerous tumor, which is often the result of injury.
Blood from the chest is a pathological condition that requires an immediate visit to the doctor. Doctors note that such a symptom indicates the presence of a serious illness.
Let's look at what diseases this symptom is typical for, how the diagnosis is made, and what treatment is prescribed.
Prevention
In order to avoid cracks in the papillary area and prevent bruising from this area, you must adhere to the following rules:
When breastfeeding, you must use special ointments and creams. It is best to apply emollients after feeding is completed to soak and moisten the nipples. You also need to change breasts when feeding so as not to cause stagnation of milk. Between feedings, pads should be used to remove excess milk and prevent it from irritating delicate skin. Monitor the condition of the mammary glands. In front of the mirror, you need to regularly examine your breasts and palpate them. If spots, lumps or different sizes of nipples are detected, you need to contact a mammologist and, if necessary, remove the tumor to prevent tumor progression
It is important to maintain an active lifestyle. Exercise regularly and eat right
Eliminate smoking from your life. Nicotine can form a harmful accumulation of microorganisms in the body. The chest is very susceptible to any influences within the body and suffers first. Wear comfortable, preferably natural, underwear. The bra should not cover the breasts too tightly and should not press anywhere. It is better to choose synthetic intimate underwear of good quality and pleasant to the touch.
Diagnosis and treatment
If a secretion with bloody spots begins to come out of your nipples, you should not delay going to the doctor, much less self-medicate. It can be dangerous for many reasons. First of all, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of developing cancer. Most traditional medicines have a pronounced warming effect, which can worsen the condition by increasing inflammation and accelerating the process of tumor development.
When there is discharge from the mammary glands, it is prohibited:
- warm the mammary glands by any possible means;
- postpone consultation with a mammologist, if there is no such specialist in the city, it is better to contact a gynecologist;
- on your own initiative, take hormonal medications, including oral contraceptives;
- squeezing out the secretion provokes its production.
The doctor will take a medical history and conduct an examination. Next, a set of laboratory and instrumental studies will be assigned:
- MRI or CT scan of the mammary glands;
- For patients over 39 years of age, mammography is prescribed; at younger ages, the procedure is indicated only if the development of breast cancer is suspected;
- Ultrasound;
- blood test for tumor markers;
- puncture of fluid from the mammary gland.
| Pathological conditions | Features of the therapeutic course |
| Nipple adenoma | An integrated approach to treatment is required - conservative and surgical methods. |
| Cystadenopapilloma | A benign neoplasm that is removed surgically. |
| Mastopathy | When a diffuse form develops, a solution of potassium iodide (25%) is injected into the nipple; in case of a nodular form, only surgery is indicated. |
| Sore nipples | Treatment of the skin with antiseptic solutions; multivitamin therapy is also indicated. |
| Mastitis | Taking a course of antibiotics, as well as topical ointments and antiseptic solutions. |
| Breast cancer | The disease in most cases requires an integrated approach, in particular surgery, radiation therapy and courses of chemotherapy. |
It is impossible to completely eliminate the likelihood of developing breast diseases, but there are preventive measures to reduce this likelihood:
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle, which includes proper nutrition and exercise;
- adequate sleep at least 6-8 hours every day;
- choosing high-quality underwear made from natural materials - bras must fit in size.
Ivanova Svetlana
General practitioner of the second category, transfusiologist, 29 years of experience
Diagnosis and treatment of problems with the musculoskeletal system (lower leg) and abdomen.
- pain and discomfort in the abdomen;
- bruises and injuries of the lower leg;
- cough, chest pain;
- acute respiratory infections, ARVI;
- food poisoning;
- cold;
- runny nose;
- general malaise;
- headache;
- aching joints;
- elevated temperature.
- Diploma in the specialty “General Medicine (Medical and Preventive Care)”, Chuvash State University named after. I.N. Ulyanova, Faculty of Medicine (1990)
- Internship in the specialty “Selected Issues of Therapy”, Kazan State Medical Academy (1996)
Refresher courses
- “Nephrology issues for therapists”, State Institute for Advanced Training of Physicians named after V.I. Lenin (1995)
- “Therapy”, Kazan State Medical Academy (2001)
- “Transfusiology”, Russian Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation (2003)
- “Therapy and Pulmonology”, St. Petersburg Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education of the Federal Agency for Health and Social Development (2006)
- “Transfusiology”, St. Petersburg Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education of the Federal Agency for Health and Social Development (2007)
- “Transfusiology”, Institute for Advanced Medical Studies of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Chuvashia (2012)
- “Therapy”, Institute for Advanced Medical Studies of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Chuvashia (2013)
- “Therapy”, Peoples' Friendship University of Russia (2017)
Place of work: MedCenterService clinic on Kurskaya
Breast cancer is the leader among cancer diseases affecting the fairer sex. It is no coincidence that every woman is recommended to carefully examine and monitor the condition of her breasts. Any formations, discharge, pain, discomfort in the mammary gland are a cause for concern, especially if blood is flowing from the nipples. Let's try to figure out why this happens and what to do in such a situation.
conclusions
A competent approach to identifying diseases will certainly prevent serious consequences and maintain health. Bringing together the main causes of discharge from the mammary gland, we can highlight the main thing:
- Any discharge appearing from the nipples, except milk in pregnant and lactating women, indicates disorders in the body and requires diagnostics.
- Pathology can be detected in a timely manner by regularly examining the breasts and visiting a mammologist.
