Da!Zachatie
Website about pregnancy, from planning to birth
Popular
Pregnancy by week: week one
Home › Infertility
Is it possible to get pregnant with adhesions and find the reasons for their appearance? Synechiae, also known as adhesions, are compactions of connective tissue that impede the patency and elasticity of the uterine canals. Quite often, for this reason, blockage of the fallopian tubes occurs, making a long-awaited pregnancy impossible.
- 1 Causes of adhesions in the fallopian tubes and symptoms
- 2 Methods for treating adhesions
- 3 Possibility of pregnancy in the presence of adhesions
- 4 Results
Diagnostics
The presence of adhesions in the abdominal cavity can be suspected in patients who have previously undergone pelvic inflammatory diseases, surgical operations on the pelvic and abdominal organs, and in women suffering from endometriosis.
However, only in half of the patients with more than two risk factors for the development of adhesions in the anamnesis, adhesions are detected during laparoscopy (an operation during which small holes are made in the anterior abdominal wall through which an optical device is inserted to examine the cavity and special surgical instruments). A gynecological examination suggests the presence of adhesions in the abdominal cavity with a probability of 75%. Obstruction of the fallopian tubes according to hysterosalpingography (a contrast agent is injected into the uterus, X-ray images are taken) and ultrasound examination with a high degree of certainty indicate the presence of adhesions, but the patency of the fallopian tubes does not exclude the presence of adhesions that seriously impede pregnancy. Conventional ultrasound does not reliably detect the presence of pelvic adhesions. Today, the method of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR, or magnetic resonance imaging, MRI) seems to be very promising in diagnosing the adhesive process. Using this method, images are obtained that reflect the “state of affairs” at different levels.
The main method for diagnosing adhesions is the laparoscopy method. It allows not only to detect the presence of adhesions and assess the severity of the adhesive process, but also to carry out treatment.
There are three stages of the adhesive process according to laparoscopy:
Stage I: adhesions are located around the fallopian tube, ovary or other area, but do not interfere with the capture of the egg;
Stage II: adhesions are located between the fallopian tube and the ovary or between these organs and other structures and can interfere with the capture of the egg;
Stage III: either torsion of the fallopian tube occurs, or it is blocked by adhesions, or a complete blockade of egg capture.
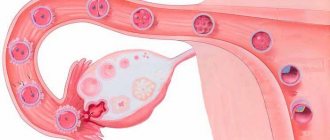
Functioning of healthy pipes
The fallopian tubes are two extensions that emerge from the body of the uterus and lead to each ovary ( paired female reproductive glands located in the pelvic cavity
).
Their function is to ensure that the mature egg (the female gamete of humans, animals, higher plants, as well as many algae and other protists, which are characterized by oogamy
) has the opportunity to leave the ovary to meet the sperm. If there is an adhesive process in the pipe, contraction in the pipe is difficult.
In addition, adhesions can serve as a prerequisite for pathological changes in the surface of the tube, which consists of small eyelashes that capture the egg after its maturation. But the loss of the given opportunity does not make the woman infertile; it only reduces the chances of getting pregnant if there are adhesions in the tubes. It is also worth mentioning that poor patency of the fallopian tube can serve as a prerequisite ( this is a statement intended to substantiate or explain some argument
) the development of an ectopic pregnancy, since the fertilized egg does not reach its destination. In more advanced cases, we can talk about peritoneal infertility, which is caused by the presence of adhesions in the lumen between the tubes and the ovaries.
Treatment of retroflexion
Since the retroflex position of the uterus is not a disease, there is no need to treat it if there are no clinical manifestations. As a rule, this location of the uterus does not affect anything. If treatment is carried out, it is aimed at eliminating the cause of the formation of retroflexion, and not at the bend itself.
Treatment of retroflexion is most often carried out for infertility, pain in the lower abdomen, constipation, dysmenorrhea, inflammatory processes and other causes of its formation.
Curvature of the cervix takes a long time to treat and requires a lot of labor. But even in this case, the treatment process does not always end successfully.
