Modern rhythm, ecology and other various factors have shown a dynamic increase in gynecological diseases among women. 90% of female representatives have at least once encountered one or another illness in their entire lives. Uterine fibroids have become one of the most common diseases in recent years. Statistics show that over the past 5 years the number of patients with this pathology has increased by as much as 7%. Symptoms of the disease are characterized by bleeding and other discharge. They are an integral part of the disease and appear even after the fibroids are removed. What they can be, what is typical for the norm, and what indicates pathology - read in this article.
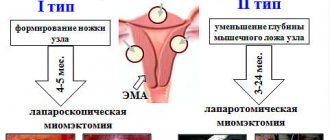
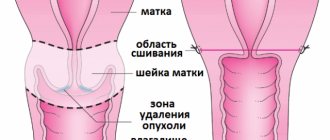
Types of surgeries to remove fibroids
Modern gynecology offers various operations to remove uterine fibroids, each of which has its own indications and characteristics. The main indication for the operation:
- Help if it is impossible to get pregnant - if a woman is already ready for IVF, cleaning from myomatous nodes will help her conceive a child.
- The appearance of heavy uterine bleeding, which resembles menstruation, but can occur on any day of the cycle.
- The size of the myomatous node is more than 11-12 weeks.
- Rapid growth of the tumor, which causes additional risks for the woman.
- Emergency surgery is required if uterine fibroids are accompanied by the development of a disease such as endometriosis.
All types of surgical intervention are selected individually, depending on factors such as the patient’s age, the presence of concomitant chronic diseases, and how quickly the tumor grows.
Among the main types are:
- embolization of blood arteries;
- laparoscopy;
- laparotomy;
- hysterectomy.
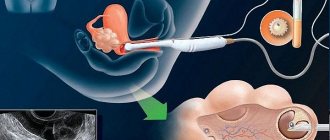
Arterial embolization is a minimally invasive surgical method that is considered one of the most effective. Local anesthesia is used for this procedure. The essence of embolization is that a special microcatheter is inserted into the uterine artery through the internal and femoral iliac arteries.
This method helps to block the blood vessels that feed the myomatous seals, which leads to the cessation of their blood supply. As a result, the nodes begin to gradually dry out and decrease in size.
Laparoscopy is one of the most effective, safe and gentle methods of surgical treatment, through which even the most complex myomatous node is removed. It is carried out using a special device - a laparoscope. The whole procedure lasts no more than half an hour. During this time, 2-4 thin punctures are made in the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity, through which a special instrument with a miniature video camera is inserted, the image from which is displayed on the monitor.
IMPORTANT! In most cases, laparoscopy is used to remove subserous uterine fibroids, that is, those located in the abdominal region. This technique is characterized by a low degree of trauma and the absence of painful sensations. This type of surgical treatment has such a feature as a short recovery and the absence of rough scars and cicatrices.
Laparotomy is a surgical intervention through which both single and multiple myomatous nodes are removed. The surgical procedure involves making an incision on the surface of the abdominal wall, after which the surgeon begins to remove the fibroid tumors. Each patient notes that this is a complex operation in which rehabilitation lasts quite a long time.
Hysterectomy – can be either subtotal or total. The subtotal form of intervention involves amputation of the organ, while the ovary and cervix are preserved.
Total hysterectomy is the complete removal of the affected uterus, adnexa and cervix. It must be remembered that the disadvantage of this method is a serious hormonal imbalance, since hormones begin to be produced in incorrect proportions. Abdominal surgery leaves behind such a result as a wide and deep seam. After some time, a rough scar or scar forms in its place.
Sick leave after removal of uterine fibroids can last up to 29 calendar days. In some cases, this period may decrease or increase depending on the patient’s condition.
What kind of discharge occurs with uterine fibroids?
The nature of discharge from uterine fibroids depends on concomitant conditions complicating the disease. Normally, vaginal mucus does not cause discomfort to a woman. The discharge is clear or milky and has no odor. When the appearance of fibroids is accompanied by colored discharge, we are talking about pathology. Uterine bleeding often accompanies a benign tumor.
If the discharge becomes unusual, you should consult a doctor to perform a differential diagnosis. It will be impossible to get rid of unpleasant symptoms without finding out their cause.
Reasons and factors
The cause of a benign neoplasm in the uterus is hormonal instability. If earlier the pathology was detected mainly in patients in adulthood, now fibroids are detected at the age of 20-30 years. At the same time, not every woman produces unusual mucus from the vagina. If the tumor size is small, there are no disturbing signs at all.
Numerous studies have made it possible to establish the factors on which the formation of myomatous nodes depends. Women at risk include:
- Having a hereditary predisposition (if your grandmother and mother had fibroids).
- Self-administering hormonal medications.
- Those who have not completed their childbearing function before the age of 35 years.
- Those with chronic pathologies of the uterus and other reproductive organs.
- Suffering from blood diseases.
Kinds
With fibroids, there may be blood discharge, which becomes heavy during menstruation, and in the middle of the cycle looks like spotting. The patient may also complain of prolonged periods, which significantly impairs her well-being.
Often, the discharge contains endometrial clots that look lumpy. The absence of menstrual bleeding also sometimes accompanies myomatous nodes. In this case, the discharge is scanty and occurs over a long period of time.
Often this condition is accompanied by changes in the functioning of the ovaries.
Myometrial dysfunction may be accompanied by yellow or greenish discharge, which indicates the presence of an inflammatory process.
If the mucus is white, contains lumps and has a sour smell, then the woman has fibroids and thrush.
Based on the nature of the discharge, separate conditions can be assumed. However, only an examination will help confirm your guesses: a smear, blood test and ultrasound.
Bloody
Small nodular fibroids are often accompanied by bloody discharge that has a liquid consistency. They are protracted and exhausting for the body. The reason for the formation of this symptom is the uneven growth of the mucous layer of the reproductive organ, caused by a hormonal imbalance.
The separation of endometrial cells at the site of the node is uneven. It occurs gradually, so the patient observes prolonged bleeding, which she considers to be unusual menstruation. Menstruation with a benign tumor can be delayed for 2 weeks. At the same time, the interval between bleedings is reduced.
If the separation of the endometrium occurs in the middle of the cycle, small amounts of blood are released. The patient complains that she has spotting after her period. The volume of bloody mucus is insignificant, there are no clots or lumps in it.
Heavy menstrual bleeding in women is the first sign of a benign neoplasm. Small tumor sizes do not cause additional symptoms, but the size of the uterus is already becoming larger. Therefore, during a gynecological examination, this pathology can be assumed on the basis of an increase in the volume of the reproductive organ, taking into account complaints about blood discharge.
Scarlet blood from the vagina can be released when fibroids are located in the cervical cavity.
The prolapse of the node is accompanied by pain and a change in the consistency of vaginal mucus. In addition to prolonged menstruation, the patient complains that she has copious watery discharge during the menstrual cycle.
Brown
In addition to the fact that menstruation becomes more abundant, a woman may be bothered by brown vaginal mucus. This symptom indicates the submucous appearance of the node and its significant size.
The active growth of a benign tumor causes stretching of the myometrium. As a result, the mucous membrane lining the uterine cavity also stretches. The walls of the vessels cannot withstand the stress and rupture.
The blood coagulates and takes on a dark hue.
Myoma, accompanied by brown discharge, usually has an impressive size. At the same time, the patient may experience pain in the lower abdomen.
They intensify during physical activity and sexual contact. After intimacy, the volume of brown smudge increases.
A large benign neoplasm may interfere with future pregnancy.
Brown discharge, caused by damage to the vascular wall, often leads to anemia, deterioration in general health and decreased performance. The patient complains of drowsiness, apathy and chronic fatigue.
