Around the middle of each cycle, women undergo a special process called ovulation, which is considered the most significant of all stages of the menstrual cycle. But sometimes some deviations occur, and ovulation does not occur in the middle of the cycle, but immediately after menstruation, the so-called. early ovulation. The presence of such deviations can somewhat complicate the onset of conception, because it is during the ovulatory period that this important event occurs.
Ovulation concept
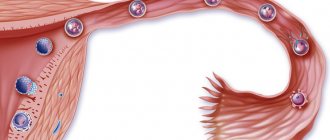
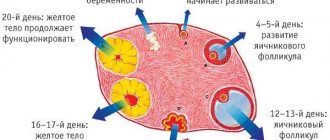
Ovulation is a specific physiological process characterized by the release of a female cell from the ovary due to follicular rupture. At the first stage of the cycle, under the influence of FSH, the follicle grows, reaching approximately 2 cm, after which rupture occurs and the cell is released into the abdominal cavity - the ovulatory period begins. Then, after about a day, the luteinizing phase begins, when the egg begins to move through the tube into the cavity of the uterine body. If fertilization has occurred, the cell is implanted into the uterine wall, but if there has been no conception, the cell dies in the fallopian tube.
The whole process is controlled by the hypothalamus, a small brain center located in the diencephalon. Sometimes the ovulatory period occurs earlier, i.e. the egg leaves the ovary almost immediately after the end of menstruation, approximately on the 8-10th day of the cycle. Then early ovulation is diagnosed, which most often occurs due to hormonal imbalances that occur against the background of many factors.
Description of the ovulation process
Ovulation is the process in the female body through which a mature egg is released from the follicle. During the first stage of the cycle, the follicle grows under the influence of the hormones estrogen and progesterone. Around the second week of the menstrual cycle, hormones reach their peak, causing the follicle to burst. The egg is released and travels through the fallopian tube into the uterine cavity. The entire process from follicle rupture to fertilization, whether it happens or not, is called ovulation.
The process takes place under the control of the hypothalamus. The correct hormonal background ensures timely maturation and release of the egg. This happens exactly in the middle of the cycle, that is, for a standard menstrual period of 28 days equals 15 days.
Sometimes it happens that the egg is released earlier than expected. As a rule, this occurs as a result of hormonal imbalances.
The release of the cell between days 8 and 10 of the menstrual cycle is called early ovulation.
Why does the ovulatory period occur prematurely?
The global scientific community does not yet have a consensus on the specific causes of such a phenomenon as early ovulation. Many people believe that the cause is due to its random nature. Experienced gynecologists are of the opinion that the reasons for early ovulation are hidden in hormonal imbalance. In general, the reasons why the early ovulatory period begins come down to the following factors:
- Psycho-emotional disorders;
- Disturbances in the balance of estrogen and progesterone hormones, as well as luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormone, i.e. hormonal imbalances;
- Frequent stressful conditions, nervous overstrain, emotional exhaustion, etc.;
- Dysfunctional disorders of the adrenal cortex;
- Excessive gonadotropin synthesis in the anterior pituitary lobe;
- Inflammatory lesions in the reproductive system;
- Infectious lesion of bacterial or viral origin;
- Unclear etiology of early egg release;
- The use of certain medications and alcohol abuse, nicotine addiction;
- Changes in climatic conditions;
- Colds and flu conditions;
- Abortion and its consequences;
- Employment in hazardous industries;
- Intense training;
- Disrupted day and sleep patterns.
Such factors may well provoke various kinds of imbalances. In addition, each factor can affect other systems of organisms. A typical example of such an impact is low immune status, which leads to various kinds of infectious and viral pathologies. Therefore, to avoid this, it is recommended to avoid such factors that can affect ovulation.
Throughout life, a woman periodically experiences ovulatory shifts in different directions, i.e., not only premature, but also late release of the female cell may occur. It also happens that in one cycle not a single cell may mature (anovulation), or two cells come out at once. If the early release of the egg regularly occurs, then such a picture is considered a deviation from the norm. If ovulation came ahead of time only once, then this phenomenon is not considered a pathology.
Why does premature ovulation occur?
