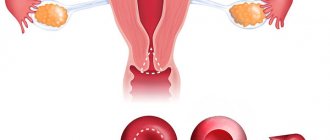
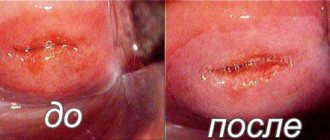
Pathological changes in the epithelium of the cervix require immediate treatment to avoid life-threatening consequences. Conization of the cervix is a surgical intervention during which a specialist removes the affected part of the cervical canal.
The operation is performed by excision of damaged tissue in the shape of a cone, the base of which is the epithelial tissue of the cervix, and the apex is the depth of the cervical canal. The area of tissue removed during surgery is subjected to subsequent histological examination. Thanks to conization of the cervix, it is possible not only to remove damaged tissue, but also to achieve a complete recovery for the woman.
Methods and features of the operation
Conization of the cervix is performed in a hospital setting; the degree of surgical intervention and the method of its implementation depend on the patient’s condition and the level of pathological changes.
This procedure is prescribed for dysplasia of various stages, erosive lesions of the mucous surface and if a cancerous tumor is suspected. This intervention is contraindicated in the presence of sexually transmitted infections such as gonorrhea, chlamydia, trichomoniasis and other sexually transmitted diseases.
During the examination, laboratory methods determine the presence or absence of cancer cells. If the biopsy result is positive, more in-depth studies and appropriate treatment are prescribed.
If the last stage of cervical cancer is diagnosed, the entire organ is removed to prevent further spread of metastases and their development into malignant neoplasms in neighboring areas.
If dysplasia is detected - the predominance of atypical cells in the epithelial layer, removal of the damaged area is necessary, while the organ is preserved.
To prevent further progression of the pathology, during excision, part of the healthy flesh is captured (about five millimeters), which increases the size of the wound surface, but eliminates the risk of recurrent manifestations of the disease.
Surgery is performed immediately after the end of the menstrual cycle, which eliminates possible pregnancy and increases the time frame for healing of the wound surface.
Indications
It is used in the diagnosis of oncological pathologies and for therapeutic purposes. It also helps to choose the optimal treatment, if necessary.
Recommended for:
- the presence of atypical cells in the cytological analysis;
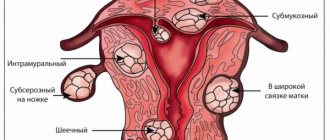
- pathological changes in the cervical epithelium (pseudo-erosions, erosions, cysts, polyps);
- ectropionic cervix;
- cervical deformities formed in the postpartum period after severe traumatic childbirth;
- with diagnosed dysplasia of the cervical epithelium of II-III degree with histological confirmation.
Causes
In modern gynecology, a direct connection has been proven between the appearance of dysplasia, in particular, grade 3, and HPV. This virus, entering a cell, causes cellular mutations.
- family history;
- chronic inflammatory and infectious processes in the pelvis;
- disorders in the immune system;
- smoking;
- hormonal imbalance;
- onset of sexual activity at a young age;
- cervical injuries;
- disorderly intimate life.
In most cases, the clinical picture of dysplasia is absent. Characteristic signs usually appear as the disease progresses to stage 3 and after the addition of infection.
Among the symptoms with the development of grade 3 dysplasia are:
- nagging pelvic pain;
- genital discomfort;
- pathological discharge, which may be accompanied by an unpleasant odor;
- contact discharge during sexual intercourse and gynecological examination.
The absence of symptoms in dysplasia necessitates regular preventive examinations and examinations. Timely diagnosis and surgical treatment, which for grade 3 dysplasia usually includes electroconization, ensures the woman’s complete recovery
The conization procedure occupies a special place in the lives of nulliparous women.
- after conization it is more difficult to get pregnant;
- the barrier function of the uterus decreases in the way of inflammatory diseases, which in themselves negatively affect the possibility of pregnancy and healthy childbirth;
- high risk of miscarriage and premature birth after 16 weeks of pregnancy;
- birth by cesarean section;
- Reproductologists often refuse IVF to women with conization of the cervix due to a history of dysplasia.
Unlike conization, PDT is a non-traumatic therapeutic method. It targets neoplasia in two directions at once:
- destroys tumor and virus-infected cells,
- destroys the papilloma virus in the mucous membranes of the cervix and cervical canal.
By using PDT for treatment, we preserve the integrity of the cervix and uterus and restore immunity at the organ level. A healthy cervix reliably protects itself and the uterus from infections, it is ready for conception, for full independent pregnancy and childbirth.
