View prices
Skip to main
FRAU KLINIK expert of the first channel
Frau Clinic
Network of plastic surgery and cosmetology clinics of Professor S.N. Blokhin and Dr. Wolf I.A.
Sign up
+7 Daily from 9:00 to 21:00
- Plastic surgery
- Before and after
- About the clinic
- Media
Sign up Tel: +7 (495) 120 06 10
YouTube
- home
- Gynecology
- Cervical amputation
Procedures and problem solving Cervical amputation is a gentle organ-preserving surgical intervention performed in gynecology for the purpose of radical treatment of underlying and precancerous conditions.
Surgeries to remove the cervix
Knife amputation
A direct indication for the use of this technique is the diagnosis of early stage cancer. Amputation of the organ is performed using a surgical instrument (scalpel) by excision followed by removal of the cervix, parametrial tissue and upper vaginal part. At the same time, the woman’s reproductive ability does not suffer (this method is considered gentle, since the surgeon’s lancet does not affect such important organs as the ovaries and fallopian tubes).
Cone-shaped electroexcision (radio wave conization)
Used for severe diseases (for example, tumors and dysplasia). The operation is performed in a specially equipped surgical room. To remove the organ affected by the disease, a diathermoelectrosurgical device is used, as well as a special electrode (Games-Rogovenko), the peculiarity of which is the ability to adjust the radio wave length depending on the anatomy of the cervix. In order to protect healthy vaginal tissue from radio wave exposure, a special rubber cuff is used, which the doctor inserts into the vagina.
This technique has its contraindications. So, it cannot be used when:
- pathologies in the structure of the cervix in nulliparous women of reproductive age,
- the patient has a history of a diagnosis of “preinvasive cervical canal cancer”,
- acute inflammatory disease of the genital organs,
- leukocytosis.
Video fragment of the behavior of radio wave conization of the cervix
Laser amputation
It is used for dysplasia and benign formations that threaten to develop into malignant tumors. The main advantage of the procedure is that the surgeon does not remove the entire organ, but only cauterizes the area where the tumor is located. Amputation is performed using a surgical loop, which is a current conductor. Scar tissue forms at the site of exposure over time.
This technique has its drawbacks. Surgery using currents can lead to infertility. For this reason, it is not recommended for young girls.
Ultrasound amputation
The method of removing the cervix using an ultrasound method is similar in principle to laser amputation and has similar indications and consequences. The only difference is that tissue removal is performed using ultrasound.
Cryodestruction
The method is based on the principle of exposing diseased areas to cold. Cervical tissue is cooled to -180 degrees using liquid nitrogen. Low temperatures contribute to the destruction of cell membranes and tissue death.
Radiosurgical technique
Removal of cervical tissue occurs through the non-contact destructive effect of radio waves on the cells of the organ. To perform the operation, the Surgiton device (manufactured in the USA) is used. This method is considered the safest and also has a number of advantages:
- radio waves do not burn healthy tissues,
- painlessness of the procedure,
- the possibility of use in the treatment of diseases of the genitourinary system in nulliparous women of reproductive age.
Cost of the operation
Removal of the cervix can be performed free of charge under the compulsory medical insurance policy. The main method used in this case is making cuts with a scalpel. Not every hospital has equipment for laser or other types of removal.
Prices for paid services start from 40,000 rubles. In Moscow, the average cost of the procedure is 70,000 rubles. The more sophisticated technology is used, the more expensive the operation will be. In some clinics, you must pay separately for anesthesia and examinations.
Recovery and aftermath
For 7 days after the operation, the patient should be under the supervision of medical staff. She should be provided with the following medical services:
- prescription of painkillers (if required);
- prescribing antibiotics to reduce the risk of inflammation;
- installation of a urinary catheter.
After discharge, the patient must follow medical recommendations:
- It is necessary to minimize intense physical activity;
- You need to stop using tampons for a while;
- It is not recommended to take too hot baths or showers for 6 weeks.
Sex after cervical removal
Many women who have undergone cervical amputation fear an inadequate sex life. Gynecologists are rushing to dispel these fears. Due to the sensitivity of the vaginal walls, patients retain the ability to experience orgasm. The only inconvenience is long-term abstinence (for 6 weeks) from sexual intercourse with your partner.
