It is mandatory to visit a gynecologist. Doctors recommend doing this regularly about twice a year. This will make it possible to detect possible pathologies in a timely manner. Bloody discharge after examination by a gynecologist is often physiological and does not require treatment. However, during the examination it is also possible to introduce an infectious process. It is also possible that the examination coincided with the day the menstruation began. Often, small amounts of bleeding are normal. The sign indicates that small vessels were damaged during examination. This happens when material is collected. The symptom will disappear on its own throughout the day.
Women should undergo regular examinations by a gynecologist.
What are the dangers of inspections?
Rarely, a woman may find spotting after a gynecological examination. This symptom occurs during sampling and is caused by damage to small vessels. Blood is released in small quantities.
Regular visits to the gynecologist allow you to monitor women's health and start treatment on time if necessary. A careless examination can lead to severe pain in the abdomen and rapid bleeding. This condition requires emergency medical attention.
The gynecologist can use the palpation method. In this case, the localization of organs is palpated and adhesions are detected. This procedure often causes discomfort and pain in the abdominal cavity.
During an examination, a doctor may introduce an infection.
During examination, an infection may occur. The highest risk of such a complication is present in women who are forced to urgently consult a doctor during menstruation. It is at this time that the body is most vulnerable.
What are the causes of spotting after a gynecological examination?
When conducting a gynecological examination, specialized instruments are used. It is thanks to this that it is possible to give an objective assessment of the condition of the reproductive organs.
Instrumental examination often causes mechanical damage to the mucous membranes of the vagina.
The resulting microtraumas lead to the release of blood in small quantities. Usually the symptom manifests itself against the background of the gynecologist’s use of speculums. It is they who accidentally damage the integrity of the walls.
Sometimes a speculum can damage the mucous membrane during examination
Other causes of bleeding are presented in the table.
| Taking a smear | To study the natural microflora, a smear is taken for further diagnosis. To do this, the top layer of the vagina is scraped off. This also leads to damage to small vessels. Bleeding in this case is insignificant. The bleeding stops after 2-4 hours without outside help. |
| Woman's experiences | The woman herself may be to blame for the appearance of bloody secretions. Girls who are very nervous and worried when going to an appointment encounter this symptom. Sudden movements during examination lead to the appearance of the sign. |
| Vascular fragility | Some women have fragile blood vessels from birth. In this case, the symptom will appear after each visit to the gynecologist. |
| Additional procedures | Most often, the examination leads to bloody smear when additional procedures are performed. Discharge may appear, for example, after cauterization of erosion. In this case, prolonged bleeding is likely. The blood will come out over the course of a week. Additionally, there is a pulling sensation in the lower abdomen. |
Bleeding due to the above reasons is not dangerous. The symptom disappears on its own. No additional treatment is required. It is important to monitor for additional signs that arise.
It is also worth noting that sometimes the day of the examination coincides with the date of the onset of menstruation. In this case, the blood that comes out may be menstrual. That is why, first of all, when spotting appears, it is important to remember when the last critical days were.
Sometimes discharge is just the beginning of your period
What to do if cervical erosion bleeds?
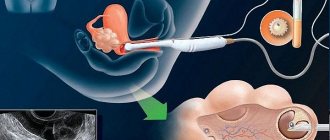
If contact bleeding appears after sex, douching, a gynecological examination, or for no apparent reason, you should contact a gynecologist. The doctor will definitely examine the cervix in the speculum. In this case, the defect on the mucous membrane – erosion – will be clearly visible. To find its cause and determine the type of formation, you need to undergo an examination, which includes:
- Smear for oncocytology,
- Survey smear from the vagina for microflora,
- Screening for STIs (including HPV),
- Colposcopy,
- Biopsy (according to indications),
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (if other causes of erosion are suspected).
Video colposcopy allows the doctor to clearly show the patient the condition of the cervix.
Additionally, blood and urine tests and a hemostasiogram may be prescribed. These examinations are necessary in order to find the cause of erosion (if conventional methods were not enough or there is a suspicion of concomitant pathology).
Further tactics will depend on the results of the examination. The following methods can be used in the treatment of cervical diseases:
- Drug treatment (anti-inflammatory drugs, agents that accelerate regeneration, immunostimulants, antiviral therapy when HPV is detected),
- Destructive treatment – destruction of the pathological focus (radio wave, laser, argon plasma cauterization, DEK, cryodestruction),
- Surgical treatment (conization of the cervix).
The choice of method will depend on the type and size of erosion, as well as the presence of complications. Before using destructive methods of influence, it is necessary to relieve inflammation and cure chronic cervicitis. Treatment of profusely bleeding erosion can be carried out on an emergency basis. If cancer is suspected, consultation with a gynecological oncologist is indicated.
Useful video about which discharge is considered normal and which is not
When the discharge is pathological
The pathological nature of the discharge should not be ruled out. After examination, so-called contact bleeding may appear, which indicates the course of any disease of the reproductive system.
Endometriosis can manifest itself as bloody discharge. The condition is also accompanied by regular nagging pain in the lower abdomen. Symptoms occur during menstruation and after examination. On other days, the pathology may not manifest itself in any way.
