Unfortunately, when planning a pregnancy, many women encounter problems that interfere with this process. One of them is endometrial hypoplasia. In our article we will tell you what it is and provide methods for treating this deviation.
- Brief description of the disease What is it?
- What is the danger
- Diagnostics
Features of development
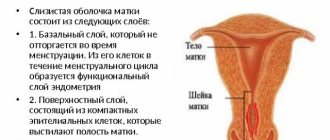
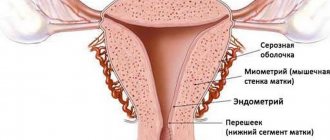
Endometrium - what is it? This term refers to the mucous layer lining the inner uterine surface. This layer has a complex structural structure, which includes the following fragments:
- glandular epithelial layer;
- main substance;
- stroma;
- blood vessels.
The endometrium performs important functions in the female body. It is the mucous uterine layer that is responsible for the attachment of the fertilized egg and the onset of a successful pregnancy. After conception, the endometrial blood vessels provide the fetus with oxygen and essential nutrients.
Proliferation of the endometrium promotes the growth of the vascular bed for normal blood supply to the embryo and the formation of the placenta. During the menstrual cycle, a number of cyclic changes occur in the uterus, divided into the following successive stages:
- The endometrium in the proliferation phase is characterized by intensive growth due to the proliferation of cellular structures through their active division. In the proliferation phase, the endometrium grows, which can be either a completely normal physiological phenomenon, part of the menstrual cycle, or a sign of dangerous pathological processes.
- Secretion phase - At this stage, the endometrial layer is prepared for the menstrual phase.
- Menstrual phase, endometrial desquamation - desquamation, rejection of the overgrown endometrial layer and its removal from the body with menstrual blood.
To adequately assess the cyclic changes of the endometrium and the extent to which its condition corresponds to the norm, it is necessary to take into account factors such as the duration of the menstrual cycle, the stages of proliferation and the secretive period, the presence or absence of dysfunctional uterine bleeding.
Why is the endometrium needed?
The endometrium consists of:
- glandular epithelium;
- integumentary epithelium;
- blood vessels;
- stroma - connective tissue.
This complex system must work clearly and harmoniously for the successful attachment of a fertilized egg and the development of the embryo inside the uterus. After conception, the endometrium grows and develops, forming new blood vessels and glands, which should later become part of the placenta and provide the embryo with oxygen and nutrients.
This is how a healthy endometrium works, having the correct thickness, structure and maturity. If the endometrium develops incorrectly and insufficiently (hypoplasia), pregnancy will not occur or will be terminated in the early stages (spontaneous abortion).
The normal thickness of the endometrium directly depends on the day of the female cycle: at the very beginning, during menstrual bleeding, the old endometrium is completely rejected and excreted from the body along with the blood, and after 3-4 days it begins to grow again, and by 24-28 days its thickness should be more than one centimeter.
Phases of endometrial proliferation
The process of endometrial proliferation includes several successive stages, which corresponds to the concept of normality. The absence of one of the phases or failures in its course may mean the development of a pathological process. The entire period takes two weeks. During this cycle, follicles mature, stimulating the secretion of the hormone estrogen, under the influence of which the endometrial uterine layer grows.
The following stages of the proliferation phase are distinguished:
- Early - lasts from 1 to 7 days of the menstrual cycle. At the early stage of the phase, the uterine mucosa changes. Epithelial cells are present on the endometrium. Blood arteries practically do not twist, and stromal cells have a specific shape that resembles a spindle.
- The middle phase is a short phase that occurs between the 8th and 10th days of the menstrual cycle. The endometrial layer is characterized by the formation of certain cellular structures formed during indirect division.
- The late stage lasts from 11 to 14 days of the cycle. The endometrium is covered with convoluted glands, the epithelium is multilayered, the cell nuclei are round in shape and large in size.
The stages listed above must meet the established norm criteria, and they are also inextricably linked with the secretory phase.
Phases of endometrial secretion
The secretory endometrium is dense and smooth. Secretory transformation of the endometrium begins immediately after completion of the proliferation stage.
Experts distinguish the following stages of secretion of the endometrial layer:
- Early stage - observed from 15 to 18 days of the menstrual cycle. At this stage, secretion is very weakly expressed, the process is just beginning to develop.
- The middle stage of the secretion phase occurs from days 21 to 23 of the cycle. This phase is characterized by increased secretion. A slight suppression of the process is noted only at the end of the stage.
- Late - for the late stage of the secretion phase, suppression of secretory function is typical, which reaches its peak at the onset of menstruation itself, after which the process of reverse development of the endometrial uterine layer begins. The late phase is observed in the period from 24-28 days of the menstrual cycle.
Proliferative diseases
Proliferative endometrial diseases - what does this mean? Typically, the secretory type endometrium poses virtually no threats to a woman’s health. But the mucous uterine layer during the proliferative phase grows intensively under the influence of certain hormones. This condition carries a potential danger in terms of the development of diseases caused by pathological, increased division of cellular structures. The risks of developing tumors, both benign and malignant, increase. Among the main pathologies of the proliferative type, doctors identify the following:
Hyperplasia is a pathological growth of the uterine endometrial layer.
This disease is manifested by such clinical signs as:
- menstrual irregularities,
- uterine bleeding,
- pain syndrome.
With hyperplasia, the reverse development of the endometrium is disrupted, the risks of infertility increase, reproductive dysfunction and anemia develop (against the background of heavy blood loss). The likelihood of malignant degeneration of endometrial tissue and the development of cancer also increases significantly.
Endometritis is an inflammatory process localized in the mucous membrane of the uterine endometrial layer.
This pathology manifests itself:
- uterine bleeding,
- heavy, painful menstruation,
- vaginal discharge of a purulent-bloody nature,
- aching pain localized in the lower abdomen,
- painful intimate contacts.
Endometritis also negatively affects the reproductive functions of the female body, provoking the development of complications such as problems with conception, placental insufficiency, the threat of miscarriages and spontaneous termination of pregnancy in the early stages.
Uterine cancer is one of the most dangerous pathologies developing in the proliferative period of the cycle.