Unfortunately, no one is immune from re-infection with HPV. Therefore, I strongly recommend that my patients treat partners who are carriers of high oncogenic risk HPV and carefully choose new ones.
Therefore, even if there are indications, do not rush to make a decision in favor of the surgical method of conization. Below I will tell you in detail how conization of the cervix occurs and the prognosis for recovery after it.
I want to give you enough information so that you can decide for yourself whether you need this procedure or not.
Restoration of the menstrual cycle
After conization using modern methods (radio wave and electrocoagulation), the patient can return home on the same day, having previously spent several hours under the supervision of doctors.
If weakness, dizziness or severe pain are not observed, the patient is discharged from the hospital. Next, she must regularly undergo preventive examinations and follow all the gynecologist’s prescriptions in order to prevent possible deviations that will negatively affect reproductive health.
The recovery period proceeds for each woman purely individually, depending on the age and characteristics of the body. During the healing of the wound, sick leave is not issued, with the exception of temporary inconveniences and uncomfortable conditions; representatives of the fair sex lead a normal lifestyle and do not need to limit their ability to work.
Healing after conization is not always easy and smooth. In young women, cell regeneration, and therefore the restoration of soft tissues, occurs faster than in older women.
Concomitant diseases and inflammatory processes that complicate recovery also play a role in this. In this case, a pulling pain and discomfort in the perineal area may occur in the lower abdomen.
Drug treatment in the postoperative stage consists of a course of antibacterial and restorative drugs. The dosage and duration of taking medications is prescribed by a specialist depending on the woman’s general well-being and her body’s ability to recover.
After damage to the integrity of the surface layer, tissues are completely restored after three to four months. After a year, it is necessary to undergo colposcopy and repeat cytological analysis.
After surgery, menstruation usually comes on time, in some cases there may be a delay of several days, it all depends on the individual characteristics of the body and the nature of the intervention performed.
READ MORE: Cytology leukocytes 80 100
If all instructions are followed, the menstrual cycle is quickly restored, and all reproductive functions are preserved. If bleeding lasts more than two weeks, this is a reason to visit an antenatal clinic.
Possible complications
The only immediate complication can be considered intense bleeding after conization, inflammation (temperatures above 37.5° C require medical attention) and narrowing of the cervical canal (stenosis) during the healing process, which can be completely resolved on an outpatient basis. But long-term complications are much more serious.
After conization, the anatomy of the organ and vagina changes, and the cervix shortens. A short cervix and changes in the composition of the secretion of the plug in the cervical canal cannot fully serve as a barrier between the external environment and the uterus. The risk of developing infectious diseases of the uterus and appendages increases. And the higher the operation is performed, the higher the risks.
The course of the healing process after conization largely depends on the patient’s compliance with the prescribed regimen. Any violations, including sexual intercourse, physical activity, skipping prescribed medications and failure to maintain proper hygiene, can lead to various complications. Acceleration of the healing process can be achieved by therapeutic methods of conservative treatment, including prevention of the disease that led to surgery.
With any surgical procedure there is a risk of infection. To avoid infection, vaginal suppositories with a local antiseptic are prescribed. Sexual contacts during the healing period of a postoperative wound are excluded, since this is one of the most likely cases of infection.
The appearance of bloody discharge is most often a consequence of the separation of the scab. Gradually they contract, which indicates normal wound healing. Pain characteristic of inflammation can occur against the background of infectious inflammation of the area. Examination of the outer part of the cervix allows you to determine the nature of the inflammation and prescribe treatment. Thus, the main complication after conization is infection of the injured area.
After surgery, menstrual irregularities are observed in the first three months. The very first menstruation often occurs with heavy discharge. This is a reaction of the reproductive system associated with restructuring. The extent of cycle disruption directly depends on the healing process with the formation of epithelium.
Postoperative spasms of the cervix can lead to its contraction, which also leads to difficulty in the natural release of menstrual blood and the occurrence of pain during the first menstruation after manipulation, and the occurrence of inflammatory processes.
Consequences after conization of the cervix are rare today. However, they are possible. These are bleeding, infections, stenosis of the cervical canal (narrowing).
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency may also develop - a violation of the obturator ability of the cervix, which can lead to miscarriage (the cervix does not hold the fetus) and the penetration of infection into the uterine cavity. But this is a rare complication of cervical conization. Scars on the uterus are also rare today, since electrocoagulation is not used.
Possible complications are infection of the wound at the time of surgery, inflammation of its surface, scar formation, and bleeding when large vessels are damaged. More long-term consequences of conization may be spontaneous termination of pregnancy in the early stages or premature birth.
