Treatment of fibroids with hormones is one of the effective methods of conservative therapy. This is due to the identified relationship between a woman’s hormonal background and the appearance of myomatous nodes. Scientists studying this problem have determined that the development of the disease invariably begins against the background of increased levels of estrogen, androgens, progesterones and gonadotropins in the patient’s body. Initially, it was believed that neoplasms appear due to increased estrogen levels and decreased progesterone levels. Treatment of uterine fibroids with hormonal drugs was carried out in accordance with this erroneous conclusion. Recent studies have revealed that tumor development occurs due to an excess of progesterone, and the level of estrogen does not play such an important role. That is why new methods of conservative treatment of uterine fibroids with hormones provide for the normalization of progesterone levels. This allows you to achieve the desired result in the form of reduction of myomatous nodes.
Birth control pills
The use of oral contraceptives is advisable in young patients with myomatous nodes with a diameter of no more than one and a half centimeters, in whom the disease is asymptomatic. Individual selection of the product and its correct administration allows you to achieve a number of positive effects:
- reduction of myomatous nodes;
- normalization of hormonal levels;
- increased libido;
- normalization of the menstrual cycle;
- reduction of pain symptoms.
It is worth noting that such hormonal drugs for fibroids can achieve a temporary effect. After stopping their use, fibroids may begin to develop again. Oral contraceptives are divided into two groups:
- gestagens: “Microlut”, “Lactinet” (extremely rarely used for the treatment of fibroids);
- combined: “Silest”, “Janine” (modern, safe and effective).
Indications for treatment of fibroids with hormonal drugs
In many cases, with the help of hormonal therapy, it is possible to avoid traumatic surgery, but the use of hormones is not always justified. Indications for such treatment for uterine fibroids:
- Small tumor size (up to 2 cm, and the size of the uterus is up to 12 weeks of pregnancy);
- Single nodes or several, but small in size;
- Lack of rapid growth;
- When the tumor is localized in the wall of the uterus (intramural fibroids);
- Subserous fibroids with small size and lack of growth;
- Absence of severe pain;
- For large fibroids as preoperative preparation.
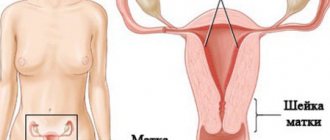
Types of fibroids
Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists
They have an inhibitory effect on the production of gonadotropin, which causes artificial menopause in the patient, which in 50% is accompanied by regression of myomatous nodes. The products in this group include: “Decapeptyl”, “Zoladex”, “Buserelin”, and others. The drugs have side effects such as:
- tides;
- increased sweating;
- depressive states;
- decreased libido.
To minimize such events, doctors use minimal doses of estrogen or intermittent agonist regimens.
Hormonal drugs
In modern medicine, three groups of hormonal drugs are actively used for uterine fibroids:
- Oral contraceptives (COCs);
- Gonadotropin releasing hormone agonists;
- Antiprogestagenic agents.
There are also drugs that are used less frequently and drugs that have since been disproven as effective, but some doctors still prescribe them.
Combined oral contraceptives
This group of drugs in the treatment of uterine fibroids is used only in young patients in the case of nodes up to one and a half centimeters with an asymptomatic course. They cause tumors to stop growing and decrease in size, but the effect of treatment is temporary. If you stop taking the pills, the fibroids may grow back. Read more in the article “Contraceptive pills for uterine fibroids.”
Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists
These drugs, due to hormonal changes (inhibition of gonadotropin), cause women to develop artificial menopause. In this case, in 50% of women, fibroids regress and their growth stops. Drugs in this group include:
- Decapeptyl is triptorelin in solution for injection. Injected daily subcutaneously. For a long course, it is more convenient to use Decapeptyl Depot.
- Decapeptyl-depot is a drug for prolonged injections (effect for 28 days). It is convenient to use for long-term treatment.
- Diferelin – contains triptorelin acetate as an active substance. Available in injection solution with different dosages - 0.1 mg for subcutaneous, 3.75 mg for intramuscular and 11.25 mg for intravenous administration. For fibroids, 0.5 mg is administered subcutaneously for a week, then 0.1 mg for three weeks. The 3.75 mg depot form is used on the third day of the cycle, and then once every 28 days for six months.