Complications
In some cases, amputation of the cervix is accompanied by complications, among which purulent infections, sepsis, and bleeding are most often observed. When an operation is performed by an unqualified doctor, necrosis of the vaginal dome may develop.
In order to exclude the presence of unpleasant complications, the gynecologist prescribes a routine examination. 2 weeks after amputation, you need to make sure that the rehabilitation period is proceeding smoothly.
Extirpation, or trachelectomy, is an operation to remove the cervix, which is a low-traumatic surgical procedure and is prescribed for a number of pathologies of the genital organs.
Amputation of the cervix is carried out in the following cases:
- in the early stages of cancer (only the cervix is damaged, and the surrounding organs are completely healthy);
- with cervical hypertrophy - it occurs in the presence of pathological processes of the reproductive system (prolapse of the uterus, inflammatory processes);
- with chronic endocervicitis;
- with ectropion - uterine rupture during difficult childbirth or late abortion;
- in the presence of erosions that cannot be treated;
- if there are cervical deformities, for example, scars, congenital anomalies.
Preparing for surgery to remove the cervix involves taking tests (blood, urine). If there is a suspicion that a malignant tumor has formed on the cervix, then you need to undergo magnetic resonance and computed tomography, as well as a biopsy. The blood will also be checked for the presence of tumor markers. If there are inflammatory processes in the body, then surgery is possible only after they are completely cured.
1-2 days before surgery you need to take a laxative to cleanse your intestines. You can also do a cleansing enema. You also need to remove pubic and perineal hair.
Indications for surgery
Cervical amputation may be performed in the following cases:
- Cancerous and precancerous conditions, provided that surrounding organs and tissues are not affected.
- Constantly arising polyps against the background of chronic inflammation of the cervical wall.
- Severe injuries, for example, ruptures during childbirth, organ deformation.
- Erosion that cannot be cured by alternative methods.
- Prolapse or lengthening of the cervix.
Important! The decision to remove is made by the doctor. If there is an opportunity to perform plastic surgery while preserving the organ, then it should be used. The specialist must carefully weigh the risks of surgery and the possible spread of cancer.
Types and procedure for cervical amputation surgery
Amputation of the cervix is carried out in two ways:
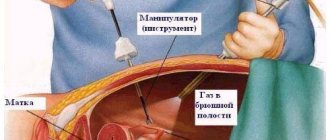
- laparoscopically;
- through the vagina.
Laser, electric current, ultrasound, radio rays, and cold can also be additionally used. The average duration of the operation is about half an hour. If there are any complications (such as bleeding), it may take longer.
General and local anesthesia is used. Regional anesthesia has recently become very popular: an injection is given into the spinal canal, as a result of which the sensitivity of the entire lower part of the body is turned off. After the patient has fallen asleep under anesthesia, doctors begin the operation.
Removal of the cervix can be carried out using three methods:
- according to Schroeder, when the tissues of the anterior and posterior lips of the neck are excised with a wedge;
- according to Sturmdorf - the remote part is a funnel (cone) that goes deep into the neck;
- high amputation - complete removal of the cervix, while the surgeon makes incisions on the vaginal mucosa.
During the operation, depending on the complexity of the pathology, only the cervix or the cervix along with part of the vagina can be removed. Then the doctor puts stitches. In most cases, self-absorbing threads are used, less often - nylon threads.
All other organs are preserved, which in the future allows the woman to become pregnant and give birth to a healthy baby.
Even with a properly performed operation, the following complications can occur:
- relapse – after some time the disease may form again;
- damage to the bladder - most often occurs if it was not emptied before surgery;
- slipping of ligatures, which can subsequently cause bleeding;
- high risk of infection (sepsis, suppuration, peritonitis);
- prolapse of intestinal loops through the vagina;
- necrosis of the vaginal dome.
If such consequences cannot be treated conservatively, additional surgical intervention will be required.
Types of surgery
Trachelectomy is divided according to the method of access into:
- Transvaginal (through the vagina);
- Laparoscopic (through a puncture in the abdomen).
The first is performed most often because it is the least invasive and does not leave scars on the body. Laparoscopy is used if the cervix is removed along with the uterus or transvaginal access is difficult. Sometimes the operation itself is performed through the vagina, and through laparoscopy, nearby lymph nodes are removed. This is necessary to prevent the spread of cancer cells through the vessels.