Patients over 50 years of age are most susceptible to this malignant disease. The disease manifests itself as active exophytic growth simultaneously with concomitant infiltrating germination into muscle tissue. The danger of this type of oncology lies in its practically asymptomatic course, especially in the early stages of the pathological process.
Treatment of endometrial hypoplasia
Endometrial hypoplasia is the abnormal development of the mucous layer of the inner lining of the uterus, or rather, the failure of its growth. The result of this type of pathology is very often a diagnosis of infertility.
Why is the endometrium needed?
The endometrium consists of:
- glandular epithelium;
- integumentary epithelium;
- blood vessels;
- stroma - connective tissue.
This complex system must work clearly and harmoniously for the successful attachment of a fertilized egg and the development of the embryo inside the uterus. After conception, the endometrium grows and develops, forming new blood vessels and glands, which should later become part of the placenta and provide the embryo with oxygen and nutrients.
This is how a healthy endometrium works, having the correct thickness, structure and maturity. If the endometrium develops incorrectly and insufficiently (hypoplasia), pregnancy will not occur or will be terminated in the early stages (spontaneous abortion).
The normal thickness of the endometrium directly depends on the day of the female cycle: at the very beginning, during menstrual bleeding, the old endometrium is completely rejected and excreted from the body along with the blood, and after 3-4 days it begins to grow again, and by 24-28 days its thickness should be more than one centimeter.
Causes of hypoplasia
The main factors causing hypoplasia.
- A congenital disorder and deficiency of the hormone estradiol, which is produced during the proper development of follicles. Estradiol is responsible for the maturation of the endometrium and the accumulation of progesterone receptors in it.
- Hormonal disorders and disruptions in a woman’s body.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system (thyroid disease).
- Severe damage to the endometrium as a result of carelessly performed curettage (abortion, cleansing, medical procedure) or other surgical intervention.
- Impaired blood supply to the pelvic area, which can occur as a result of injury, infectious diseases, surgical interventions, or be congenital.
- Endometritis is an inflammatory process in endometrial tissue.
It is important not only to start treatment of endometrial hypoplasia on time, but also to correctly determine the cause of its occurrence, because not only the choice of treatment method, but also the prognosis of recovery largely depends on this.
Symptoms
Most often, hypoplasia (thinned endometrium) does not manifest itself in any way in a woman’s everyday life and is detected only at the stage of pregnancy planning. However, an experienced doctor may suspect a problem based on the following signs:
- late puberty and the onset of the first menstruation later than 15 years;
- lack of full development according to the female type (figure, type of hair growth, facial features);
- cycle failures, short cycle;
- too scanty and painful menstruation;
- inability to have an orgasm – anorgasmia.
Women who managed to become pregnant with a diagnosis of hypoplasia may face:
- threats of abortion or termination of pregnancy;
- severe toxicosis;
- weakness of labor;
- poor dilatation of the cervix during childbirth;
- bleeding during the postpartum period.
Treatment options
Before prescribing therapy, a number of studies are carried out.
- Blood test for hormones: progesterone, follicle-stimulating hormone, luteotropic hormone. The analysis is taken on days 20-22 of the cycle.
- Ultrasound examination of the uterus to measure the exact thickness of the endometrial layer. When hypoplasia is suspected, ultrasound is often performed dynamically, every 4-7 days throughout the cycle, to identify the time of failure and suggest the cause of its occurrence.
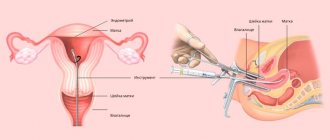
- Hysteroscopy of the uterus (examination of the uterus from the inside using a miniature camera).
- Histological examination of the uterine mucosa - endometrial biopsy.
Treatment of thin endometrium is prescribed depending on the cause of the disease. There are two possible directions that can be applied either separately, simultaneously or sequentially:
- drug treatment;
- surgery;
- physiotherapy.
Drug treatment is most often used for disorders caused by a deficiency or imbalance of sex hormones. It consists of individual selection of hormonal agents. Depending on the results of the examinations, they are prescribed.
- Combined oral contraceptives - normalize hormone levels and gradually restore the proper functioning of the uterine mucosa.
- A course of estradiol injections (“Divigel”). This drug often allows you to quickly increase the required volume of tissue.
- Progesterone preparations (Utrozhestan or Duphaston) help the mucous membrane to “ripen,” which is a necessary condition for conception. This therapy helps and reduces the risk of miscarriage in the future, when hypoplasia is in the initial stages of development.
It is believed that the synthesized progesterone that Duphaston consists of has fewer side effects and is better absorbed, in contrast to the more natural Utrozhestan.
If hypoplasia is caused by chronic inflammatory processes in the pelvic area, the doctor will first treat infectious diseases. In this case, antibacterial drugs, immunomodulators, as well as suppositories that normalize the vaginal microflora can be prescribed in combination.
Surgical treatment consists of stimulating the growth of the mucosa through physical action:
- curettage of the uterine cavity (cleaning) followed by expansion of the endometrium using conservative hormonal therapy;
- stimulating endometrial growth using a hysteroscope is a fairly “young” method of treating hypoplasia, which, according to research, allows you to stimulate growth in the current cycle due to the gentle touch of the device to the walls of the uterus.
Physiotherapy for a diagnosis of hypoplasia is aimed mainly at improving blood supply in the pelvic area and uterus and is used as an auxiliary method:
- gynecological massage;
- laser therapy;
- diathermy;
- ozokerite therapy.
Homeopathy treatment
Homeopathic doctors consider Hormel drops to be one of the best and truly harmless methods for increasing thin endometrium. The drug allows you to normalize hormonal balance and activate estrogen production.
Drops are taken in courses over a long period of time.
Homeopathic medicines do not have a scientifically proven effect, however, many women claim that this particular treatment helped them conceive and bear a healthy child.
Treatment with traditional and non-traditional methods
- Taking herbal decoctions (sage, hogweed, red brush, plantain leaves, peony, raspberry leaves and others).
- Douching with infusions of herbs (celandine).
- Hirudotherapy - treatment with leeches.