- Zoladex - capsules for subcutaneous administration of 3.6 mg and 10.8 mg. One 3.6 mg capsule is designed for 28 days (treatment begins on the 3rd day of the cycle), the course lasts six months.
- Lucrin depot is a leuprorelin preparation in powder form, from which a suspension for injection is prepared. It is packaged in double-chamber syringes or vials. Injections can be made intramuscularly or intravenously once a month at a dosage of 3.75 mg.
- Buserelin is a drug available in various dosage forms, including nasal sprays, implants, and solutions for intramuscular administration. The doctor chooses the best form to use and the required dosage, based on the characteristics of the disease.
Side effects of GnRH agonists
Side effects when taking drugs of this group are due to the phenomenon that they cause, namely the development of pharmacological menopause. In this case, not only are there no periods, but also:
- Tides arise;
- Sweating increases;
- Nervousness increases, mood worsens;
- Libido decreases;
- Calcium metabolism is disrupted, leading to osteoporosis.
To prevent side effects, doctors often prescribe low doses of estrogen or intermittent regimens of GnRH drugs.
Antiprogestogens
The mechanism of action of this group of drugs is based on their ability to connect to progesterone receptors, thereby blocking their work. The effect of progesterone on myomatous cells decreases, and tumor growth stops.
The main antiprogestogen used in the treatment of uterine fibroids is mifepristone. There are many drugs containing it as an active substance:
- Gynepristone;
- Agesta;
- Genale;
- Mifeprex;
- Mifegin;
- Ginestril
- And others.
The action of all these means is the same. The only difference is the price and country of origin.
A distinctive advantage of mifepristone drugs is the lack of progestational activity, that is, they do not affect the level of estrogens and calcium metabolism. But there is also a minus - use is possible only for small fibroids and the effect is also temporary.
Progestins, or “pure” gestagens
These drugs contain pure progesterone, which is why they are called “pure” gestagens, or progestins.
For some time, drugs from this group were the drugs of choice for fibroids, since the causes of their appearance were considered to be an increased level of estrogen, and gestagens reduce their production. But subsequent studies showed that estrogens do not affect tumor growth; elevated levels of progesterone are to blame. Therefore, the use of progestins - progesterone analogues - for uterine fibroid disease is not only not advisable, but also leads to progression of the disease. However, the doctor may prescribe these hormonal drugs for uterine fibroids for other purposes, for example, to treat endometriosis or maintain pregnancy (if there is a threat of miscarriage due to progesterone deficiency).
Preparations from the progestin group:
- Duphaston is a drug based on dydrogesterone, available in tablet form. It is used for uterine fibroids with concomitant endometriosis, threatened miscarriage, ovarian cysts, and as hormone replacement therapy.
- Norkolut is a drug widely used in gynecology for various pathologies. The active substance in it is norethisterone. Available in tablets.
- Depo-Provera is a drug in tablets or suspension for intramuscular administration. Used for contraception, treatment of uterine bleeding, endometriosis, endometrial, kidney, and breast cancer.
- Provera is a medroxyprogesterone tablet. Used for malignant neoplasms and metastases in the endometrium, mammary glands, kidneys and prostate, as well as for the treatment of anorexia and cachexia syndrome.
- Escluton is a synthetic gestagen in tablets, based on linestrenol. Used primarily for hormonal contraception.
- Orgametril is a drug of Linestrenol. It is used for the treatment of menstrual disorders (dysfunctional uterine bleeding, with a decrease or disappearance of menstruation), premenstrual syndrome, endometriosis, benign breast tumors, in complex hormone replacement therapy.
- Primolut-Nor contains norethisterone. Used for the treatment of premenstrual syndrome, infertility, endometriosis, adenomyosis, mastopathy, endometrial cancer, menopause, for the purpose of contraception and cessation of lactation.
Nowadays progesterone-containing tablets for fibroids are used very rarely. In the indications this disease remained only in Norkolut and Primolut-Nora.
Side effects of progestins:
- The ability to cause proliferation of uterine fibroids;
- Increase in body weight;
- Rashes, acne;
- Hirsutism, excessive sweating;
- Edema;
- Deterioration of mood, sleep disturbances;
- Allergic reactions;
- With long-term use, the development of thrombosis and thromboembolism.
17-ethynyl-testosterone derivatives
Derivatives of 17-ethynyl-testosterone are classified as androgens. They bind to estradiol, progesterone and androgen receptors in the ovaries, thereby reducing proliferation in the myometrium. This group of drugs includes:
- Danoval;
- Danol;
- Danodiol;
- Vero-Danazol.