The nature of the treatment directly depends on the reasons for the backward bending of the uterus. Often a set of therapeutic procedures is prescribed by specialists, which includes:
- Massage aimed at improving blood supply to the pelvic tissues, increasing the elasticity of adhesions, reducing pain and raising the uterus;
- Balneotherapy allows you to increase muscle tone and speed up metabolic processes;
- Herbal treatment;
- Taking homeopathic remedies that stimulate muscle endurance and elasticity;
- Taking vitamins;
- Mud treatment;
- A set of therapeutic exercises aimed at training the muscles of the perineum, allowing you to lift the uterus and allow it to assume a normal position.
In cases where retroflexion is the result of inflammatory diseases, anti-inflammatory treatment and restorative therapy are necessary. If the bend of the uterus is caused by an adhesive process, then medications that resolve adhesions are prescribed, and in more complex cases, surgical dissection of the adhesions cannot be avoided. Surgical treatment is also necessary in cases of detection of neoplasms that cause retroflexion.
During the treatment period, it is recommended to follow the following recommendations, which are also a prevention of uterine bending:
- During sleep, take a lying position on your stomach;
- Avoid strenuous physical activity and prolonged standing;
- Do not tolerate the urge to urinate or have bowel movements;
- Maintain a work and rest schedule;
- Treat inflammation of the pelvic organs in a timely manner;
- Choose sports and strength training that do not require strong tension in the pelvic floor muscle tissue;
- Observe strict hygiene of intimate places;
- Eat healthy foods, etc.
Treatment for each case of posterior bending of the uterus is individual and is selected for each individual woman separately.
Therapy methods
Depending on the specifics and neglect of the disease, treatment of the adhesive process is carried out using conservative or surgical methods. In addition to the main treatment, doctors often prescribe a visit to a physiotherapy room and a set of special exercises.
Medicines
To relieve pain caused by stretching and changing the shape of the uterus as the size of the fetus increases, painkillers are used. Excessive contraction of the uterine muscles and increased tone can lead to oxygen starvation of the fetus and the formation of toxins. During pregnancy, Spazmalgon or Baralgin are most often prescribed in the form of injections.
To stop the inflammatory process, which often accompanies the formation of adhesions, anti-inflammatory drugs based on paracetamol, aspirin or ibuprofen are used. The use of any medications while carrying a child must be agreed with your doctor.
When an adhesive process develops against the background of endometriosis, doctors prescribe the use of hormonal drugs such as Duphaston, Progesterone or Utrozhestan. Such medications help stabilize hormonal balance and help relieve pain.
Physiotherapy and massage
Physiotherapy, massage and a special set of exercises will help work out all muscle groups, increase their elasticity, strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, and normalize blood circulation. In addition, such manipulations help restore the anatomically correct position of the internal organs, stretching the existing bridges and preventing their further strengthening and compaction.
The intensity and frequency of exercise, types of procedures can only be prescribed by a doctor. Self-treatment, massage or improper exercise can cause irreversible consequences for the health of the mother and child.
Surgery
Laparoscopy - dissection of adhesions
Surgery is a last resort and is used only when other treatment methods have not brought the desired results. The question is raised about performing laparoscopy to cut the connecting bridges.
How do adhesions affect pregnancy?
Synechiae are connective tissue cords in which blood vessels and nerve endings can pass. They can be of different densities - from woody to mucus-like, of different sizes and connect tissues of the same organ or different ones. It all depends on the cause of their occurrence, the duration of the process and individual predisposition to adhesions.
In the uterine cavity
The reasons for the formation of adhesions may be different. Synechiae in the uterine cavity (synechia) can be of an inflammatory nature or be a consequence of traumatic damage to the endometrium. It is extremely rare that adhesions are congenital.