- Acupuncture (accupuncture/acupuncture) is the insertion of sterile needles into energetically active points on the human body.
- Clay compresses.
- Saturation of the body with vitamins using vegetable and fruit juices (carrot juice, beet juice, pineapple, grapefruit and tangerine juice).
- Treatment with infusion of honey, Cahors and aloe.
- Taking flaxseed oil.
Endometrial hypoplasia is a complex disease that requires long-term treatment under the supervision of a specialist. The prognosis for recovery largely depends on the degree of neglect of the disease and the reasons for its occurrence.
Never self-diagnose or treat diseases of the reproductive system. Only an experienced doctor and strict adherence to treatment recommendations can lead to a complete recovery.
Source: https://ginekola.ru/ginekologiya/matka/kak-lechitsya-gipoplaziya-ehndometriya.html
Medication
Medicines are used when an imbalance of hormones or sexually transmitted infections that cause inflammation have been detected. The following remedies are used to restore hormonal balance:
- Combined oral contraceptives - necessary to restore endometrial function and hormone levels;
- Homeopathic medicines, for example, Hormel;
- Preparations containing estradiol (Divigel) - promote faster growth of the required amount of tissue;
- Products with progesterone (Duphaston);
Utrozhestan and Duphaston help the mucous membrane to mature, creating good conditions for conception, fertilization and gestation. Hormonal medications reduce the risk of spontaneous miscarriage.
Immunomodulators, antibiotics and agents for restoring vaginal microflora help eliminate pathologies that could cause endometrial hypoplasia. In addition to drug treatment, physiotherapy is prescribed, and in advanced cases, surgery is used.
Physiotherapy is needed to improve blood circulation. For this purpose, gynecological massage, ozokerite therapy, laser exposure, and diathermy are used.
Surgical
The method is used to stimulate the growth of the functional layer. A slight mechanical effect on the uterus is performed using a hysteroscope. In addition, the inner layer can be removed, and then conservative hormonal therapy is prescribed, due to which the endometrium is renewed.
Surgical treatment is prescribed in the following cases:
- Ineffectiveness of drug therapy.
- There are contraindications to taking hormonal drugs.
- Repeated precancerous hypoplasia.
- Atypical hyperplasia during menopause.
Sometimes doctors prescribe cryodestruction, cauterization or laser ablation. During treatment, the pathological area is removed, and a new, healthy endometrium is formed in its place. The treated area is independently removed along with blood clots, the mucous membrane is restored as after menstruation.
Other methods - folk remedies
In the early stages, good results are achieved by non-traditional therapy that improves blood circulation in the pelvis. The most commonly used folk remedies and methods are:
- Mud therapy – clay or mud is applied to the lower abdomen in the form of a compress for 2 hours;
- Medicinal peony tincture - the extract is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:2 and taken 2 ml 3 times a day;
- Hirudotherapy – leeches relieve congestion and activate blood circulation;
- Acupuncture - special needles affect certain points, thereby improving overall health;
- Sage - a decoction is taken orally or used for douching in order to normalize estrogen levels;
- Flaxseed oil – the product is taken on an empty stomach, 1 tbsp;
- Endovasal galvanization - the method activates the pituitary gland area, due to which the cells actively synthesize hormones.
The danger of suppressing proliferation
Inhibition of proliferative processes in the endometrial layer is a fairly common phenomenon, characteristic of the menopause and the decline of ovarian functions.
In patients of reproductive age, this pathology is fraught with the development of hypoplasia and dysmenorrhea. During processes of a hypoplastic nature, thinning of the mucous uterine layer occurs, as a result of which the fertilized egg cannot attach normally to the wall of the uterus, and pregnancy does not occur. The disease develops against the background of hormonal disorders and requires adequate, timely medical care.
Proliferative endometrium - a growing mucous uterine layer, can be a manifestation of the norm or a sign of dangerous pathologies. Proliferation is characteristic of the female body. During menstruation, the endometrial layer is shed, after which it is gradually restored through active cell division.
For patients with reproductive disorders, it is important to take into account the stage of endometrial development when conducting diagnostic examinations, since in different periods the indicators may have significant differences.
The diagnosis of hypoplastic endometrium can only be established based on the results of a histological examination. This pathology is one of the main causes of female infertility.
Briefly about the disease
By the term “hypoplasia,” doctors mean underdevelopment of all tissues of an organ or one of its parts. If a woman is diagnosed with hypoplastic endometrium, what does this mean? Only one thing is that the upper - functional - mucous layer of the uterus is not able to develop to the required thickness.
Its thickness in a healthy woman is 0.30 - 1.30 cm and depends on the period of the menstrual cycle. The maximum is reached on days 24–27, and the minimum on days 3–4.
The problem of hypoplastic endometrium is inherent in women of fertile age. It is this that gynecologists call a fairly common cause of habitual abortions and infertility. This is explained by the special role of the endometrium in a woman’s body.
It is into the thickness of the endometrial layer that the fertilized egg is implanted. For its full attachment, the minimum thickness of the endometrium must reach 6 mm, otherwise the embryo will not be able to implant.
The blastocyst does not have the opportunity to fully penetrate the thinned layer. And even if this happens, the attachment will be fragile: in the further period, the risk of arbitrary termination of pregnancy in the very early stages increases.
In this case, a mixed hypoplastic type of endometrial tissue is most often diagnosed.
The following features are typical for mixed hypoplastic endometrium:
- poor development of the functional layer;
- the basis of the mucosa is represented by indifferent glands;
- areas with secretory changes are identified.
Hypoplastic endometrium is most often detected in the following cases:
- in women of reproductive age with diagnosed ovarian hypofunction;
- in premenopausal patients. A typical symptom is the development of uterine bleeding.
Hypoplastic endometrium is often detected in women during menopause.
Is treatment possible?
In order for the thickness of the endometrium during early pregnancy to correspond to the norm, and in the future to avoid problems during pregnancy, it is necessary to eliminate the problem of thin endometrium even before planning.
Anovulation, amenorrhea, bicornuate uterus, polycystic ovary syndrome, oligospermia, salpingoophoritis, asthenozoospermia, oophoritis, teratozoospermia, endometriosis can lead to infertility.