According to the method of implementation, there are three types of operations:
- Cone-shaped;
- Wedge-shaped;
- High amputation with vault transplantation.
The incision can be made with a knife, electric current, laser, radio wave exposure or cryodestruction. Each method has its own indications and contraindications for use, but the essence of the operation does not change. Thus, electrical destruction of tissue is not recommended for young, nulliparous women. And laser trachelectomy is indicated for benign neoplasms and dysplasia.
Also, surgical intervention may differ in the type of suture material. Can be used:
- Self-resorbable;
- Silk threads.
In the latter case, the sutures will have to be removed some time after the operation.
Local or general anesthesia is used. The choice depends on the patient’s condition and her wishes.
Recovery after cervical amputation
The patient remains in hospital for approximately one to two weeks under the supervision of a physician. Among the symptoms that a woman experiences after surgery are drowsiness, lethargy, apathy, and fatigue. During the first few days, you will experience pain in the lower abdomen, so painkillers are prescribed. Dark brown discharge may also appear. The patient will also take antibacterial drugs to eliminate the possibility of infection. For the first time, she is fitted with a urinary catheter.
After discharge, rehabilitation does not end, but continues for about 1-1.5 months at home. During this time you must adhere to the following rules:
- You cannot swim in open reservoirs, pools, or visit a sauna or bathhouse.
- Refrain from sexual relations.
- Tampons should not be used if there is any kind of discharge.
- You need to protect yourself from possible pregnancy for at least six months.
- Do not lift weights weighing more than 4-5 kg.
- Walk often, but walks should not be too long.
- From about 3-4 weeks you should do light yoga and Pilates exercises.
- Two weeks after cervical amputation, you should definitely visit a doctor.
- Further examinations and tests by a gynecologist are carried out in the following sequence: 1.5 months after the operation, gynecological examination, smear for cytological analysis, colposcopy, MRI (if necessary):
- every three months for a year, a smear for cytology;
- If the indication for surgery was an oncological tumor, then the examination must be completed every quarter for 5 years.
Patient reviews
The main issue that concerns women who have undergone surgery is the possibility of pregnancy. Many patients are faced with the inability to conceive a child. In their reviews, they describe the tests and studies they have completed and talk about their hopes. But not everyone succeeds in having offspring.
In some women, on the contrary, pregnancy occurs only after surgery, especially if the indication for removal of the cervix is a tumor located there. It blocked the path for sperm and after getting rid of the tumor, conception became possible.
Many women who, despite all their efforts, were unable to conceive or carry a child, need the help of a psychotherapist. On forums and in thematic communities they write about their condition: melancholy, disappointment.
Is it possible to have a baby after removing the cervix?
All cervical amputation operations are aimed at stopping the pathological process in the reproductive system and preserving reproductive function. If the disease was detected early, then in most cases this is exactly what happens. If the pathology is very complex, then, naturally, the percentage of the probability of becoming pregnant and giving birth to a child is much lower.
Infertility can be one of the consequences of the operation if the cervical canal narrows, and this in turn affects the decrease in the amount of cervical mucus. Obstruction of the fallopian tubes may also be the cause. If these pathologies cannot be cured, in the absence of contraindications, you can become pregnant using in vitro fertilization or artificial insemination.
There are also cases when a woman becomes pregnant without difficulty, but cannot bear a child, since the cervix is very weak and cannot support the fetus. In such cases, special sutures are placed on the cervix and pessaries (special devices for supporting the uterus) are used.
Start your path to happiness - right now!
Cervical amputation is a surgical intervention on a woman’s internal genital organs, which is often used for the surgical treatment of certain diseases. This operation is considered a gentle method of surgical treatment, which is widely used in gynecology. The degree of benign and malignant formations of the female genital organs increases exponentially every year, which requires new treatment methods. Moreover, treatment methods should be as organ-preserving as possible in order to preserve not only the reproductive function of the female body, but also to maintain the normal hormonal background of a woman, necessary for the normal functioning of many organs and systems. One such operation is cervical amputation.