Most processes in a woman’s body depend on menstruation. During this period, an uneven increase in hormones begins:
- progesterone;
- estrogen;
- luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormone.
Premature ovulation can occur due to:
- colds,
- stress,
- overwork,
- acclimatization,
- poor diet or sleep patterns,
- drinking alcohol and certain medications.
The causes of early ovulation include inflammatory processes, a recent abortion and postpartum period, malfunction of the ovaries, disturbances in brain activity, etc.
With a 28-day cycle, egg maturation occurs by the end of the second week, early ovulation occurs on the 12th day or earlier. Women with this feature have a short follicular phase (this is the time from the beginning of menstruation to the release of the egg). Normally, its duration is from 12 to 16 days.
Early and late ovulation may occur due to the same reasons. Sometimes these conditions are normal, but sometimes they indicate malfunctions in the body. The onset of the process earlier than the middle of the cycle can occur in older women, as their ovarian reserve functions decrease.
What are the dangers of premature ovulation?
In general, experts believe that there is nothing dangerous or terrible in such a phenomenon as early ovulation, except for unexpected pregnancy in girls who are protected by the method of calculating ovulation, that is, they are protected during sexual intercourse on “dangerous” days. But sometimes premature ripening can indicate serious health problems.
In addition, the premature onset of the ovulatory period can have an extremely negative impact on the chances of conception. Simply put, if a woman has been trying to conceive for a long time, calculates favorable days, and has unprotected sexual intercourse on these days, then she most likely will not be able to get pregnant. The fact is that the calendar calculation method assumes the onset of the ovulatory stage approximately in the middle of the cycle.
If a premature ovulatory period occurs due to various kinds of disturbances in organic activity, then gynecological intervention is required. In some cases, the use of hormonal drugs is necessary to correct ovulation. But quite often ovulation occurs ahead of time due to individual intraorganic characteristics.
Signs and symptoms
To detect premature egg release, you need to track your cycle for at least 3 months. With a 28-day cycle, ovulation should be expected on days 12-16, with a 30-day cycle - on days 13-17.
If a woman begins to feel the following symptoms shortly after her period, most likely she has entered the ovulatory phase earlier than usual:
- increased viscosity of cervical mucus;
- soreness of the mammary glands;
- increased sexual desire;
- aching pain in the abdomen.
Signs of premature egg release can be monitored by measuring urine LH levels using ovulation tests.
How else can you determine early ovulation?
Determining the peak of basal temperature is a reliable sign of egg release, available to any woman at home. However, this method also has disadvantages: for at least six months you need to strictly follow the measurement procedure, record the result, build a graph and analyze it together with a gynecologist.
The most accurate way to determine the release date of an egg is to measure the diameter of the follicle using ultrasound (folliculometry). For obvious reasons, this measurement is not available to all women.
An informative home method is to use the ovulation texts mentioned above. If the egg is released early, it is better to use reusable cassette devices, devices for determining ovulation by saliva, or purchase a large number of disposable test strips, starting to use them immediately after the end of menstruation.
If the failure occurs once, there is no reason to worry. Problems with conception may occur if the pathological condition persists for more than 3 months. At the same time, the menstrual cycle is shortened, and menstruation comes earlier than usual.
Signs of the early ovulatory period
When the egg is already mature and ready to be released, characteristic hormonal fluctuations occur in the endocrine system, which are manifested in increased levels of follicle-stimulating hormone and prolactin hormone. Against the background of such changes, many characteristic manifestations arise that any woman can notice if she listens more carefully to her body. So, signs of early ovulation:
- Nagging pain in the uterine area;
- Increased gas formation;
- Nipple hypersensitivity;
- Breast engorgement, soreness;
- Sudden mood swings from sadness and despair to joy and fun;
- The mucus discharge from the vagina changes, it becomes viscous and abundant;
- Sexual desire noticeably increases, nature itself indicates to the woman that she is ready for procreation.
How early ovulation can affect conception
The ovulatory stage and conception have a fairly close relationship. Conception cannot occur unless there is ovulation. Since this period takes a fairly short time, conception can occur exclusively on these days, as well as during sexual intercourse a couple of days before ovulation. If there is no sex on dangerous days, then certain difficulties may arise with conceiving a baby.