Treatment with hormones from this group is practically not carried out, although regimens for their use have been developed. Most often they are prescribed for concomitant endometriosis. Small nodes may shrink and stop growing during such therapy.
Side effects:
- Androgen-like effects;
- Liver dysfunction, jaundice, abdominal pain, nausea;
- Sleep and emotional disorders;
- Menstrual irregularities, hot flashes, breast tenderness;
- Allergic reactions.
19-norsteroid derivatives
This is a group of steroid hormones that block estrogen and progesterone receptors in the myometrium, and thereby cause involutional changes in the uterus. Products from this series include:
- Gestrinone (Nemestran)
- Dienogest (Visanne)
- Dienogest in combination with estrogens is part of the drugs Zhanin, Qlaira, etc.
They are not used to treat uterine fibroids. They are mainly prescribed to treat endometriosis or reduce the intensity of uterine bleeding. Combination drugs are used as hormonal contraception.
Side effects:
- Menstrual irregularities, hot flashes, formation of ovarian cysts;
- Skin rashes (acne);
- Alopecia;
- Migraines, decreased libido, irritability;
- Abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, etc.
Side effects most often appear in the first 30 days of taking the drug. Then they disappear or decrease.
Androgens
Androgens suppress the production of steroid hormones in the ovaries, causing myometrial atrophy and decreased function of the mammary glands. The most popular drugs from this group:
- Testosterone propionate (Agovirin, Androfort, Malestron, etc.) is available in solution for injection, performed intramuscularly.
- Testenate is an androgenic drug in the form of ampoules with a solution for intramuscular administration (pack of 10 pieces, 1 ml each). Apply 2 times a month. The course consists of 10-15 injections.
- Tetrasterone is a solution for intramuscular injection. Contains esters with different absorption rates, which allows for a prolonged effect - up to 4 weeks after a single administration.
These drugs are more often used in men - as hormone replacement therapy for sexual underdevelopment, sexual dysfunction, etc. These drugs are especially popular among athletes who are gaining muscle mass. In women, they are used to treat menopausal disorders (if there are contraindications for the administration of estrogens), uterine bleeding, during radiation therapy for malignant tumors of the breast and ovaries. Currently, uterine fibroids are practically not used in conservative therapy.
Side effects:
- Hypertrichosis, deepening of the voice, seborrhea, acne and other symptoms of hyperandrogenism in women;
- Pain, itching, hyperemia at the injection site;
- Negative effect on the liver;
- Water and electrolyte imbalances.
Antiandrogens
Antiandrogens block androgen receptors in target tissues (including the myometrium), which reduces the activity of physiological androgens in the body. As a result, hyperplasia and hypertrophy of the myometrium decreases, and fibroids regress. At the same time, the synthesis of androgens remains at the same level. But this is in theory. In practice, antiandrogens have not found widespread use due to their low effectiveness.
- Cyproterone acetate (Androcur) is available in tablets for daily use and ampoules with solution for injection once every 2 weeks. The course of treatment is six months.
- Finasteride (Proscar) – tablets for oral administration once a day for 4-6 months.
Side effects:
- Allergic reactions;
- Weakening libido;
- Effect on the liver (activation of liver enzymes);
- It causes sexual dysfunction in men.
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
After menopause in women, uterine fibroids decrease on their own, as the level of sex hormones decreases.
Hormone replacement therapy, prescribed to relieve the unpleasant symptoms of menopause, is carried out with progestin drugs, and can provoke the growth of tumors. Therefore, in each specific case, the doctor has to evaluate the benefits and risks of HRT.
In recent years, in women with uterine fibroids, drugs from the group of norsteroid derivatives (Cliogest, Trisequence), which have a pronounced antiproliferative effect in the myometrium, and small doses of estrogens have been used for hormone replacement therapy. Thus, it is possible to reduce the severity of menopausal symptoms by controlling the size of the tumor.
In modern medicine, the choice of hormonal drugs is very wide. Therefore, the doctor must determine which drug from which group to prescribe. Each doctor, when choosing a particular hormone, relies not only on theoretical justification and individual characteristics of the course of the disease, but also on his own clinical practical experience. This allows him to carry out hormonal therapy for uterine fibroids with maximum effect.