Operation
Cone-shaped (according to Sturmdorf)
It is considered the most common technique for amputation of the cervix and involves removing the entire mucous membrane of the cervical canal, which is subsequently lined with new healthy tissue. Surgical procedures are performed in several stages:
- exposure of the cervix with subsequent fixation using Museau forceps;
- resection of the cone-shaped part, starting in the area of the external pharynx and ending in the very depths of the cervical canal;
- detachment and elevation of the remaining part of the mucous membrane to the cervical canal.
Finally, stitches are applied.
Amputation of the cervix according to Sturmdorf
Wedge-shaped (according to Schroeder)
This technique of cervical amputation is used relatively rarely. The operation is carried out in the following sequence:
- exposure and fixation of the cervix;
- transverse dissection of the tissue on both sides of the cervical canal so as to create two zones;
- cutting out a wedge-shaped flap of that part of the tissue that has undergone pathological changes;
- formation of the external pharynx.
The final stage is also suturing.
It involves transplantation of the vaults, is indicated for cervical hypertrophy, and is quite often supplemented by vaginal plastic surgery (posterior colporrhaphy and levatoroplasty).
The choice of cervical amputation technique is determined by the nature of the injury and the degree of hyperplasia. An alternative to classical surgery is diathermic cryodestruction of the part of the cervix that has undergone hypertrophy.
Indications and technique for cervical amputation
Firstly, it is necessary to find out the cases in which surgical methods of treatment are generally discussed, including amputation of the cervix. Many pathologies of the female genital organs can be treated conservatively, which in certain cases allows the disease to be completely cured. If drug treatments are ineffective, then surgery can be used. There are diseases for which surgical treatment is recommended as the first line, since the consequences of conservative treatment can be unpredictable. Such pathologies include primarily background and precancerous diseases of the female genital organs:
- Metaplasia of the cervix.
- True cervical erosion.
- Background pathologies in the form of leukoplakia without cell atypia.
- Minor postoperative traumatic defects of the cervix.
- Small cervical cysts.
- Foci of endometriosis or small endometrioid cysts in the cervix.
- Cervical polyps are multiple or single.
- Ectropion of the cervix.
These pathologies require surgical treatment, and the extent of surgical intervention is decided in each case individually. There are several types of surgical interventions:
- simple hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus and cervix;
- extended hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus with the cervix and appendages;
- total hysterectomy is the removal of the cervix, body, appendages and regional lymph nodes;
- Cervical amputation is the removal of only the cervix.
Regarding cervical amputation, there are cases where this treatment method is widely used. Indications for cervical amputation include:
- Benign formations of the cervix - polyps, condylomas.
- Myomatous node of the cervix.
- Cervical cyst.
- Endometriosis of the cervix.
- Malignant tumors of the cervix - stage 1 cervical cancer.
- Lengthening of the cervix, scar deformation, narrowing or obstruction of the cervix.
- Uterine prolapse, complete or incomplete.
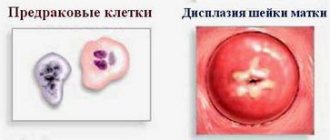
- Dysplastic processes of the cervix
Amputation of the cervix for dysplasia is carried out very often, since this is a local process that responds well to treatment using this method. Cervical metaplasia is a disease in which there is a disruption of the normal structure of the epithelial cover, which does not reach the basement membrane, that is, the process is shallow. Surgical treatment of cervical epithelial dysplasia is carried out for CIN-II and CIN-III. This tactic is due to the fact that conservative treatment at this level is ineffective, and during this time malignancy is possible. In this case, a special cone-shaped amputation technique is used, in which a fragment of altered tissue is excised far in depth, which makes it possible to effectively cure the pathology.
Preparation for cervical amputation includes general clinical aspects - this is, first of all, an accurately established diagnosis. Before deciding on such an intervention, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination by a doctor using instrumental and laboratory research methods. First, you need to undergo colposcopy, which allows you to accurately visualize the changes that will need to be removed, as well as the presence of concomitant pathologies. It is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis of diseases, and if necessary, a histological examination to prevent complications. It is very important, before amputating the cervix for malignant tumors or cervical metaplasia, it is necessary to accurately determine the extent of tissue damage. After all, amputation of the cervix is an organ-preserving operation, and an insufficient volume of surgery can contribute to the deterioration of the condition, so it is necessary to conduct a histological examination without fail. Also, when preparing for cervical amputation, it is necessary to conduct a study of the microflora of the internal genital organs to identify possible pathogenic microorganisms that can cause a postoperative infectious complication. Therefore, in some cases, it is even recommended to carry out local preventive treatment with a combined antibacterial drug in the form of suppositories before the procedure.
