Hyperplasia in the mucous membrane of the cervical canal almost always has a benign course. This disease is associated with the use of gestagen-containing medications. The exact definition of the reasons causing the occurrence of endocervical hyperplasia is not fully understood, but progesterone and other drugs that support the active effects of this hormone play an important role in the development of this process.
Cervical hyperplasia
The term " cervical hyperplasia " primarily refers to the epithelium and refers to the proliferation and excess growth of cells.
This process is diagnosed only by histological examination and does not have clear clinical manifestations. Since the cervix is lined by two types of epithelium - stratified squamous and glandular, hyperplasia can be of two types.
Hyperplasia of the cervical epithelium is a compensatory-adaptive reaction related to background precancerous processes.
The risk of tumor transformation in women of reproductive age is quite low. In pre- and menopausal women, any stimulation of cell growth is dangerous, which requires great vigilance.
If morphological signs of atypia are detected, the process should be classified as tumor.
Glandular hyperplasia of the cervix
The most common cause of the development of glandular hyperplasia is dishormonal disorders, in particular, an increase in the level of estrogen in a woman’s body.
Estrogens stimulate synthetic processes and directly control cell proliferation. Hyperplasia of the glandular epithelium most often occurs in young girls, this is due to the development of hormonal levels. During reproductive age, an increase in estrogen levels is usually observed with cysts and hormone-producing ovarian tumors, as well as obesity and hormone replacement therapy. Hyperplastic mucosa forms papillae of various sizes, and sometimes polyps of the cervical canal. The progression of the process can lead to a displacement of the glandular epithelium to the outer part of the cervix with the formation of the so-called papillary pseudo-erosion of the cervix. Active proliferation of the epithelium can lead to the development of microglandular hyperplasia, a condition in which the glandular epithelium begins to form multiple small glands. Sometimes the glands can become distended and form cysts, in which case the term “cystic hyperplasia” is used. Often microglandular hyperplasia of the cervix develops simultaneously with endometrial hyperplasia and uterine cancer, especially in peri- and menopausal women. This is due to the fact that estrogens affect all target organs, including the endometrium. If glandular hyperplasia of the cervix is detected, it is necessary to conduct a full examination of the female genital area. Glandular hyperplasia is diagnosed only by histological examination of the material, i.e. if a cervical biopsy or cervical canal curettage was performed. Treatment should be based on excluding the underlying process, since proliferation of the cervical epithelium is only a consequence. After removing excess mucous membrane, duphaston is usually prescribed to neutralize the estrogen effect. Duphaston is a progestogen-based drug and is an estrogen antagonist.
Squamous hyperplasia
This type of hyperplasia refers to reactive changes in the squamous epithelium that covers the outer part of the cervix. Proliferation of squamous epithelial cells is characterized by thickening of the epithelial layer and expansion of the basal germ layer - basal cell hyperplasia. Among the causes are chronic inflammation and viral damage to the epithelium, especially damage by the human papillomavirus. The epithelium can also thicken in response to any irritation, be it physical, mechanical or chemical. If all provoking factors are excluded, squamous epithelial hyperplasia goes away without a trace. In morphological diagnosis, it is important to differentiate basal cell hyperplasia from impaired maturation of squamous epithelium, as this may be a consequence of dysplasia. Sometimes these processes are combined, since with grade 1 dysplasia there is also an expansion of the growth zone with active proliferation and atypia of cells.
The photo on the left shows normal squamous epithelium, on the right - hyperplasia, characterized by expansion of the basal germ layer, an increase in cell size and density.
Conclusions:
1. Cervical hyperplasia is a benign reactive process, but over a long period of time it can be a source of tumor growth. 2. Increased levels of estrogen and chronic inflammation are the main cause of the development of hyperplastic processes in the cervix. 3. Treatment should be comprehensive and aimed at finding the underlying pathology.