Another rare complication of cervical conization is narrowing of the cervical canal. This causes infertility. After conization, the likelihood of a woman developing endometriosis increases.
Complications with modern types of conization are observed quite rarely (1-2%).
- Bleeding.
- Attachment of infection with the development of inflammation.
- Cicatricial deformity of the cervix.
- Miscarriage (spontaneous abortion and premature birth).
- Endometriosis.
- Menstrual irregularities.
Condition of the cervix after conization
Complications after conization of the cervix may include the following conditions:
- Bleeding after conization of the cervix. Occurs in approximately 5% of cases.
- Cervical canal stenosis. The frequency of occurrence is from 1 to 5% of cases. This complication may subsequently cause difficulties when trying to become pregnant after cervical conization.
- Inflammatory process. Accompanied by pain, itching, increased body temperature.
- Miscarriage. Spontaneous abortion or premature birth are likely.
- Cicatricial changes in the cervix.
- Endometriosis.
- Menstrual irregularities.
Although complications after the procedure are quite rare, if any of the listed symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a doctor. Self-medication is extremely dangerous and can cause a significant deterioration of the condition.
The course of the healing process after conization largely depends on the patient’s compliance with the prescribed regimen. Any violations, including sexual intercourse, physical activity, skipping prescribed medications and failure to maintain proper hygiene, can lead to various complications. Acceleration of the healing process can be achieved by therapeutic methods of conservative treatment, including prevention of the disease that led to surgery.
With any surgical procedure there is a risk of infection. To avoid infection, vaginal suppositories with a local antiseptic are prescribed. Sexual contacts during the healing period of a postoperative wound are excluded, since this is one of the most likely cases of infection.
The appearance of bloody discharge is most often a consequence of the separation of the scab. Gradually they contract, which indicates normal wound healing. Pain characteristic of inflammation can occur against the background of infectious inflammation of the area. Examination of the outer part of the cervix allows you to determine the nature of the inflammation and prescribe treatment. Thus, the main complication after conization is infection of the injured area.
The operation as such should not affect pregnancy in the absence of a hormonal factor. In gynecological practice, there are cases of INC (isthmic-cervical insufficiency) after conization of the cervix, which often leads to miscarriages. But this phenomenon is not associated with the operation as the only provoking factor.
After surgery, menstrual irregularities are observed in the first three months. The very first menstruation often occurs with heavy discharge. This is a reaction of the reproductive system associated with restructuring. The extent of cycle disruption directly depends on the healing process with the formation of epithelium.
Postoperative spasms of the cervix can lead to its contraction, which also leads to difficulty in the natural release of menstrual blood and the occurrence of pain during the first menstruation after manipulation, and the occurrence of inflammatory processes.
Diagnosis and treatment
The following methods are used to detect pathology:
- gynecological examination;
- smear for oncocytology;
- PCR research;
- extended colposcopy;
- biopsy;
- blood test for tumor markers, syphilis and HIV;
- bacterial culture and general smear;
- hormonal diagnostics;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
The main research method is cytological diagnosis, which involves taking material from different parts of the cervix to identify atypical cells and the inflammatory process.
If atypical cells are detected, the patient is prescribed an extended colposcopy using special reagents, and if cancer is suspected, a cervical biopsy is prescribed.
Treatment of grade 3 dysplasia is predominantly surgical, which most often consists of conization of the cervix. At the initial stage or during pregnancy, observational tactics may be used. The patient regularly visits the doctor and undergoes examination.
The progression of pathology is an indication for the use of surgical techniques.
- Conization. This intervention refers to organ-preserving tactics. The operation involves removing a cone-shaped area of the cervix that includes abnormal tissue. The amputated tissue contains fragments of the cervix and cervical canal. Manipulation is carried out for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Conization of the cervix can be performed in different ways.
1. Knife. The operation is performed with a scalpel. In modern gynecology, such conization is used infrequently due to its high morbidity. In addition, there are more effective and gentle methods.
2. Laser. Conization using a laser beam is considered the most expensive.
3. Electroconization. This intervention is otherwise called loop conization. This is the most common type of conization.
- High amputation. With this tactic, radical amputation of the cervix occurs, which is recommended for grade 3 dysplasia and oncological alertness. The high amputation method allows you to stop the progression of the malignant process.
Before conization and other surgical interventions, a woman performs the necessary examination:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- diagnosis of syphilis and hepatitis;
- general urine analysis;
- flora smear;
- PCR swab;
- colposcopy;
- biopsy.
Conization of the cervix can have negative consequences.