The technique for amputating the cervix depends on the type of amputation and the specific use of a particular technique.
First, cervical amputation can be performed vaginally, open laparotomy, and laparoscopically. The laparoscopic method is the most minimally invasive, but it does not allow for revision and is limited in its use for malignant tumors of the cervix. Laparotomy allows you to examine all changes in the surrounding tissues. As for the vaginal method, it is widely used to treat cervical dysplasia.
Based on the method of using the leading method, there are many types of this intervention:
- knife - this is the use of a simple scalpel;
- ultrasonic – removal using ultrasound power;
- radio wave;
- cryodestruction - the use of low temperature to treat diseases of the cervix;
- laser amputation - the use of a laser scalpel to amputate small defects of the neck. The most progressive and new method of amputation.
Cervical amputation has different levels, depending on the degree of changes in the cervix. Thus, a distinction is made between high amputation, low amputation, wedge-shaped and conical.
High cervical amputation is an intervention that is performed when the cervix is lengthened, as well as when there are hypertrophic changes in its structure. In this case, the operation is performed with maximum removal of the cervix. This amputation is also possible if the cervix and cervical canal are narrowed. Such amputation does not allow a woman to become pregnant and carry a child with normal childbirth, therefore it is performed in women of childbearing age only for absolute indications.
Knife wedge amputation of the cervix is technically simpler and is performed by excision of the anterior and posterior lips of the cervix in the form of a wedge, and then placing two sutures on the horizontal incisions formed. Such surgery can be performed to excise polyposis or cervical hypertrophy.
Cone-shaped amputation of the cervix is a very simple intervention, which is widely used for cervical metaplasia. The essence of the method is to cut out the epithelium of the cervix in the form of a cone, depending on the depth of the lesion. This method has its advantages, since the risk that any cells will remain deeper is minimal, since the area is cut out to the basement membrane or even deeper if necessary.
Amputation of the cervix according to Sturmdorf is a cone-shaped amputation technique described by this doctor, which consists of a circular incision above the lesion with further sutures from the beginning of the incision, which pass through all layers of the cervix. With such an intervention, it is very important to ensure normal sutures without damaging the bladder.
Preparation
In preparation for surgery, it is necessary to undergo instrumental and laboratory diagnostics:
- colposcopy;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- histological examination;
- cytology smear from the cervix and cervical canal;
- general and biochemical blood test;
- coagulogram;
- general urinalysis, etc.
Excision of the cervix is carried out only according to indications and after the appropriate diagnosis has been made. Proper management of the postoperative period allows you to avoid negative consequences and complications.
Consequences and complications after cervical amputation
Amputation of the cervix is considered a surgical intervention, so preoperative preparation and special management of the postoperative period are necessary to avoid possible complications.
One of the consequences of such a procedure may be stenosis of the cervical canal of the cervix, especially when the procedure is performed in the area of the external os of the cervix. Such a narrowing may be clinically insignificant, but if it is of a significant size, then bougienage of the cervical canal may be necessary in the future. This narrowing occurs due to a large defect in the mucosa, which, after healing, forms a scar, which contributes to the narrowing of the lumen. Also, complications after amputation of the cervix may occur earlier in the form of bleeding, which occurs when blood vessels are injured. In this case, the bleeding can be very massive, which requires significant measures. The cause of this bleeding may be the failure of the sutures, so it is necessary to check their condition. If there is any suspicion of bleeding, it is necessary to conduct a thorough examination in order to inspect not only the uterine cavity, but also the ectopic space.
The consequences of amputation can manifest themselves in the form of complications of the operation itself in the event of injury to neighboring organs - the bladder or rectum. This rarely happens, since doctors have experience and relevant qualifications.
Discharge after amputation of the cervix can also be one of the consequences that occurs due to infection of the cervical cavity or due to increased secretion of the glands during their intensive proliferation. If the discharge is mucous, light in small quantities, then there is no need to worry, since this is a normal phenomenon of such an intervention, associated with active proliferation and secretion of cells at the site of the defect being formed. In case of green, purulent discharge with an unpleasant odor, you should consult a doctor to treat the infectious process.