Diagnostics
To make an accurate diagnosis, certain studies and tests are required. Usually on days 20-33 of the menstrual cycle, the doctor prescribes blood tests for hormones such as:
- luteinizing hormone;
- progesterone;
- follicle stimulating hormone.
Did you know? According to studies and statistics, about 16% of pregnancies do not occur due to the endometrium not matching the cycle phase in which embryo implantation should occur.
They also prescribe a dynamic ultrasound examination - this means that during one menstrual cycle it is necessary to do the procedure several times on the days that the doctor prescribes.
To obtain more accurate information about the condition of the endometrium, a biopsy may be prescribed. This procedure involves microscopic examination of uterine tissue.
Treatment
The main task in the treatment of hypoplasia is to remove the cause that led to the development of the disease. In most cases, the disease develops against the background of hormonal imbalance. In such a situation, therapy is carried out with hormonal medications containing progesterone - Duphaston, Utrozhestan, Luteina.
In some situations, estrogen-containing medications may be prescribed. The approach to prescribing treatment should be individual and take into account the entire medical history.
In addition, the effectiveness of physiotherapeutic procedures (laser therapy, diathermy, ozokerite treatment) was noted.
Possible complications
Unfortunately, it is not always possible to overcome the disease. For example, if the cause of the development of pathology is congenital underdevelopment of the uterus, it is almost impossible to cure hypoplasia. With such a diagnosis, most often the only way out is surrogacy.
If there is a mild degree of hypoplasia, the pathology can be eliminated. Of course, this will take a long time, so the sooner you start treatment, the better.
If you let everything take its course and do not take any measures to combat the disease, most likely this will lead to infertility. In addition to the fact that a woman will not be able to have children, other diseases of the reproductive system may develop.
Causes of pathology
What it is – hypoplastic endometrium – is clear, but what are the reasons for the development of the pathological condition? Doctors tend to believe that provoking factors can be:
- chronic endometritis;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system, accompanied by hormonal imbalances;
- damage to the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, causing disruption of the ovaries;
- damage to the basal layer of the uterine mucosa as a result of surgery or other medical procedures, in particular curettage;
- abnormalities in organ development;
- predisposition to pathology at the genetic level;
- insufficient ovarian function;
- disruption of the processes of gonadotropin synthesis by the hypothalamic-pituitary system;
- sexual infections;
- disruption of the receptors, if the cells of the functional layer of the endometrium stop fully accepting estrogens, then this condition can also cause its thinning.
Most often, hypoplastic endometrium is formed as a result of hormonal disorders. They can occur not only in an adult woman, but also in childhood and adolescence.
Predisposing factors may include:
- deviations that occurred during intrauterine development;
- chronic pathologies of the endocrine and cardiovascular systems;
- active smoking;
- addiction;
- frequent stressful situations;
- state of hypovitaminosis;
- pathological exhaustion of the body - cachexia.
In a nulliparous woman, the longitudinal size of a healthy uterus is 7 cm. If reproductive function has already been achieved, then this figure increases to 8 cm. With the development of endometrial hypoplasia, the size of the organ decreases significantly. The situation is also changing. The cervix becomes longer, resembling a cone.
Infantile uterus and pregnancy
With an embryonic type of uterus, pregnancy can occur only with the use of assisted reproductive technologies, but often it is necessary to resort to surrogacy with the woman’s egg.
The childhood type of hypoplasia makes pregnancy possible, but pregnancy is associated with the risks of premature birth, placental abruption, abnormal position of the fetus in the uterus, and premature rupture of amniotic fluid.
With the teenage type of anomaly in combination with preserved ovarian function, problems with conception and pregnancy usually do not arise. In the early postpartum period, uterine contractions need to be monitored.
Symptoms and signs
There are several signs by which a woman may suspect that she has a hypoplastic endometrium.
Its signs are:
- Late menarche. In girls with a similar deviation, the first menstruation begins late - after turning 16 years old and later;
- Current of menstruation. Deviations from the norm, typical for hypoplastic endometrium, are severe pain, lack of periodicity in bleeding, short menstruation, too scanty/heavy discharge.
Diagnosis and treatment
To diagnose hypoplastic endometrium, the patient is prescribed a comprehensive examination.
The woman will be recommended:
- conducting an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs in certain phases and days of the cycle (on days 2-5, in the second phase);
- hysterosalpingography. The technique is an X-ray examination of the fallopian tubes and uterus;
- clinical blood test;
- determination of the level of hormones of the first phase: LH, FSH, estradiol and the second phase (progesterone);
- examination of vaginal smears for flora;
- PCR for sexually transmitted infections;
- determination of thyroid hormone levels.
To exclude deviations in the functions of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, MRI of the brain and sella turcica is prescribed.
A gynecologist can also detect signs of hypoplastic endometrium during a vaginal examination. These become:
- narrowing and shortening of the vagina;
- reduction of vaginal vaults;
- conical shape of the cervix.
Treatment is prescribed based on the results obtained. It is long-lasting, and the pattern depends on the degree of endometrial thinning.
The main therapeutic method is hormone replacement therapy. When prescribing hormone-containing drugs, both the degree of hypoplasia and the cause that provoked it are taken into account.
In addition to taking medications, a woman may be recommended physical therapy. Completion of the full course is required. Good results are shown by:
- laser therapy;
- ozokerite therapy;
- diathermy.
The main goal of physiotherapy is to improve blood circulation in the tissues of the uterus.
Hormonal drugs for the treatment of endometrial hypoplasia
Today, more and more women suffer from infertility. There are many reasons for this, one of them is endometrial hypoplasia. The pathology is characterized by underdevelopment of the internal mucous membrane of the uterus, which covers the surface of the organ. The endometrium consists of connective tissue, integumentary and glandular epithelium, and blood vessels.
To successfully become pregnant, this complex system must function correctly; any malfunctions do not allow the egg to attach to the uterus and the embryo to develop inside it. A healthy mucosa has normal thickness, maturity and structure.
When the endometrium is too thin, it is unable to hold a fertilized egg. In addition, there is poor development of glandular tissue and blood vessels. This whole process is called hypoplasia of the functional layer.
