Each patient should know about how conization of the cervix occurs and about recovery in the postoperative period. What complications may occur, what to do if they occur, and when you can get pregnant after conization. Preliminary examination of the answers to these questions is essential for the correct psychological disposition before the intervention.
Compliance with medical prescriptions is the key to successful recovery after the procedure
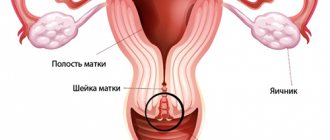
Indications for conization
Conization is prescribed in case of detection of visible pathological areas on the cervix, with confirmation of dysplastic changes in the epithelium to clarify the diagnosis and prompt correction of the pathology. The range of conditions under which this procedure is implemented includes:
- detection of areas with altered epithelial structure during colposcopy;
- detection of cellular atypia in smears;
- established dysplasia of 2-3 degrees;
- erosive changes in the cervix;
- leukoplakia;
- polyps;
- ectropion;
- scars after injuries, ruptures and manipulations on the neck;
- recurrent dysplasia after cryodestruction, electrocoagulation, laser treatment.
When necessary
The operation is performed in cases of visible pathological changes in the cervix and in the presence of cervical epithelial dysplasia in smears.
Among the indications for the procedure, the main ones are:
- pathological changes in the cervix;
- laboratory confirmed dysplasia of 2-3 degrees;
- negative result of examination of discharge from the cervix.
Conditions for which surgical intervention is recommended:
- changes in the epithelium identified during colposcopic examination;
- dysplasia 2-3 degrees;
- eversion of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal (ectropion);
- erosion;
- presence of polyps;
- scar deformities;
- leukoplakia;
- recurrence of dysplasia after previous treatment with other methods.
Surgery may be performed to clarify the diagnosis. The extracted area is sent to the laboratory for histological analysis and, based on its results, the presence or absence of cervical cancer is judged.
Purpose and procedure for surgical intervention
The main purpose of the procedure is to remove pathologically changed areas both to confirm the diagnosis and to correct the condition. The operation involves the following stages:
- Removal of an area of altered mucous lining, including healthy tissue within 5-7 millimeters.
- Histology after conization of the cervix. The removed area is sent to the laboratory for further examination. Doctors study what the epithelium of the cervix looks like, whether there are pathological changes in it and how widespread they are.
- If invasive cancer is excluded during the study and in the absence of dysplasia in the edges of the removed area, the pathological process is considered radically cured.
- If there are any doubts regarding the complete removal of the area of dysplasia or if invasive cancer is confirmed, conization serves as a diagnostic step, and after it is carried out, more radical measures are prescribed.
Execution Process
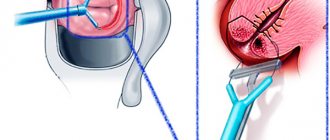
The operation does not require prolonged hospitalization: it is performed on an outpatient basis or in a one-day hospital stay. The intervention is performed under local anesthesia or shallow intravenous anesthesia. If necessary, the woman is given sedatives.
The patient sits in a gynecological chair, and the doctor conducts an examination using mirrors. Next, a Lugol test or a solution of acetic acid is performed. After this, the cervix is treated with an anesthetic (Novocaine or Lidocaine). Then the surgical operation itself takes place using the chosen method. Excised tissue must be sent for histological examination.
Various methods have been developed to carry out this operation:
- laser;
- radio wave;
- loop;
- knife.
The laser method involves excision of tissue using a directed high-intensity beam. This is a low-complexity intervention that is safe and effective. Using a laser, you can simultaneously coagulate bleeding vessels and sterilize the operated area. The only drawback of this method is the high cost.
Radio wave or electroconization is carried out using a special apparatus that generates high-frequency alternating currents that destroy tissue. Today this is the most common method.
The loop method is an improved radio wave technique. During the operation, the surgeon uses an electrode with a loop of the required size to excise tissue.