Antiprogestogens
Drugs in this group are capable of blocking the functioning of progesterone receptors, thereby stopping the production of progesterone, an increased level of which leads to the development of fibroids. So they stop growing. Most often, Mifestron is used for treatment, but modern manufacturers offer many drugs that contain it: Ginestril, Zhenale, Mifegin. "Mifestron" is often prescribed as a hormone after removal of uterine fibroids . Its advantage is that it does not affect the level of estrogen in the blood and does not lead to a malfunction of the mammary glands, cardiovascular system, or endocrine glands.
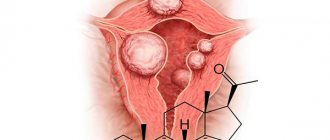
Myomatous nodes and predisposing factors
Myoma is a benign neoplasm that develops from the muscular layer of the uterus. Its growth is associated with hormonal imbalance, which can occur in women of different ages, but is most common during the reproductive and menopausal periods. Experts have identified a number of factors predisposing to the appearance of formations:
- The presence of menstrual dysfunction (late onset of menstruation, pain and profuseness).
- A large number of abortions and surgical interventions in the uterine cavity.
- Late onset of sexual activity and irregular intimate relationships, no history of pregnancy.
- Somatic diseases such as hypertension, obesity, thyroid disorders.
- A sedentary lifestyle combined with emotional overload.
- The presence of fibroids in blood relatives.
- All gynecological diseases accompanied by an increase in estrogen in the blood.
Proper nutrition (diet)
The goal of the diet for uterine endometriosis and fibroids is to slow down the process of estrogen production. The level of the hormone depends on the amount of animal fat and the state of the immune system. It is important to normalize metabolism, since cell mutation leads to the development of a tumor, and metabolism plays an important role here.
You should eat.
- Fiber. Reduces estrogen levels and the risk of developing fibroids by more than 30%. Consume at least 400 g of fruits and vegetables daily.
- Oat and wheat bran. Reduce cholesterol, remove toxins, burn fat.
- Sea fish. Source of protein and fatty acids. Use at least 3 times every 7-10 days.
- Legumes. They contain saponins and fibers that prevent cell division by affecting the process of DNA synthesis. Soy and its derivatives have pronounced antitumor properties.
- Hazelnuts, almonds, walnuts. They reduce cholesterol, increase the level of female hormones, restore cells and connective tissues, and remove toxins.
- Sprouted wheat. Contains a rich complex of amino acids, vitamins, micro- and macroelements, enzymes.
- Green tea. Eliminates the effect of free radicals, contains antioxidants and polyphenols that inhibit the growth of pathological cells.
Follow your diet, it's important
From which it decreases
Only pituitary hormones can have an inhibitory effect on the tumor process. They are called gonadotropic, that is, affecting the sex glands - gonads. These include follicle-stimulating and luteinizing. It has long been known that during menopause, when they are elevated, fibroids resolve. The release of gonadotropins into the blood is provided by the gonadotropic releasing factor of the hypothalamus. Therefore, by introducing its analogue from the outside, tumor growth can be stopped.
The disadvantage of these hormones to reduce formation is that they cannot completely change hormonal levels. Although their effect is long-lasting, after its cessation the tumor completely restores its ability to grow.
In addition, they create an artificial menopause in the body with its manifestations - hot flashes, sweating, vaginal dryness, sexual desire disorders, bone tissue destruction. Because of these effects of hormones, the use of these drugs is advisable only for preoperative preparation.
Symptoms of menopause
Clinical manifestations of myomatous nodes
As mentioned above, the growth of fibroids often occurs asymptomatically, and only after reaching a certain size does the tumor begin to be accompanied by clinical symptoms, which should alert any woman. However, in a small percentage of patients, the neoplasm does not manifest itself in any way and is detected only during an examination by a gynecologist, so it is important not to forget to visit your doctor annually.
The manifestations of fibroids are varied, they depend on the localization of the process, the shape and size of the tumor, and on which organs are compressed by the tumor. The most common symptoms of fibroids:
- uterine bleeding;
- lower abdominal pain;
- a feeling of heaviness and compression in the suprapubic region;
- the presence of a palpable formation in the lower abdomen.
There are three types of fibroid growth:
- submucosal;
- intermuscular;
- subperitoneal.
Depending on the type of growth, complaints may vary.