Another pathological root cause is the presence of polypous formations. Bleeding after examination will appear if the tumor has affected the cervical canal. The risk of injury during examination increases. The greatest risk of damage is when using mirrors.
The cause may be polyps or neoplasms in the uterus
The root causes include endometrial hyperplasia. The condition is characterized by thickening of the mucous membrane. Even minimal exposure ends in bleeding.
With erosion there is constant bleeding. On examination, the bleeding increases.
Blood occurs as a result of a miscarriage. In the early stages, pregnancy may not manifest itself in any way. Even the doctor may not notice the fertilized egg. Active actions will lead to endometrial detachment and miscarriage as a result.
Another possible cause is malignant neoplasm. For a long period of time the condition does not manifest itself in any way. A small amount of bloody mucus may be released.
Bleeding requires contacting a doctor if accompanied by pathological signs.
If you have any alarming symptoms, be sure to consult a doctor
Discharge in pregnant women
Bloody discharge of varying degrees of intensity may also appear in pregnant women after a routine examination. Why is this happening? Often the cause is a careless inspection. The mucous membrane becomes loose during pregnancy and the slightest mechanical impact can injure it. The volume of discharge is small. The discharge stops on its own within 2-3 days.
Examination of the vagina may provoke bleeding in low placenta previa. This is a pathology in which the placenta is located in the lower parts of the uterus. Presentation can be complete or partial. Women with such a physiological feature require special attention. Vaginal examinations are performed only as a last resort, as this can cause excessive hemorrhage and placental abruption. A careless examination may result in a risk of miscarriage. Bleeding in this case may be accompanied by lethargy, nausea, and dizziness.
Light spotting should not cause much concern if the blood is bright scarlet, the discharge is insignificant and there are no symptoms associated with the disease (itching, burning, swelling, redness, pain, high temperature). But if the next day after the visit to the gynecologist the bleeding has not stopped and discomfort appears, then you should see a doctor to determine the cause.
Can there be discharge after examination during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, the amount of any activity in the vagina decreases. The most careful examinations should occur in the early stages. Inspection is possible no earlier than 4 weeks. After manipulation, there is a risk of minor bleeding.
When carrying a child, a bloody secretion can be caused by:
- damage to mucous membrane tissue;
- discharge of the mucus plug;
- damage to the internal genital organs;
- placental abruption.
Discharge that occurs in late pregnancy should not cause distress. In this case, the secretion should not be accompanied by other pathological symptoms such as itching or burning.
At 40 weeks, a small amount of discharge is usually a harbinger of impending labor. In the second trimester, a symptom may indicate hormonal changes.
What different vaginal discharge may indicate, watch in this video:
When to see a doctor
Some symptoms require immediate medical attention. Do not hesitate to visit a medical facility if:
- heavy bleeding;
- bright red or scarlet shade of discharge;
- discharge accompanied by intense unbearable pain;
- discharges different from the norm;
- increased body temperature;
- dizziness;
- surges in blood pressure;
- severe nausea and vomiting;
- general weakness and malaise;
- unpleasant and pungent odor of discharge.
All of these signs indicate the development of pathologies. Additional consultation with a doctor is needed to identify abnormalities and begin treatment.
What to do if you have discharge
If the discharge is excessive and is accompanied by additional symptoms, then the first thing to do is calm down. Extra worries will definitely not do any good. Scanty daubing is usually the norm. Consulting a doctor will not be superfluous.
Unauthorized taking of medications is prohibited
A symptom that is suspicious requires contacting a doctor.
If the bleeding is profuse and accompanied by a number of signs, call an ambulance. See also: how to stop bleeding at home.
It is strictly forbidden to take any medications at your own discretion. You should not take painkillers until the ambulance arrives. Otherwise, establishing an accurate diagnosis will be difficult.
Other causes of bleeding in women
Erosion is not the only cause of bleeding from the genital tract. Bleeding of varying intensity can also occur with other diseases:
- Uterine fibroids,
- Endometrial hyperplasia,
- Endometriosis,
- Endometrial and cervical polyps,
- Uterine cancer,
- Inflammation of the uterus and appendages,
- Ovarian diseases,
- Incipient miscarriage or regressing pregnancy,
- Ectopic pregnancy.
The cause of discharge outside the menstrual cycle can be various pathologies of the female reproductive system.
Uterine bleeding is a dangerous condition that threatens a woman’s life. Such bleeding can be very heavy, with clots, accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen and impaired consciousness. Self-medication in this case is unacceptable, and you should see a doctor as soon as possible.
Sometimes bleeding from the rectum due to polyps or hemorrhoids is mistaken for vaginal discharge. The exact cause of this condition can only be determined after a complete examination.
Signs indicating the development of concomitant pathology:
- Menstrual irregularities,
- Lower abdominal pain,
- Copious discharge with an unpleasant odor,
- Disorders of urination and defecation,
- Infertility.
These symptoms are often attributed to erosion, but such manifestations are not typical for this pathology. Uncomplicated erosion does not cause pain, does not lead to the appearance of discharge other than bloody contact, and does not affect the menstrual cycle, pregnancy and childbirth. If such symptoms occur, you should look for another cause of the problem.
It is important to know
Even in the presence of erosion, bleeding may be associated with another gynecological pathology, so you cannot do without consulting a doctor.