What's happened
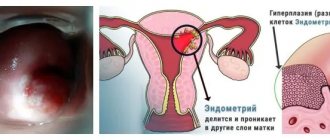
The uterus includes the body and cervix. The inner surface is covered with the mucous membrane, the uterine cavity is covered with the endometrium, and the cervical canal is covered with the endocervix. Hyperplasia is a pathological and abnormal proliferation of the epithelium with thickening of the mucosa.
The disease is benign in nature. At the same time, hypertrophy begins to develop. At the initial stage, pathology can only be detected by microscopic examination.
With glandular hyperplasia, the mucous membrane grows unevenly. Focal formations lead to thickening of the upper layer of the endocervix.
At the same time, cell reproduction is sharply activated, as a result of which various nodes appear. This pathology is similar to cervical erosion, so it is important to make an accurate diagnosis, since cauterization will only worsen the situation.
In the cystic form, the cervical canal is covered with pathogenic cavities. Simple hyperplasia is characterized by a slight increase in the glandular layer and the absence of changes in cell nuclei and blood vessels.
On this topic
Is it possible to cure fibroids?
- Victoria Navrotskaya
- July 9, 2021
If a complex form is diagnosed, this indicates a significant proliferation of the epithelium. The structure of the nuclei is not disturbed, but the cells themselves are modified.
Atypical hyperplasia is considered the most dangerous type of disease. Here, both cellular structures and nuclei change.
The moderate form develops between the simple and complex types of the disease. The peculiarity of this variety is that during development there is most often no clinical picture.
Cytological diagnosis of cervical diseases
Cytological examination of smears from the cervix allows one to assess the condition of the mucous membrane, the presence or absence of signs of pathological processes (reactive, precancerous, tumors). When other laboratory methods identify an infectious agent (human papillomavirus, bacterial and parasitic infections), the cytological method allows one to evaluate the body’s response to the infectious agent, the presence or absence of signs of damage, proliferation, metaplasia or transformation of the epithelium. It is also possible, by examining a smear, to determine the cause of changes in the epithelium (the presence of inflammation with an approximate or confident determination of pathogenic microbiota (microflora), pathological processes associated with hormonal, medicinal, mechanical, radiation effects on the woman’s body and the cervix, conditions fraught with the risk of dysplasia and cervical cancer, and when they develop, establish the correct diagnosis.In this regard, cytological examination is used both for screening (smears from a visually normal cervix) and in the presence of changes in the mucous membrane visible during a gynecological examination.
Prevention
It is very difficult to prevent the occurrence of the disease, since the pathology can affect everyone. But to minimize the risk, it is necessary to undergo a routine gynecological examination every six months. If possible, avoid abortions and use hormonal drugs for contraception.
It is necessary to promptly begin to treat inflammatory processes of the genital organs and other gynecological diseases. Carefully monitor the state of the endocrine system. Regular exercise or other physical activity also helps prevent hyperplasia.
A properly selected diet helps restore reproductive function and helps maintain immunity. Overweight women are advised to reconsider their diet and go on a low-calorie diet. Food should be healthy. The menu should contain foods high in protein, vegetables, fruits, and dairy products. Fatty foods and alcoholic beverages are excluded from the diet. Meals are small and frequent.
Receiving material
Cervical cancer most often develops in the transformation zone, it is preceded by background processes and intraepithelial lesions (epithelial dysplasia), which can be located in small areas, so it is important that material is obtained from the entire surface of the cervix, especially from the junction of squamous and columnar epithelium . The number of altered cells in a smear varies, and if there are few of them, then the likelihood increases that pathological changes may be missed when viewing the specimen. For effective cytological examination it is necessary to consider:
- During preventive examinations, cytological smears should be taken from women, regardless of complaints, the presence or absence of changes in the mucous membrane. Cytological examination should be repeated at least once every three years;
- it is advisable to obtain smears no earlier than on the 5th day of the menstrual cycle and no later than 5 days before the expected start of menstruation;
- you cannot take material within 48 hours after sexual intercourse, use of lubricants, vinegar or Lugol’s solution, tampons or spermicides, douching, insertion of medications, suppositories, creams into the vagina, including creams for performing ultrasound examinations;
- pregnancy is not the best time for screening, as incorrect results are possible, but if you are not sure that the woman will come for examination after childbirth, it is better to take smears;
- for symptoms of acute infection, it is advisable to obtain smears for the purpose of examining and identifying pathological changes in the epithelium, the etiological agent; Cytological control is also necessary after treatment, but not earlier than 2 months. after completing the course.
