Are uterine fibroids removed independently or together with the uterus?
Uterine fibroids are a disease of the female reproductive system that occurs against the background of hormonal imbalances. This pathology is localized in the uterus and has many manifestations. The symptoms of this disease bring inconvenience and discomfort in a woman’s life. In addition, at a young age, uterine fibroids can cause infertility. Many women, when diagnosing the disease, have a question: “Is the uterus removed for fibroids?” If minor fibroid nodes are identified, hormonal therapy or conservative myomectomy may be prescribed. Is it possible to remove fibroids without removing the uterus and then get pregnant? Undoubtedly, conservative myomectomy is one of the methods of treating such conditions as infertility.
Removing fibroids while preserving the uterus is better for the body, since this organ is the point of application for ovarian hormones.
Services table
| Service name | Price |
| Promotion! Initial consultation with a fertility specialist and ultrasound | 0 rub. |
| Repeated consultation with a fertility specialist | 1,900 rub. |
| Initial consultation with a reproductologist, Ph.D. Osina E.A. | 10,000 rub. |
| Hysteroscopy | RUB 22,550 |
| Ultrasound gynecological expert | RUB 3,080 |
| Therapeutic and diagnostic laparoscopy (difficulty category 1) | 65,500 rub. |
| Therapeutic and diagnostic laparoscopy (difficulty category 2) | RUB 82,200 |
| Program "Women's Health after 40" | RUB 31,770 |
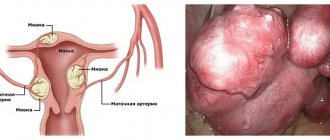
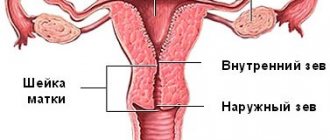
What is uterine fibroid
Myoma is a hormone-dependent nodular neoplasm that arises from the myometrium, the muscular layer of the uterus. The serous membrane (peritoneum) of the uterus and the internal mucous membrane (endometrium) do not participate in the pathological process, they only cover the surface of the tumor.
The disease is characterized by the appearance of nodes in the walls of the uterus. They can grow into the abdominal cavity.
The tissue structures of the tumor may consist only of hypertrophied muscle fibers or include additional layers of connective tissue (fibromyoma). Homogeneous muscle tissues with a soft structure are called leimomia.
Uterine fibroids can develop in different directions. The tumor is located in the lumen of the reproductive organ (submucosal). There are variants of the location of fibroids with separation of the muscle layer, thickening and deformation of the uterine wall (interstitial fibroids), as well as with protrusion of the myomatous node into the abdominal cavity (subserous localization). It is possible to place myomatous nodes with dissection of the broad ligament of the uterus (intraligamentary localization).
New growths are recorded both on the stalk and on a broad base, in rare cases immersed in the middle muscle layer.
Although fibroids are a benign neoplasm, there is a risk of malignancy (1%). Often the development of a tumor is accompanied by serious complications that lead to the decision to undergo surgery.
The need for surgery
The treatment method for fibroids depends on the degree of the disease, the size of the nodes and the dynamics of their growth.
In this case, the following indications for surgical intervention are distinguished:
- constant pain in the lower abdomen. At the same time, the discomfort does not go away, but has increasing dynamics;
- the presence of bleeding or chronic discharge with red ichor;
- disruption of the cyclicity of menstruation, which can lead to disruption in the female reproductive system;
- severe signs of anemia (nausea, weakness, pallor of the face and limbs);
- severe compression of neighboring organs by the tumor and disruption of the digestive and genitourinary systems;
- the size of fibroid nodes in diameter is more than 6 cm;
- causeless increase in tumor size (3 cm per year);
- the presence of a genetic predisposition and other signs for the transition of fibroids to a malignant formation;
- the appearance of other fibroids;
- the formation of fibroids “on a stalk”, which can lead to its twisting and a sharp deterioration in the general condition of the woman;
- chronic gynecological diseases (polycystic ovary syndrome, changes in the functioning of the endocrine system).
Indications for removal of fibroid nodes
Removal of uterine fibroids (myomectomy) is indicated for nulliparous women of reproductive age. In some cases, when the cause of difficulties in conceiving a child is deformation of the uterine cavity due to submucosal or large interstitial nodes, removal of the tumor is considered a treatment for infertility. Removal of fibroids is carried out after conservative therapy does not reduce the size of the tumor and does not affect the intensity of its growth.
Indications for surgical intervention are also:
- Large mima sizes (12 weeks pregnancy or more);
- The presence of concomitant pathological processes, such as ovarian cancer or endometriosis;
- Necrosis of the myomatous node caused by torsion of the leg or other factors leading to malnutrition of the tumor;
- Impaired functionality of organs located close to the uterus, for example, disruption of the intestines or bladder;
- Severe pain syndrome;
- Risk of malignancy of the tumor;
- Heavy bleeding that cannot be corrected, as well as regular uterine bleeding leading to anemia;
- Intensive growth of tumor and myoma nodes.
The decision to remove fibroids is made if the tumor interferes with conception or bearing a child. An indication for radical removal of fibroids along with the reproductive organ may be the large size of the tumor, the specificity of its location or development.
You may be interested in: Diagnosis of uterine fibroids and size for tumor removal surgery
Myomas vary in size:
- small , when the tumor is no more than 2 cm (5-week pregnancy);
- medium , when the tumor size is 2-6 cm (11-week pregnancy);
- large , when the size of the fibroid is more than 6 cm (12 - 15 week pregnancy);
- gigantic , when the uterus enlarges to the size of a 16-week pregnancy.
Surgical treatment is used for all tumor sizes if there are indications for this (necrotic processes in the tumor, impediment to conception). However, in most cases, tumors that are 12 weeks pregnant or more must be removed.
