Liquid in the space of Douglas
The retrouterine space is localized in the abdominal cavity, behind the uterus. In medicine, it is also called the pouch of Douglas. On certain days of the menstrual cycle, the accumulation of fluid in the retrouterine space in small quantities is considered normal. In other cases, it indicates the presence of a gynecological disease.
Douglas space - description
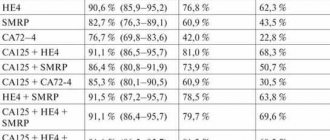
Fluid behind the uterus can be detected by ultrasound. To clarify the nature of its origin, a puncture is required. It is done during laparoscopic surgery. The material is taken with a 20 ml syringe. If necessary, the process of taking material is accompanied by ultrasonic monitoring. This avoids damage to the pelvic vessels. The resulting liquid sample is sent for laboratory testing. Additionally, a vaginal smear is taken and a blood test is performed.
An insufficient amount of material taken during puncture does not indicate the absence of pathologies. Blood collection may be hampered by adhesions in the pelvic area. In this case, the diagnosis is clarified through other laboratory tests.
Adhesive process - description
6.1. Abdominal puncture
Purpose of the operation: evacuation of ascitic fluid in case of abdominal dropsy.
Methodology: the puncture is made along the midline of the abdomen. The puncture point is chosen in the middle of the distance between the navel and pubis. The bladder must be emptied first. The patient is seated on the operating or dressing table. The surgical field is treated with alcohol and iodine. The skin and deep layers of the abdominal wall are anesthetized with a 0.5% novocaine solution.
The skin at the puncture site is incised with the tip of a scalpel. The puncture is made with a trocar. The surgeon takes the instrument in his right hand, displaces the skin with his left and, placing the trocar perpendicular to the surface of the abdomen, pierces the abdominal wall, removes the stylet and directs a stream of liquid into the pelvis. To avoid a rapid drop in intraperitoneal pressure during fluid extraction, which could lead to collapse, the external opening of the trocar is periodically closed. In addition, the assistant tightens the abdomen with a towel as the ascitic fluid flows out.
What happens during and after ovulation?
Ovulation is the period of increased fertility in a woman. It is accompanied by the release of the egg into the abdominal cavity. Normally, it occurs in the middle of the menstrual cycle. In the first half of the cycle, the egg matures in the dense capsule of the follicle. It is surrounded by follicular fluid. During ovulation, the walls of the follicle are torn, as a result of which its contents are released along with the egg into the retrouterine space. This process is facilitated by a sharp jump in LH levels in the body.
If a woman attends an ultrasound after ovulation, the doctor will find fluid in the pouch of Douglas. Its quantity depends on the volume of the follicle and the day of the menstrual cycle. The most fluid can be seen the day after ovulation. 3-5 days after the follicle ruptures, it is completely absorbed. Based on its presence, doctors often confirm that ovulation has occurred.
In addition to the fluid, there must be a corpus luteum in the ovary where the egg matured.
Basic Concepts
First, you need to understand what the space of Douglas is in women, where it is located and what functions it performs. It is a kind of pocket formed by the peritoneal fold and stretching from the posterior uterine wall to the rectum. In women, the pouch of Douglas is the deepest part of the abdominal cavity.
This formation received its name thanks to James Douglas, who was an English anatomist who lived in the 18th century and devoted his life to the study of the rectouterine cavity.
Causes of fluid in the pouch of Douglas
Fluid can enter the retrouterine space for a number of reasons. If it is present throughout the entire menstrual cycle, then we are talking about diseases of the reproductive system. The most common causes of fluid accumulation behind the uterus include:
- Adnexit;
- Complications of ectopic pregnancy;
- Cystic formation (More about follicular cyst and polycystic disease);
- Peritonitis;
- Ovulatory syndrome;
- Hyperstimulation of the appendages;
- Endometriosis;
- Hydrocele of the ovary;
- Malignant formations.
If the nature of the origin of the fluid is pathological, the woman notices the occurrence of other symptoms. Most often, diseases of the genital organs are accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen. It may be accompanied by a specific odor of vaginal discharge and problems with urination. General health also worsens. Low-grade fever may occur.
Inflammation and treatment
Penetration of fluid into the retrouterine space can be triggered by an inflammatory process. It affects the following organs of the reproductive system:
- Bladder;
- Uterus;
- Appendages;
- Fallopian tubes.
Inflammation occurs when the genitals are overcooled or as a result of the development of infectious diseases. If after ovulation the fluid resolves on its own, then treatment will be required for inflammation. Initially, studies are carried out to determine the cause of inflammation. A blood test will show an increase in the number of leukocytes and ESR. Depending on the result, the method of treatment is selected.
ESR erythrocyte sedimentation rate test - description
Drug therapy includes taking antibiotics. They are administered intravenously or intramuscularly. Treatment is carried out in a hospital. Additionally, vitamin therapy is carried out. If the appearance of fluid is due to the presence of an abscess, an operation is performed during which the source of inflammation is eliminated. To prevent adhesions, the use of Longidaza vaginal suppositories is prescribed. Additionally, physiotherapeutic treatment is carried out. The course includes 7-10 procedures of magnetic therapy, electrophoresis or ultrasound.
6.2. Laparocentesis
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcreatorsru
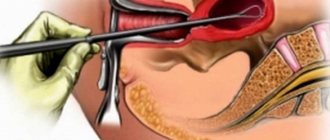
Laparocentesis is a puncture of the peritoneum with the introduction of a drainage tube into the cavity. The puncture is performed by a doctor (Fig. 6.1).
Indications: ascites, peritonitis, intra-abdominal bleeding, pneumoperitoneum.
Contraindications: coagulopathy, thrombocytopenia, intestinal obstruction, pregnancy, inflammation of the skin and soft tissues of the abdominal wall.
Equipment and instruments: trocar for puncture of the abdominal wall with a diameter of 3-4 mm with a pointed mandrel, a drainage rubber tube up to 1 m long, a clamp, a syringe with a volume of 5-10 ml, 0.25% novocaine solution, a container for collecting ascitic fluid, sterile tubes , dressing material, sterile cotton swabs, sterile tweezers, skin needles with sterile suture material, scalpel, adhesive plaster.
Methodology: the doctor and the nurse assisting him put on caps and masks. Hands are treated as before surgery, sterile rubber gloves are worn. It is necessary to ensure complete sterility of the trocar, tube and all instruments in contact with the skin. The puncture is performed in the morning, on an empty stomach, in the treatment room or dressing room.
The patient empties his bowels and bladder. The patient's position is sitting, or in severe cases lying on the right side. As a premedication 30 min. Before the study, 1 ml of a 2% solution of promedol and 1 ml of a 0.1% solution of atropine are administered subcutaneously. The puncture of the abdominal wall is carried out along the midline of the abdomen at the middle of the distance between
Presence of bloody fluid in the retrouterine space
Hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity requires urgent medical intervention. This condition is considered extremely dangerous to the health and life of a woman. Blood pools behind the uterus if there is serious damage to the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or digestive organs. The following symptoms are typical for this situation:
- Pain in the lower abdomen and lower back;
- Weakened state;
- Dizziness, loss of consciousness;
- Bloody vaginal discharge.
Physiological causes of blood accumulation behind the uterus include menstruation and the postpartum period. In these cases, ultrasound monitoring is carried out only if there is an urgent need.
Pathological accumulation of blood can be caused by a rupture of the fallopian tube as a result of an ectopic pregnancy. The rupture is caused by the growth of the fetus in an atypical place. This happens when the tubes become obstructed or their contractility is impaired. In order to timely diagnose the abnormal location of the embryo, you need to visit an ultrasound room and analyze the dynamics of the hCG hormone. According to statistics, most often a pathological pregnancy is diagnosed before the tube ruptures.
Once blood is detected in the pouch of Douglas, surgery will be required. Initially, measures are taken to pump out the blood. The next step is to eliminate the source of the problem. In case of an ectopic pregnancy, part of the fallopian tubes is removed.
6.10.1. Puncture of the joints of the upper limbs
PUNCTURE OF THE SHOULDER JOINT
If there are appropriate indications, puncture of the shoulder joint can be performed both from the anterior and posterior surfaces. In order to puncture the joint from the front, the coracoid process of the scapula is probed and an injection is made directly under it; the needle is advanced posteriorly, between the coracoid process and the head of the humerus, to a depth of 3-4 cm.
Rice. 6.14. Puncture of the shoulder, elbow and wrist joint.
PUNCTURE OF THE ELBOW JOINT
The arm is bent at the elbow joint at a right angle. The needle is inserted posteriorly between the lateral edge of the olecranon and the lower edge of the epicondilis lateralis humeri, directly above the head of the radius. The superior inversion of the joint is punctured above the apex of the olecranon process, moving the needle down and anteriorly. Puncture of the joint along the medial edge of the olecranon is not used due to the risk of damage to the ulnar nerve (Fig. 6.14b).
PUNCTURE OF THE RADIAL JOINT
Since the articular capsule on the palmar surface is separated from the skin by two layers of flexor tendons, the dorsal radial surface is a more accessible place for puncture. The injection is made on the dorsal surface of the joint area at the intersection of the line connecting the styloid processes of the radius and ulna with the line that is a continuation of the second metacarpal bone, which corresponds to the space between the tendons m. extensor policis longus et m. extensor indicis (Fig. 6.14c).
What pathologies is he talking about?
The accumulation of blood in the pouch of Douglas is often accompanied by uterine bleeding. Possible reasons for its appearance include:
- Risk of miscarriage;
- Ectopic pregnancy;
- Rupture of the uterus or ovary;
- Ovarian dysfunction;
- Endometriosis;
- Pathological formations on the cervix;
- Tumor-like process;
- Bleeding after abortion.
Ectopic pregnancy - description
Most often, women mistake uterine bleeding for a hormonal imbalance, accompanied by a shift in menstruation. But the causes of the pathological process may be more serious. Therefore, it is important to visit a gynecologist immediately after detecting suspicious symptoms. Discharge that appears during pregnancy is especially dangerous. They indicate a threat of miscarriage or an ectopic location of the ovum.
Rupture of the appendage, uterus or cystic formation can be caused by active sexual intercourse, excessive physical exertion or injury. In this case, the pain will be acute. On this basis, a woman can lose consciousness.