- With conization, the anatomy of the cervix changes. As a result, the cervical canal remains dilated, which can lead to chronic infections.
- There is a risk of relapse in case of technical difficulty in performing conization, which is caused by some anatomical features of the cervix.
- After conization, the ability of the cervix to transform into the birth canal is lost, which necessitates surgical delivery.
- Conization does not affect a woman's reproductive ability, however, it increases the risks of miscarriage and premature birth.
- During conization, it is difficult for the surgeon to calculate the depth of impact; as a result, too large areas of healthy tissue may be captured. Sometimes in nulliparous patients, the doctor amputates a small amount of the affected epithelium, which leads to relapse of dysplasia.
In order to prevent the development of the inflammatory process, the patient is given antibacterial treatment. In case of severe pain, taking painkillers is indicated.
For a month after conization, a woman is not recommended to visit a sauna or swimming pool, lift weights, or use tampons. Sexual activity is also prohibited due to the risk of infection and unnecessary trauma to the damaged cervix.
Carrying out
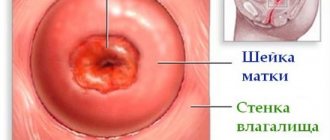
The procedure involves removing a pathologically changed area of the inner epithelial layer of the cervix. The wide side of the cone faces the vagina. It should capture the entire pathological epithelium. The narrow part of it faces the cervical canal.
Conization is carried out in the first few days after the end of menstruation. Thus, by the beginning of the next menstruation, the operation site will have already healed.
The operation is usually performed in a small operating room, in a regular gynecological chair. Conization is not a complicated operation. As a rule, it is performed under local anesthesia. Sometimes it is supplemented with drug sedation. But this is quite rare. The uterus has no painful endings, and the tissue of the cervix is numbed locally by the doctor. After the operation, there is practically no hospitalization. According to the doctor's decision, the patient after the operation can remain under observation for several hours or days.
Preparing for surgery
The preliminary examination consists of a complex of laboratory and instrumental studies:
- general blood test and biochemical;
- analysis for viral hepatitis, HIV;
- smear on the state of microflora;
- colposcopy.
Symptoms of postoperative complications
Important! If severe pain does not stop after several weeks after surgery, the level of bleeding exceeds the acceptable level, there is a significant increase in body temperature, loss of appetite, weakness and dizziness, you should immediately seek medical help.
All of the above symptoms may signal the development of potentially hazardous health conditions. They can arise due to an unprofessional operation, a surgeon’s error, or failure to comply with postoperative restrictions.
An open wound can become infected during surgery, which can lead to the development of an inflammatory process. After conization, the cervix becomes shorter, the anatomical structure of the reproductive organ changes, which entails a violation of the barrier functions that prevent the penetration of viruses and bacteria into the internal environment.
Moreover, the larger the surgical field, the higher the risk of inflammation. Then a repeat operation is possible, the purpose of which is to eliminate the pathological process and its negative consequences.
Every woman who has undergone surgery on the internal genital organs, including conization, inevitably faces pain during the recovery period.
READ MORE: Cytology signs of chronic inflammation
If the surgical intervention itself is painless thanks to anesthesia, then after leaving the anesthesia, sensitivity is restored, and intense nagging pain occurs in the lower abdomen.
During the recovery process, the tone of the muscles of the uterine body returns to normal, contractile activity increases, which is expressed in cramped pain. This condition is quite tolerable and goes away completely within ten days.
Rehabilitation period
In the first few weeks, there may be pain in the lower abdomen. The process of restoration of the mucous membranes can take six to eight weeks.
In order for the rehabilitation period to be as successful as possible, during the first few months it is recommended:
- Do not lift anything weighing more than 3 kg;
- Refuse sexual intercourse;
- Do not use tampons;
- Do not take medications or foods that have the property of thinning the blood (chicory, Aspirin);
- Avoid visiting solariums.
It is important to remember that deterioration in health, bleeding and increased body temperature are a direct reason to immediately consult a doctor.
Electroconization
Electroconization is a surgical tactic during which the affected fragment of the cervix is excised in the form of a cone using special electrodes.
Therapeutic tactics are widely used for grade 3 dysplasia. After electroconization, a tissue sample is examined histologically, which makes it possible to accurately determine the pathology of the cervix and subsequently prescribe appropriate therapy.
In general, electroconization is performed if:
- dysplasia 2 and 3 degrees;
- questionable colposcopy results;
- pathological processes of the cervical canal;
- opposite results of cytology and histology;
- dysplasia of the 3rd degree, combined with cervical deformation;
- ineffectiveness of other treatment methods.