Indications for surgical intervention
The following describes situations when it is worth performing an operation to remove fibroids or the organ as a whole (regardless of how old the woman is):
- If the size of the myomatous node corresponds to the period of pregnancy after the 12th week;
- If uterine fibroids increase catastrophically quickly (for 4 or more weeks of pregnancy);
- When myomatous nodes manifest themselves with frequent and heavy bleeding (both menstrual and intermenstrual), the patient develops general anemia due to blood loss, accompanied by pallor of the skin, poor health and fainting;
- If fibroids cause severe pain (severe cramps during menstrual bleeding, abdominal pain due to tumor compression of neighboring organs and nerve endings in the spine);
- If an ultrasound examination reveals irreversible changes in the myomatous node (its necrosis, rupture, infection);
- When the patient has uterine fibroids of a subserous or sumbucous type, growing on a long stalk, through which it connects to the organ. There is a high probability of torsion of the leg, which may result in severe uterine bleeding (if the fibroid is submucosal) or peritonitis (if the node is peritoneal);
- If the fibroid is located in the cervical area;
- If the myomatous node is located submucosally on a thin long stalk and is visible in the lumen of the cervix, it begins to “be born”, it can be removed surgically by twisting the stalk;
- In preparation for IVF;
- If the patient is diagnosed with infertility associated with a myomatous node, its size or location;
- When fibroids cause miscarriages or miscarriages.
If disturbances in the functioning of neighboring vital organs are diagnosed:
- Urination is impaired, urine stagnates in the bladder, which can cause inflammation or the formation of sand and stones;
- The back wall of the bladder is compressed, urine is thrown back into the ureter, which can provoke pyelonephritis and other inflammatory diseases, cause dilation of the renal pelvis (hydronephrosis);
- The process of defecation is disrupted (the rectum is pinched), which is why the patient experiences prolonged constipation, threatening poisoning of the body;
- Compression of the nerve endings near the rectum occurs, which causes radiculitis (severe lower back pain) and pain in the heart and lower extremities.
Contraindications
Myectomy is not allowed in the presence of large or multiple nodes, when the tumor is located in the cervical region, or when active growth of fibroids is registered in a patient who is in menopause. Limitations for myectomy are the patient’s severe somatic condition, the presence of current infectious and septic ailments, and problems with general anesthesia. In such cases, alternative treatment methods without general anesthesia are chosen and combined with conservative therapy.
It is also not allowed to remove fibroids if:
- profuse and uncorrectable uterine bleeding (menometragia), leading to severe anemia and a risk to the patient’s life;
- large-scale necrosis of the neoplasm, especially if it is accompanied by a secondary bacterial infection, septic endometritis, thrombosis, or when there is a possibility of developing peritonitis;
- severe disruption of the functioning of organs located near the uterus (bladder, ureters, intestines), caused by their displacement and compression by a large myomatous node or an enlarged reproductive organ.
If the above conditions are present, a hysterectomy is performed.
Non-surgical treatment of fibroids
Treatment of fibroids without surgery is carried out if the size of the tumor does not exceed 2 cm, and the course of the disease is not aggravated by various factors. In the absence of severe pain, uterine bleeding and excessive growth of pathology, the following conservative methods of therapy are used.
- The use of drug therapy in the form of taking hormonal drugs of various spectrums of action (Progesterone, Utrozhestan, Duphaston, Danazol). Medicines are also prescribed to suppress ovulation and accelerate menopause (Janine, Buserelin, Zoladex, Regulon). The combination of medications reduces the excessive production of hormones and helps slow down the development of the tumor.
- Carrying out myolysis. The method is based on the effect of electric current or laser, which destroys the tumor. The procedure is carried out if there are no more than 5 nodes up to 3 cm in size. They also use cryotherapy using liquid nitrogen, which freezes the pathology.
- Physiological procedures. Techniques are used that can quickly eliminate the inflammatory process and slow down the rate of tumor growth. The most popular methods: magnetic radiation, electrophoresis, baths with medicinal drugs. All manipulations are carried out after the completion of the menstrual cycle.
- FUS ablation procedure. A non-invasive treatment method in which the fibroid is exposed to ultrasound through a tomograph. If there are multiple nodes, the process is not carried out, as it does not give a positive result.
- Traditional medicine is used as an auxiliary and supportive method of non-surgical treatment of fibroids. It is recommended to use decoctions or teas based on natural substances containing phytoestrogens (herbs, essential oils). All prescriptions require consultation with your doctor before taking them directly.
- The use of hirudotherapy (treatment with leeches). This procedure allows you to reduce the outflow of blood in the veins and speed up metabolic processes in the body. However, the technique has a number of contraindications: anemia, poor blood clotting, low blood pressure. When using this method, it is necessary to obtain the approval of the attending physician.
Preoperative preparation
Before the operation, the woman undergoes a complete gynecological examination to exclude diseases similar to uterine fibroids. Held:
- colpocytology . Allows you to study cells taken from the cervix to exclude tumor malignancy;
- smears on the flora . Gives the opportunity to identify inflammatory and infectious processes against which gynecological operations are not performed;
- aspirate from the uterine cavity . The examination allows us to exclude the presence of an oncological process;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs . The study is aimed at clarifying the size of the uterus, the nodes in it, and allows us to clarify the feasibility of the chosen method of tumor removal.
Laboratory tests are carried out:
- blood analysis;
- coagulogram, hemostasiogram;
- analysis for hepatitis, syphilis, HIV;
- determination of blood group, Rh factor;
- ECG.
5 days before surgery (associated with removal of the formation), antianaerobic and antibacterial drugs are prescribed. If there are pathologies of the thyroid gland, corrective treatment is carried out.
2-3 days before surgical treatment, a slag-free diet is recommended (it is necessary to exclude unrefined vegetables and fruits, wholemeal bread, fatty meats, fish and poultry, cabbage). You can drink without restrictions until the last 8 hours before surgery. Depending on the access and volume of surgical treatment, 1–2 cleansing enemas are given before the operation: the evening before and the morning of the operation. On the day of surgery, the bladder is emptied.
2 hours before surgery on the uterus, a drug is administered intravenously to reduce the risk of infectious diseases.
Hygienic treatment of the perineum and anterior abdominal wall is performed on the day of surgery in a hospital setting to reduce the risk of developing inflammation of the hair follicles and damage to the epithelium.
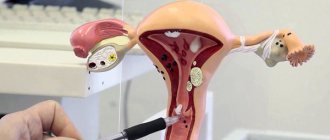
Surgical options
Before the operation, the gynecologist conducts a full bimanual examination, prescribes instrumental methods (magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound diagnostics), and assesses possible risks.