Yellow
If menstrual function is not impaired due to fibroids, and the discharge between bleedings has a yellow tint, it is highly likely that we can talk about an infection and an inflammatory process.
The cause of the development of the disease is the proliferation of pathogenic or opportunistic microorganisms. They are able to penetrate the vagina, and from there enter the uterus after unprotected sexual intercourse.
Also, inflammation of the reproductive organs can occur when pathogens spread through the bloodstream or lymph flow.
Bacterial vaginosis is a common companion to fibroids. The disease is characterized by the proliferation of opportunistic microorganisms as a result of a decrease in the body's resistance. The pathology is not considered dangerous and can be easily treated, but in the absence of timely assistance it becomes more complicated.
Vaginitis and endometritis are considered more serious diseases, in which a woman develops yellow discharge from the genital tract. Myoma is not associated with these pathologies, but can be combined with them.
Metritis - inflammation of the myometrium - is a frequent companion to fibroids. The disease can be determined using laboratory diagnostics. With yellow discharge, the patient also has complaints:
- itching of the labia;
- burning in the perineum;
- abdominal pain;
- discomfort during urination and sexual intercourse;
- infertility;
- menstrual irregularities;
- increase in body temperature.
Consistency
When a myomatous node forms, the consistency of vaginal mucus changes. The determining role for this indicator is played by the type of pathological process and the size of the tumor.
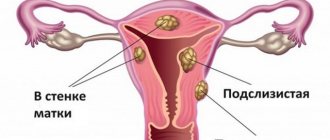
If a subserous myoma with a stalk has formed, then the mucus practically does not change. The neoplasm grows towards the abdominal cavity and does not deform the endometrium. It should be noted that such fibroids have mild symptoms and do not prevent pregnancy.
An intramural tumor distorts the consistency of the discharge, but only slightly. The severity of clinical manifestations is determined by the size of the tumor. The larger the size of the fibroids, the more the consistency changes.
If a submucous tumor has a stalk and grows into the cavity of the reproductive organ, the consistency of the discharge changes greatly. The mucus becomes thicker due to the detached scales of epithelial tissue. In the middle of the menstrual cycle, the discharge is thick, and with the onset of bleeding it thins out.
As fibroids grow, the consistency of vaginal discharge changes more. Clots and blood streaks appear in the mucus. When infected, a woman may notice an admixture of pus.
Important! The discharge does not normalize on its own. Unusual manifestations can only be eliminated by treating fibroids. To carry out therapy, you must contact a gynecologist.
Treatment
If the patient is bothered by white, yellow, brown or red discharge caused by the formation of fibroids, then treatment is prescribed. The regimen is selected individually, taking into account the type of tumor, its size, concomitant diseases of internal organs, the patient’s age and the need for reproductive function in the future.
The use of hormonal drugs can achieve positive results for small fibroids. With the help of medications it is possible to regulate the menstrual cycle. Correcting the functioning of the ovaries can make bleeding less profuse and short-lasting.
If the fibroids are large, the patient is prescribed removal of the tumor-like formation. Depending on the location of the fibroids, a suitable technique is selected.
If the tumor grows inside the myometrium, then the arteries feeding the tumor are “switched off”. The manipulation is minimally invasive and minimally traumatic.
When the node grows into the pelvic cavity, surgical intervention is performed, which involves removing the tumor.
The radical method of treating fibroids is hysterectomy. Surgery is prescribed for large tumors when treatment with alternative methods is not possible.
After surgical treatment of fibroids, a woman experiences slight bleeding. Bloody discharge is a natural reaction of the body. The cavity of the reproductive organ contracts, and damaged vessels cannot be restored instantly.
Therefore, in the first days after surgical treatment, a woman’s discharge is bright red, and by the end of the week it becomes brown. Gradually the ichor brightens, the mucus becomes barely pink.