The concept of hypoplasia
Endometrial hypoplasia is a disease in which there is underdevelopment of the uterine mucosa lining its surface. This layer creates the right environment for the egg to move into the uterine cavity. If the endometrium is too thin or a hyperplastic process is observed, the egg cannot attach normally, and as a result there is no pregnancy.
For successful fertilization, the thickness of the functional layer should be 7-13 mm, it depends on the menstrual cycle. At the very beginning, the old endometrium is excreted along with the blood, and after 3 days a new one develops.
On days 25-28 of the cycle, the normal thickness of the layer is at least 1 cm. Cases have been recorded when, with hypoplasia, the egg was still attached to the uterus, but weakly, which caused miscarriage in the early stages.
Most often, the pathology appears in women of reproductive age, sometimes diagnosed together with ovarian dysfunction. Often the disease develops as a result of a decrease in the level of female hormones estrogen.
The cause of hormonal imbalance may be menopause or improper functioning of the ovaries. In some cases, the endometrium grows excessively, then hyperplasia is diagnosed.
Both types of disorders lead to infertility or miscarriages.
Reasons for development
There are several reasons why uterine endometrial hypoplasia occurs. The main factors in the development of pathology are:
- Hormonal disorders - low estrogen levels are provoked by abnormalities in the functioning of the endocrine system or due to the presence of diseases such as cysts, inflammation, etc.
- Poor circulation - the problem appears due to the formation of fibroids, uterine prolapse, cervical bending, vascular and heart diseases.
- Inflammatory or infectious processes in the pelvis - genital infections and chronic inflammation lead to adhesions and scars, as well as changes in cell structure.
- Abortions and frequent curettage - during the procedure, the basal layer is damaged, which subsequently disrupts the development of the endometrium.
- Heredity - congenital disorders cause improper growth of the functional layer.
Other reasons can provoke the development of pathology, for example, vitamin deficiency, stress, taking alcohol or drugs, smoking, and exhaustion of the body.
How it manifests itself
In ordinary life, the hypoplastic endometrium does not manifest itself in any way; the first symptoms appear during the planning period for fertilization. An experienced doctor can determine diseases by how the girl develops, whether she has periods, etc.
The main symptoms of the pathology are:
- Long absence of pregnancy;
- Cases of miscarriage and miscarriages;
- The presence of adnexitis, endometritis and other diseases of the reproductive system;
- Abortion, curettage;
- The appearance of menstruation after 16 years;
- Irregular, scanty menstruation;
- Dissatisfaction with sex life;
- Insufficient hair growth.
The above signs of endometrial hypoplasia should be taken into account, but not guided by them for independent diagnosis. Only after a complete examination can the doctor confirm or deny the presence of pathology.
How to diagnose
Hypoplasia can be suspected during a routine examination. The doctor notices insufficient pubic hair, changes in the shape of the cervix and external genitalia, and signs of immaturity. To confirm the diagnosis, additional examination is carried out, which includes:
- Ultrasound - allows you to determine the thickness of the functional layer and the degree of development of hypoplasia.
- X-ray examination.
- A blood test that determines hormone levels.
- Hysterosalpingoscopy.
- Biopsy of the uterus.
In some cases, the presence of pathology is determined by the presence of adhesions and folds in the uterus. To determine abnormalities in the functioning of the pituitary gland, an MRI of the brain is performed, a smear is taken for sexually transmitted infections, and a blood test is taken to determine glucose levels. After confirmation of hypoplasia, the doctor individually selects the treatment method.
How to treat hypoplasia
Endometrial hypoplasia and its treatment should be determined only by the attending physician. Therapy is selected depending on the stage of thinning of the mucosa. To eliminate the disease, 3 methods are used - surgical, drug and physical therapy.
Often women try to get rid of pathology on their own using folk remedies. Acupuncture, hirudotherapy and other methods aimed at improving blood circulation are also used.
Let's look at all the ways to enlarge the endometrium in more detail, so that a woman can prepare in advance for what awaits her during the therapy period.
Medicines are used when an imbalance of hormones or sexually transmitted infections that cause inflammation have been detected. The following remedies are used to restore hormonal balance:
- Combined oral contraceptives - necessary to restore endometrial function and hormone levels;
- Homeopathic medicines, for example, Hormel;
- Preparations containing estradiol (Divigel) - promote faster growth of the required amount of tissue;
- Products with progesterone (Duphaston);
Utrozhestan and Duphaston help the mucous membrane to mature, creating good conditions for conception, fertilization and gestation. Hormonal medications reduce the risk of spontaneous miscarriage.
Immunomodulators, antibiotics and agents for restoring vaginal microflora help eliminate pathologies that could cause endometrial hypoplasia. In addition to drug treatment, physiotherapy is prescribed, and in advanced cases, surgery is used.
Physiotherapy is needed to improve blood circulation. For this purpose, gynecological massage, ozokerite therapy, laser exposure, and diathermy are used.
The method is used to stimulate the growth of the functional layer. A slight mechanical effect on the uterus is performed using a hysteroscope. In addition, the inner layer can be removed, and then conservative hormonal therapy is prescribed, due to which the endometrium is renewed.
Surgical treatment is prescribed in the following cases:
- Ineffectiveness of drug therapy.
- There are contraindications to taking hormonal drugs.
- Repeated precancerous hypoplasia.
- Atypical hyperplasia during menopause.
Sometimes doctors prescribe cryodestruction, cauterization or laser ablation. During treatment, the pathological area is removed, and a new, healthy endometrium is formed in its place. The treated area is independently removed along with blood clots, the mucous membrane is restored as after menstruation.
In the early stages, good results are achieved by non-traditional therapy that improves blood circulation in the pelvis. The most commonly used folk remedies and methods are:
- Mud therapy – clay or mud is applied to the lower abdomen in the form of a compress for 2 hours;
- Medicinal peony tincture - the extract is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:2 and taken 2 ml 3 times a day;
- Hirudotherapy – leeches relieve congestion and activate blood circulation;
- Acupuncture - special needles affect certain points, thereby improving overall health;
- Sage - a decoction is taken orally or used for douching in order to normalize estrogen levels;
- Flaxseed oil – the product is taken on an empty stomach, 1 tbsp;
- Endovasal galvanization - the method activates the pituitary gland area, due to which the cells actively synthesize hormones.
