Reasons for growth
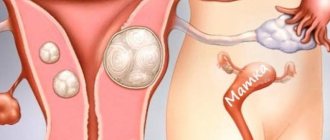
The formation of a tumor in the uterus always occurs due to hormonal imbalance. Uncontrolled estrogen synthesis provokes active division of glandular and muscle cells. Prerequisites for active growth of fibroids are:
- Decreased physical activity, sedentary lifestyle and obesity.
- Endocrine and autoimmune pathologies.
- Poor nutrition with a predominance of foods high in preservatives, dyes and flavor enhancers, which can provoke a tumor process in the body.
- Pathologically reduced immunity.
- Bad habits.
- The presence of a chronic inflammatory process in the genitals caused by sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
Women over 45 years of age are at risk, since the most pronounced hormonal imbalance is observed during menopause.
Symptoms and growth rates
Clinical manifestations indicating active growth of uterine fibroids are as follows:
- An increase in the volume of the abdomen, which indicates the impossibility of wearing familiar clothes, which now press in the belt.
- A feeling of heaviness and fullness in the lower abdomen, which is especially evident when bending forward and squatting.
- Frequent urination, which is caused by increased pressure from the uterus on the bladder.
- The development of persistent constipation, which indicates compression of the intestines by the enlarged uterus and disruption of its natural peristalsis.
- Periodic bleeding that does not stop on its own.
- Aching pain in the lower abdomen and lower back.
- Increased body temperature, general weakness, which may indicate the addition of an infectious-inflammatory process.
Aching pain in the lower abdomen is one of the symptoms of uterine fibroids.
Such signs indicate an urgent need for surgical intervention and removal of fibroids. The tumor can increase in size, reaching the size of a large grapefruit. Increased pressure on nearby organs causes disruption of their performance, which is fraught with the development of a number of complications.
The abdomen with fibroids in each patient increases at a certain speed. This process is influenced by the following factors:
- The severity of hormonal imbalance - the greater the difference in hormone production, the faster the fibroid grows.
- The presence of chronic and autoimmune diseases.
- Individual characteristics of immunity.
On average, the belly increases by 3-4 cm per year. Only surgery and hormonal therapy can stop this process.
Does the belly grow with uterine fibroids?
The abdomen grows with uterine fibroids, the size of which corresponds to 14–16 weeks of pregnancy. The uterus can compress the small and large intestines, affecting the innervation of the abdominal muscles. As a result, the stomach is “blown out” and does not retract well.
Flatulence, provoked by an enlarged uterus, also affects the tone of the abdominal wall and digestion. In this case, nagging pain occurs in the pubic region, where the ligaments of the organ are attached.
Also, the abdomen can grow with small uterine fibroids. Swelling of the muscle wall is one of the primary factors in abdominal protrusion. In addition to vasospasm, the flow of blood from the internal organs is disrupted, which further provokes discomfort and growth.
Diagnostic methods
The presence of a tumor, its type, dimensions and the further course of the disease can be determined using comprehensive diagnostics, which includes:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs is effective when fibroids are located outside the uterus. Shows the presence of a neoplasm and its echo signs.
- Transvaginal ultrasound allows you to determine the presence of a tumor, its size and the extent of the tumor process.
- MRI and CT scans show the most accurate results, but are expensive procedures.
- Biopsy is a histological examination of the structure of the tumor, which shows the presence or absence of cancer cells.
- Colposcopy is effective when the tumor is located in the cervical area.
- Colonoscopy helps determine the degree of compression of the intestine by a neoplasm.
- Urethroscopy - shows the degree of compression of the bladder by the tumor.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs is one of the methods for diagnosing uterine fibroids.
The most accurate way to assess the condition of the uterus is hysteroscopy. Using special equipment, they penetrate the uterine cavity through the vagina and cervix, assessing the thickness of its walls, dimensions and number of fibroids.
Only with a comprehensive examination can you obtain a complete picture of the disease, on the basis of which a decision is made on the further method of treatment and a prognosis is made.
Clinical manifestations
It depends only on the woman whether she attends preventive examinations and how quickly her disease is detected. Treatment of myomatous nodes in the early stages is carried out conservatively and gives good results. There are a number of clinical manifestations that occur when a myomatous node reaches a diameter of 30 mm and its further growth; they require immediate contact with a gynecologist:
- abdominal enlargement while maintaining total body weight;
- the appearance of lumps in the abdomen;
- intense long menstruation and spotting between them;
- cycle failures;
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach;
- pain symptoms in the abdominal area, radiating to the lower back;
- problems with urination and bowel movements.