Electroconization is contraindicated in inflammatory and infectious processes, as well as in diagnosed cervical cancer.
Conization, in particular electroconization, is carried out at the beginning of the cycle. The electroconization procedure is performed using a special apparatus that contains different electrodes and an electric generator.
The duration of the manipulation is no more than twenty minutes. The patient consents to the procedure, which is performed under general anesthesia.
During electroconization, a plastic gynecological speculum and colposcope are used. Lugol's solution is applied to the cervix, which helps to identify pathological areas by the absence of color.
Then a current is passed through the installed electric loop and the selected area of the cervix is amputated at a depth of several millimeters. The tissue sample thus obtained is sent for histological examination.
For several days after electroconization, bloody discharge and pelvic pain are observed.
The disadvantages of electroconization include:
- inability to control the depth of amputated tissue;
- possibility of bleeding and infection;
- scar formation;
- narrowing and fusion of the cervical canal;
- recurrence of dysplasia;
- menstrual irregularities;
- risk of miscarriage and premature birth in subsequent pregnancies.
If, after electroconization, a woman has increased bleeding, an unpleasant odor and intense pain, or a deterioration in her general health, she should immediately contact a medical facility.
Conization is one of the main methods of treating grade 3 cervical dysplasia. If grade 3 dysplasia is left untreated, the following complications may occur:
- proliferation of atypical areas of the epithelium;
- gradual weakening of immunity due to tumor growth;
- malignant tumor degeneration;
- development of metastases;
- the appearance of signs of intoxication.
Dysplasia at grade 3 is a serious disease that belongs to precancerous pathologies. And even after conization, there is a risk of relapse.
Indications and contraindications for cervical conization
Indications for the procedure are:
- dysplasia of cervical epithelial cells, grade 2-3, confirmed histologically;
- identification of a large pathological area of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal during colposcopy;
- detection of dysplasia based on the results of a cytological smear (Papanicolaou test).
In other words, conization makes it possible to clarify whether patients with cervical dysplasia have foci of invasive cancer or whether it is still possible to prevent the development of a malignant process. Contraindications to conization may include:
- infectious processes occurring in the vagina, uterus and appendages;
- invasive cancer confirmed by histological examination.
Bleeding after conization
Any surgical operation associated with dissection of soft tissue and disruption of the integrity of small capillaries and larger blood vessels entails bleeding in more than five cases out of a hundred.
Bleeding after surgical procedures can be either moderate or excessively profuse, and last for twenty days. A spotting discharge may appear, the dirty brown color and unpleasant odor of which indicate the presence of infection.
The recovery period is characterized by disruptions in the menstrual cycle, with the first and second periods after the operation being more abundant than those that occurred before.
The norm is considered to be minor bleeding within two to three weeks after surgery, not accompanied by pain. This is a natural phenomenon during the repair process, which spontaneously stops over time.
Important! The most serious complication after conization of the cervix is stenosis of the walls of the cervical canal, which occurs in two percent of patients. The narrowing of the passage becomes an obstacle to pregnancy, so women whose plans include having a child do not undergo conization.
READ MORE: Leukocytes in cytology during pregnancy
Preparing for surgery
Any operation requires preliminary preparation. Before conization, a woman needs to undergo urine and blood tests, a biopsy of the tissues to be operated on, colposcopy, and a smear for microflora.
On what day is cervical conization performed? The manipulation is carried out after the end of menstrual bleeding in the first phase of the cycle. Thanks to this approach, the wound surface that is formed during the operation will have time to heal before the next period. Before the operation, at least 8 hours before the operation, the woman is not recommended to eat.
The procedure can be performed using local or general anesthesia. The duration of the manipulation depends on the diagnosis. On average it lasts approximately 30 minutes.
Histology after conization of the cervix is mandatory. The biopsy specimen is sent directly from the operating room to the laboratory for careful examination. If malignant cells are detected in it, the woman will be prescribed appropriate treatment after conization of the cervix.
Discharge
The appearance of discharge after excision of soft tissue is an integral part of the recovery period. There is no need to worry when discharge mixed with blood occurs due to minor damage to small vessels - everything will stop as the wound heals.
A week after the patient is discharged home, the amount of discharge may increase, this is due to the release of a scab, which is localized at the wound site. The crust is formed mainly after radio wave conization and covers the open wound surface, which is the “entry gate” for harmful microorganisms.
As it heals, the scab comes out of the cervical canal on its own, around the seventh day. This is a natural process that accompanies surgery using special means.