The likelihood of pregnancy is affected by the location of adhesions, their number, as well as concomitant changes in the endometrium. As a rule, there is thinning and a decrease in vascularization (filling with blood vessels), which leads to impaired implantation of the fertilized egg. Adhesions in the uterine cavity rarely do not affect pregnancy. They may not appear clinically for a long time, and when planning pregnancy, they become a cause of infertility, since:
- close the cervical canal from the inside - the location of synechiae in the cervical canal or above the internal os creates a mechanical obstacle for sperm on the path of their advancement; such localization of synechiae can even significantly complicate the procedure for intrauterine embryo transfer into the uterine cavity during IVF;
- interfere with implantation - numerous synechiae in the body of the uterus interfere with the attachment of the fertilized egg to the endometrium, therefore, even in the case of successful fertilization, the pregnancy is terminated at a short period;
- disrupt the passage of blastocysts from the fallopian tubes - when synechiae are located in the area of the mouths of the fallopian tubes, the fertilized fertilized egg cannot penetrate the uterine cavity, which can ultimately lead to an ectopic pregnancy.
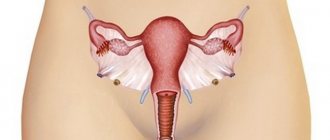
Adhesions around the uterus involving the fallopian tubes. Adhesions (synechia) inside the uterine cavity.
In the pelvis - around the ovaries, fallopian tubes, intestines
In this case, adhesions are a consequence of previous inflammatory processes or surgical interventions. They are formed outside the internal genital organs - the uterus, fallopian tubes, and attract loops of the small and large intestines, the bladder, folds of the peritoneum, and ligaments to them.
One of the most common causes of infertility is tubal factor. In this case, a mechanical obstacle is created on the path of the sperm to the egg - adhesions. They can occur both outside the fallopian tubes and inside.
The most dangerous in this case are the adhesions that surround the fallopian tubes. They tighten their clearance, impairing patency. Also, connective tissue cords can “seal” the fimbrial section of the fallopian tubes, leaving other areas intact. In this case, a mature egg, leaving the ovary, cannot enter the fallopian tube, which leads to infertility.
In this case, there is a high probability of the formation of hydrosalpings - an accumulation of fluid in the fallopian tubes.
Severe adhesions between intestinal loops, ovaries and fallopian tubes can lead to the formation of a single conglomerate of organs, which also disrupts their function and causes severe pain and impossibility of pregnancy.
Adhesions between intestinal loops can cause an abnormal location of the ovaries - away from the fimbrial part of the fallopian tubes, as a result, even normal ovulation does not lead to pregnancy, since the sperm cannot penetrate here.
Thus, adhesions in the pelvis increase the risks of the following complications and diseases:
- infertility;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- hydrosalpings;
- chronic pelvic pain.
And here is more information about planning a pregnancy with one fallopian tube.
Types of disease
Experts divide the disease into genital and extrageital.
In genital endometriosis, the main pathological foci are located in the reproductive organs:
- in the uterus itself;
- in the cervix;
- in the fallopian tubes;
- in the ovaries;
- in the vagina.
This lesion is called adenomyosis, or otherwise internal endometriosis.
If other organs of the abdominal or pelvic region are affected, this is external endometriosis.
With adenomyosis, menstrual bleeding becomes heavier and longer, which can provoke anemic diseases.
In the extragenital course of the disease, the main pathological foci are localized in other organs of the female body. This could be the bladder, intestines, lungs and even more distant organs.
In this case, during menstruation, endometrial cells continue to function and are rejected, which leads to the formation of internal hematomas.
Symptoms
Often the pathology passes without obvious symptoms. The first symptoms may appear several years after the start of the process.
Adhesive disease manifests itself:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lower back;
- menstrual irregularities;
- painful periods;
- unpleasant sensations during physical activity, sexual intercourse;
- intestinal disorders;
- temperature rise.
The pain syndrome during the disease is mild. It manifests itself as a dull pain covering one side. A change in the nature of discomfort indicates complications of the adhesion between the uterus and ovary.
In this case, the pain is severe, because the patency of the fallopian tubes is impaired. As a result, the menstrual cycle is disrupted. The duration of the delay is 2-3 months.
The adhesive process is characterized by a yellowish-green discharge. A bloody “spot” may appear.
Is it possible to get pregnant with hydrosalpinx?