Premature cell release can lead to unwanted pregnancy, as well as cause infertility, due to the fact that it will be quite difficult for a woman to determine the ovulatory peak, and, therefore, to calculate the most favorable days for pregnancy. Even with regular periods, ovulation may occur prematurely. A similar disorder is quite often observed in patients who have recently given birth and are breastfeeding. Therefore, gynecologists recommend that such mothers approach the issue of contraception responsibly, choosing drugs that are acceptable during lactation in order to avoid unexpected pregnancy.
Early release of the egg and pregnancy
Constant monitoring of menstruation provides a woman with a picture of the state of the patient’s reproductive system. If a cell leaves the follicle, but pregnancy does not occur, then there is no need to immediately suspect pathology; often such a phenomenon is quite normal. Pregnancy with early ovulation is quite possible. If it happens, it will indicate that conception did not occur in the middle of the cycle, but somewhat earlier. Moreover, in isolated cases, it is quite possible for two ovulatory periods to occur during one cycle. This is possible if the eggs mature in two ovaries at different times of the cycle.
It is not at all uncommon for there to be no ovulatory stage during the cycle. But this is not a pathology. You should be concerned if there is no ovulation for several cycles. Such signs may indicate pathology of reproductive functions, so the help of a specialist is necessary.
Is it possible to get pregnant if you ovulate early?
Pregnancy with early ovulation is not considered uncommon, in cases with a full-fledged follicle and healthy seminal fluid. Problems may arise with planning, since it is difficult to correctly calculate the time of follicle maturation.
Women who protect themselves using the “calendar” method should not forget that early ovulation and pregnancy are not mutually exclusive. This contraceptive option is not recommended for those who have a regular cycle and the egg leaves the ovaries in due time.
But there are also disadvantages to early ovulation and conception: the egg may be released underdeveloped, and therefore there is a high risk of early pregnancy termination. If fertilization has occurred, then the signs of pregnancy during early ovulation are not noticeable.
When do the first signs of pregnancy appear?
Signs of pregnancy may not be noticed immediately; a woman may attribute them to a slight malaise. The fertilized egg enters and implants in the uterus after a week. Before this period, pregnancy is extremely difficult to determine. You can judge the onset of conception by the following signs:
Basal temperature
A change in basal temperature in the early stages almost always indicates fertilization. It is measured in the mouth, vagina or rectum. In the latter case, it is called rectal and the indicators are mainly checked there. The measurement should take place every morning at the same time. To do this, place the thermometer 3 cm into the anus and leave for 5 minutes.
It is better to record the results; in most cases, an increase and growth above 37 degrees indicates conception, but can be caused by illness, stress or certain medications.
Discharge
Discharge during ovulation in early pregnancy appears under the influence of the hormones progesterone and estrogen, but may be completely absent. After the fertilized egg is implanted in the uterus, hCG begins to enter the bloodstream. As a rule, a woman assumes pregnancy after a missed period. Before this day at conception it is typical:
- mucus secretion;
- pink, white or beige liquids.
In the case of pink discharge, this means the implantation period.
This is the name for the period when the fertilized egg attaches to the endometrium, damaging the blood vessels and connecting with the cervical fluid, creating a pink tint. Such a signal can be dangerous if the fact of conception has already been established.
Can ovulation occur in early pregnancy?
Pregnant women do not have an egg, and its release can harm the woman and the fetus. A mature egg is needed only for fertilization and further development of the fetus. If conception has occurred, then the body no longer needs to produce it; this process should not occur during pregnancy.
Methods for calculating ovulation
You can calculate the ovulatory period using various methods. For example, the most accessible and most reliable method is the use of test strips. This method is most suitable for patients with regular cycles. If menstruation comes at different times, it is difficult to roughly predict the days of ovulation. Such tests are quite expensive, so it is impossible to carry them out every day. But if financial solvency allows, then during daily testing on certain days you can see two bright stripes. When they are as bright as possible on the test, then ovulation has occurred.
If the cycle is irregular, then it is better to use basal measurements, which must be carried out over several months. Then, by comparing the graphs, you can determine whether the ovulatory period may occur prematurely, or whether it comes later than usual. The temperature is measured at one time, in the morning. You cannot get out of bed; prepare the thermometer in the evening, shaking it in advance.