Treatment
To reduce the impact of provoking factors and the risk of malignancy, hyperplasia is removed. To detect even minor lesions, diagnostic curettage is performed with a hysteroscope.
After this, surgical intervention is carried out in the form of the use of liquid nitrogen or laser. Malignant formations are eliminated along with the uterus.
After curettage, hormonal drugs are prescribed to stimulate endometrial restoration, normalize the menstrual cycle and reproductive function. For this, oral contraceptives are used to compensate for the lack of progesterone and regenerate the uterine mucosa.
Preparation of drugs
Transfer of the sample to a glass slide (traditional smear) should occur quickly, without drying out or losing mucus and cells adhering to the instrument. Be sure to transfer the material to the glass on both sides with a spatula or brush.
If it is intended to prepare a thin-layer preparation using the liquid-based cytology method, the brush head is disconnected from the handle and placed in a container with a stabilizing solution.
Fixation of strokes
performed depending on the intended staining method.
Papanicolaou and hematoxylin-eosin staining are the most informative in assessing changes in the cervical epithelium; any modification of the Romanovsky method is somewhat inferior to these methods, however, with experience, it allows one to correctly assess the nature of the pathological processes in the epithelium and the microflora.
The cellular composition of smears is represented by desquamated cells located on the surface of the epithelial layer. When adequate material is obtained from the surface of the mucous membrane of the cervix and from the cervical canal, the cells of the vaginal portion of the cervix (stratified squamous non-keratinizing epithelium), the junction or transformation zone (cylindrical and, in the presence of squamous metaplasia, metaplastic epithelium) and cells of the cervical canal enter the smear. columnar epithelium). Conventionally, cells of multilayered squamous non-keratinizing epithelium are usually divided into four types: superficial, intermediate, parabasal, basal. The better the epithelium’s ability to mature, the more mature cells appear in the smear. With atrophic changes, less mature cells are located on the surface of the epithelial layer.
Causes and treatment of endocervical hyperplasia
Hyperplasia in the mucous membrane of the cervical canal almost always has a benign course. This disease is associated with the use of gestagen-containing medications.
The exact definition of the reasons causing the occurrence of endocervical hyperplasia is not fully understood, but progesterone and other drugs that support the active effects of this hormone play an important role in the development of this process.
Forms of endocervical hyperplasia
Hyperplasia in the mucous membrane can differ in its structure and its manifestations are usually divided into the following forms:
- glandular, in which thickenings are formed in the mucous membrane of the endocervix, usually of an uneven focal nature. The glands in this case are different in shape and covered with endocervical epithelium. This pathology is most often found in patients with menstrual irregularities and changes in the cervix that occur as a result of inflammatory diseases;
- glandular-cystic, with dilated cystic glands covered with flattened epithelium;
- microglandular form, characterized by the proliferation of small polyps with closely located small glands. Lined with epithelium with mucous secretion. A similar option is possible in young patients with an irregular menstrual cycle;
- a cystic form of hyperplasia of the cervical canal with an increased number of glands lined with squamous epithelium. This condition is facilitated by a violation of the venous blood supply in the cervical canal;
- microglandular form of an atypical nature, with a large number of small structures of the glandular type. Often in the precancerous stage.
Endocervix examination
Most often, women do not experience significant symptoms of cervical endocervical hyperplasia. Only some of them feel slight mucous discharge or scanty blood-streaked discharge that occurs between menstruation and during sexual intercourse.
When visiting a medical facility if there is a suspicion of pathologies developing in the cervix, an examination is carried out using an ultrasound device. There are various diagnostic methods that allow you to carefully examine the lining of the cervix and detect changes that have occurred in it.