Natural pregnancy with active hydrosalpinx is almost impossible, but there is still a chance, albeit insignificant. Whether a woman becomes pregnant or not will depend on certain factors, including:
- duration of illness. If there was liquid in the tubes for a long time, it could damage the fimbriae that are involved in the process of conception. The longer the patient delays treatment, the less chance of natural conception;
- severity of the disease. If the inflammation is very severe and affects the endometrium and ovaries, it will not be easy to get pregnant;
- localization of adhesions. If hydrosalpinx has affected only one fallopian tube, you can become pregnant naturally with one (healthy, without adhesions or inflammation) fallopian tube, although the chances are naturally lower than with two.
The health status of the sexual partner is also important. Nowadays, a fairly large number of men are susceptible to decreased reproductive efficiency without knowing it.
When planning to conceive, men are advised to have a spermogram.
If you have hydrosalpinx, you can get pregnant, but only if the second fallopian tube is healthy. Some women often refuse treatment for hydrosalpinx, hoping that pregnancy will happen anyway.
Doctors always insist on immediate treatment, because even with hydrosalpinx on one fallopian tube, an ectopic pregnancy can develop. If conception occurs in a damaged fallopian tube, the embryo may begin to develop there without being able to exit into the uterus.
Hydrosalpinx on one side
If only one fallopian tube is affected, no matter which side, doctors recommend starting to plan conception only after final treatment and a period of rehabilitation. If the damaged tube is removed, the chances of conception will increase
Various risks and probabilities of complications during pregnancy characteristic of hydrosalpinx will also be reduced.
Damage to fimbriae
After ovulation, the egg should go straight into the fallopian tube. Fimbriae (special hairs at the entrance to the pipe) should help her with this. They capture the egg and send it into the fallopian tube, where it should meet sperm. If hydrosalpinx develops, these villi can stick together. This leads to their subsequent atrophy.
This is what fimbriae look like. With hydrosalpinx, they can become damaged and never recover.
It is impossible to restore the functionality of the fimbriae. Yes, during laparoscopy you can restore the fallopian tube (do plastic surgery). This will restore patency, but in the absence of properly functioning fimbriae it is impossible to guarantee conception. Doctors believe that if the fimbriae are damaged (glued together), it will not be possible to become pregnant naturally, even with complete patency of the fallopian tubes. With hydrosalpinx on both sides, there is only one way out - IVF after laparoscopy.
Prevention of possible complications
It is worth getting rid of education before conception. With some types of disease, pregnancy cannot occur. In others it can, but during pregnancy it continues to grow, creating risks for the health of the baby and the expectant mother. There is a situation in which the bubble disappears as the fetus grows.
In any case, the doctor should monitor the condition and changes in the formation during pregnancy, and if the condition worsens, prescribe appropriate treatment or offer to remove the cyst surgically.
When planning a child with an ovarian cyst, constant medical supervision is required. Only he will be able to determine its type and predict how the formation will affect conception and gestation.
Symptoms and diagnosis of uterine endometriosis
Enometriosis of the uterus is a progressive disease that can sometimes be asymptomatic, and in this case a woman finds out about it by chance, for example, during a routine examination with a gynecologist.
The main symptoms of uterine endometriosis are as follows:
- Disruption of the menstrual cycle (dysmenorrhea) in varying degrees of severity. Usually the cycle is shortened and irregular.
- Heavy and prolonged menstruation (hyperpolymenorrhea), accompanied by the release of blood clots and pain.
- Premenstrual, intermenstrual and postmenstrual spotting. They occur more often with widespread endometriosis. A woman who experiences frequent blood loss suffers from iron deficiency anemia, her skin turns pale, she quickly gets tired and feels drowsy.
- Pain. Chronically disturbing and significantly worsens during menstruation, especially when the pathology spreads to the uterosacral ligaments. The cause of pain is the development of adhesions in endometriotic heterotopias, secreting fluid with a high content of prostaglandins, stimulating uterine contractions and toning the vessels. Bursting pain in endometriosis during menstruation is the result of menstrual blood entering the endometriotic lesion with its irritation. They are poorly controlled by analgesics and antispasmodics.