Endometrial hypoplasia and pregnancy
Too thin endometrium negatively affects conception, the process of gestation and the birth of a child. A woman can become pregnant, but this is fraught with the following consequences:
- Early miscarriages.
- Severe toxicosis.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- The most difficult birth.
During childbirth, labor becomes sluggish, the cervix dilates poorly, and heavy bleeding occurs after birth. Patients diagnosed with endometrial hypoplasia require special monitoring.
Before planning fertilization, it is advisable to cure endometrial pathology in order to avoid complications and negative consequences. With minor deviations, pregnancy and childbirth can proceed normally, but such cases are rare.
Reviews
A woman diagnosed with endometrial hypoplasia is often interested in the opinions of already cured patients. Below are reviews of girls who successfully got rid of pathology.
My husband and I decided to have a baby, but, unfortunately, nothing worked out. The hospital diagnosed hypoplasia and prescribed treatment. I had a curettage done and was prescribed to take Proginova 6 pieces a day. The new endometrium has already grown, now I am gaining thickness with hormonal drugs. In six months we will try to conceive a child again, I hope everything will work out.
All year I suffered from constant delays. I was never diagnosed, so I went to another clinic. There they prescribed Duphaston, I drank it and the cycle was restored, but then it went wrong again.
Recently they did an ultrasound and found hypoplasia. It turned out that my endometrium is only 5 mm, which is why my periods are irregular. They prescribed curettage, hormonal therapy and physical therapy.
I am undergoing treatment and my cycle is normal again.
Ekaterina, 32 years old
I couldn’t get pregnant, I went to the hospital, and there I found out that I had hypoplasia and atresia of the follicles. I was prescribed Duphaston, I take it regularly. On the fifth day of treatment, my period started, and after 3 months I became pregnant.
Nowadays, many women suffer from infertility, one of the reasons for which is endometrial hypoplasia. This condition is characterized by underdevelopment of the inner lining of the uterus. For a successful pregnancy, a sufficient thickness of this layer is necessary. In cases of endometrial thinning, the fertilized egg cannot implant in the uterus and the embryo does not develop.
General information
Endometrial hypoplasia is an underdevelopment of the inner lining of the uterus. This layer is responsible for the movement and further consolidation of the fertilized egg in the uterus. In cases where the endometrium is too thin, the egg cannot attach and, accordingly, pregnancy does not occur.
Most often, the disease affects women of childbearing age and is sometimes combined with ovarian dysfunction.
Etiological factors
There are several reasons for thin endometrium in the uterus. The main ones include:
Hormonal changes are a reduced concentration of estrogen caused by problems in the endocrine system or the presence of inflammation, cysts, and so on.
- Frequent curettage and abortions: as a result of these manipulations, the basal layer is damaged and, as a result, the formation of the endometrium is disrupted.
- Infections and inflammatory processes in the pelvic area. Chronic inflammation and infections of the genital area are fraught with the appearance of scars and adhesions, as well as changes in the cellular structure.
- Compounded heredity: congenital anomalies cause inadequate formation of the functional layer.
- Impaired blood circulation, which is a consequence of cervical bending, vascular and heart diseases, uterine prolapse and the occurrence of fibroids.
Smoking, exhaustion, stress, drug addiction, vitamin deficiencies, and alcoholism can be provoking factors.
Clinical manifestations
So, the main manifestations of the disease are:
- the occurrence of menstruation after the age of sixteen;
- scanty and irregular menstrual flow;
- prolonged non-occurrence of pregnancy in the absence of contraception;
- weak hair growth;
- history of miscarriages and miscarriages;
- dissatisfaction with sexual relations;
- curettage and abortion;
- the presence of endometritis, adnexitis and other pathologies of the reproductive sphere.
All these signs are characteristic of endometrial hypotrophy, but it is impossible to make a diagnosis on their own based only on them. Only after a complete comprehensive examination can a doctor confirm the presence/absence of this disease.
Diagnostic measures
The doctor can assume the presence of hypoplasia during a routine examination. At the same time, signs of immaturity of the genital area, weak pubic hair, and irregular shape of the cervix and genitals attract attention. In order to confirm the presence of hypoplastic endometrium, additional physical examination methods are prescribed:
- Ultrasound. This helps determine the thickness of the endometrium and determine the degree of its hypoplasia.
- Biopsy.
- X-ray method.
- Hysterosalpingoscopy.
- Study of hormonal profile. Determination of hormone concentrations in the blood.
Sometimes the presence of the disease is determined by the detection of adhesions in the uterus. If it is necessary to confirm abnormalities in the pituitary gland, an MRI is performed.
In addition, for diagnostic purposes, patients are prescribed a blood test to study the concentration of glucose in it, as well as a smear examination for the presence of sexually transmitted infections.
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor individually selects the appropriate therapy.
Source: https://ginekologiya-urologiya.ru/preparaty/gormonalnye-preparaty-dlya-lecheniya-gipoplazii-endometriya
Forecast
If the cause of the disease is underdevelopment of the uterus, then treatment of hypoplastic endometrium becomes lengthy and ineffective. Severe forms of congenital structural anomalies are recognized by medicine as incurable. The likelihood of pregnancy is minimal. If the functions of the ovary are not impaired, then the only available method is surrogacy through IVF.
The result of treatment of the pathology depends on the degree of thinning of the endometrium and the cause that caused it. That is why you need to contact a qualified specialist for help.
Endometrial hypoplasia is a pathological condition characterized by thinning of the functional uterine layer, the main task of which is to create favorable conditions for the attachment of a fertilized egg and its subsequent development.
The hypoplastic endometrium prevents the onset of gestation. And even if implantation has occurred, it will not be reliable enough; the pregnancy can be terminated at any stage.
Preventive measures and forecasts
When diagnosing the fertile type of uterine infantility, the possibility of conception is excluded. In this case, pregnancy is possible only with the use of assisted reproductive technologies (ART). If the generative function of the gonads is preserved, in vitro fertilization (IVF) is used using oocytes ready for insemination.