The most effective of them are:
- Manual inspection method. As a result of examination on a gynecological chair, a conclusion is made about the possible expansion of the passage of the cervical canal. During an internal visual examination, endocervical hyperplasia is characterized by thickened folding of the mucosa, especially noticeable if it stands out in the lumen of the canal in the form of polyps. The endocervix during this period has an enhanced vascular pattern and its membrane secretes significantly more mucus. Examination of the cervix using mirrors, colposcopy or cytological techniques does not allow obtaining an accurate picture of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal. To confirm internal pathology, the most reliable information can be obtained from a histological examination of scrapings of the mucous membrane of the cervix.
- Ultrasound examination of the endocervix . When examining the female genital organs using ultrasound for other complaints, special attention is paid to the examination of the endocervix. To conduct an examination of young girls who have no experience of sexual activity, an ultrasound examination is carried out without internal penetration into the vagina, but with the help of a special sensor placed on the abdominal wall.
- Endocervical biopsy method , in which scrapings of the endocervix are examined in the laboratory under a microscope.
Treatment methods for endocervical hyperplasia
Treatment of cervical endocervical hyperplasia is carried out with curettage of the inner lining of the cervix.
This operation is performed under hysteroscopic control so as not to ignore possible manifestations of focal hyperplasia formed in the corners of the uterus.
The complexity and extent of the intervention largely depends on the individual physical condition of the patient, her age and the possibility of the desired pregnancy, as well as the severity of the developing pathology and diseases occurring during a given period.
After the operation, hormonal medications are prescribed to restore the functions of the endocervix.
After completing a course of drug treatment, it is necessary to periodically visit a gynecologist to prevent possible relapses. During this period, the patient needs to undergo an ultrasound examination every six months to exclude the possible development of oncological formations of the cervix and its mucous membrane.
There is another method used to treat pathologies of the endocervix membrane - using laser cauterization. This method is used to cauterize focal lesions to remove the pathology.
This method allows you to preserve not only the functions of the endocervix, but also the patient’s ability to subsequent motherhood.
Radical methods using surgery and complete removal of the uterus along with the cervix are used only as a last resort, when the pathological process leaves no chance of recovery and to save the woman’s life.
Preventive measures
An important condition for preventive measures for endocervical hyperplasia comes down to early diagnosis of the disease. This is one of the main measures to prevent the occurrence of malignant cells.
Women going through menopause are at greatest risk of developing into malignant neoplasms.
The following points should also be included in the prevention of endocervical hyperplasia:
- refusal of physiotherapeutic procedures;
- immune system support;
- avoid abortion;
- regular sex life;
- competent use of contraceptives;
- reduce the intake of hormonal drugs;
- maintain normal body weight, especially during menopause;
- allocate time for recreational physical education;
- Do not get carried away with using tampons during menstruation, use them in cases of extreme necessity, as they can injure the vagina.
Disease prognosis
The prognosis of endocervical hyperplasia depends on the causes of the pathological process that has arisen, as well as on the severity of its course. The greatest likelihood of a favorable outcome will be obtained in case of timely diagnosis of the disease and proper treatment.
It must be remembered that neglect of one's health and untreated hyperplasia can not only lead to infertility, but also cause more serious diseases, for example, oncology.
As a rule, it is better to prevent most diseases or treat them at an early stage than to struggle with the severity of its manifestations for a long time.
Functions of the endocervix
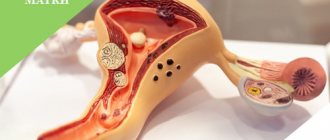
The main role of the process of childbirth in the female body is assigned to the uterus. A new life begins to develop in it and comes out of it into the light. This transition occurs through the cervix, inside which there is a canal called the cervical canal.
The endocervix is the mucous membrane lining the inner surface of the cervical canal.
The lining of the endocervix consists of pores capable of secreting a certain amount of cervical mucus, the nature of which directly depends on the phase of the ongoing menstrual cycle and hormonal levels.