After its release, the discharge will decrease, but will not stop altogether, because the damaged surface may bleed for several months, which is not considered a manifestation of pathology.
At this time, the cellular layer is restored, tissues undergo a regeneration process, and the body strengthens. This is a natural process that does not require additional measures to speed it up.
If you experience heavy vaginal discharge with characteristic signs of infection, you should immediately consult a specialist. This pathology requires urgent measures in the form of drug treatment.
After operation
How is healing going? This question worries no less than the question about the operation itself. After the procedure is performed, the postoperative period may differ slightly from patient to patient. This depends on the condition of the neck, the size of the removed element, and the characteristics of the operation. As a rule, postoperative pain is similar to that accompanying menstruation. Just as compelling. But longer. The discharge will be bloody or watery in any case. Their volume can be significant. If it exceeds the volume typical for normal menstruation, then you should consult your doctor. Many people report cessation after 2 weeks, on average. However, up to 4 weeks is possible. Complete healing occurs after 4 months. But all postoperative manifestations disappear within a month. Darkish, even somewhat brownish, or watery pink discharge after conization is normal.
After about a week, the scab comes off from the wound. The volume of discharge may increase slightly. Some patients note that they definitely felt the scab coming off. An increase in discharge and its darkening, characteristic of the discharge of a scab, may not be pronounced.
Your period usually comes on time. However, they are more abundant. Next time their volume will be normalized.
Anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs are quite sufficient for pain relief.
It is strictly forbidden to take drugs that promote bleeding and reduce blood clotting: Aspirin, Warfarin.
The recommendation about how long you should not sit after surgery remains ambiguous. Sometimes it is recommended to refrain from sitting for a week. Or they don’t make such a restriction. It depends on the scope of the operation itself, and on the opinion of a particular doctor.
Taking a hot shower, visiting saunas, baths, and sex is excluded for a month. Sports activities must be cancelled. You cannot lift weights exceeding 3 kg.
Pregnancy and childbirth after conization
Women who want to give birth to a second child, as well as those who have not yet given birth, are recommended to treat cervical pathologies using more gentle methods than tissue excision.
However, if surgery is unavoidable, it is advisable to choose less traumatic methods, such as laser and radio wave conization. After complete recovery, you can plan to conceive only after a year, otherwise an insufficiently healed wound may become inflamed, which will complicate the course of pregnancy.
In general, conization does not negatively affect the fertilization process, which cannot be said about pregnancy and childbirth. Sometimes a large area is excised to remove all the damaged tissue, which can cause weakening of the muscle tissue.
Under pressure from the fetus, the cervix may open ahead of schedule, which can trigger the onset of premature labor. To avoid this, a special suture is placed on the cervix, which is removed before childbirth.
After surgery, as the wound heals, scar tissue forms, the elasticity of the walls decreases, which causes complications during natural childbirth.
During pregnancy and after childbirth, a woman should be under the close attention of medical professionals, which will reduce the risk of developing postpartum complications.
Treatment of bleeding
Here you need to pay attention to the period of bleeding. If they occur immediately after surgery, doctors will determine the need for local hemostatic procedures. Sometimes tampons with hydrogen peroxide or adrenaline are enough, but there are situations when it is simply impossible to do without surgical stopping of bleeding.
As for very long and heavy menstrual flow, they do not need treatment, because the cycle is restored over time. Sometimes symptomatic therapy is prescribed for a severe drop in red blood counts.
After conization of the cervix, discharge is an inevitable phenomenon, so you should not worry too much. But increased attentiveness will not hurt, especially in the first few months after the procedure. It is best to go to the hospital if you have any suspicions and consult with your doctor in order to correct the situation in time and prevent the occurrence of more serious complications.
A woman’s health is a fragile vessel. Very often, cervical diseases are diagnosed that are associated with inflammatory processes or are their consequence: erosion, dysplasia, ectopia, cancer.
Modern medicine offers a unique treatment method - conization. The essence of the treatment procedure is to remove a cone-shaped section of the surface of the cervical canal or part of the damaged muscle tissue. Often the procedure is performed not as a treatment, but as a research and diagnosis of the underlying disease.
The well-being of women after cervical surgery is determined by many factors. The postoperative period after conization of the cervix occurs individually for each woman: it depends on concomitant diseases, the state of the immune response and the chosen method of medical intervention.