The course of pregnancy in patients with severe endometrial hypoplasia is associated with a high probability of spontaneous abortion and complicated delivery.
In women with miscarriage syndrome, intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) is performed as part of surrogacy. With minor changes in the structure of the reproductive organ and normal secretion of steroid hormones by the ovaries, the chances of conception and successful pregnancy increase by 45-50%.
Features of hypoplasia
The diagnosis of “hypoplasia” is made when a woman has underdevelopment of the functional layer of the uterus.
Mixed endometrium is quite common, i.e., both healthy and pathologically altered areas of the mucosa are simultaneously present in the organ cavity.
The causes of the pathology are quite numerous. These can be hormonal imbalances, impaired general circulation, inflammatory processes, abortions and diagnostic curettages, which negatively affects the condition of not only the endometrium, but also the cervix.
Hypoplastic endometrium significantly reduces the likelihood of a successful pregnancy, since it is characterized by a significant thinning of the functional uterine layer.
Reasons for development
Endometrial hypoplasia is a condition accompanied by underdevelopment of the functional layer of the uterus, as a result of which a fertilized egg cannot penetrate the surface of the mucosa and begin its development.
It is customary to identify several groups of causes that act as provocateurs of this gynecological pathology. This:
- Hormonal disorders. Most often, women with a similar diagnosis have estrogen deficiency. Its shortage is due to poor functioning of the endocrine system, the presence of cystic formations, and various inflammations.
- Circulatory disorders. Myoma, cervical flexion or uterine prolapse, and pathologies of the cardiovascular system can act as a provoking pathological factor.
- Frequent abortions, diagnostic curettages. During the procedure, it is possible that the basal layer may be injured, which negatively affects the process of growth (thickening) of the endometrium.
- Hereditary predisposition. Existing congenital disorders can cause the development of hypoplasia.
- Inflammation/infection of the pelvic organs. Diseases from the group of STDs acquired during unprotected sex, as well as inflammation that occurs in a chronic form, not only cause the formation of scars and adhesions, but also cause changes in the cells of the uterine mucosa.
Other factors can also cause the disease: lack of vitamins, smoking, physical exhaustion.
Brief description of the disease
Let's look at what this disease is and what its danger is.
What is this?
Endometrial hypoplasia is one of the common pathologies, characterized by underdeveloped inner mucous membrane of the uterus.
Important! During an abortion - curettage, instruments can damage the basal layer of the endometrium, which will lead to hypoplasia, which cannot be treated, and as a result, the inability to bear a child in the future.
This membrane covers its surface and is called the endometrium. It is necessary so that the fertilized egg can be successfully implanted in the uterus.
What is the danger
Quite often, women with thin endometrium are diagnosed with infertility. This is due to the fact that in the presence of a thin layer of the uterine surface, implantation of the embryo becomes difficult. Even if the fertilized egg somehow “gets hooked” on the endometrium, there is a high probability of premature termination of pregnancy.
Endometrial diseases are: endometritis, endometriosis, metroendometritis, adenomyosis.
Symptoms of the disease
Hypoplasia is characterized by the development of the following symptoms:
- late onset of menstruation - discharge begins after the age of 16;
- irregular menstrual flow accompanied by severe pain;
- defective body development;
- anorgasmia – inability to experience orgasm.
As the disease progresses, the woman is diagnosed with algodismenorrhea, a condition accompanied by heavy bleeding against a background of severe pain and poor health.
Sex life also suffers. The woman does not experience sexual arousal or desire.
If the disease develops in girls at an early age, then the child exhibits a clear delay in sexual and physical development. This is expressed as follows:
- the pelvis remains narrow;
- the mammary glands are poorly expressed;
- During puberty, there is insufficient pubic hair growth;
- the external genitalia are underdeveloped.
Hypoplasia can occur in isolation, but sometimes the vaginal mucosa, labia majora and minora, and uterine appendages are involved in the pathological process.
Complications of hypoplasia
Against the background of endometrial hypoplasia, a woman develops various complications.
- Hypoplasia of the uterus. Improper development of the endometrium can cause the formation of another serious pathology - uterine hypoplasia. In this case, the cervical canal lengthens, and the anatomical position of the organ body changes. The combination of such factors almost completely eliminates the possibility of pregnancy.
- Miscarriage. Once a pregnancy has begun, it can be terminated on its own at any stage.
- Violation of the monthly cycle. In addition to not ovulating, some women don't have periods at all.
- Ectopic pregnancy. Against the background of pathology, there is a high probability of egg attachment outside the uterine cavity.
Complications during pregnancy
Endometrial hypoplasia and pregnancy have long been considered incompatible conditions: women have been diagnosed with infertility. An underdeveloped functional layer does not interfere with the process of conception - the fusion of female and male germ cells, but significantly complicates the attachment of the embryo to the walls of the uterus and its further development.
Uterine hypoplasia can occur together with ovarian hypoplasia.
Pregnancy is not excluded, but serious complications may accompany it. This:
- spontaneous abortion in both early and late stages;
- toxicosis;
- ectopic pregnancy.
If pregnancy ends in childbirth, then most often there is poor labor activity: contractions are weak, and the cervix dilates very slowly. During the postpartum period, a woman suffers from heavy bleeding and therefore needs careful medical supervision.
Experts recommend treating the pathology before planning conception, which will prevent the development of serious complications.
Symptoms
Most often, hypoplasia (thinned endometrium) does not manifest itself in any way in a woman’s everyday life and is detected only at the stage of pregnancy planning. However, an experienced doctor may suspect a problem based on the following signs:
- late puberty and the onset of the first menstruation later than 15 years;
- lack of full development according to the female type (figure, type of hair growth, facial features);
- cycle failures, short cycle;
- too scanty and painful menstruation;
- inability to have an orgasm – anorgasmia.
Women who managed to become pregnant with a diagnosis of hypoplasia may face:
- threats of abortion or termination of pregnancy;
- severe toxicosis;
- weakness of labor;
- poor dilatation of the cervix during childbirth;
- bleeding during the postpartum period.