In addition to participating in the process of fetal advancement, during labor, the cervix is also assigned some other functions. The structural features of the canal in the internal structure of the cervix make it possible to carry out the protective function of the endocervix, carried out using a biological barrier.
The formation of a mucous plug in the endocervix, containing substances with bactericidal properties, protects the uterus from the penetration of pathogens of infectious diseases.
The cervix, using an internal canal, connects the uterus to the vagina, which allows for the monthly removal of secretions and sloughed endometrial mucosa from the body of the uterus at the end of the menstrual cycle. In such a situation, the excretory function of the endocervix is performed.
The endocervix can be subject to various pathological changes occurring in the cervical canal. The most common case is the occurrence of neoplasms on the mucous membrane of the endocervix in the form of cysts or polyps.
These tumor processes are easily detected by ultrasound examination.
Depending on the degree of development and pathological condition, a technique is selected, which can be carried out in a conservative or surgical correction way.
Source: https://zaberemenetkak.ru/zhenskoe-besplodie/giperplaziya-endotserviksa-chto-eto-takoe.html
Interpretation of cytological examination results
The most common at present is the Bethesda classification (The Bethesda System), developed in the USA in 1988, to which several changes have been made. The classification was created to more effectively transfer information from the laboratory to clinical doctors and ensure standardization of treatment of diagnosed disorders, as well as follow-up of patients.
The Bethesda classification distinguishes squamous intraepithelial lesions of low grade and high grade (LSIL and HSIL) and invasive cancer. Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions include changes associated with human papillomavirus infection and mild dysplasia (CIN I), high-grade - moderate dysplasia (CIN II), severe dysplasia (CIN III) and intraepithelial carcinoma (cr in situ). This classification also contains indications of specific infectious agents that cause sexually transmitted diseases.
To designate cellular changes that are difficult to differentiate between reactive states and dysplasia, the term ASCUS - atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (squamous epithelial cells with atypia of unclear significance) has been proposed. For a clinician, this term is not very informative, but it directs the doctor to the fact that this patient needs examination and/or dynamic monitoring. The Bethesda classification has now also introduced the term NILM – no intraepithelial lesion or malignancy, which combines normal, benign changes, and reactive changes.
Causes
A possible cause is long-term use of oral contraceptives. In this case, signs of the disease appear only in certain areas.
Often, however, proliferation of the glandular epithelium of the cervix occurs due to various pathologies. The disease is observed in girls who have an inflammatory process in the vaginal tissues, infectious processes in the organs of the reproductive system. The likelihood of developing a pathological process is higher if similar changes occur in the cervical canal; cervicitis of any etiology is observed.
This disease is a response to unwanted microflora: the body seeks to get rid of microorganisms, increasing secretion. To enhance secretion, additional glandular cells have to be formed.
Possible hormonal imbalances.
The level of female sex hormones: estrogen and progesterone is especially important.
Another possible cause is cervical injury. If a woman has suffered a difficult birth, a large number of abortions, traumatic medical procedures, regeneration processes are launched. Against their background, areas of glandular epithelium are formed in the cervical area.
Forecast
The outcome of the disease depends on the type of hyperplasia and the degree of development of the pathological process. A complete cure is possible, or the appearance of a malignant tumor with an unfavorable outcome is possible.
The older the patient, the less favorable the prognosis. The outcome is also negatively affected by the presence of diseases of the endocrine system and metabolic problems. Recurrent disease can lead to complete removal of the uterus. In postmenopausal women, hyperplasia often becomes malignant or leads to precancerous conditions.
Signs and symptoms
Signs of pathology may not appear for a long time. The woman may not notice any changes. Often pathology is discovered only at an appointment with a gynecologist. A woman, however, may notice symptoms of the pathology that caused the proliferation. There may be irregularities in the menstrual cycle, bleeding between menstruation, and there may be no ovulation in the presence of regular menstruation. There may be pain in the vaginal area, copious discharge that has an unusual color or smell.