- Painful sexual intercourse (dyspareunia), making intimate life difficult or impossible.
- Disorder of urination, its pain (dysuria).
- Infertility, miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy.
Endometriosis is diagnosed with high accuracy during ultrasound, using transvaginal sensors to determine all changes in the structure of the endometrium and prescribing it for the second phase of the menstrual cycle (23-25 days), and hysteroscopy is performed according to indications.
IVF during adhesions
If your doctor has suggested IVF due to advanced adhesions, you should know about some rules that will significantly increase your chances of getting pregnant.
- It is necessary to conduct a study for the presence or absence of a common complication of adhesions - sactosalpinx. This disease is an accumulation of fluid in the tubes, which interferes with the normal movement of the fertilized egg.
- Be sure to visit an immunologist and undergo the necessary diagnostics, which will help you find ways to increase the chances of implantation of the fertilized egg.
IVF is often prescribed due to the fact that the adhesive process was provoked not only by previous operations, but also by an infectious lesion. In such cases, especially if the infection tends to spread quickly, the fallopian tube or tubes will be removed completely. This once again leads the couple to use the in vitro fertilization method.
Is it possible to get pregnant if the tubes are obstructed: brief statistics
Synechia of the female reproductive organ is a serious disease that requires qualified treatment. If treatment is not carried out, then adhesions harm not only the uterus, but can also cause severe pain, infertility and negatively affect neighboring internal organs.
Not all types of adhesions lead to short-term dangerous complications, but if you ignore treatment, complications will certainly make themselves felt. Brief statistics of pregnancy during adhesions:
- 85% of women who underwent surgery on the uterus, including caesarean section, have adhesions. With timely diagnosis and treatment, 50% of women give birth to healthy children.
- 95% of the causes of synechiae formation occur after a long-term inflammatory process that has not previously been treated. Pregnancy with a successful outcome is observed only in 20% of women who took timely measures to eliminate the pathology.
- With chronic diseases of the genitourinary system, only 5% of women with adhesions manage to conceive and give birth to a child.
As can be seen from statistics, the earlier diagnosis and treatment were carried out, the greater the chance of giving birth.
What are adhesions?
The organs of the abdominal cavity and small pelvis (uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, bladder, rectum) are externally covered with a thin shiny membrane - the peritoneum. The smoothness of the peritoneum, combined with a small amount of fluid in the abdominal cavity, ensures good displacement of the intestinal loops, uterus, and fallopian tubes. Therefore, normally, the functioning of the intestines does not interfere with the capture of the egg by the fallopian tube,1 and the growth of the uterus during pregnancy does not interfere with the normal functioning of the intestines and bladder.
1The fallopian tube is a thin, hollow tube extending from the uterus, connecting the uterine cavity to the abdominal cavity. After the egg is released from the ovary into the abdominal cavity, it travels through the fallopian tube into the uterine cavity.
Inflammation of the peritoneum - peritonitis - is a very dangerous disease. And the more dangerous it is, the more space it occupies in the abdominal cavity or small pelvis. But there is a mechanism in the body that limits the spread of peritonitis - the formation of adhesions.
With the development of the inflammatory process in the pelvis, the tissues at the site of inflammation become swollen, and the surface of the peritoneum is covered with a sticky coating containing fibrin (the protein that forms the basis of the blood clot). The fibrin film on the surface of the peritoneum at the site of inflammation glues adjacent surfaces to each other, resulting in a mechanical obstacle to the spread of the inflammatory process. After the end of the acute inflammatory process, adhesions in the form of transparent whitish films can form in places where internal organs stick together. These adhesions are called adhesions. The function of adhesions is to protect the body from the spread of a purulent-inflammatory process throughout the abdominal cavity.
The inflammatory process in the abdominal cavity does not always lead to the formation of adhesions. If treatment is started on time and carried out correctly, the likelihood of formation of adhesions is reduced. Adhesions form when an acute process becomes chronic and the healing process extends over time.