Menstruation after amputation of the cervix should recover completely, with a regular cycle. It is important to ensure that their quantity does not change in comparison with previous menstruation, since changes in the amount of discharge are possible. Moreover, in the case of scars after surgery, a mechanical barrier to normal menstruation may be created, which will contribute to the development of hematometra - a condition of blood accumulation in the uterine cavity. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor the duration of the cycle and its main characteristics, and when everything resumes, you can calm down.
Life after amputation of the cervix is very ordinary, you can have full sex, since the hormonal levels are preserved, the number of receptors is preserved, and the vagina is not completely changed. It is also possible to become pregnant and bear a healthy child if you follow the recommendations accordingly.
The rehabilitation period lasts a month, when all damaged tissues are restored and the wound channel and suture site are healed. During this time, complete epithelization and regeneration occurs, which allows new cells to function normally. During the rehabilitation period, it is recommended not to be sexually active. After two weeks it is necessary to undergo a re-examination to assess the result of treatment.
Amputation of the cervix is an operation that is widely used in gynecology and is a very effective method, since it allows you to radically remove all histological changes in the cervix. At the same time, there are different methods for performing this operation, the choice of which depends on the type of pathology. It is necessary to conduct a complete preoperative examination, as well as to properly manage the postoperative period. The treatment result is positive and the prognosis for full recovery is positive if all recommendations are followed.
The most common operation in gynecology is the removal of important reproductive organs of the female genital area - the uterus and cervix.
The consequences after removal of the cervix are severe, but this operation is performed exclusively on patients who have been diagnosed with cervical cancer.
What consequences to expect after removal of the cervix, how life will develop after this operation - such questions worry all women who are facing amputation of the uterus. If surgery is necessary, then the woman should know in advance about possible complications in the postoperative period, and also find out whether there are positive reviews after removal of the cervix. The more a woman is informed about the diagnosis, the easier it is for her to adapt in the period after surgical manipulation. For patients who do not have children, it is important to know whether pregnancy is possible after this operation, and if so, how safe pregnancy will be after removal of the cervix. The attending physician must report in detail how dangerous the disease is, provide feedback after removal of the cervix, prescribe clinical diagnostic examinations to determine the state of the body at the time of surgery: general blood test, general urinalysis, biopsy, colposcopy, magnetic resonance imaging.
In case of cervical cancer, the surgical procedure of hysterectomy and removal of the cervix is prescribed. The consequences of this:
- Heavy bleeding
- Formation of pus in hematomas
- Peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum)
- The body's inflammatory response to infection (sepsis)
In the late postoperative period - necrosis of the vaginal vault, prolonged debilitating bleeding, prolapse of intestinal loops. The recovery period after the procedure should be given a lot of attention; this is important, since the long-term consequences of cervical amputation cause discomfort, and do not exclude the appearance of negative reviews after removal of the cervix.
Recently, doctors have been using vaginal hysterectomy, total hysterectomy, and radical hysterectomy. Hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the uterus. Vaginal hysterectomy is a method in which the cervix is preserved after amputation of the uterus. In this case, there is a high risk of developing cervical cancer, which subsequently requires removal of the cervix. The consequences and reviews of such surgical intervention are negative, the rehabilitation period is long, and pregnancy does not occur after removal of the cervix. A type of hysterectomy in which the cervix remains after the hysterectomy is recommended for women who already have children.
A total hysterectomy is a surgery in which the uterus and cervix are removed. After removal of the uterus, a woman is forever deprived of childbearing function. When performing a radical hysterectomy, the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, pelvic lymph nodes, and amputation of the cervix are removed. The results of such surgical intervention leave a negative imprint on the woman’s health and her future life. After the operation there is a rehabilitation period, during which the following recommendations must be followed:
- Avoid heavy physical labor
- Limit sexual contact for the first 6 weeks after surgery
- Do not use sanitary tampons
- Avoid bathing and swimming for the first six weeks
- Take hormonal contraceptives as prescribed
- Limit active sports activities
According to numerous reviews, after surgery to amputate the cervix, a woman will be able to return to her previous rhythm of life in a month and a half.