The menstrual cycle is an indicator of women's health. When the cycle is regular and without any unusual symptoms, a woman can be sure that her reproductive organs are in order. Each woman has her own individual cycle: for some it is short-term, and for others it is long. It must be restored two years after the girl first started menstruating.
Should I be concerned if I have a short menstrual cycle?
The nature of menstruation
The duration of a standard cycle is 28-31 days. Normal individual deviations are allowed within seven days.
If the duration is less than 21 days, then in medicine it is called a short menstrual cycle.
Let's try to understand the reasons and features of this concept.
The scientific name for this physiological process is proyomenorrhea. It is characterized by frequent bleeding, often every two weeks. In this case, the discharge lasts no more than three days and does not require pads with high absorbency.
If fertilization occurs, the hormone progesterone begins to predominate in the woman’s body. If conception does not occur, the production of this hormone stops. And the endometrial layer covering the uterine cavity is rejected. This causes bleeding every month. The length of your menstrual period is influenced by many factors, such as heredity, lifestyle, and hormonal characteristics.
The approximate start of menstruation is at 13 years of age, and the end at 40-55 years of age. Gradually, the duration of the menstrual cycle decreases. This is due to a decrease in ovarian activity. It is worth excluding from the list of suspicions the first two years after the start of menstruation, since at this moment the body is being adjusted. Also, in the last few years before menopause, disruptions and a reduction in the duration of bleeding may be observed.
Normal discharge
In order to understand why a shortened menstrual cycle is dangerous, it is necessary to consider the parameters of the normal process:
- spotting lasts 3-7 days;
- the duration of the monthly period is 21-35 days;
- the volume of bleeding should be in the range of 50-80 ml.
Particular attention should be paid to the fact that menstruation, that is, bloody discharge, should be red, and not brown and spotting. The color change marks the end of menstruation.
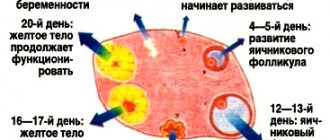
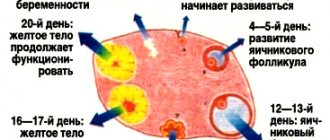
The first phase of the menstrual cycle is accompanied by the production of the female sex hormone estrogen in the ovaries. Estrogen affects the growth of the endometrium in the uterine cavity. Meanwhile, in the ovaries, based on hormonal changes, a follicle grows in which the egg matures. This process ends in the middle of the cycle approximately on the 14th day with ovulation - the rupture of the follicle and the movement of the egg into the fallopian tubes.
In the second phase, the egg moves into the uterine cavity through the fallopian tubes. During this period, she is ready for healthy fertilization. Oddly enough, the lifespan of an egg is approximately a day. If at this time there is no meeting with the sperm, then she dies. In place of the detached egg, a corpus luteum appears in the ovaries, in which the hormones progesterone are produced.
The second phase occupies the second half of the menstrual period. If fertilization does not occur at this time, the endometrial layer is rejected and the process begins again with bleeding.
The ability of sperm to fertilize an egg extends for 3-5 days after ejaculation. Approximately 6-7 days after ovulation, the fertilized egg is implanted in the uterine cavity. All processes in the female body are inextricably linked with time. As they say: everything has its time. Therefore, a reduction in discharge and the duration of the menstrual cycle affects the possibility of conception.
Fertilization
The main reproductive task of every woman is to conceive, bear and give birth to a healthy child. Any changes in hormonal levels and in the duration and structure of menstruation entail risks that reduce the possibility of fertilization.
Any, even the slightest, changes in the process of maturation and release of the egg from the ovaries entail changes in the hormonal background and change the process and time spent by the egg in the fallopian tubes on its way to the uterine cavity.
Changes in the nature and structure of the discharge can also cause adhesions and scarring in the fallopian tubes. They interfere with the normal passage of the egg. And sometimes they don’t miss it at all, which can lead to an ectopic pregnancy. These processes also cause hormonal imbalances.
Differences in the nature, structure or frequency of discharge should be a reason to consult a doctor to find out the causes of such symptoms. Otherwise, an advanced form of female disease can lead to infertility.
Time frame for the restoration of the menstrual cycle
Most non-breastfeeding women experience menstruation 6-8 weeks after birth . Breastfeeding women generally do not menstruate for several months or during the entire period of breastfeeding, although in some of them menstrual function resumes soon after the end of the postpartum period, that is, 6-8 weeks after birth.
Here you should not look for either a norm or a pathology, since the timing of the restoration of the menstrual cycle after childbirth is individual for each woman. This is usually associated with lactation. The fact is that after childbirth, a woman’s body produces the hormone prolactin, which stimulates milk production in the female body.
At the same time, prolactin suppresses the formation of hormones in the ovaries, and, therefore, prevents the maturation of the egg and ovulation - the release of the egg from the ovary. If the baby is entirely breastfed, that is, eats only breast milk, then his mother’s menstrual cycle is often restored after the start of complementary feeding.