The knife method is becoming a thing of the past today. This is a common operation in which the removal of damaged tissue is carried out using a scalpel. This technique requires a long period of rehabilitation; it is unsafe and fraught with complications.
Preparation for the procedure
The intervention is recommended after the end of menstrual bleeding. This is explained by the fact that during the first phase of the cycle, the level of estrogen increases, which promotes increased proliferation of the epithelium, and, accordingly, faster recovery after surgery.
The preparatory stage is extremely important
Before implementing conization you should:
- take a general blood and urine test;
- donate blood for syphilis, HIV, hepatitis B and C;
- donate blood for hemostasis indicators;
- donate blood to determine its group and Rh factor;
- undergo fluorography;
- undergo a cardiogram;
- undergo an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs (as prescribed by a doctor);
- if inflammation of the cervix and vagina is detected before surgery, measures are taken for complete cure;
- get examined by a therapist.
Types of cervical excision and technique
Contraindications for carrying out
Conization cannot be carried out in the following cases:
- Active inflammation in the vagina and cervix.
- Biopsy-proven invasive cancer.
- Acute infections.
- Poorly defined boundaries of dysplastic changes.
- Excess of the boundaries of the pathological focus beyond the limits of conization.
- Decompensation of chronic pathologies (heart, kidney, liver failure, hypertension, diabetes mellitus).
- Blood clotting disorders.
How is radio wave conization performed?
Conization of the cervix using the radio wave method includes several stages: preparation, radio wave exposure, postoperative recovery period.
Preparation for the procedure
To prepare, you need to do the following approximately 2 weeks before the intervention:
- General blood and urine tests.
- Test for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis C and B.
- A smear to determine the inflammatory process.
- Colposcopy. To identify pathological cells.
- Determination of individual blood factors - Rh factor and group.
- An electrocardiogram to exclude possible contraindications and complications after the procedure.
- Fluorography. This examination is indicated for any medical indication. It is mandatory to take it at least once every six months.
- Examination and consultation with a therapist. The specialist gives a general conclusion on radio wave manipulation.
Reasons for refusal to carry out radio wave conization may be:
- poor blood clotting;
- a large affected area that is indicated to be treated in other ways;
- the presence of infectious etiology in the body;
- existing inflammation in the cervix, vagina;
- confirmation of the presence of invasive cancer;
- unclear boundaries of the affected epithelium, which require additional studies;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases: diabetes mellitus, heart, kidney, liver failure;
Preparation is an important stage for carrying out high-quality medical manipulation. Any deviation from the norm will require treatment and restoration of any pathology. After treatment, a repeat examination is carried out, based on the results of which a decision is made to carry out conization.
Radio wave conization process
For conization, an electrode with the required loop size is selected. The area to be treated is increased by several millimeters from the size of the affected area. The electrode is rotated clockwise. Then, the cut area is sanded and sutured with special threads, which dissolve on their own as the tissue heals.
The procedure is subject to pain relief using intravenous or local anesthesia.
Conization procedure
The entire process takes approximately 15 minutes. In complicated situations it can last up to 30 minutes. It is recommended to carry out the operation no later than in the first week after the end of menstruation. In the first phase of the cycle, active production of estrogen occurs, which promotes rapid healing and complete restoration of the mucous epithelium of the cervix.
Cervical plastic surgery: purpose and operation
Recovery period
During the recovery period, the following recommendations exist:
- Avoid sexual intercourse for at least 3 weeks.
- Do not take baths or showers with hot water.
- Reduce physical activity to a minimum.
- Do not use tampons to avoid infection or inflammation.
- Consult your doctor for permission to take certain medications.
After 3 weeks, complete recovery occurs and possible restrictions are lifted. During the recovery period, slight bleeding is observed. There is mild pain that is easily relieved with painkillers. If there is heavy bleeding for three days, you should visit a doctor.