Adhesions can interfere with the normal functioning of internal organs. Impaired mobility of intestinal loops can lead to intestinal obstruction. Adhesions affecting the fallopian tubes, uterus, and ovaries disrupt the entry of the egg into the fallopian tube, the movement of sperm along the fallopian tube, the meeting of sperm and egg, and the advancement of the embryo after conception to the place of attachment in the uterine cavity. In gynecology, adhesions can cause infertility and pelvic pain.
Video on the topic
Researcher, obstetrician-gynecologist, author of books on women's health, founder and director of the International Academy of Healthy Life in Toronto, Canada on how to treat adhesions on the ovaries:
The prognosis will be favorable regarding pregnancy. If the process is not advanced, drug treatment and physiotherapeutic procedures help. The operation is avoided.
Is adhesions in the uterus or fallopian tubes a harbinger of complications for pregnancy or a real chance of remaining infertile? Further in the article we will consider the probability of pregnancy in the presence of synechiae in the uterine cavity or in the tubes.
Causes of pipe obstruction
Depending on the causes, the severity of the pathology and the possibility of its cure are determined. Immediately after determining the factors influencing the obstruction of the fallopian tubes, doctors will be able to assess the chances of a cure rate and the likelihood of a problem-free pregnancy.
Common causes of fallopian tube pathologies:
- Diseases that cause inflammation in the ovaries. Not only clearly manifested inflammatory diseases are possible, but also unnoticed infections of the reproductive system, due to which the mucous membrane constantly becomes inflamed and gradually increases in size. The cause of these phenomena is often chlamydia, fungal infections or cytomegalovirus infection.
- Tuberculosis of the genital organs. Medical reference books indicate that this disease very rarely manifests itself in the reproductive system, but modern people are more susceptible to it. At the moment, there are many patients who have not undergone a full examination and are not receiving treatment, but are still affected by this disease. When an infertile woman has poor immunity and often gets sick, then when diagnosing fallopian tube obstruction, this aspect should also be checked.
- Operations on any organs located in the pelvic areas.
- Endometriosis.
- Abortions (if complications occur).
- The passage of an ectopic pregnancy (before the formation of obstruction of the fallopian tubes).
- Violations of the structure of the fallopian tubes (these are congenital anomalies, sometimes treatment is impossible).
- Tumors (benign and malignant), the formation of polyps on the inner surface of the walls of the fallopian tubes.
Video - obstruction of the fallopian tubes. Why does it occur?
Diagnostics
The faster and more clearly doctors can identify a pathological process or other disorders of the fallopian tubes, the more accurate and correct the treatment will be.
First, it is determined whether a woman ovulates regularly. For this, an ultrasound is performed. Usually its standard form is sufficient, but sometimes transvaginal is prescribed. The woman's sexual partner donates sperm. If all tests are normal for both people, and the woman ovulates regularly, then the problem of the inability to get pregnant most likely lies in obstruction of the fallopian tubes.
Diagnostic tests:
- Hydrosonography (USGSS) is an alternative to transvaginal ultrasound. This study is inaccurate, but absolutely safe (low-traumatic and without radiation). Before the procedure, a safe liquid is injected into the uterine cavity to smooth out its walls. The liquid will then gradually flow out. With normal patency of the tubes, it is first directed into them, and then passes into the abdominal cavity. When the tubes are blocked, the uterus stretches and the contents remain in it. If the obstruction is partial, then the fluid will flow along the correct path, but this process will be slow. It is impossible to see the full picture of the pathology using this method, but its presence can be determined.
- GHA is more informative, but recently it has been used quite rarely. Effective in diagnosing tuberculosis of the fallopian tubes. During this diagnostic method, the doctor injects a radioactive substance into the uterus, and after a few minutes several pictures are taken.
- Laparoscopy is intended not only for accurate diagnosis, but also for minimally traumatic treatment. To conduct the study, a special solution is injected into the uterine area. His movements are monitored using a video camera.
- Transvaginal hydrolaparoscopy involves examining the condition of the fallopian tubes and adjacent genital organs through a small incision in the vagina using a video camera.