If the child is mixed-fed, that is, in addition to breast milk, the baby’s diet includes formula, then the menstrual cycle is restored after 3-4 months. With artificial feeding, when the baby receives only formula, menstruation is restored, as a rule, by the second month after birth.
Causes
What is worth paying attention to, in addition to the reduction in the frequency of monthly discharge:
- chronic diseases (not related to the female genital organs);
- infectious diseases;
- changes in blood clotting;
- lack of vitamins C and K;
- inflammation of the female genital organs;
- changes in the endocrine area;
- ovarian cysts or tumors;
- changes in the genital organs (uterine inflection);
- fatigue, nervous tension or physical injury.
All these indicators directly or indirectly affect the duration of the menstrual period. Therefore, quite often, visiting a gynecologist alone cannot be limited. It is worth weighing all possible changes in the body over the last period.
Shortened cycle
Reducing the periods of work of the female genital organs can apply to both the first and second phases. All these processes are purely individual. They can accompany the postpartum or post-abortion periods, which are accompanied by sudden changes in the woman’s hormonal background.
A shortened cycle is often characterized by normal ovulation, but it occurs about a week earlier than standard. Sex hormone levels and basal temperature correspond to the period of ovulation. And in most cases, fertilization is possible without medical intervention.
It is for these reasons that women are advised to be especially careful during breastfeeding. Although nature tries to protect young mothers from conceiving during lactation. However, there is always a risk. Therefore, breastfeeding should not be considered a contraceptive. After childbirth, the hormonal levels are adjusted again and gradually. During this period, disruptions in the regularity of menstruation may occur.
Any changes in menstruation should be accompanied by monitoring of basal temperature. It, as an indicator, will reflect all deviations in the normal process of hormonal changes.
First menstruation after childbirth
The first menstruation after childbirth is often “anovulatory”: the follicle (the vesicle in which the egg is located) matures, but ovulation—the release of the egg from the ovary—does not occur. The follicle undergoes reverse development, and at this time the disintegration and rejection of the uterine mucosa begins - menstrual bleeding.
Subsequently, the ovulation process resumes and menstrual function is completely restored. However, ovulation and pregnancy may occur during the first months after birth.
The restoration of menstrual function is influenced by many factors, such as:
- the course of pregnancy and complications of childbirth,
- woman’s age, proper and nutritious nutrition,
- adherence to sleep and rest patterns,
- presence of chronic diseases,
- neuropsychic state and many other factors.
Diagnostics
Any symptoms of changes in the monthly female processes should be a reason to visit a gynecologist. In addition to the usual examination, you will need an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe an additional ultrasound of the endocrine system. Based on the results of the ultrasound, an additional detailed blood test may be prescribed to determine the level of hormone levels. It may be necessary to study not only female sex hormones, but also thyroid hormones.
During the interview, the gynecologist may ask about basal temperature indicators. Therefore, it is recommended to take information about temperature changes with you. Of course, if it has not been measured, then you should not postpone your visit to the doctor. However, it will greatly facilitate the diagnosis of a shortened menstrual cycle.
In medicine, there are two types of such cycles:
- two-phase;
- single-phase.
The first is characterized by a short period of increased basal temperature, approximately six to seven days. At this time, normal ovulation and follicle maturation occur, but the corpus luteum disappears too quickly. This causes a risk of developing infertility and requires urgent treatment with hormonal drugs.
The second, on the contrary, is characterized by a smooth curve that does not have a sharp increase. This means that ovulation does not occur, the follicle does not mature or does not mature to the required extent, and the corpus luteum does not form at all. In this case, we are talking about the possible formation of cysts, which is also fraught with infertility and dysfunction of the female genital organs, including surgical intervention.
In some difficult cases, the result of hysteroscopy may be needed for diagnosis. This procedure is an examination of the uterine cavity with a special device. Curettage of the walls of the uterine cavity may also be additionally prescribed. This is necessary if there is a suspicion of the presence of cancer cells in the female genital organs. The result of curettage is sent for histological examination.
The sequence of restoration of menstrual function
After the birth of a child, the work of all endocrine glands, as well as all other organs and systems, returns to its pre-pregnancy state. These important changes begin from the moment the placenta is expelled and last approximately 6-8 weeks.
During this time, important physiological processes occur in a woman’s body: almost all changes that occur in connection with pregnancy and childbirth in the genitals, endocrine, nervous, cardiovascular and other systems undergo; the formation and flourishing of the function of the mammary glands occurs, which is necessary for breastfeeding.
The normal menstrual cycle is a coordinated mechanism of the ovaries and uterus, so the process of restoring the functioning of these organs is inseparable from each other. The process of involution (reverse development) of the uterus occurs quickly. As a result of contractile muscle activity, the size of the uterus decreases. During the first 10-12 days after birth, the uterine fundus drops approximately 1 cm daily.