Treatment of pathology
The treatment regimen for the disease is individual in each specific case and is based on the results of laboratory and instrumental studies. The duration of therapy depends on two factors:
- degree of thinning of the functional layer;
- current state of the endometrium.
Modern medicine offers three methods of treating endometrial hypoplasia:
- medicinal;
- physiotherapy;
- surgical
They can be used simultaneously, separately or in parallel.
Medication
Medicines are prescribed if a woman is diagnosed with a hormonal imbalance or genital infections, accompanied by the development of an inflammatory process.
Hormonal drugs are selected individually. Most often used in the therapy process:
- COCs (combined oral contraceptives). They help regulate the level of sex hormones, which over time helps restore the thickness of the endometrium and its functional properties.
- Products containing estradiol. Drugs in this group promote faster growth of the endometrial layer to the thickness required for pregnancy.
- Medicines that contain progesterone. In the vast majority of cases, women are prescribed Duphaston or Utrozhestan. They accelerate the maturation of the mucosa and help in creating the most favorable conditions for the development of a fertilized egg. In addition, the products reduce the likelihood of miscarriage by strengthening the cervix.
Medicines from the homeopathic group, in particular Hormel, may be offered for use.
When identifying diseases of the genital area that can provoke the development of endometrial hyperplasia, the following are used:
- immunomodulators;
- drugs from the group of antibiotics;
- products that restore vaginal microflora.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is part of the general therapy for endometrial hypoplasia. The techniques used help improve blood circulation in the uterus. This:
- laser treatment;
- hirudotherapy;
- diathermy;
- acupuncture;
- ozokerite therapy.
Additionally, therapeutic exercises, adherence to the principles of dietary nutrition, and gynecological massage are prescribed.
Surgical
A surgical technique in the form of light exposure of the uterine mucosa with a hysteroscope is used if taking pills does not give the expected therapeutic result. The procedure helps stimulate the thickening of the functional layer, which guarantees the successful implantation and consolidation of the fertilized egg and the beginning of gestational development.
Indications for surgical treatment of endometrial hypoplasia, in addition to the ineffectiveness of drug therapy, are:
- presence of contraindications to taking hormonal drugs;
- precancerous form of hypoplasia;
- atypical course of the disease, especially during menopause.
In some cases, cryodestruction, laser ablation or cauterization techniques are practiced. During the procedure, the pathological area of the endometrium is removed, which is then replaced with a new layer of healthy cells . After treatment, the removed tissue leaves the uterus on its own, and the mucous membrane is restored.
Other methods, folk remedies
Treatment of endometrial hypoplasia of the uterus is successfully complemented by folk methods. Good results are given by:
- warm clay compresses - the product is diluted with warm water to a consistency convenient for application and applied to the lower abdomen (projection of the uterus) for 2 hours;
- tincture of medicinal peony - the product is diluted with clean water in a ratio of 1:2, the composition must be taken three times a day, 2 ml;
- sage decoction (take 1 tablespoon of dry product per 200 ml of boiling water) - used for oral administration, as well as for vaginal sanitation in order to restore estrogen levels;
- flax oil - the product must be taken in the morning (after waking up) before meals, 1 tbsp. l.
The endovasal galvanization technique shows excellent results. It is based on the activation of the pituitary gland, which ultimately leads to the active synthesis of sex hormones necessary for the body.
Endometrial hypoplasia, diagnosed at an early stage, is well treated. In the case of an advanced or congenital form of the pathology, the likelihood of complete recovery is extremely low. That is why, if suspicious symptoms develop (pain, heavy menstruation, irregular periods, absence of pregnancy), a woman is recommended to seek qualified medical advice and, if necessary, undergo therapy adequate to the condition.
Treatment options
Before prescribing therapy, a number of studies are carried out.
- Blood test for hormones: progesterone, follicle-stimulating hormone, luteotropic hormone. The analysis is taken on days 20-22 of the cycle.
- Ultrasound examination of the uterus to measure the exact thickness of the endometrial layer. When hypoplasia is suspected, ultrasound is often performed dynamically, every 4-7 days throughout the cycle, to identify the time of failure and suggest the cause of its occurrence.
- Hysteroscopy of the uterus (examination of the uterus from the inside using a miniature camera).
- Histological examination of the uterine mucosa - endometrial biopsy.
Treatment of thin endometrium is prescribed depending on the cause of the disease. There are two possible directions that can be applied either separately, simultaneously or sequentially:
- drug treatment;
- surgery;
- physiotherapy.
Drug treatment is most often used for disorders caused by a deficiency or imbalance of sex hormones. It consists of individual selection of hormonal agents. Depending on the results of the examinations, they are prescribed.
- Combined oral contraceptives - normalize hormone levels and gradually restore the proper functioning of the uterine mucosa.
- A course of estradiol injections (“Divigel”). This drug often allows you to quickly increase the required volume of tissue.
- Progesterone preparations (Utrozhestan or Duphaston) help the mucous membrane to “ripen,” which is a necessary condition for conception. This therapy helps and reduces the risk of miscarriage in the future, when hypoplasia is in the initial stages of development.
It is believed that the synthesized progesterone that Duphaston consists of has fewer side effects and is better absorbed, in contrast to the more natural Utrozhestan.
If hypoplasia is caused by chronic inflammatory processes in the pelvic area, the doctor will first treat infectious diseases. In this case, antibacterial drugs, immunomodulators, as well as suppositories that normalize the vaginal microflora can be prescribed in combination.
Surgical treatment consists of stimulating the growth of the mucosa through physical action:
- curettage of the uterine cavity (cleaning) followed by expansion of the endometrium using conservative hormonal therapy;
- stimulating endometrial growth using a hysteroscope is a fairly “young” method of treating hypoplasia, which, according to research, allows you to stimulate growth in the current cycle due to the gentle touch of the device to the walls of the uterus.
Physiotherapy for a diagnosis of hypoplasia is aimed mainly at improving blood supply in the pelvic area and uterus and is used as an auxiliary method:
- gynecological massage;
- laser therapy;
- diathermy;
- ozokerite therapy.