There are a number of contraindications when surgery cannot be performed:
- Cardiac and respiratory failure.
- Allergic reaction to iodine if uterine artery embolization is planned.
- Acute period of inflammatory process or oncology at the level of the pelvic organs.
After confirming the fact of the operation, the surgeon chooses the option of surgical access depending on the size of the fibroid, concomitant pathology, and the patient’s age.
Myomectomy
Surgical organ-preserving intervention for the purpose of isolated removal of a myomatous node of the body or cervix. There are several techniques - hysteroscopy, laparoscopy or laparotomy.
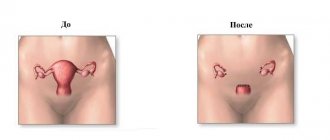
Extirpation (removal) of the uterus
Removal of fibroids along with the uterus (hysterectomy) is prescribed when conservative methods are ineffective, as well as in the case of severe compression on adjacent pelvic organs.
Online access options:
- Laparoscopic. A gentle type of operation with quick post-operative recovery and minimal cosmetic defect. The incision for the laparoscope and manipulator is pinpoint, which heals with virtually no scar on the surface of the skin.
- Laparotomy. The operation is an “open” approach through the anterior abdominal wall, so rehabilitation will take a long time.
Depending on the planned volume of resection (removal), hysterectomy is divided into:
- Complete (supravaginal). The body and cervix are completely removed, the vagina remains intact.
- Incomplete. Only the body of the uterus is resected. Applicable when nodes are localized exclusively in the body or fundus of the uterus.
- Radical. Removal of the entire uterus and upper third of the vagina.
With any method, the ovaries and fallopian tubes are not removed. After surgery, the removed organ is necessarily sent for histology to exclude oncological pathologies.
On what day of the cycle is removal performed?
Removal of uterine fibroids is sometimes carried out on an emergency basis, regardless of the day of the cycle. Myectomy in such cases is performed laparotomically. Urgent surgical intervention is required in case of internal inflammation, necrosis of fibroids, or torsion of the tumor stalk.
Myectomy is performed laparoscopically and hysteroscopically, without making abdominal incisions. The procedure is performed using devices equipped with special instruments and a video camera. When performing this type of intervention, visibility of the uterine cavity is important. Myectomy on the first or second day of the cycle is complicated by unclear vision due to menstruation. A cloudy image can lead to accidental rupture of the vessel and difficulty in determining the location of the injury in order to promptly electrocoagulate. Removal of fibroids during menstruation is complicated by a high risk of infection, since during this period the inner layer is separated from the walls of the uterus, which leads to an increased risk of damage and infection.
It is considered optimal (when there are no emergency indicators) to perform the operation on days 7–10 of the menstrual cycle. During this period, you can be sure that there is no pregnancy and you can easily determine the nature of postoperative discharge.
What treatment will be required after surgery?
If hysterectomy led to surgical menopause, then gynecologists select medications for hormone replacement therapy (HRT). They come in mono form or as a combination of drugs.
The duration of HRT is determined individually by the treating gynecologist, depending on the severity of postoperative menopausal syndrome. The minimum period of therapy is 3 months, the maximum until the proper onset of menopause (approximately 50 years).
Monopreparations (Gynodian-depot, Klimara, Divigel). Contains estrogens and is used exclusively after hysterectomy. They are not suitable as a therapy for natural menopause due to the high risk of tumor development. Produced in the form of solutions for intramuscular injections, patches, gels.
Combined drugs (Femoston, Klimonorm, Trisequence, Livial). They contain estrogens and gestagens. Prescribed after relief of the main manifestations of posthysterectomy syndrome.
To prevent osteoporosis against the background of early menopause, medications with calcium are prescribed.
Important! Only a specialist can draw up an adequate treatment regimen, taking into account many individual indicators. Self-administration of medications is extremely dangerous to health.
Methods for removing uterine fibroids
When choosing a method for removing uterine fibroids, doctors give preference to minimally invasive methods that preserve the uterus, especially when the patient is under 40 years old and plans to have a child.
The choice of surgical tactics is determined by the clinical situation, concomitant pathologies, the location of the myomatous formation, the patient’s intention to have children in the future, the size of the node tumor, the type of fibroid and other individual factors.
Among the common surgical methods for removing myomatous nodes, abdominal, laparotomy, laparoscopic, hysterectomy or hysteroscopic operations stand out as effective.
Laparotomy
Laporotomy involves removing fibroid nodes through an abdominal puncture. Such operations are not performed often, since there are less invasive surgical methods for removing myomatous tumors.
Basically, laparotomy myomectomy is used for the growth of large nodes in the abdominal or pelvic cavity, when active progression of the tumor with deformation of the uterine body is observed. The procedure is indicated for large myomatous nodes (12 - 15 week size).
After the operation, the patient spends several days in the hospital until the incision heals. The rehabilitation period is 2 – 4 weeks.
Laparoscopy
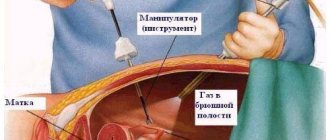
Laparoscopic myectomy is the most preferred method of surgical removal of fibroids. The procedure is performed through punctures in the abdominal wall. The wounds are small and heal quickly, leaving no marks. The patient remains in the hospital for about 7 days after the intervention.
Indications for laparoscopy are the size of the nodes no more than 0.8 cm, the enlarged uterus is more than 15 weeks old. During the procedure, up to 4 nodules with a total diameter of no more than 1.5 cm can be removed. The method is applicable for interstitial and subserous tumors no larger than 5 cm. Access to the problem area is provided through a small incision and therefore the intervention is low-traumatic and cannot cause adhesions. The operation is performed with special equipment - a laparoscope, which is inserted through the uterine cavity through a puncture on the abdominal wall. The camera is inserted through the umbilical ring, the same puncture is used to inject CO2 into the abdominal cavity, which is necessary to expand the space between the walls of the internal organs, in order to obtain a normal view and a place for safe manipulation.
The removal process is completed by applying double-row endoscopic sutures to the bed of the node, which contributes to the further formation of a full-fledged scar that will retain its integrity during pregnancy.
The severed myomatous node is removed using morcellators through the existing puncture. In some cases, the application of an additional colpotome hole is required.
Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopic myomectomy for uterine fibroids is performed using a hysteroscope - a special instrument that is inserted into the uterine cavity in an intervaginal manner. The method is used when it is necessary to remove a single node located on the back or front wall of the reproductive organ. The operation is performed on an outpatient basis. The optimal time for intervention is the first week of the menstrual cycle. A hysteroscope is a device with a camera, a light source and a device that is inserted into the uterine cavity through an artificially dilated cervical canal. The doctor controls the actions using a monitor. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia, sometimes spinal anesthesia is used if necessary.
Transcervical hysteroscopy is not used for nodes larger than 5 cm, which are difficult to evacuate through the cervical canal. The downside of this method is considered to be dense postoperative scars on the wall of the uterus, the likelihood of adhesions and endometriosis.
Generally, hysteroscopic myomectomy is not accompanied by blood loss. A woman who has undergone such an intervention retains the ability to give birth naturally.
Is it possible to do without surgery?
Basically, it is necessary to remove the uterus after the age of 40, when the woman does not plan to have any more children and the organ is no longer needed. In this case, doctors are required to monitor the condition of the tumor(s) in advance, find out how much they are progressing, and whether it is worth intervening surgically. The main indication for surgery is the patient’s age after 40 years and the size of the myomatous nodes exceeding the gestation period of 12 weeks and growing rapidly over time (more than 4 weeks per year) . It is also necessary to remove the organ if doctors suspect that uterine fibroids have begun to degenerate into a malignant cancerous tumor (sarcoma). Then, hysterectomy is allowed in young women (under 40 years old) who have not had children in order to save their lives.
There are many cases where, after 40 years, uterine fibroids themselves begin to decrease with the onset of menopause (due to a lack of female hormones in the body) and disappear after some time altogether. This usually takes several years. In this case, the operation to remove the organ can be postponed or even canceled - it will not be needed.
If one or more myomatous nodes are detected, it is necessary to undergo a full examination so that the doctor, having a complete picture of the patient’s health condition, makes a decision on the advisability of surgery. In women under the age of 40, surgeons try to remove fibroids while preserving the organ or most of it.
After 40 years, doctors agree that the best option during menopause would be complete removal of the uterus to avoid relapses (recurrence of fibroids) and cancer.
Postoperative period
Immediately after the end of the anesthesia (if the procedure is performed under general anesthesia), a fairly pronounced pain syndrome appears. It is treated with painkillers.
The postoperative period includes electrophoresis and other physiotherapeutic procedures: drug correction of hormonal balance, antianemic therapy, spa treatment, mud baths.
The rehabilitation period after removal of uterine fibroids takes about 1 month in most cases.
Nutrition
It is important to balance your diet within 2-3 days. After surgery, intestinal functions may be temporarily impaired. Constipation should not be allowed to occur, since a strained act of defecation leads to divergence of the seams. Nutrition on the first day is based on liquid and semi-liquid meals, and restoration of the normal diet is allowed after 6-8 days.
If fibroids have caused the development of chronic iron deficiency anemia or when surgery was accompanied by large blood loss, iron-rich foods should be introduced into the woman’s diet. Additionally, antianemic iron-containing medications are prescribed.
Recommendations after discharge from hospital
In order for wounds to heal quickly, it is recommended to avoid sexual intercourse during the postoperative period. Strict adherence to the diet is necessary. During the first few months, visiting the bathhouse, sauna and solarium is not allowed.
Light physical activity such as gymnastics, dancing, daily walking, and swimming are useful. During this period, you need to dress according to the weather; you should not wear tight synthetic underwear.
It is necessary to maintain a sleep-wake schedule and avoid stressful conditions.
In general, rehabilitation after fibroid removal is 6 months; after the time has elapsed, the woman can return to her normal lifestyle. It is recommended to visit a gynecologist every six months and undergo an ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
How will life change after hysterectomy?
After surgery, there are 2 types of discomfort possible – physical and emotional. If the physical one can be stopped with the help of medications, then the emotional situation is more complicated.
Only the ovaries can produce hormones in the female body. The job of the uterus is to bear a child. Therefore, if during the operation only the uterus was removed, then signs of menopause (hot flashes, weight gain, changes in skin turgor, vaginal dryness, early aging) are usually not observed. But in some cases, hysterectomy can provoke an earlier onset of menopause. This condition is called posthysterectomy syndrome, which comes in three types:
- Transitional (transitory). It occurs several months after surgery and lasts for a limited period of time (maximum up to a year). Most often it occurs in young women.
- Persistent. All clinical menopausal manifestations have been present for more than a year with a trend of constant stable deterioration.
The most difficult thing that happens to a woman immediately after surgery is the inability to perceive herself fully. Her husband can help her with this first of all. If this problem cannot be solved within the family, then you should seek advice from a psychologist. With its help, the psycho-emotional component is leveled and internal balance is restored. The woman begins to accept her new physical condition.
For how long is sick leave issued?
The attending physician issues a certificate of incapacity for work for a period of no more than 15 days; it can be extended by a medical commission.
The average recovery time after removal of uterine fibroids using minimally invasive methods is 15 days. The woman is in the hospital for 5–7 days, since during such a period constant medical supervision is required. Subsequent recovery takes place at home. In the standard course of postoperative recovery, sick leave after removal of fibroids lasts up to 45 days.
Doctors' recommendations to speed up recovery
To ensure that fibroids do not remind of themselves after surgery, and that rehabilitation takes less time, patients must strictly follow certain rules. Doctors recommend the following:
- wearing a special bandage and training using the Kegel system helps to avoid prolapse of the vaginal walls;
- urination disorders associated with weakened bladder ligaments and a lack of estrogen are eliminated with the help of exercises to strengthen the abdominal muscles and therapy with hormonal drugs;
- Constant monitoring of the condition of adhesions and sutures will reduce the likelihood of pain and other negative consequences;
- sanitation and suturing of the fistula tract will avoid secondary infection;
- minimizing the discomfort caused by premature menopause after hysterectomy is carried out by hormonal therapy and physiotherapy.
With postoperative depression, the patient also needs the help of specialists. Constant communication with the doctor, the friendly attitude of relatives and friends helps to get rid of the inferiority complex and a speedy return to normal life.