Signs may be noted during a gynecological examination. A woman has pseudo-erosions, areas on the cervix that differ in color. Glandular epithelial cells are present in those structures where they should not normally be located, and their concentration becomes higher. There may be a local increase in temperature and swelling of the mucous membranes.
Treatment
How to treat hyperplasia of the cylindrical layer of the uterus in women is determined by the attending doctor based on the examination results. In most cases, surgical treatment is performed, as a result of which the overgrown tissue is removed.
Drug treatment is used only in the earliest stages. Hormonal medications are prescribed that help restore the balance of hormones, prevent further tissue growth, and reduce already overgrown uterine cells.
To improve their general condition, patients can use folk remedies, but only with the permission of the treating doctor.
Diagnostics
What is proliferation of glandular epithelium, the girl will be explained in gynecology. If you have any suspicions, you should consult a female doctor: a specialist will ask about the symptoms that have appeared, conduct a visual examination of the patient, and prescribe the necessary tests.
A colposcopy is performed, during which a smear is taken. Atypical areas are detected using magnifying devices and special dyes. The obtained material is necessary for cytological and histological studies.
A biopsy may be required; A tissue sample with suspected pathological changes is taken for analysis. An ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs is required. You will need to submit urine and blood samples for general analysis. They study the hormonal background of a woman. Histological examination will be required; the material is obtained by scraping.
If the doctor suspects the development of oncological processes, you will have to additionally undergo magnetic resonance and computed tomography.
Disease prognosis
The prognosis of endocervical hyperplasia depends on the causes of the pathological process that has arisen, as well as on the severity of its course. The greatest likelihood of a favorable outcome will be obtained in case of timely diagnosis of the disease and proper treatment. It must be remembered that neglect of one's health and untreated hyperplasia can not only lead to infertility, but also cause more serious diseases, for example, oncology. As a rule, it is better to prevent most diseases or treat them at an early stage than to struggle with the severity of its manifestations for a long time.
How to treat
Treatment should be selected by the doctor, taking into account the cause, type of disease, and individual characteristics of the patient. When glandular epithelial cells proliferate, complex therapy is required.
For infections and inflammation, the gynecologist will prescribe antibiotics. The choice of product depends on what microorganisms will be detected when examining a smear for microflora. If there are hormonal changes, you will have to take special medications to normalize the condition. In advanced cases, a woman is fitted with a uterine device, which lasts for 5 years.
Damaged areas of epithelial tissue are subjected to destruction. It is carried out using various methods: exposure to radio waves, lasers, electric current or low temperatures. After this, rapid regeneration is observed, most often the epithelium is restored without pathological changes.
When malignant neoplasms are detected, doctors use surgery. Sometimes the uterus has to be amputated; This means that this woman will no longer be able to give birth.
Urgent medical intervention is most often not required.
However, the pathology cannot be ignored: it will not go away on its own.
To reduce the risk of developing the pathology again, you should strengthen the immune system. To do this, the doctor may prescribe immunostimulants and vitamin complexes. In addition, lifestyle changes and abstinence from promiscuous sexual intercourse will be recommended.
Preventive measures
An important condition for preventive measures for endocervical hyperplasia comes down to early diagnosis of the disease. This is one of the main measures to prevent the occurrence of malignant cells. Women going through menopause are at greatest risk of developing into malignant neoplasms. The following points should also be included in the prevention of endocervical hyperplasia:
- refusal of physiotherapeutic procedures;
- immune system support;
- avoid abortion;
- regular sex life;
competent use of contraceptives;
- reduce the intake of hormonal drugs;
- maintain normal body weight, especially during menopause;
- allocate time for recreational physical education;
- Do not get carried away with using tampons during menstruation, use them in cases of extreme necessity, as they can injure the vagina.
Causes
A possible cause is long-term use of oral contraceptives. In this case, signs of the disease appear only in certain areas.
Often, however, proliferation of the glandular epithelium of the cervix occurs due to various pathologies. The disease is observed in girls who have an inflammatory process in the vaginal tissues, infectious processes in the organs of the reproductive system. The likelihood of developing a pathological process is higher if similar changes occur in the cervical canal; cervicitis of any etiology is observed.