Treatment
The only way to stop the growth of the abdomen is to remove the tumor and eliminate all the causes accompanying the development of the tumor process. The effectiveness of therapy is achieved only when it is carried out comprehensively. It is impossible to get rid of fibroids with one pill, so it is important to prepare for a long period of treatment and rehabilitation.
Conservative treatment
Indicated in cases where, for a number of reasons, it is not possible to undergo surgery. Tumor growth-restraining therapy is prescribed, which is based on restoring hormonal levels. The following groups of drugs are used:
- Hormones - the choice of type, dose and duration of treatment depends on the individual characteristics of the body and complex diagnostic data.
- Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs are appropriate when there is an inflammatory process caused by the activity of pathogenic microflora. Often used in the presence of chronic diseases of the genital organs.
- Drugs for symptomatic treatment - in the presence of persistent constipation, laxative drugs are indicated. Pain and discomfort in the abdomen are relieved with complex analgesics and antispasmodics.
Hormonal drugs are also used after surgery. Their task is to normalize the functioning of the endocrine system in order to prevent the re-formation of fibroids.
Chemotherapy drugs are prescribed when a tumor biopsy shows the presence of cancer cells. Chemistry is prescribed in courses, after which the diagnosis is repeated and the result is evaluated.
The effect of medications is supported by physiotherapeutic procedures that can have a beneficial effect on fibroids, slowing down their growth. The most effective of them are:
- Magnetotherapy – helps strengthen local immunity and slow down the tumor process.
- Electrophoresis - suppresses the inflammatory process, normalizes tissue trophism and prevents the active growth of fibroids.
- Mud treatment - mineral mud compresses help not only stop the growth of a tumor, but also reduce its size, triggering natural regeneration mechanisms in the body.
Magnetic therapy is one of the methods for treating uterine fibroids.
A woman’s condition should be monitored monthly, especially if surgery is not possible.
Diet and body weight control are recommended. Physical exercise and calculating your daily calorie intake will help with this. If you have a sedentary lifestyle, it is recommended to do a warm-up every hour, which will reduce the manifestations of congestion in the pelvic organs.
Surgical removal
There are three options for removing fibroids:
- Organ-conserving surgery allows you to preserve the uterus and its functionality. It is carried out using laparoscopy, which is a minimally invasive treatment method. An endoscope and a loop scalpel are inserted through a puncture in the abdominal cavity, with the help of which the tumor is safely excised.
- Resection of part of the uterus - if there are several tumors, they are located in close proximity to each other and grow through all layers of the uterus, then this area is removed using abdominal surgery.
- Resection of the entire uterus - the muscular organ is removed along with the appendages in the case when the tumor completely affects all layers, which is fraught with the development of a number of pathological processes.
After the manipulation, a rehabilitation period begins. The most difficult recovery is after complete resection of the uterus. Complex symptomatic therapy with medications is prescribed. Further quality of life directly depends on how ready a woman is to change her lifestyle and follow all the recommendations of specialists.
How quickly do myomatous nodes grow?
It is worth noting that once myomatous nodes arise, they may not manifest themselves in any way for a long time, remaining small in size. In this case, the belly does not grow with fibroids. Moreover: there are practically no clinical manifestations of the disease that attract the attention of women and force them to consult a gynecologist. However, if hormonal levels are not stabilized and appropriate treatment is not carried out, neoplasms can begin to grow - and this is often quite intense. Over the course of a year, they can increase by several centimeters in diameter. What affects their growth rate?
- the patient's metabolic parameters;
- level of hormonal changes;
- activity of the immune system;
- type of myomatous node: rapid growth occurs with a large number of vessels in it;
- location of the myomatous node: neoplasms located in the muscle layer do not develop as intensively as submucosal ones.
Possible complications and risks
Myoma can reach impressive sizes, which are 3-5 times larger than the dimensions of the uterus itself. The tumor puts increased pressure on nearby tissues and organs, causing disruption of metabolic processes. This in turn provokes the development of a number of complications:
- Intestinal dysfunction (constipation, lack of peristalsis).
- Frequent urination (every 3-5 minutes).
- The appearance of bleeding during physical exertion or mechanical damage to the integrity of the fibroids.
- The development of a number of endocrine diseases associated with hormonal imbalance.
In the absence of timely treatment, the risk of death increases. This is preceded by necrosis of fibroid tissue, which is accompanied by an extensive inflammatory process and sepsis, as well as the degeneration of the tumor into cancer, the metastases of which spread with lymph flow to all tissues and organs. Early diagnosis and annual visits to the doctor will minimize the risks of complications associated with the growth of fibroids.