Hormonal levels can be maintained if surgery reveals the possibility of saving the patient one of the ovaries.
Drug therapy
Rehabilitation after removal of uterine fibroids is accompanied by taking medications. This therapy is individual in nature. The use of:
- means for relieving pain (analgesics, NSAIDs);
- drugs to thin the blood and prevent blood clots (anticoagulants);
- blood-forming agents
- immunostimulants;
- vitamins
Since removal of fibroids causes changes in the reproductive system, most women require hormonal medications after surgery. Even if the uterus is not affected, there is excessive secretion of estrogen and decreased levels of progesterone, which indicates a hormonal imbalance and increases the risk of relapse of the pathology.
What is forbidden to do after surgery
To avoid complications during the rehabilitation period after surgery to remove uterine fibroids, the following is not allowed:
- maintaining an overly active lifestyle (avoid long trips, especially air travel);
- be exposed to excessive physical exertion (protect the abdominal muscles, the weight of objects lifted should not exceed 2 kg);
- have sex within the next 1.5–2 months (if libido decreases, immediately inform your doctor about this);
- swimming, especially in open water, visiting baths and saunas (to avoid infection);
- neglect hygiene.
Dietary recommendations
Nutrition in the period after surgery to remove fibroids plays a special role. The menu should consist of products that prevent gas formation and constipation. Dehydration is not allowed. With a high calorie content, the diet should be rich in proteins, vegetable fats and carbohydrates.
When dieting, preference is given to lean meat and fish, fresh vegetables, fruits and dairy products. You should refuse:
- jelly;
- jelly;
- baked goods;
- sweets;
- strong tea, coffee and carbonated drinks.
Products included in the diet should be prepared by boiling or baking. After removal of uterine fibroids, you should not consume fried or smoked foods, as well as alcohol in any form.
Daily regime
One of the conditions for speedy rehabilitation is maintaining a healthy lifestyle and maintaining a daily routine. To do this you need:
- spend more time outdoors;
- take walks;
- distribute work and rest evenly;
- ensure complete, healthy sleep;
- avoid stressful and conflict situations;
- reduce the time spent in front of the TV or at the computer.
Calmness, reading books, listening to light music, etc. contribute to improving your condition and recovery.
Consequences of the operation
Removal of uterine fibroids is not considered a dangerous or difficult procedure. However, the operation can cause certain complications:
- infectious lesions of the wound area during or after the intervention;
- risk of relapse;
- the occurrence of atherosclerotic diseases or breast cancer.
Possible consequences of the operation include the likelihood of premature termination of pregnancy in the future, pathological course of labor (caesarean section is recommended) and the development of adhesions.
There may be some spotting in the first few days, but this is not your period. To determine the length of the cycle, you need to take into account only the start date of the previous menstruation. The monthly cycle after removal of fibroids is generally restored within 35–40 days. Lengthening or shortening of 1 - 2 subsequent cycles is acceptable and is considered within normal limits.
After removal of uterine fibroids, specific complications are possible, such as complications after anesthesia, damage to nearby organs, the development of inflammation, problems with intestinal patency and peritonitis.
According to experts, the risks of consequences are much lower than the likelihood of losing the uterus and reproductive function after a hysterectomy, which is performed when the pathological process is advanced.
Consequences of removal of the uterus with fibroids
When the uterus is removed, ovarian function decreases. According to medical statistics, the risk of breast and kidney tumors increases. Bacterial vaginosis often occurs.
Most long-term effects are associated with a decrease in the amount of estrogen, which also accelerates the aging process of the body.
Complications after surgery are infectious. The safest in this regard are laparotomy and laser methods.
Based on available reviews from women who have undergone hysterectomy, situations can be generalized. What causes the most fear is the method of surgery. In second place are concerns about personal life and intimate relationships after 45 years. The third is the long-term consequences of the operation.
When is pregnancy possible?
It is important to know that myomectomy does not lead to the disappearance of menstruation and the onset of premature menopause.
Preservation of the ovaries and uterus allows the patient to maintain reproductive function. Pregnancy after removal of the uterus is possible after complete restoration of the functional abilities of the endometrium.
It is better for a woman after such an operation to plan a pregnancy no earlier than 3 months after the intervention. Sexual intercourse is allowed only after 6 weeks. Compliance with deadlines is especially important if laparotomy myomectomy was performed with suturing of the uterine wall.
Post-castration syndrome or consequences of hysterectomy
The consequences of removing the uterus can be:
It is necessary to completely remove the uterus only if there is a good reason for it: there are no “extra” organs in the human body!
Alternative methods
If a situation arises when surgical intervention is not advisable or there are certain contraindications to them, alternative methods of removing uterine fibroids are used. These methods include the use of laser, FUS ablation, and uterine artery embolization.
Laser therapy
The use of a laser beam is a gentle therapeutic technique. The laser's impact is dosed and directed only to the problem area. The intervention is bloodless and leaves no scars on the uterine body.
The recovery period after such an intervention is no more than three days. The method is safe and highly effective, approved by leading experts and popular among patients.
Embolization
This intervention is an expensive method of myoma treatment. The effectiveness of the method is quite high compared to surgical removal of fibroids. The essence of the procedure is as follows: under local anesthesia, a microcatheter is passed through the femoral artery and an occlusive solution of polyvinyl alcohol is injected through the vessels.
Nutrition to the neoplasms comes through the vessels. After administration of the drug, the supply pathways are blocked and the flow of blood into the myomatous nodes is stopped. As a result, they shrink in size and lose functionality.
After embolization, the patient may complain of pain in the lower abdomen, which disappears after a few hours.
If the procedure is not carried out correctly, purulent processes and infarction of the uterine body may occur, which leads to the removal of the reproductive organ.
The procedure is not recommended for subserous nodes. Some patients develop amenorrhea (absence of menstruation) after UAE.
Fuz – ablation
The method refers to conservative methods of treatment. The essence of the procedure is focused ultrasound evaporation of the fibroid node under MRI control.
Ultrasound waves are fixed on the tumor, heat it up to 90 degrees, which leads to cellular destruction of the tumor. The method is effective, but is not used often, only in the case of localization of fibroid formations on the anterior wall or on the uterine fundus. Treatment is indicated for nodes measuring 2–9 cm.