This disease is a response to unwanted microflora: the body seeks to get rid of microorganisms, increasing secretion. To enhance secretion, additional glandular cells have to be formed.
Possible hormonal imbalances.
The level of female sex hormones: estrogen and progesterone is especially important.
Another possible cause is cervical injury. If a woman has suffered a difficult birth, a large number of abortions, traumatic medical procedures, regeneration processes are launched. Against their background, areas of glandular epithelium are formed in the cervical area.
Functions of the endocervix
The main role of the process of childbirth in the female body is assigned to the uterus. A new life begins to develop in it and comes out of it into the light. This transition occurs through the cervix, inside which there is a canal called the cervical canal. The endocervix is the mucous membrane lining the inner surface of the cervical canal. The lining of the endocervix consists of pores capable of secreting a certain amount of cervical mucus, the nature of which directly depends on the phase of the ongoing menstrual cycle and hormonal levels.
In addition to participating in the process of fetal advancement, during labor, the cervix is also assigned some other functions. The structural features of the canal in the internal structure of the cervix make it possible to carry out the protective function of the endocervix, carried out using a biological barrier. The formation of a mucous plug in the endocervix, containing substances with bactericidal properties, protects the uterus from the penetration of pathogens of infectious diseases. The cervix, using an internal canal, connects the uterus to the vagina, which allows for the monthly removal of secretions and sloughed endometrial mucosa from the body of the uterus at the end of the menstrual cycle. In such a situation, the excretory function of the endocervix is performed.
The endocervix can be subject to various pathological changes occurring in the cervical canal. The most common case is the occurrence of neoplasms on the mucous membrane of the endocervix in the form of cysts or polyps. These tumor processes are easily detected by ultrasound examination. Depending on the degree of development and pathological condition, a technique is selected, which can be carried out in a conservative or surgical correction way.
- 4 minutes to read
Hyperplasia is considered an excessive increase in cells of tissue structures. Damage to this pathology of the female genital organs is most common. The cervix and the uterus itself especially suffer from the growth. If left untreated for a long time, the disease can lead to dire consequences.
Content
Signs and symptoms
Signs of pathology may not appear for a long time. The woman may not notice any changes. Often pathology is discovered only at an appointment with a gynecologist. A woman, however, may notice symptoms of the pathology that caused the proliferation. There may be irregularities in the menstrual cycle, bleeding between menstruation, and there may be no ovulation in the presence of regular menstruation. There may be pain in the vaginal area, copious discharge that has an unusual color or smell.
Signs may be noted during a gynecological examination. A woman has pseudo-erosions, areas on the cervix that differ in color. Glandular epithelial cells are present in those structures where they should not normally be located, and their concentration becomes higher. There may be a local increase in temperature and swelling of the mucous membranes.
Prevention measures
To avoid the development of hyperplasia, regular preventive measures are necessary. To do this, a woman needs:
- promptly treat identified diseases that can provoke the formation of cervical hyperplasia: ovarian tumors, pathologies of the liver, gallbladder, pelvic inflammation;
- go to the gynecological office regularly: the frequency of visits is determined only by the attending physician, most often it is once a year;
- regulate your own body weight, since obesity is a risk factor that provokes the formation of pathology.
In case of menstrual irregularities, it is necessary to study the hormonal levels, because changes in hormone levels can provoke the active development of the disease. When diagnosing pathology and concomitant diseases, the doctor will select an individual treatment regimen, an optimal set of drugs that will help to quickly cope with the disease and prevent complications from occurring.
Diagnostics
What is proliferation of glandular epithelium, the girl will be explained in gynecology. If you have any suspicions, you should consult a female doctor: a specialist will ask about the symptoms that have appeared, conduct a visual examination of the patient, and prescribe the necessary tests.
A colposcopy is performed, during which a smear is taken. Atypical areas are detected using magnifying devices and special dyes. The obtained material is necessary for cytological and histological studies.