Ultrasound diagnostics is also considered a reliable method, which allows monitoring the process of follicular maturation. It is better to carry out the examination vaginally, starting from the seventh day of the cycle, repeating the procedure every two days.
Why is this happening
The main reasons for early ovulation:
- time before menopause;
- short follicular phase;
- smoking, alcohol and caffeine abuse;
- stress;
- sudden loss or sudden weight gain;
- early ovulation may occur after discontinuation of OCs (oral contraceptives);
- sexually transmitted diseases;
- a sudden change in normal daily activities;
- Irregular menstrual cycle caused by gynecological hormonal diseases.
Any hormonal imbalance can disrupt the duration and staging of the menstrual cycle. The maturation of the egg in the ovarian follicle is stimulated by follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and its release is associated with the action of luteinizing hormone (LH). Both of these substances are produced in the pituitary gland under the control of the hypothalamus. A change in the level of these hormones leads to disruption of the ovulatory mechanism.
Premature onset of the ovulatory phase is associated with high FSH levels.
A decrease in ovarian activity inevitably occurs with age. At birth, a girl has about 2 million eggs. During each menstrual cycle, hundreds of them die, and only one matures. The exception is hyperovulation, when more than one egg matures in one cycle.
By the age of 30, a woman has lost more than 90% of all eggs. As menopause approaches, the pituitary gland, through a feedback mechanism, begins to secrete more and more FSH to compensate for the lack of ovulating follicles. This leads to menstrual irregularities.
The consequences of constant early ovulation are the release of immature eggs and infertility.
According to research, smoking causes disruption of the ovulatory cycle and affects female fertility. When a woman smokes more than 20 cigarettes a day, it is almost impossible for a woman to fully mature her egg. The same can be said about the effects of alcohol and caffeine.
Treatment
Restoring the previous ovulation regime is quite possible.
- For this, patients are prescribed hormone therapy.
- But the problem is that many patients do not attach serious importance if ovulation has moved at least five days earlier or later than normal. But early ovulation requires contacting specialists.
- Patients who have such abnormalities are often prescribed hormonal injections into the navel or abdomen.
- During the therapy period, estrogen levels, progesterone and other hormones are constantly monitored.
Before treatment, the patient undergoes a full examination to exclude possible contraindications to hormone therapy, as well as to identify the real cause of the deviation and prescribe the most effective treatment.
How to normalize the ovulatory cycle
When early ovulation occurs, a woman needs to bring her cycle back to normal. Doctors strongly recommend going to the hospital in cases where the release of gametes occurs earlier than the middle of the cycle by five or more days for three months in a row. The doctor will be able to prescribe effective therapy only after identifying the cause and factors that accompany the pathology.
The need to bring the cycle back to normal is explained by the fact that if the germ cell matures untimely and incompletely, a future pregnancy may end in a miscarriage or may never occur. It will be possible to prevent the onset of such consequences with the help of medications that not only solve the problem of early ovulation, but also make complex biochemical processes in the body of the expectant mother stable.
Treatment is prescribed only by a doctor. In general, therapy includes the use of the following:
- medications that can increase the formation of FSH and LH (for example, Clostilbegit) - they must be taken by patients with gynecological diseases (problems with the production of sex hormones) and infertility; they have a beneficial effect, as a result of which the egg matures at the right time;
- vitamins (for example, pyridoxine, folic or ascorbic acid) - they need to be taken to bring the cycle back to normal, as well as to gradually prepare the female body for fertilization of the egg;
- progestogens (including: Utrozhestan, Dufacton) + Femoston - they must be used in combination to overcome infertility; this combination affects the thin endometrium, increasing its thickness, and also prepares the uterus for union with the fertilized egg.
Preventive actions
To avoid such a deviation, you need to avoid early ovulation causes. You also need to completely change your life by giving up smoking, limiting alcohol intake, adjusting your daily routine, rest, work and sleep patterns. In addition, the patient needs to avoid stressful and conflict situations and overwork, relieve nervous tension, etc. Taking vitamins, active life and strengthening the immune defense can be a serious preventive measure against a possible ovulatory shift in any direction.