The stage of recovery of the body in the postoperative period after conization of the cervix is characterized by the following points:
- regeneration of the mucous membranes takes a period of time from 6 to 8 weeks, during the first 2-3 weeks pain in the lower abdomen is observed, with dynamics of intensification from physical activity;
- a deep wound is formed at the site of the removed tissue area, which is accompanied by bleeding in the first days after conization;
- the period of complete recovery is significant and amounts to more than one month;
- Gradually, as the wound heals, it becomes covered with a scab if conization was carried out using a laser or radio wave method. Active healing occurs under the scab, and at a certain point it separates from the cervix and comes out naturally. This may be accompanied by renewed bleeding. Separation of the scab occurs 10–14 days from the moment of conization. But these terms are individual and determined by the size of the removed part of the cervix.
To successfully complete the course of treatment, women must follow a number of recommendations:
- lack of sexual intercourse;
- the use of hygienic tampons is unacceptable;
- no douching, bath, swimming pool, hot bath or sauna allowed;
- You should not take medications and herbal preparations that thin the blood (Aspirin, Trental, cinquefoil, chicory, etc.);
- refuse physical activity, do not lift loads exceeding 3 kg;
- You cannot stay in the open sun for a long time, much less sunbathe (including in a solarium).
The postoperative regeneration period is accompanied by moderate pain and bleeding. You can relieve pain symptoms by taking the drugs Ketonal, Drotaverine, Ibuprofen.
Signs that require going to the hospital:
- body temperature above 37°C;
- heavy bleeding that does not tend to decrease;
- unbearable itching;
- sharp pain in the groin area, lower back.
Stages of recovery
Any intervention in the anatomy of the cervix, including conization of the cervix, entails a long postoperative recovery period. For the most part, recovery is due to the behavior of the patients: taking all medications prescribed by the doctor, hygiene, avoiding sexual contact, and maintaining an exercise regimen.
The conization operation is performed only with sterile instruments, but the risk of infection remains both during and after the intervention. To minimize the likelihood of infection, the doctor may prescribe a course of antiseptic suppositories. It is to prevent infection from entering the wound that a woman should maintain sexual rest, avoid taking a bath and visiting the pool.
A complication in the postoperative period, such as bleeding, is associated with damage to the vessels of the cervix. If clotting processes are disrupted, blood clots do not form sufficiently. Also, when a large scab passes away, heavy bleeding may occur, requiring consultation with a doctor.
Radio wave, laser methods, as well as the diathermoconization method allow the formation of a scab. Its release will be accompanied by increased secretions. After cleansing the operation area, the discharge will decrease and become physiological in nature. A woman should be concerned about factors such as an increase in the abundance of discharge, an uncharacteristic appearance (cheesy consistency, yellow color), and a strong unpleasant odor.
Since conization surgery involves removing an area of affected tissue, the regeneration process may take longer than expected. To speed up healing, drugs such as Panthenol, Methyluracil, Levomekol are used.
If the patient experiences itching or burning, this may be a symptom of an infection. Discomfort is accompanied by an increase in temperature and increased discharge. Preventive treatment in the postoperative period may include antimicrobial suppositories such as Hexicon, Terzhinan, Rumizol.
The operation performed may affect the nature of the menstrual cycle: increased discharge, increased duration, pain. Such changes are observed in the first months after removal of a section of the cervix. After complete restoration of the body and stabilization of the woman’s psychological background, the menstrual cycle returns to normal.
If conization was carried out for dysplasia, then treatment in the postoperative period will be supplemented with antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs. During surgery, human papillomaviruses are dispersed into the vaginal walls, which can subsequently lead to relapse. That is why treatment includes agents that suppress the reproduction of viruses.
The main issue that worries women in the postoperative period is the possibility of future pregnancy after conization of the cervix. If the patient expects the birth of a child in the near future after the operation, then the doctor must select a minimally traumatic method of treatment, in particular, radio wave. The doctor will warn the woman about the need to delay pregnancy for at least one and a half to two years after conization.
Experts stipulate the danger of premature birth and miscarriage due to the likelihood of weakening the functions of the cervix under the weight of the fetus. To avoid this risk, the gynecologist may perform suturing or applying a pessary. A caesarean section is often performed, but predicting the process of delivery is only possible by assessing the dynamics of the condition of the cervix during pregnancy. Childbirth can take place after conization either naturally or surgically.
Conization of the cervix is the most effective method of treating precancerous changes in the epithelial structure. Timely diagnosis and treatment of the disease in the postoperative period will allow the woman to maintain her reproductive functions.
Negative points
Any surgical intervention and treatment of cervical diseases can lead to serious consequences. Complications arise in conditions of poorly performed surgery, the complexity of the woman’s underlying disease, or her non-compliance with recommendations.