A biopsy may be required; A tissue sample with suspected pathological changes is taken for analysis. An ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs is required. You will need to submit urine and blood samples for general analysis. They study the hormonal background of a woman. Histological examination will be required; the material is obtained by scraping.
If the doctor suspects the development of oncological processes, you will have to additionally undergo magnetic resonance and computed tomography.
How to treat
Treatment should be selected by the doctor, taking into account the cause, type of disease, and individual characteristics of the patient. When glandular epithelial cells proliferate, complex therapy is required.
For infections and inflammation, the gynecologist will prescribe antibiotics. The choice of product depends on what microorganisms will be detected when examining a smear for microflora. If there are hormonal changes, you will have to take special medications to normalize the condition. In advanced cases, a woman is fitted with a uterine device, which lasts for 5 years.
Damaged areas of epithelial tissue are subjected to destruction. It is carried out using various methods: exposure to radio waves, lasers, electric current or low temperatures. After this, rapid regeneration is observed, most often the epithelium is restored without pathological changes.
When malignant neoplasms are detected, doctors use surgery. Sometimes the uterus has to be amputated; This means that this woman will no longer be able to give birth.
Urgent medical intervention is most often not required.
However, the pathology cannot be ignored: it will not go away on its own.
To reduce the risk of developing the pathology again, you should strengthen the immune system. To do this, the doctor may prescribe immunostimulants and vitamin complexes. In addition, lifestyle changes and abstinence from promiscuous sexual intercourse will be recommended.
Removal of pathologies
To minimize the influence of risk factors and the likelihood of pathology degenerating into cancer, some doctors recommend removing it. Almost always, a specialist uses diagnostic curettage, which is performed using a hysteroscope. This procedure allows you to detect even the slightest foci of disease.
Then the doctor prescribes surgical treatment. This takes into account the woman’s age, desire to have a child, and the presence of concomitant pathologies. Laser and liquid nitrogen treatment may be prescribed for treatment. If the cells degenerate into cancer, removal of
the uterus
.
Treatment
A woman is prescribed a course of hormonal medications. This is necessary in order to actively restore the endometrium, normalize the menstrual cycle, improve reproductive function, and smooth out the development of menopause.
Basically, doctors recommend taking oral contraceptives that contain estrogen and gestagen. These hormones effectively compensate for progesterone deficiency, actively restore the uterine epithelium, and prevent pregnancy.
When hyperplasia is accompanied by other gynecological conditions that are pathological in nature, additional treatment is prescribed to eliminate the identified pathology.
If hyperplasia was detected in time, and the woman began to treat it in a timely manner, the disease can completely go away. But an advanced disease is more difficult to treat and can cause cancer, infertility, and death. Therefore, if any alarming symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a gynecologist.
Consequences and forecasts
If treatment is started in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable in most cases. Pathological glandular epithelium rarely forms again, the woman is completely cured. The need for surgery is rare. Reproductive function is fully restored; a woman is able to conceive on her own, bear a healthy child, and give birth without outside intervention. The focal form in most cases ends in complete cure.
Adverse outcomes are most often observed in advanced stages of the disease. Infertility develops.
If a relapse occurs, other drugs are used for treatment. If the drugs were effective, the dosage is increased.
To increase the likelihood of a favorable outcome, it is necessary to detect pathology in a timely manner. To do this, you should regularly visit a gynecologist: since the symptoms are mild, the disease may not be noticed by external signs even in advanced forms.
Complications
Endocervical hyperplasia is a benign pathology. However, the disease progresses rapidly and often leads to serious consequences. If the pathogenic process is started and treatment is not started in a timely manner, then pronounced symptoms appear.
Heavy bleeding after sexual intercourse, during and between menstruation often leads to the development of anemia. This condition is extremely dangerous for the health and life of a woman.
With significant thickening of the epithelium, the patient stops ovulating and infertility occurs. In advanced cases, a benign disease transforms into a cancerous formation, which is deadly.