Fuse ablation is contraindicated in cases of unrealized reproductive function, infertility, or subserous pedunculated myoma nodes.
Removal of fibroids is an organ-preserving intervention and does not lead to severe and irreversible consequences. Timely removal of myomatous nodes and proper treatment in compliance with the instructions of doctors allows you to maintain reproductive function and live a healthy and fulfilling life.
How to properly treat fibroids without removing the uterus
Unfortunately, one of the most common gynecological diagnoses among patients throughout the post-Soviet space is uterine fibroids.
In Russia alone, the number of patients with a similar diagnosis is at least 70%. But why then has there recently been an increase in the number of women choosing to solve this problem in Israel? What is the reason that more and more patients from the CIS countries trust their health to Israeli specialists, and not to doctors from local clinics? The answer is simple - a completely different approach to women’s health.
“The best cure for a headache is the guillotine,” this joke from the category of “black” humor is known to many. But the saddest thing is that when treating uterine fibroids, most specialists from the CIS countries, in all likelihood, adhere to exactly the same principle: we remove everything that interferes. And the worst thing is that the moral aspect, given such an inadequate approach of the post-Soviet healthcare system, does not particularly bother some doctors.
The objective reality is this: most specialists practice “the old fashioned way”, considering surgery to remove uterine fibroids (myomectomy) the most radical and effective treatment, and many have only a vague idea about modern methods of treating the disease. In addition, it is sad to realize, but this problem also has a material context: for many specialists involved in the surgical treatment of uterine fibroids, operations to remove them are the main source of income.
And the medicinal method of treating patients in the CIS only causes bewilderment from fellow gynecologists from other countries: why should the drug Duphaston be prescribed everywhere to stop the growth of uterine fibroids, if it, being an analogue of the female hormone progesterone, only provokes rapid tumor growth?! And if so, then again there is only one thing left - surgery... A vicious circle, isn’t it? One of the leading Russian gynecologists considers such, if I may say so, “treatment” simply barbaric towards a woman.
Meanwhile, who, if not doctors, should know about the sad consequences of such, to put it mildly, solution to the problem. After all, any woman is a potential mother, so what kind of future awaits someone who was “cured” in this way during her childbearing years?!
In addition, patients with such a diagnosis are unlikely to have information that removal of the uterus entails equally serious consequences:
- the risk of developing thyroid cancer and breast cancer increases many times;
- “posthysterectomy syndrome” develops (similar to menopause), which leads to faster aging;
- there is a significant increase in body weight and, as a result, a decrease in quality of life, including sexually.
Of course, doctors do not impose anything on anyone: after all, this is only your decision. Formally, a patient diagnosed with uterine fibroids is registered at a local clinic, and that’s where everything ends happily. It’s good if a woman is periodically observed by a gynecologist, but many of those who live in the countries of the former USSR prefer to do without this, hoping for the traditional “maybe it will pass.” Those women who are concerned about the diagnosis and periodically visit a gynecologist are still offered, after several years of observation, to remove the fibroid without preserving the uterus (provided that the patient does not plan to give birth). Hence the sad statistics: every 2-3 residents of the post-Soviet space who have reached the age of 55 have had their uterus removed; In more than 70% of cases, the uterus was completely removed.
So is there a way out of the vicious circle caused by the once developed standards of Soviet medicine, which have long since become obsolete?
Israeli specialists guarantee the effectiveness of treatment, which allows preserving all reproductive functions of the uterus and avoiding serious consequences resulting from surgical removal of this organ. In most cases, during diagnosis, the decision is clear - preservation of the uterus and its reproductive functions.
Such treatment effectiveness in Israel is achieved by using one of three main methods of treating uterine fibroids:
1.UAE method (uterine artery embolization)
The method is based on the difference between the level of blood supply to the tissues of the uterus and fibroids. The uterus, being one of the organs of the reproductive system, has a powerful circulatory system. But fibroids are just a neoplasm and, having an underdeveloped circulatory system, die when the arteries are blocked. The appointment of UAE will help to avoid surgical intervention, saving the woman from long-term rehabilitation, physical and psychological discomfort and risks associated with myomectomy (hysterectomy surgery): damage to the bladder, intestines, fallopian tubes; peritonitis, development of intestinal obstruction, bleeding; a large number of risks associated with the use of anesthesia.
During the procedure, a catheter is inserted into the femoral artery under local anesthesia, through which emboli (ball size 300-700 microns) enter. It is these balls that block blood access to the uterus. The same manipulations are repeated on the other femoral artery. All treatment for uterine fibroids in an Israeli clinic takes only 1 day. The procedure is carried out under the influence of adequate radiation from an X-ray machine for 15-40 minutes. The rehabilitation period after UAE lasts no more than 7 days, and after surgery to remove the uterus (myomectomy), recovery can last up to 6 weeks.
Unlike Russian diagnostic standards, in Israel, when treating uterine fibroids, neither its size, nor location, nor duration of formation have any significance. The most important result when using UAE is the ability to plan a pregnancy within a few months after the procedure. With treatment in Israel, a woman no longer has to worry: there will be no recurrence of uterine fibroids. Whereas when performing a myomectomy, the result will be inconsistent: in half of the patients who have undergone surgery to remove uterine fibroids, the nodes grow back.
ExAblate focused ultrasound treatment
This is a revolutionary non-invasive method of treating fibroids, developed by Israeli high-tech specialists. The method does not require surgery or hospitalization of the patient. The procedure uses focused ultrasound waves to create high temperatures in the fibroids, combined with magnetic resonance imaging to accurately visualize the location of the internal organs.
When ultrasound waves are focused on the fibroid, much like a magnifying glass focuses light, the ultrasound waves heat and destroy the fibroid tissue. During the procedure, the doctor uses the system to monitor the treatment process and accurately determine the location of the fibroids. In addition, the system allows the doctor to measure the temperature inside the fibroid and thus determine the success rate of the procedure.
Advantages of using focused ultrasound:
- The procedure is non-invasive and does not require surgery or hospitalization
- The procedure is practically painless, there are no serious side effects
- The procedure does not damage the uterus and is also suitable for women interested in preserving fertility
- The procedure allows for a quick return to normal lifestyle (within one to two days)
How long does the procedure take? The procedure is performed lying on a special procedure table installed inside a standard magnetic resonance scanner for three to four hours, depending on the size of the fibroids.
How is the procedure performed?
- During the entire procedure, you will lie inside the magnetic resonance scanner. The doctor will begin the procedure with several MRI scans of the pelvis to identify the fibroids (or fibroids) on magnetic resonance images of the pelvis.
- At the beginning of the procedure, a thin beam of focused ultrasound aimed at the uterine fibroids will heat the tissue for 15 seconds.
- An MRI will be taken after each warm-up cycle to image the fibroid as it is being treated and measure its temperature. After this, the system will move to the next point. The entire cycle will repeat every 90 seconds until the entire process is completed.
- The procedure typically involves 30-100 separate pulses of focused ultrasound over three to four hours.
- After the procedure is completed, additional MRI images are taken to determine the success of the treatment.
How will you feel during the procedure?
Feeling of warmth on the skin or inside the body in the pelvic area. During focused ultrasound treatment, you may feel something like a muscle spasm during each cycle. During the procedure, your doctor will explain to you what sensations are normal and show you how to stop the procedure using the safety button, which you will hold in your hand, if you feel anything bothering you.
How long will it take after the procedure before you feel better? According to your initial symptoms. Research has shown that most women experience relief from fibroid-related symptoms within three months of the procedure.
3.Laparoscopic surgery
This technique is used both independently and in cases where the uterine fibroids have too large nodes and UAE may not be sufficient to positively resolve the problem of a planned pregnancy. Operations of this kind, carried out in Israeli clinics, are characterized by low trauma and minor blood loss and are absolutely safe for patients.
4. Method of abdominal surgery for uterine fibroids
Operations of this kind are very labor-intensive, and their implementation is trusted only to specialists of the highest level, of whom there are many in Israel. Abdominal surgeries for uterine fibroids can be considered a high degree of aerobatics, similar in level of scrupulousness and jewelery only to the skill of Leskov’s Lefty, who was able to stamp his name on a flea savvy by Tula masters. During the operation, the specialist needs not only to “pick out” the fibroid nodes with exceptional precision, but also to scrupulously palpate with his fingertips all externally intact tissue, so as not to miss a single, even nascent nodule that is not yet visible to the diagnostic apparatus. And the second stage of the operation requires no less precision and skill from the surgeon, because he needs to stitch the uterine tissue layer by layer to eliminate the possibility of sutures coming apart during a subsequent pregnancy.
Of course, there are specialists of this level in the CIS countries, but the situation needs to be assessed objectively: their number hardly exceeds several dozen. But the demand for this kind of surgery is quite high... but not many people can perform truly professional and high-quality abdominal surgery for uterine fibroids in Russian clinics.
Food for thought
1. Women who have heard the diagnosis of “uterine fibroids” should not rush to accept the doctor’s offer to undergo surgery to remove the uterus. Such operations have long been, unlike in the CIS countries, not the only correct solution to the problem. Among all treatment methods for this disease, removal of the uterus ranks last. And if the gynecologist advises you of this kind of operation, then consult another specialist. Remember that treatment of uterine fibroids is carried out individually, based on the situation of each patient, and does not fall under the standard “cut to hell.” Remember: surgical treatment may be the only correct solution for only a small proportion of women.
2. You should not take various kinds of herbal remedies (herbs) and dietary supplements (Indipol, Epigalat, Stella, etc.) as medicines, since they do not have any therapeutic effect on fibroids and will not relieve you from the need for further treatment. A number of hormonal drugs can only stop the growth of myomatous nodes or reduce their size, but no more. And the effect of this kind of “treatment” will be short-term and insignificant. Remember: none of the dietary supplements, homeopathic preparations and herbal remedies so actively recommended in the post-Soviet space have ever undergone clinical tests for compliance with international standards, which means there is no guarantee of their safety and effectiveness.
3. Each of the myomatous nodes grows from one muscle cell of the uterus during its damage due to inflammatory processes, surgical trauma to the uterus, or the breakdown of one or more genes. Subsequently, their growth is influenced by sex hormones (mainly progesterone), so an increase in nodes is observed during pregnancy and in the second phase of the menstrual cycle. When menopause occurs, uterine fibroids regress. But the use of drugs that simulate artificial menopause, which makes it possible to reduce nodes, gives only a temporary effect. After the cessation of the effect of such drugs, the nodes acquire their previous size and the symptoms of the disease (pressure on the bladder, pain) return again.
4. You should not hope that uterine fibroids will disappear after menopause: in some patients, myomatous nodes not only do not shrink, but even begin to grow. In some cases, this can lead to uterine bleeding even after menopause.
It should be remembered: the use of hormonal therapy, dietary supplements and herbal medicines to relieve menopausal symptoms can provoke an increase in uterine fibroids.
5. In some cases, the size of the uterus together with the nodes can reach enormous sizes (up to the size of a full-term pregnancy!), disrupting the functions of the abdominal organs, which leads to the development of various diseases. The growth of such uterine fibroids can be asymptomatic, and the growth of the abdomen can only be regarded as excess weight.
6. The development of uterine fibroids can result in prolonged and excessive menstruation, which over time leads to the development of chronic anemia. In turn, anemia leads to decreased immunity, chronic fatigue, hair loss, sagging skin, etc. Iron deficiency anemia leads not only to oxygen starvation of tissues, but also to disruption of the functions of important organs, as a result of which tachycardia, headaches are added to the above symptoms pain, dizziness, cardiac dysfunction.
Reviews from women
Dear readers, was this article helpful? What do you think about removal of uterine fibroids, have you encountered such a situation. Leave your feedback in the comments! Your opinion is important to us, and it will be useful for other women!
Ksenia
“After examination by a gynecologist, they advised me to have a myomectomy and remove the myomatous node. I was very worried, I thought it would be terribly painful, and from a psychological point of view it was also difficult. However, after a conversation with the doctor, I calmed down. All functions of the uterus and ovaries after removal of fibroids laparoscopically are preserved, and the rehabilitation period is short. I took the plunge and am very pleased with the results. All the unpleasant symptoms that prevented me from living normally for years have disappeared, and I feel good.”