By 10-14 days after the operation, the discharge ends and becomes normal.
Forecast
For small fibroids the prognosis is favorable. The neoplasm responds well to treatment. Relapse with the appearance of discharge is observed in only 2 patients out of 100. If you refuse therapy, the probability of tumor growth will be 50%. It is safe to say that strange discharge will appear over time.
Vaginal mucus without blood (except during menstruation) is normal. Changes in color, consistency, structure and other organoleptic characteristics are considered a deviation.
At the first signs, you should consult a doctor and undergo an examination. Myoma is a benign tumor that is not prone to malignancy. However, it needs to be monitored.
Growth control allows doctors to prescribe correction in a timely manner and avoid complications.
Source: https://VrachMatki.ru/mioma/vydeleniya
Rehabilitation period
The postoperative period after removal of uterine fibroids can last a varying amount of time, depending on the type of intervention. After surgery, the patient is not recommended to remain on long-term bed rest. The first rise from the bed is recommended 10-12 hours after the operation; you need to start moving slowly around the clinic room. This is an excellent prevention of congestive processes in the pelvic area, as well as an effective way to help prevent further relapse of the disease.
If a woman’s well-being does not deteriorate, she is not bothered by nausea or vomiting, which can be caused by pain relief, they must begin to introduce drinking into the patient’s diet. This could be a few sips of still mineral water, unsweetened tea, compote or fruit drink.
IMPORTANT! The recommendation for a speedy recovery also concerns nutrition - food should be as simple and natural as possible. It is best if it is liquid porridge, lean broth, stewed or boiled vegetables. It is recommended to focus on products rich in iron and protein compounds - lean meats, liver, fish, pomegranates. This will help relieve irritation of the rectum and normalize stool.
After removal of uterine fibroids, it is important to remember a few rules:
- A diet will help you recover faster - you should stop eating baked goods and wheat bread, legumes, white cabbage, and strong black coffee for a while.
- A woman needs to ensure sexual rest by eliminating sex from her life for 8-12 weeks.
- You cannot engage in sports or any type of physical activity, restrictions must be observed for at least 12 weeks.
- Under no circumstances should the uterus be overcooled or overheated; this will help prevent complications after surgery.
Mandatory elements during recovery include regular walking in the fresh air, physiotherapy, and special therapeutic exercises. It is very useful to wear special shapewear or a bandage - this will help muscle tissue recover faster and relieve discomfort.
To restore hormonal levels in the female body, hormonal medications are used. Most often, the use of Diferelin, Janine, as well as the dietary supplement Wobenzym is recommended.
Laparoscopy. Removal of uterine fibroids. Six months later.
diagnosed uterine fibroids six years ago. But there was no talk about the operation then, because... she was small. I took all kinds of hormones periodically, but the fibroids still grew. And when it became larger in size than the uterus, it had to be removed. I’ll say right away that she didn’t cause me any discomfort. I didn’t feel any bleeding or cycle disruptions. But the thought that a foreign organ was living inside me and “threatening” me with all sorts of consequences confirmed my decision to have surgery.
Since the fibroid was located outside the uterus and not inside, it was possible to remove it using the laparoscopic method rather than the strip method.
Preparation for the operation was standard:
– passed a package of tests (the list differs slightly in different clinics)
– after six in the evening do not eat anything
- do a cleansing enema in the evening
– Do not eat or drink in the morning.
Of course, I was afraid of anesthesia. Moreover, this was my first time. I was afraid not to wake up. And when the preparatory process had already begun in the preoperative ward, I was seized with such horror that I wanted to get up and run away from there. But we, women, are strong)) So I pulled myself together, and everything went well. More precisely, like in a fog. I remember how they injected me with anesthesia into my spine. Then I remember breathing through the tube somehow erratically. I thought it was me falling asleep, but it turned out that I was already waking up after the operation))
They moved me to the ward, I was all sleepy and drugged. But the first thought is phew, I’m alive))
Then the hardest part began. The stitches began to hurt. By the way, I had four stitches. It was very painful to turn over and change position. And when it was time to get up, it was a complete nightmare. The stitches pulled and hurt so much that I simply could not straighten up. She walked like a crooked Grandma Yozhka.