- You cannot self-medicate - the diagnosis must be made by a doctor.
Bloody discharge in nursing mothers
Mothers also often notice that colostrum or milk gradually changes in consistency
Young mothers who have recently (before 3 months) given birth to a baby pay attention to the nipples. The milk can be traditional white or yellow
This is not a reason to worry, since lactation is restored within 3 months from the date of birth of the child.
If you notice that there are black or blue dots in the milk that look like small strings, do not be alarmed. This is not a disease or pathology. The mammary gland touches the walls of the channels in the milk ducts.
More transparent milk is called “hind milk”; it appears after the baby expresses or sucks out the main portion (50-70 ml).
This type of milk is suitable for supplementary feeding of the baby after porridge, vegetables and fruits. The peculiarities of the mother’s body should also be taken into account, since blood clots may also appear during feeding.
The reasons for their occurrence are justified by unstable lactation, when a woman tries to independently express more milk with her hands or a breast pump, causing injury to the ducts. In this case, blood in breast milk can occur due to mechanical damage, as well as due to a viral and infectious disease. If you squeezed the nipple too much or grabbed too much of the areola while expressing, there is a chance that the skin has cracked. The resulting wound bleeds, causing blood to leak into the milk. If there is blood inside the breast, an ultrasound scan should be performed to identify hollow and dark areas in the fatty tissue area of the breast.
There are other reasons that lead to bleeding, and they are associated with the onset of the third trimester of pregnancy. Bloody spots can be excreted in milk, which is not dangerous for women.
Effective Treatments for the Condition
The features of the therapeutic approach to bloody secretions from the mammary glands depend on what specific disease caused them.
Below are common breast pathologies in which red liquid appears spontaneously or under pressure from the nipples.
| Diseases | What treatment method is prescribed? |
| Nipple adenoma | The only option is surgical intervention. |
| Mastopathy | For the diffuse type, a 25% solution of potassium iodide is injected into the nipple. For the nodular type, the only surgical method is used. |
| Mastitis | Antibiotics. Antiseptic solutions and ointments. |
| Breast cancer | Exclusively carrying out the operation. |
| Sore nipples | Antiseptics. Multivitamin therapy. |
| Cystadenopapilloma | Eliminated surgically. |
In addition, it is necessary to refuse a contrast shower, choose a comfortable bra (that does not compress the breast), do not overheat the breasts in the bath and do not perform self-massages.
Taking medications
For mild stages of some diseases, drug therapy is prescribed. For example, the following drugs may be prescribed:
- Osmapox. Nursing women should take into account that the active substances of the antibiotic may pass into breast milk to some extent, so dosage adjustment is necessary.
- Hiconcil. An effective and safe antibiotic, can be used during pregnancy and pregnancy.
- Flemoxin-Solutab. A popular antibiotic, it is relatively harmless and does not contain sugar. It has no contraindications during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Vishnevsky ointment. Antiseptic with good healing characteristics. It has no contraindications other than allergies to components.
- Arnica. A natural medicine that has regenerative properties. A small amount of the drug is rubbed into the skin of the nipple. It is allowed to use no more than three times a day.
- Traumeel S. Anti-inflammatory and hemostatic agent, has wound healing properties. Apply 2-3 times a day, lightly rubbing into the nipples.
- Medela PureLan gel, which exhibits antiseptic capabilities. Heals microcracks in the nipples and areola area well and quickly. It does not contain artificial dyes, it is absolutely safe for babies, and has no contraindications.
If necessary, hormonal therapy and vitamin and mineral complexes are prescribed.
To treat cancer, only an integrated approach with hormonal and chemotherapy is required.
The formation of papillomas inside the breast ducts cannot occur without immunomodulators, vitamin complexes, antitumor and antiviral drugs, and antioxidants. Antibiotics are used to treat the inflammatory process.
Phytotherapy
The use of traditional medicine recipes for bleeding from the nipples is permissible only if you are sure that they are caused by injuries or microcracks, and not by more serious diseases.
It is almost impossible to cure benign formations and papillomas with homemade ointments and compresses, so they must be used together with prescribed medications.
A nursing woman can lubricate injured nipples:
- Breast milk.
- Fat.
- Sea buckthorn or rosehip oil (can be replaced with other natural oil).
- Carrot-apple juice.
The following folk recipes have good healing properties:
| Means | Application |
| Black poplar bud ointment | Ointment from poplar (black) buds has a good healing effect. Take 2 tablespoons of dry buds, grind into powder and combine with butter. Lubricate damaged nipples. |
| Flaxseed gruel | Grind the seeds and boil in milk to make a thick porridge. Wrap the warm pulp in gauze and apply to the damaged areas of the chest. |
| Kalanchoe juice | Squeeze the juice from the leaves of the plant, soak a bandage in it and apply it to the nipples. |
Treatment with surgery
When benign lumps form in the breast structure, causing red discharge, surgical treatment is used, thereby preventing their degeneration into a malignant form.
Types of operations used:
- Partial breast abandonment, when a tumor is removed in a designated area of the breast while preserving a significant part of the breast. This type of surgery is used only for small lumps. If a relapse of the disease occurs, the gland is completely removed.
- Complete excision of the breast. In some situations, the pectoralis minor or major muscle is removed along with it. If possible, the surgeon may leave the skin and nipple of the breast, which later allows the insertion of a prosthesis.
- With a certain history, individual lymph nodes can be removed, which prevents severe complications.
Even more interesting: