Most IVF protocols involve stimulation of ovulation. This makes it possible to obtain a larger number of eggs, increasing the chance of successful conception and embryo transfer. But even without such a procedure, to obtain an egg you have to do an ovarian puncture. All these manipulations lead to the fact that the ovaries after IVF undergo changes that do not quite correspond to those that occur during a natural pregnancy. In most cases, the changes are reversible and do not cause concern to the woman. But there are a number of complications directly related to the work and condition of the ovaries. They require timely treatment.
Ovarian cysts: types and diagnosis
The primary detection of cystic formation occurs as part of an ultrasound examination. On ultrasound, neoplasms even of very small size are visible.
There are certain standards for ultrasound diagnostics for cystic formations. Ultrasound is performed at different phases of the cycle and over several months. Because functional cysts - follicular cyst and corpus luteum cyst - usually disappear on their own within several menstrual cycles or with the necessary therapy.
If a cystic formation is detected, tests for tumor markers are also prescribed (CA 19-9, CA 125, CA 15-3, CA 72-4, He 4). High oncogenic risk indicators are an indication for consultation with a gynecological oncologist. There is no other method to make sure that this is not a malignant formation. If the results for tumor markers are negative, treatment tactics are variable. The prognosis for entering an IVF program is also individual and depends on many factors.
Ultrasound examination in the presence of a cervical cyst
In most cases, in the absence of symptoms of the disease, a cervical cyst is detected during colposcopy. However, to clarify the nature of the disease, the doctor always prescribes an ultrasound examination in the presence of cystic formations of the uterus, which is preferably performed with a vaginal sensor. It allows you to identify changes in the structure of the tissue of the cervix, see how vascularized it is, what the size of the cyst is and how deep it lies.
Ultrasound examination of the cervix for a cyst does not differ significantly from echoscopy of the uterus itself. If the examination is carried out from the anterior abdominal wall, then a special gel is applied to the lower abdomen and a special sensor of the ultrasound machine is moved along it. When using a transvaginal sensor, a condom is put on, lubricated with gel and inserted into the vagina.
Follicular cyst and IVF
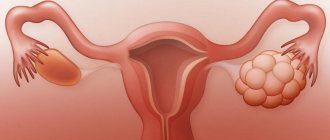
A follicular cyst is a dominant follicle that grew to ovulate, but ovulation did not occur (most often for hormonal or inflammatory reasons) and it continued to grow.
Diagnosis and treatment algorithm for suspected follicular cyst:
- Ultrasound on days 5-9 and 18-23 of the cycle;
- blood test for tumor markers (CA 19-9, CA 125, CA 15-3, CA 72-4, He 4);
- dynamic observation for at least 2 cycles;
- if the test for tumor markers is negative, hormonal therapy may be prescribed.
A cyst larger than 3 cm before IVF is a contraindication for the program. In all other cases, the question of the need for preparatory therapy and the possibility of entering into an IVF protocol with a follicular cyst is decided individually.
{vivod-form-receive}
What is hyperstimulation
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome is a condition in which multiple enlargement of the gonads occurs due to the growth of several follicles. Depending on the severity of the pathology, these pelvic organs increase several times from 3-4 cm. The gonads can grow up to 20 cm.
Hyperstimulated ovaries appear in women who use assisted reproductive technologies. Isolated cases of OHSS occurring in the natural cycle, without the use of hormonal agents, have also been documented. Hyperstimulation during IVF occurs most often, since the protocol necessarily uses drugs that stimulate follicle growth. This condition can be determined by the characteristic clinical picture:
- ascites – accumulation of aqueous substance in the peritoneal cavity (the abdomen “swells”);
- pain in the lower abdomen (the severity of the symptom depends on the severity of the pathology);
- difficulty breathing resulting from the effect of fluid on the diaphragm in the pleural area;
- nausea accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea (appears due to irritation of the digestive tract);
- anasarca - accumulation of fluid in the lower part of the body, manifested by severe swelling of the arms, fingers, legs and peritoneum;
- decrease in pressure indicators;
- impaired diuresis (less urine is produced).
Corpus luteum cyst and IVF
Corpus luteum cyst usually appears in the second phase of the menstrual cycle, after ovulation. This cyst may not disrupt the cycle or interfere with pregnancy; it also goes away on its own within a few months. If it does not go away, we may be talking about a true ovarian tumor.
Diagnosis and treatment algorithm for suspected corpus luteum cyst:
- Ultrasound on days 5-9 and 18-23 of the cycle;
- blood test for tumor markers (CA 19-9, CA 125, CA 15-3, CA 72-4, He 4);
- dynamic observation for at least 2 cycles
- if the test for tumor markers is negative, hormonal therapy may be prescribed.
A corpus luteum cyst before IVF is not a contraindication for the protocol. If the corpus luteum cyst does not go away, a 10-day course of treatment is usually sufficient, after which IVF can be done.
{vivod-form-receive}
Causes of cervical cysts
- Childbirth. When the mucous membrane of the cervix is damaged during childbirth, epithelization occurs quite quickly. At this time, the functioning of the glands may be disrupted and the ducts may become blocked, which leads to the formation of a cervical cyst.