By the end of the 6-8th week after birth, the size of the uterus corresponds to the size of a non-pregnant uterus (in nursing women it may be even smaller). Thus, the weight of the uterus by the end of the first week is reduced by more than half (350-400 g), and by the end of the postpartum period it is 50-60 g. The internal os and the cervical canal are also quickly formed. By the 10th day after birth, the canal is completely formed, but the external pharynx is still passable for the tip of the finger.
The closure of the external pharynx is completed completely in the 3rd week after birth, and it takes on a slit-like shape (before birth, the cervical canal has a cylindrical shape).
The speed of involution may depend on a number of reasons: general condition, woman’s age, characteristics of pregnancy and childbirth, breastfeeding, etc. Involution can be slowed down in the following cases:
- in weakened women who have given birth many times,
- in primigravidas over 30 years of age,
- after pathological childbirth,
- with the wrong regimen in the postpartum period.
After the separation of the placenta and the birth of the placenta, the uterine mucosa is a wound surface. Restoration of the inner surface of the uterus usually ends by 9-10 days, restoration of the uterine mucosa - at 6-7 weeks, and in the area of the placental area - at 8 weeks after birth. During the healing process of the inner surface of the uterus, postpartum discharge - lochia - appears.
Their character changes during the postpartum period. The nature of lochia during the postpartum period changes in accordance with the processes of cleansing and healing of the inner surface of the uterus:
- in the first days, lochia, along with decaying particles of the inner lining of the uterus, contain a significant admixture of blood;
- from the 3-4th day, lochia acquires the character of a serous-sucrose fluid - pinkish-yellowish;
- by the 10th day, the lochia become light, liquid, without any admixture of blood, their number gradually decreases;
- from the 3rd week they become scanty (contain an admixture of mucus from the cervical canal);
- at 5-6 weeks, discharge from the uterus stops.
The total number of lochia in the first 8 days of the postpartum period reaches 500-1400 g, they have a specific smell of rotten leaves.
With slow reverse development of the uterus, the release of lochia is delayed, and the admixture of blood lasts longer. When the internal pharynx is blocked by a blood clot or as a result of a bend in the uterus, an accumulation of lochia may occur in the uterine cavity - lochiometer.
The blood accumulated in the uterus serves as a breeding ground for the development of microbes; this condition requires treatment - the use of medications that contract the uterus or, at the same time, washing the uterine cavity.
In the postpartum period, the ovaries also undergo significant changes. The reverse development of the corpus luteum, a gland that existed in the ovary during pregnancy at the site of the egg released into the abdominal cavity and then fertilized in the tube, ends.
The hormonal function of the ovaries is restored completely, and the maturation of follicles - vesicles containing eggs - begins again, i.e. the normal menstrual cycle is restored.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the cause of the disease and the nature of its course. As mentioned above, the main risk is the threat of infertility. Therefore, immediate treatment is required for any changes in the menstrual cycle.
If the cause is infectious sexual diseases, then it is necessary to eliminate them and then restore the vaginal microflora to eliminate the possibility of relapse. In case of inflammation of the appendages, it is necessary to undergo antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy. Sometimes treatment requires stimulation to increase the duration of the cycle, and hormonal drugs are prescribed. And when the long-awaited fertilization occurs, the first trimester requires special supervision from a doctor.
Changes in monthly bleeding are another reason to think about your health. It is necessary to evaluate the reasons that could lead to these changes. And if you suspect the presence of an infectious or inflammatory process in the body, you need to contact a gynecologist, who will diagnose and, if necessary, prescribe treatment. It is better to start treating early than to continue treating late.
How to treat short female cycle
Treatment of short female cycles is possible only after undergoing an examination. Self-medication is dangerous. Only a correct diagnosis will allow you to go on a rehabilitation course and get an excellent result.
If a gynecological pathology is detected, the doctor prescribes medications that solve this problem. Infections or inflammations today are treated in 2-4 weeks. Most often, the process takes place at home, all procedures are painless. Modern drugs can solve such problems without complications.
When diagnosing an ectopic pregnancy, and a short cycle may be a sign of it, the doctor will offer several options for solving the problem. Depending on the period, the optimal course for recovery will be adopted.
If the cycle failure is caused by hormonal disorders, then the endocrinologist prescribes drugs that restore the balance of estrogens and gestagens in the body. This treatment is longer, taking from 2 to 6 months. You need to get tested regularly to see changes. But such therapy is necessary for the full functioning of the whole organism.
If the cause is anovulation or improper maturation of the follicle, it is important to undergo a course of therapy to avoid infertility. The cycle is restored within a few months, and this procedure helps to balance reproductive function. It is not recommended to abandon such treatment if a woman plans to have more children.
If the cycle has shortened due to age-related changes, the endocrinologist will prescribe medications that make it easier to survive menopause. They make a woman’s life easier, help avoid mood swings, temperature changes and difficulties with menstruation.