The main negative aspects of the conization procedure in the postoperative period are presented as follows:
- bleeding (about 5% of operations have such consequences);
- infectious-inflammatory process;
- pain syndrome;
- scarring;
- stenosis;
- isthmic-cervical insufficiency (ICI) during pregnancy, which provokes spontaneous miscarriage or premature birth.
ICI does not always develop after conization. Since its cause is both a hormonal imbalance and a congenital disorder of the ratio of the muscle and connective tissue components, the operation may not affect the pregnancy process.
Prevention
Absolute recovery occurs within a period of 1 to 4 months. During this postoperative period, the doctor prescribes several preventative examinations. The first visit to the doctor can be scheduled as early as two weeks after conization. It may be necessary to submit a biomaterial sample for histology and additional tests.
If cancer cells are detected in the removed tissues during histological examination, the woman is prescribed radiation and chemotherapy, as well as additional, more radical surgical treatment.
If a woman develops stenosis or fusion of the cervical canal in the postoperative period, treatment after conization is carried out using bougienage.
Conization is a common and effective method of treatment and diagnosis of a number of cervical diseases. It can be carried out in almost any medical institution. The uniqueness of this treatment method lies in the ability to excise the damaged area and simultaneously conduct tissue examination for subsequent diagnosis. Regeneration occurs in a short time and with little risk of complications.
Consequences
According to statistics, the effectiveness of cervical conization as a method of treating dysplasia and preventing the development of oncology is quite low. There also remains a high probability of re-development of the pathology, with fifty women out of a hundred developing a more severe form of the disease within two years, up to non-invasive cancer, which leads to radical amputation of the entire organ.
Why is this happening? Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the main cause of precancerous diseases of the reproductive organs. It cannot be cured by surgical methods; the harmful virus remains in the cells of the epithelial layer and continues to actively spread.
If the presence of cancer cells is diagnosed, then surgical intervention can provoke their accelerated growth and the proliferation of metastases. Here, any drug therapy is powerless; to save the patient’s life, all reproductive organs along with appendages are removed.
Types of surgery
Modern medicine has several methods of surgical treatment. The method of conization of the reproductive organ is selected individually for each woman. The essence of the available surgical methods is presented below.
Surgical
This type of surgical treatment is currently used for special indications. Surgical excision of diseased tissue on the cervix has many disadvantages, such as a high rate of trauma, the risk of infection, and severe blood loss. The advantage of this treatment method is the high accuracy of removal of affected tissue.
Laser
This method is quite popular, but also not widely used. In this case, the high cost of the operation played an important role, as well as the need for general anesthesia for the patient.
Such a surgical intervention involves excision of diseased tissue with a laser beam or evaporation. The disadvantages of the presented treatment method are high cost and general anesthesia.
The advantages include high precision of excision and high-quality therapy.
Electrowave
How to carry out conization
On average, the duration of the procedure is 30 minutes. Everything depends not only on the complexity of the pathology and the method of conization, but also on what kind of anesthesia is used.
Before proceeding with the manipulation, the cervix must be treated with Lugol or a 3% acetic acid solution. This allows for better visualization of the affected areas, which are not stained but remain white. An examination with a colposcope is then required.
A procedure is carried out with gradual penetration deep into the tissue, and more and more tissue is captured, assessing the extent of the affected area. After cutting, the tissue is removed with tweezers, and the surface of the resulting wound is treated to stop the bleeding.
How is radio wave conization done?
For this procedure, “Surgitron” is used - an electric generator with a set of various electrodes.
The effect becomes noticeable due to exposure to high-frequency alternating current. In this case, a loop electrode removes an area of the required size.
Selecting the required electrode size, the specialist subjects it to high-frequency current. By rotating the loop electrode in the shape of a circle, pathogenic tissue is cut out, reaching a depth of up to 8 mm.
How is laser conization done?
The laser excises pathogenic tissue of the cervix, and this is achieved in a more precise way. In this way, it is possible to cut off the necessary fragment of the biopsy for subsequent study in the laboratory.
After laser conization, no subsequent course of treatment is required; the main advantage is that the patient does not lose reproductive function.
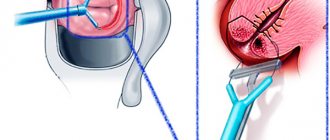
What is loop electroexcision
This is one of the methods for excision of pathological tissue from the cervix, for which a thin wire loop is used (plays the role of a scalpel). Under the influence of an electric current, the loop “cuts out” a thin layer of the cervix.
This procedure is carried out between menstruation so that it is possible to examine the cavity as best as possible. The procedure takes only a few minutes.