- Abortion. During abortion, if the specialist is unqualified, the epithelium of the cervix is damaged, which leads to the development of cysts.
- Menopause. The mucous membrane of the cervix of a woman who is beyond reproductive age becomes thinner over time, and the glands become vulnerable. They produce more mucus in response to irritation, which clogs the ducts. This is how a cervical cyst is formed.
- Infectious diseases. During the inflammatory process of the reproductive organs, the glands of the cervix become clogged and a cyst is formed.
- presence of an intrauterine device for a long time;
- the presence of an inflammatory process in the ovaries;
- metabolic and hormonal homeostasis disorders.
Endometrioid cyst and IVF
An endometrioid cyst is a true neoplasm of the ovaries. In case of initial detection, surgical removal is indicated, followed by immunohistochemical examination of the material before starting preparation for the program.
BUT: if tests for tumor markers are negative, the size of the endometrioid cyst does not exceed 3 cm, the woman has a critical decrease in ovarian reserve and the operation may lead to the impossibility of obtaining her own eggs in the future, we are considering options for obtaining eggs before removing the cyst, or IVF with an endometrioid cyst (but Before entering into the protocol, we prescribe therapy to reduce its size).
Diagnosis and treatment algorithm for suspected endometrioid cyst:
- Ultrasound on days 5-9 and 18-23 of the cycle;
- blood test for tumor markers (CA 19-9, CA 125, CA 15-3, CA 72-4, He 4);
- dynamic observation for at least 3-6 cycles.
If the patient has recurrent confirmed endometrioid cysts, the key factor in deciding the possibility of IVF with an ovarian cyst is its size. Endometrioid cysts up to 3 cm in size are an acceptable condition for the program. However, the decision is always within the competence of the attending fertility specialist.
Popular questions
If the drug is selected correctly, taking into account all chronic diseases, blood tests for hormones, ultrasound of the pelvic organs and the absence of contraindications from the mammary glands, hormonal drugs will never lead to weight gain, but on the contrary, they will eliminate hormonal imbalances in the body, and problems will disappear against their background with hair, nails and skin, if this has bothered you before.
Laser polypectomy is a modern method that allows you to remove a polyp as gently as possible without leaving scars, so you can start planning your pregnancy from the next cycle after the operation.
In 99% of cases, in our clinic, there is no need to remove sutures after laparoscopic operations, since special cosmetic stickers and sutures are used, which also do not require treatment and allow you to shower within 24 hours after the operation
No, it does not, since our clinic uses the most modern methods to treat cervical pathology without the subsequent formation of scars and deformities of the cervix. Also, after such treatment of cervical erosion, it is already possible to plan pregnancy from the next menstrual cycle.
Fortunately, for our patients, this is nothing more than a myth. The fact is that when performing plastic surgery, we restore the vaginal wall layer by layer, anatomically correctly; such a wall is not afraid of any squats! This is great because after such an operation, patients do not have to buy special circles for sitting, they can easily have lunch at the table and return to their normal lifestyle immediately after the operation.
After laparoscopic surgery, there is a restriction on sports and physical activity, which varies from 2 to 4 weeks. It depends on what kind of operation was performed. After all, laparoscopically you can remove a small ovarian cyst, or you can remove a giant uterine fibroid. Of course, the timing will be different, and in the first case you can limit yourself to a couple of weeks, and in the second you can start sports only after a month. One more important point should be remembered: the return to physical activity should be gradual, you should start exercising with half of your usual loads. This may take another one to two weeks.
All our efforts are aimed at returning you to an active and fulfilling life as soon as possible, as if the operation had never happened. Don't put off traveling and traveling, enjoy your vacation. Within 2 weeks after the operation, you will be able to freely fly by plane, be in the sun, swim, dance, and try exotic food.
Women often have numerous formations on the cervix: erosions, polyps, cysts. In this case, patients are always concerned about the question: is it possible to get pregnant with a cervical cyst (retention, nabothian glands)?
Like all female reproductive organs, the cervix is a very changing organ throughout life. Various variants of its development, diseases and borderline conditions are quite easily identified during a standard medical examination, since almost all of this organ is clearly visible when displayed in gynecological examination mirrors.
Treatment
If we talk about the treatment of a functional neoplasm, then basically it is not carried out. When regression does not occur, hormonal medications are discontinued and others are prescribed.
Doctors rarely resort to surgical intervention. The patient is offered surgery if the size of the tumor is very large and it continues to grow dynamically. Then there is the option of cyst rupture. Resection is carried out using:
- Laparoscopy. A more modern method is laparoscopy. It is a method that is gentle on the body and does not even leave a seam in the abdominal area. The rehabilitation period passes quite quickly and is also painless. Several punctures are made, and through one of them the specialist inserts a special sensor that transmits an image of the internal organs to the display. The abdominal cavity is filled with CO2, then doctors begin to eliminate the tumor.
- Laparotomy. This operation is classified as a type of abdominal operation. The surgeon makes an incision and removal occurs through it. In this case, the rehabilitation process may be delayed. The risk of certain complications also increases. However, there are also positive aspects, because this type of intervention is prescribed very rarely. If the pathology is diagnosed at the stage of pregnancy, then treatment is not carried out. The condition of the tumor is monitored by ultrasound, and it is performed very often.