I was discharged and home recovery began.
At home I walked half-bent for another week, and probably had two more limps on one leg. But my problem is that I am thin, there is no fat layer. If there was fat there, everything would go much faster.
What also bothered me was severe bloating. This is normal as long as post-operative gas is released. But I flew like a balloon for two weeks.
Possible complications after surgery
If a woman is diagnosed with uterine fibroids, removing the uterus or its affected area can have dangerous consequences for the patient. Surgery for uterine fibroids can cause several complications:
- accidentally injured healthy organ or nerve;
- bloody discharge after curettage;
- adhesions in the uterine cavity;
- the appearance of an inflammatory process affecting the abdominal cavity;
- uterine fibroids threaten a cancerous tumor that affects the breast;
- the stomach remains tense and painful for some time, this period can last up to 14 days;
- a woman may develop pain, burning and other unpleasant sensations during sexual intercourse;
- lack of sexual desire, which has a negative impact on sex life.
IMPORTANT! Uterine fibroids may occur again after removal. In this case, the patient is diagnosed with a relapse of the disease. In most cases, at the initial stage of uterine fibroids, free non-surgical treatment consisting of the use of medications is effective.
Uterine fibroids are a common gynecological disease that can be successfully treated through surgery. The type of operation is selected individually depending on the form and severity of the disease. Compliance with all the rules during the rehabilitation period will help prevent the recurrence of the disease and restore health to the female reproductive system.
Video: about the most important thing - fibroids
About the most important thing: Myoma
Video: 5 dangerous misconceptions about fibroids can make you disabled
5 dangerous misconceptions about fibroids can make you disabled! - Issue 511-12/10/14 - Everything will be fine
How to avoid hysterectomy due to fibroids?
Myoma. Doctor I...
Types of discharge
What types of discharge are there for uterine fibroids? There are three main types of atypical discharge, indicating the possible development of myomatic pathology in the uterus. They differ in the difference in condition and localization of fibroids. Some stages may not manifest themselves in this way:
- Bloody issues. They appear at the very beginning, during the primary development of the tumor. This is due to a hormonal surge occurring due to the foreign substance. The surge provokes partial rejection of the inner lining of the uterus. Blood discharge can be either abundant or scanty. They are cyclical and often increase in intensity around menstruation and decrease at other times, but it is difficult to confuse them with menstruation. The appearance of untimely discharge in which blood is observed should be checked by a gynecologist. There are a number of accompanying symptoms: aching pain in the lower abdomen, pale skin, chills and weakness, painful menstruation and sexual intercourse.
- Brown discharge. Associated with tumor growth, injury to blood vessels and tissues adjacent to the fibroid areas. The thick consistency of the discharge contains blood and dead cells. there is a direct relationship between the size of the tumor and the intensity of the brown color of the vaginal secretion.
- Yellow discharge. They indicate a strong growth of fibroids and affecting the fallopian tubes, where the inflammatory process begins. This is why a yellowish purulent secretion appears in the discharge. Associated symptoms: pain in the lateral lower abdomen, which occurs during sexual intercourse and sudden movements, itching and burning in the external genital area, difficult, painful urination.
Any discharge due to uterine fibroids is atypical, so it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor if you observe something like this. This can be caused by a malignant tumor, but it is better to solve any problem immediately and not let it get worse. After all, in the early stages everything can be resolved without consequences.
In addition to discharge, there are some other characteristic symptoms:
- constipation;
- frequent and painful urination;
- lower abdominal pain;
- bleeding during sexual intercourse;
- miscarriages;
- lower back pain;
- abdominal enlargement similar to pregnancy.