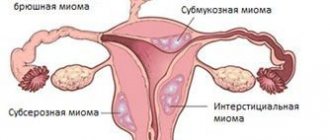
How does uterine fibroid manifest?
Myoma is an insidious disease that in many cases does not manifest itself at all. About a third of women suffering from uterine fibroids do not experience any suspicious symptoms indicating that a tumor is maturing in the body. This once again confirms the need to undergo regular preventive examinations with a gynecologist - only a specialist can identify the disease in time and prescribe treatment that will protect the woman from developing complications.
If uterine fibroids nevertheless manifest themselves, they manifest themselves with the following symptoms:
- heavy menstruation with clots, longer than usual;
- severe pain during menstruation;
- spotting outside of menstruation;
- discomfort in the lower abdomen, in the lower back, a feeling of heaviness and pressure.
With multiple myomatous nodes, these symptoms may intensify. With the active growth of tumors, a woman is bothered by frequent aching pain.
Reasons for the development of fibroids
Uterine fibroids are understood as a tumor that develops from one smooth muscle cell - under the influence of a mutation, this cell begins to divide abnormally (cloning). It has not yet been possible to definitively establish the cause of the mutation in the cell, but the following assumptions exist.
The influence of sex hormones - the peak of the disease occurs at the age of 35-40 years, at this time the woman’s level of hormones produced by the ovaries decreases, but the ability to conceive remains. After menopause, when hormone levels drop rapidly, fibroids can resolve. It should be noted that the opinion of doctors about the influence of hormonal imbalances is contradictory, but it has been proven that hormonal imbalance causes the growth of leiomyoma.
Previously, it was believed that estrogen is the main stimulator of tumor growth, but recently it has been believed that progesterone plays an important role; it, together with estradiol, supports the growth of tumors. According to the results of biochemical and molecular analyses, myomatous nodes have 3 times more progesterone receptors and 2 times more estrogen receptors than in the adjacent myometrium. In this case, the level of hormones in the blood may correspond to the norm; the increase in the node occurs due to the increased susceptibility of receptors to sex hormones.
The influence of growth factors and cytokines - biologically active compounds that affect smooth muscle cells from which myomatous nodes are formed.
Changes in the immune system. There is an opinion that the formation of fibroids resembles a protective reaction of body cells to a destructive influence.
In order to find out who is more susceptible to developing this disease, doctors studied thousands of women suffering from this pathology; the following patterns were noticed:
- Women over 40 years old are automatically at risk.
- Heredity. As a result of research, it was found that fibroids are twice as likely to select women whose close relatives have encountered this disease. Confirmation of the genetic theory is that women of the Negroid race, due to family history, are at risk for developing uterine fibroids.
- Early puberty.
- Lack of pregnancies during puberty.
- Lack of a long period of feeding the baby.
- Overweight.
What happens if myoma is not treated?
Uterine fibroids can make it impossible to get pregnant. If conception occurs, fibroid nodes can interfere with bearing a child. In approximately 20% of infertile women, uterine fibroids are the only pathology of the reproductive system.
Heavy menstruation and large blood loss, as well as intermenstrual bleeding, cause the development of anemia and deterioration in overall health: weakness, lethargy, headaches, dizziness, memory impairment. Anemia also negatively affects the condition of the skin, hair and nails.
The continuous growth of fibroids sooner or later leads to disruption of the functioning of internal organs, creating problems in the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys. For example, a large fibroid ball can compress the ureter and impair the flow of urine, causing irreversible damage to the kidney. It is also possible for fibroids to transform into a cancerous tumor.
Torsion of the fibroid stalk and its necrosis is manifested by acute pain, intoxication and high body temperature. This condition requires immediate medical attention.
Thus, fibroids can lead not only to reproductive dysfunction, but also to malfunction of other internal organs, and in some cases even threaten life.
Symptoms of pathology
A small formation is characterized by a complete absence of signs. In some cases there are minor manifestations:
- menstrual irregularities;
- pain in the lower abdomen a few days before menstruation;
- heavy and painful periods;
- inability to get pregnant;
- spontaneous termination of pregnancy in the early stages.
The severity of such symptoms depends on the location of the tumor on the body of the uterus. The most painful sensations occur when fibroids are located on the neck.
As myomatous nodes enlarge, the symptoms become more pronounced:
- A noticeable increase in the volume of menstrual flow. Often critical periods last longer, and the discharge is so abundant that anemia develops.
- Intermenstrual discharge. Between periods there is bloody or mucous discharge. The reason is irritation, inflammation and the appearance of microcracks in the tissues where the tumor has formed.
- Pain in the lower abdomen, in the lumbar region. Pulling indicate a large formation, acute appears when the tumor stalk is torsed, cramping is the cause of the development of the tumor process in the mucous tissue of the organ.
- Dizziness, pallor, general weakness. They occur as a result of anemia - a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood.
- Disruption of other organs. Compression of the intestines and bladder disrupts the natural processes of bowel movements and urination.
- Heartache. Large formations affect myocardial tone, significantly reducing it.
- Infertility. The development of nodes in the area of the fallopian tubes prevents the movement of sperm, they do not reach the egg.
Important! The presence of at least one symptom is a reason to consult a gynecologist. Early diagnosis prevents the development of other pathologies and promotes successful treatment.
Diagnosis and treatment of uterine fibroids
To diagnose fibroids, a gynecological examination, hysteroscopy, medical history and ultrasound are sufficient, and, if necessary, CT and MRI. When a diagnosis of fibroids is made, the treatment regimen for the patient is selected individually. Not all myomatous nodes require surgical intervention; in some cases, dynamic observation and conservative treatment can be limited. The basis of therapy is the use of hormonal drugs that inhibit tumor growth. The drugs are selected only by the doctor, taking into account the patient’s age, her state of health and plans for future pregnancies. Self-medication and refusal to visit a doctor for uterine fibroids are unacceptable; this can lead to irreparable consequences.