Bella
“I underwent laser therapy to remove myomatous nodes. The procedure is bloodless and does not leave scars on the uterus, which eliminates complications during childbirth if I decide to give birth to a child. I undergo regular examinations with a doctor, there are no relapses, the fibroids have stopped growing.”
Radical removal of the uterus and appendages
When fibroid tissue degenerates into cancer, radical removal of the uterus, appendages and lymph nodes in the groin is required. Such situations are rare. Usually, with late presentation, when abdominal pain has already begun, sudden weight loss. Removal of the uterus and ovaries provokes an early onset of menopause. To avoid the associated phenomena - osteoporosis, hormonal disorders, decreased libido, weight gain, increased blood pressure - it is necessary to take hormonal medications.
At a relatively young age, radical organ removal can cause depression. But surgery saves lives in serious situations. Moreover, after surgery, the woman will have to undergo several courses of chemotherapy and radiation.
Important! Regular examination and early diagnosis make it possible to completely get rid of the disease in the initial stages without resorting to surgery.
Operation methods
When removal of the uterus is inevitable, all that remains is to determine which operation is best: extription - removal of the organ along with the cervix, or supravaginal amputation, which allows it to be preserved. Also, based on the situation, surgeons decide whether to save the ovaries. Of course, the ideal option is to remove only the uterus, leaving the ovaries and cervix, because... they are extremely important for women’s health, which is already noticeably deteriorating. According to the method of execution, there are three types of operations in which the uterus can be partially removed:
Laparoscopy : three small punctures are made on the abdominal wall, a laparoscope - an instrument resembling a long knitting needle - is inserted into the hole, and the necessary manipulations are carried out with its help. This is the most gentle type of surgical intervention. 2 weeks before the operation you need to take tests, 3-4 days before you start following a special diet. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia.
Laparotomy : after the procedure, a scar will remain from the incision in the abdominal wall: its size is small and the seam will gradually become less noticeable, but the patient most likely will no longer have an ideal tummy. Modern medicine rarely uses laparotomy, preferring less traumatic methods. General anesthesia is administered, rehabilitation will take about 2 months.
Hysteroscopy - most often used. The uterus is removed through the uterine cervical canal using a hysteroscope. Such an operation keeps the abdominal wall intact, which avoids unnecessary damage and shortens the recovery period. The complete removal of an organ is a hysterectomy - the most difficult operation performed, which has the most severe consequences. This is a very serious procedure that requires preparation, including moral preparation. The operation may cause complications:
- large blood loss requiring transfusion;
- injury to the intestines or urinary tract;
- introduction of infection.
According to statistics, there is 1 death per thousand of such operations. Hysterectomy with preservation of the appendages does not bring significant hormonal changes, because the ovaries continue to secrete hormones in the same volume. Normalization of hormonal levels preserves the patient’s libido and sense of her own femininity. Complete physical rehabilitation will take several months. Psychological recovery may be delayed, especially if the ovaries are removed.
Removal of the uterus: what is dangerous, what to do?
At the end of the operation, which includes removal of the formation, patients are most afraid of complications. How to avoid them after the removal of myomatous nodes is completed?
After removal, you should monitor your health and support your weakened body. However, we do not recommend taking measures for fibroids on your own. Some women are treated with boron uterus and other means. This is prohibited! You may harm yourself.
In the first days after the intervention (removal of myomatous nodes by surgery), you should eat as many protein foods as possible. The diet should include fish, meat, egg whites, and nuts. It is necessary to drink pomegranate and beet juice, eat liver and other foods rich in iron. This will reduce the consequences of blood loss.
It is important to take a multivitamin after surgery. They will help support a weakened body, restore the balance of micro- and macroelements.
It should be understood that along with the removal of the uterus during the intervention, an infection may be introduced into the body. It is very important to recover properly. This will reduce the effects of inflammation.
The operation should not be interpreted as a disability. Take walks, do simple exercises, but don't overload. If the intervention was abdominal (liquidation of the uterus, etc.), be as careful as possible. This operation can cause a number of health problems. You need to be constantly monitored by a doctor.
Prevention of various diseases that may occur after intervention to remove the uterus or only its nodes should be carried out. It is important to understand that during this period the risk of hormonal imbalances, atherosclerosis, breast cancer, coronary heart disease, and menopause increases.
Important! If you have had not only myoma removed, but also your uterus, you should not visit the sauna, bathhouse, or spend time in the sun.
Request a call back Get a free consultation
Rehabilitation period
After removal of the uterus, the woman remains in the hospital for some time. The length of her stay there depends on the type of surgery that was chosen. If a laparoscopic hysterectomy was performed, this period may take from 3 to 5 days. But the operation, performed by the vaginal method, involves recovery in a hospital for 8-10 days.
In the first days after amputation, the patient may experience very severe pain, which can be relieved with the help of narcotic or non-narcotic drugs. Further, this symptom will subside, but may still make itself felt for several more weeks. This is the norm.
You can get out of bed after surgery with your doctor's permission. Here, too, much depends on the chosen method of intervention. Some are allowed to rise after an hour, while others are forced to wait a whole day. In any case, you cannot lie too long, since physical activity is important. Especially for intestinal motility. But you shouldn’t overdo it with loads either.
To prevent the development of thrombophlebitis, women who have undergone uterine amputation are recommended to wear compression garments. For patients over 50 years of age who have had several births, a special bandage is indicated. This corset will support the weakened abdominal walls.
Diet plays an important role during rehabilitation. You should try to exclude foods that cause flatulence from your diet. Fatty, salty, spicy, smoked, sweet, coffee, strong tea, and alcohol are also not recommended. It is advisable to eat more fiber-rich vegetables, fruits and grains.
Gymnastics also promotes speedy recovery. In particular, several months after uterine amputation, it is recommended to perform Kegel exercises. There are other specially designed complexes. It is advisable to first consult a doctor about this.
For one and a half months after the operation, it is not recommended to take a bath, visit a bathhouse or sauna. Sexual activity should be excluded for the same period. To avoid seams coming apart, you need to be careful when lifting heavy objects.
In most cases, surgical treatment for fibroids is combined with conservative treatment. During the recovery period, patients are prescribed antibiotics to exclude infection, anticoagulants to prevent vascular diseases, and receive infusion therapy to replenish lost blood.