Postoperative period: what you need to know
After conization of the cervix has been performed, the postoperative period involves gradual healing. Immediately after the end of the procedure, you need to spend about two hours in a lying position. Treatment after conization of the cervix does not require inpatient observation. The patient can go home and be regularly monitored by her gynecologist.
There may be pain in the lower abdomen for several days after the procedure.
For several days after the intervention, aching pain in the lower abdomen is possible. The pain is similar to that during menstrual bleeding. In addition, after the procedure, discharge is observed, the duration and intensity of which varies. Usually the discharge is clear, with a small admixture of blood, but it can also be light brown in color.
Sometimes the discharge stops after a week, immediately after the scab comes off after conization of the cervix, but it can continue until the next menstruation. There may be cases where the cervix bleeds even three to four months after the procedure, however, this condition requires medical supervision. The first and second menstrual bleeding after the implementation of the intervention may be somewhat heavier than usual.
The doctor should explain to the patient that about a week after the intervention, the discharge becomes more abundant, because the scab comes off after conization of the cervix. During this process, due to the rejection of the scab from the wound surface, the discharge becomes more, and the woman should not be afraid of this.
The best ways to treat cervical erosion with folk remedies
Recovery after conization
After conization using modern methods (radio wave and electrocoagulation), the patient can return home on the same day, having previously spent several hours under the supervision of doctors. If weakness, dizziness or severe pain are not observed, the patient is discharged from the hospital. Next, she must regularly undergo preventive examinations and follow all the gynecologist’s prescriptions in order to prevent possible deviations that will negatively affect reproductive health.
The recovery period proceeds for each woman purely individually, depending on the age and characteristics of the body. During the healing of the wound, sick leave is not issued, with the exception of temporary inconveniences and uncomfortable conditions; representatives of the fair sex lead a normal lifestyle and do not need to limit their ability to work. Complete healing occurs a month after the procedure; in some cases, recovery can take two or even three months.
Healing after conization is not always easy and smooth. In young women, cell regeneration, and therefore the restoration of soft tissues, occurs faster than in older women. Concomitant diseases and inflammatory processes that complicate recovery also play a role in this. In this case, a pulling pain and discomfort in the perineal area may occur in the lower abdomen.
To speed up the healing of the wound surface, a woman is recommended to follow some rules:
- you cannot take a hot bath, visit a bathhouse, sauna;
- do not swim in open waters and pools;
- do not neglect the rules of personal hygiene;
- give up bad habits such as alcohol and smoking;
- stop taking medications that thin your blood, such as aspirin;
- It is not recommended to use vaginal suppositories and tampons;
- you cannot have sex for at least two months after the procedure;
- do not douche;
- use only sanitary pads;
- limit physical activity and avoid lifting heavy objects.
Drug treatment in the postoperative stage consists of a course of antibacterial and restorative drugs. The dosage and duration of taking medications is prescribed by a specialist depending on the woman’s general well-being and her body’s ability to recover.
After damage to the integrity of the surface layer, tissues are completely restored after three to four months . After a year, it is necessary to undergo colposcopy and repeat cytological analysis.
Restrictions after the procedure
In order for recovery after conization of the cervix to be as effective as possible, any impact on this anatomical area should be limited. Recommended:
- Abstinence from sexual intercourse for a month.
- Avoid using tampons. During menstrual bleeding, you should only use pads.
- Refusal to use vaginal suppositories and tablets, douching, unless these medications and methods are prescribed by a doctor.
- Refusal to take baths (hygienic procedures should be carried out in the shower).
- Refusal to lift heavy objects weighing more than three kilograms. Physical activity should be avoided as much as possible.
- Refusal to visit baths and saunas.
- Refusal to swim.
- Prevention of overheating of the body.
- Avoid taking blood thinners (aspirin).
Possible complications
Condition of the cervix after conization
Complications after conization of the cervix may include the following conditions:
- Bleeding after conization of the cervix. Occurs in approximately 5% of cases.
- Cervical canal stenosis. The frequency of occurrence is from 1 to 5% of cases. This complication may subsequently cause difficulties when trying to become pregnant after cervical conization.
- Inflammatory process. Accompanied by pain, itching, increased body temperature.
- Miscarriage. Spontaneous abortion or premature birth are likely.
- Cicatricial changes in the cervix.
- Endometriosis.
- Menstrual irregularities.
Although complications after the procedure are quite rare, if any of the listed symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a doctor. Self-medication is extremely dangerous and can cause a significant deterioration of the condition.
Healing of the cervix after surgery
Healing after conization of the cervix occurs in a fairly short time, if the course of the postoperative period is not complicated in any way. If all medical recommendations are followed, recovery occurs quickly and with maximum efficiency.
Before the scab comes off after conization of the cervix, and for some time after, the patient experiences clear mucous discharge mixed with blood; sometimes the discharge may have a light brown tint. After the scab leaves, the process of epithelization of the wound surface begins, which is completed in approximately 3-4 months.
After this time, the doctor takes material from the cervical canal for cytological examination. Subsequently, the condition of the cervix is monitored at least once every six months for three years. If cellular atypia is not detected during this period, then after three years the frequency of examination and collection of biomaterial for research is reduced to once annually.
Consequences
According to statistics, the effectiveness of cervical conization as a method of treating dysplasia and preventing the development of oncology is quite low. There also remains a high probability of re-development of the pathology, with fifty women out of a hundred developing a more severe form of the disease within two years, up to non-invasive cancer, which leads to radical amputation of the entire organ.
Why is this happening? Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the main cause of precancerous diseases of the reproductive organs. It cannot be cured by surgical methods; the harmful virus remains in the cells of the epithelial layer and continues to actively spread. Conization is not an obstacle to this process, and in 70% a relapse of the disease is noted.
If the presence of cancer cells is diagnosed, then surgical intervention can provoke their accelerated growth and the proliferation of metastases. Here, any drug therapy is powerless; to save the patient’s life, all reproductive organs along with appendages are removed. After such an operation, a woman often needs psychological help, since she will no longer be able to have children.
Pregnancy after the procedure
Pregnancy after conization is quite possible.
Many patients are concerned about the question of whether it is possible to become pregnant after this operation and how long after this can be done. It should be noted that for nulliparous women and for women planning a second pregnancy, the gynecologist should select the most gentle methods that do not violate the structure of the cervix. If conization is still necessary, then preference is given to laser and radio wave techniques - these types of procedures are characterized by a minimal risk of complications.
Buscopan - use during pregnancy, drug analogues
Planning pregnancy is recommended one year after the intervention. In most cases, the procedure does not limit the possibility of conception. Exceptions are cases of extensive tissue resection, repeated conization, and complicated course. All this can provoke a narrowing of the cervical canal due to the progression of the adhesive process. Narrowing of the cervical canal can complicate the process of fertilization.
Due to the fact that during conization the structure of the cervix changes, pregnancy and childbirth can be complicated. The cervical canal becomes shorter and its elasticity deteriorates. In some cases, this causes miscarriage to full term: due to increased load, the cervix opens earlier than expected.
Natural delivery after excision of the conical portion of the cervix is possible, but doctors must make sure that the cervix has retained its elasticity. In most cases, a cesarean section is still recommended due to the risk of inadequate cervical dilatation during natural childbirth.
Once again about the most important thing
It is important to follow all doctor’s orders.
What should the patient know about conization? First of all:
- this operation does not last long;
- when conization of the cervix is performed, its consequences are extremely rarely negative if all restrictions are observed;
- for quick and effective recovery and prevention of complications, it is necessary to strictly adhere to all medical recommendations;
- the pain syndrome after the intervention is quite short - 1-2 days, but discharge can be observed for several weeks;
- the most important limitation is the exclusion of physical activity in the postoperative period;
- After the procedure, you should regularly visit a doctor to monitor the condition of the cervix;
- planning pregnancy after conization should also be agreed with a specialist.