To date, there are no treatments other than surgery that can permanently remove fibroids. Conservative treatment only slows down the development of the tumor, so in many cases doctors offer surgical treatment.
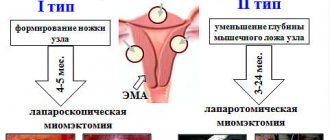
There are options for organ-sparing surgery, when the myomatous node is removed with minimal damage to the uterus. After the operation, menstrual function and the ability to bear and give birth to a child are preserved. Minimally invasive laparoscopic intervention allows the patient to recover quickly and leaves virtually no scars on the skin.
Treatment
When treating benign tumors of the uterus that are small in size, conservative therapeutic methods are used, aimed at stopping their activity that causes intensive growth and stabilizing the size of their cell nuclei. For this purpose, a low dose of oral contraceptive drugs is used to normalize the hormonal balance, as well as the introduction of an intrauterine system to restore the functioning of the ovaries; surgery is not performed in case of small fibroids.
Treatment of fibroids involves an individual selection of medications, depending on the characteristics of the patient’s condition, her age, plans for children, symptoms of the disease, tumor size and the number of nodules. Today, the following methods are used to treat myomatous formations of this nature:
- Hormonal agents that can normalize hormonal levels, reduce the production of female hormones and cause artificial menopause, which stops tumor growth.
- The use of special contraceptives that stop the growth of myomatous nodes.
- The use of a special Mirena hormonal device, which allows the required amount of hormones to be delivered directly to the uterus.
- Bringing a course of vitamin therapy designed to maintain the body's defenses.
- The use of dietary nutrition aimed at eliminating benign formations.
- Using electrophoresis with sodium or potassium iodide, which leads to a reduction in the production of sex hormones and a decrease in inflammation.
- Carrying out magnetic therapy to enhance the effectiveness of hormonal medications taken.
- Baths containing radon, which reduce estrogen production.
The formed tumors, when carrying out the most effective conservative therapy, decrease in size and stop their development, however, their center is not able to completely disappear. The result of treatment is the absence of pathological symptoms and growth of nodes, and the treatment process is considered successful if the tumor does not increase over a long period of time.
Pregnancy and uterine fibroids
It is impossible to predict in advance whether fibroids will be an obstacle to conception. If the tumor is small, pregnancy is possible. But if the tumor grows into the uterine cavity, it will interfere with the development of the fetus and may cause a miscarriage. Also, large fibroids can make the process of natural childbirth impossible. In addition, hormonal imbalance during pregnancy can lead to increased growth of fibroids and the development of complications that did not exist before pregnancy.
It follows from this that if fibroids are present, pregnancy can be planned only after a thorough examination and with regular monitoring by an experienced gynecologist.
At what size does a fibroid pose a threat?
Myomatous nodes come in three sizes:
- small – up to 2 cm;
- medium – 2–6 cm;
- large – over 6 cm.
Minor nodes usually do not cause any discomfort to a woman, and the disease is asymptomatic. A threat to health is created by large fibroids, which put pressure on neighboring organs, disrupting their function.
Doubts about whether uterine fibroids are life-threatening are usually unfounded, but the lack of timely medical care in critical situations can have disastrous consequences.
Myths about fibroids
Myth 1. Myoma can be cured with dietary supplements or folk remedies.
No dietary supplements, vitamins, herbal infusions, leeches or other similar treatment methods can get rid of fibroids. Experiments with the use of traditional medicine without the consent of a doctor can aggravate the course of the disease and require urgent surgery with complete removal of the uterus.
Myth 2. After removal of fibroids, problems with bearing a child may occur.
Rather, problems with pregnancy are more likely if fibroids are not treated. The likelihood of complications after surgery increases only if the intervention is performed by an unqualified surgeon who incorrectly sutures the uterus after removing the fibroids.
Sex after tumor removal
Surgical operations to remove fibroids are performed using several methods, so the recovery period takes different time periods. The total treatment option is removal of the uterus. This method is justified if a woman does not plan to have children in the future. After surgical removal of the uterine cavity, you can return to full sexual activity after 2 months. Sexual desire remains, the man also does not feel any changes in intimacy.
If a woman is planning a pregnancy in the future, an organ-conserving operation is performed - myomectomy. After it is carried out, the period of abstinence is about 1 month. But careful contacts are possible earlier, after the permission of the attending physician. In the postoperative period, 12-14 days after surgery, the woman should visit a gynecologist.
The effect of orgasm on a woman
Some people believe that orgasm itself is not that important for a woman. But this opinion is wrong. As a result of a prolonged lack of orgasm, a woman may become irritable, which will negatively affect her overall health. This is where the fair sex begins to think about whether it is worth maintaining a relationship with a man who cannot provide discharge to the body.
During sexual intercourse or simply sexual arousal, the body produces estrogen in large quantities. In addition, there is a rush of blood to the genitals and mammary glands. If an orgasm occurs as a result of sexual intercourse, then after 5-7 minutes the level of estrogen normalizes and the state of the reproductive system does not change. If there is no orgasm, then recovery will take at least one hour.
Thus, in the absence of orgasm, there is no outflow of blood from the genital organs, which can provoke the growth of mima or the formation of mastopathy in the mammary glands. The data presented has long been proven by experts. According to statistics, in 2/3 of patients with uterine fibroids, it turns out that they did not have regular sex life ending in orgasm. Thus, with the help of meaningful sex, you can not only improve mutual understanding with your partner, but also normalize your health, and also avoid diseases such as uterine fibroids.
For more information about uterine fibroids, watch the video: