≡ Home → Cervix → Diagnosis and treatment →
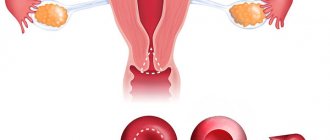
Cervical excision is the removal of affected tissue with a thin wire loop. The manipulation is carried out for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes and is indicated for deep damage to the epithelium. The technique makes it possible to identify previously undetected cervical cancer and thereby reduce the risk of dangerous consequences of carcinoma. The ease of implementation and the relatively low price of the equipment make this procedure one of the leading methods of treating cervical dysplasia.
Excision is a fairly safe and at the same time effective way to get rid of pathology. The procedure has become widespread in clinics in Western Europe. Leading medical centers in Russia also practice excision. A competently performed operation allows you to completely remove the affected tissue, prevent the likelihood of their malignant degeneration and reduce the risk of relapse. Timely therapy is the best prevention of cervical cancer and all the dangerous consequences of this condition.
Types of excision: surgical treatment options, advantages and disadvantages
In different countries this manipulation goes by different names. In the USA, loop excision is referred to as LEEP (Loop electrosurgical excision procedure). In Europe, the same operation is defined by the abbreviation LLETZ (Large loop excision of Transformation zone). In Russia, the American designation for the procedure is more often used. The procedure is also referred to as cone cervical excision.
The following types of procedure are distinguished:
- Electroexcision (diathermoexcision, diathermoelectroexcision, DEE) – the use of electric current to remove a pathological focus (this method is usually labeled LEEP);
- Radio wave excision (radio excision, RF) – the use of radio waves;
- Laser excision – using a laser beam;
- Argon plasma excision is the use of argon to remove diseased tissue.
Laser cervical excision can be performed using high-intensity laser radiation or low-power laser radiation.
| Method | Advantages | Flaws | Use in nulliparous women | Cost (Moscow) |
| Electroexcitation | Availability; Inexpensive price of equipment; | High risk of cervical scarring and cervical canal stenosis; Long period of rehabilitation; Unpleasant odor and smoke during the procedure; The need for direct contact with cervical tissue | Not recommended | From 5 thousand rubles |
| Radio wave excision | High efficiency; Non-contact exposure; Minimal thermal effect on fabrics; Fast healing period; Low risk of complications; No scarring; Well tolerated | High price | The best option for women planning pregnancy | From 9 thousand rubles |
| Laser excision | High efficiency; Non-contact exposure; Fast healing period; No scarring; Well tolerated | High price; Smoke during surgery; The risk of bleeding after excision is up to 10% | Maybe | From 7 thousand rubles |
| Argon plasma excision | Non-contact exposure; Minimal risk of complications; No scarring; Good tolerance; Possibility of immediate bleeding stop | High price | Maybe | From 7 thousand rubles |
Radio wave cervical excision is considered the best option for nulliparous women. The procedure is performed using modern devices – “Surgitron” or “Fotek”. "Fotek" allows you to perform argon plasma manipulations on the cervix, including cauterization and excision. High-quality equipment largely determines the outcome of the disease and ensures high effectiveness of therapy.
Devices for performing radio wave excision. On the left is “Surgitron” (American brand), on the right is “Fotek” (Russian).
Which method is better: laser or radio waves? It is quite difficult to answer this question unequivocally. It has been noted that when using a laser, bleeding occurs more often, and there remains a slight likelihood of scarring of the cervical canal (less than 1%). In this regard, many gynecologists prefer RV excision as the most gentle and safe method of treating pathology.
Consequences and complications
With radio wave excision, complications are minimal. However, nothing gives 100% results. Therefore, after this type of intervention the following complications may occur:
- Bleeding after surgery occurs in 2% of all cases.
- Due to the inexperience of the doctor or other factors, a woman can be damaged by healthy epithelium along with the patient.
- Scar formation if the tissue is exposed too deeply.
- Narrowing of the cervical canal. This problem can be eliminated with additional intervention.
- The appearance of inflammation due to the removal of a section of the cervix.
- Pain that will be explained by the individual pain threshold.
- Brown vaginal discharge that lasts for more than a week. If they are minor, then there is nothing to worry about. However, if blood clots come out and all this is accompanied by pain, you should immediately consult a doctor. If this is not done on time, one of the consequences may be anemia.
All these complications require seeing a doctor and treatment. The sooner a problem is noticed, the less harm it will cause.
Indications for the procedure
Purpose of the procedure:
- Diagnostic – taking a suspicious area of the cervix for histological examination (excisional biopsy);
- Therapeutic – removal of altered tissues.
In most cases, excision is therapeutic and diagnostic. The material excised with a loop must be sent for histological examination. In some situations, histology is performed on an emergency basis within 15 minutes. Such urgency is justified when cancer is suspected, when other methods have failed to prove the presence of carcinoma. Based on the results of histology, the doctor can change the treatment tactics and remove a larger volume of tissue than originally planned.
On a note
Histological examination is the only method to reliably confirm or refute cervical cancer.
Loop excision of the cervix is prescribed for the following conditions:
- Moderate dysplasia (CIN II and CIN II-III);
- Transition of the pathological process to the cervical canal (based on the results of diagnostic curettage);
- Inability to clearly determine the transformation zone during colposcopy (in this case it is impossible to cauterize the erosion);
- Inconsistency between the results obtained from cytological and histological examination (excision is indicated as a diagnostic procedure);
- A combination of dysplasia and cicatricial deformation of the cervix (both excision and conization can be performed);
- Recurrent erosion - lack of effect from conservative methods of therapy.
Loop excision is a surgical treatment method. In some cases, the doctor first suggests cauterization of the erosion and only if the treatment is ineffective, refers the patient to surgery. In case of deep tissue damage, such tactics are not justified, and excision (or conization) will be the method of choice.
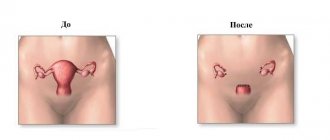
Options for pathological changes in the cervix: from inflammatory processes, which without proper treatment can develop into a precancerous condition.
Possible complications
Below is a list of possible complications and options for eliminating them.
- Bleeding, which can be either diffuse or arterial. If bleeding after electroexcision is diffuse, it is eliminated using coagulation with an electrode. If the bleeding is arterial in nature, then it is stopped using a spherical device.
- If bleeding begins immediately after surgery, begin rinsing the vagina with a vinegar solution to remove the clot.
- In rare cases, after electroexcision, inflammatory processes are observed, which manifest themselves in the form of fever, purulent discharge, and pain. In this case, the doctor will prescribe antimicrobial drugs such as Cefixime, Dixycycline, Metronidazole.
All these consequences are observed in only 2% of all women who have undergone this surgical intervention.
Contraindications for surgical treatment
Contraindications for surgery include the following conditions:
- Period of menstruation;
- Pregnancy and lactation;
- Inflammatory diseases of the genital organs.
During menstruation, cone excision is not performed. The operation is scheduled for days 5-7 of the cycle, but not earlier than monthly bleeding has completely stopped. At the time of the procedure, the cervix must be clear of discharge, otherwise tissue excision will be quite difficult. In women who have entered menopause, excision can be performed on any convenient day.
Inflammatory changes in the cervix and vagina are another reason to postpone surgery. Excision of tissue against the background of cervicitis threatens the spread of the infectious process into the uterine cavity and the development of endometritis.
Excision is not performed for diagnosed cervical cancer (even in stage 1). For intraepithelial lesions, conization can be performed in some cases. For large lesions, amputation of the cervix or removal of the entire reproductive organ is indicated.
How to prepare for surgery?
First of all, the patient will undergo standard diagnostics before she undergoes cervical surgery. Such diagnostics include:
- Examination by a gynecologist. The doctor visually determines whether the cervix is affected and to what extent. Then the gynecologist will take a standard smear to clean the vagina to determine the presence of inflammation.
- Using a colposcope and vinegar solution, the boundaries of the cervical lesion are determined. If necessary, a biopsy is taken to determine the nature of the pathology.
- An ultrasound is necessary to determine if there are pathologies in nearby genital organs, such as the ovaries and tubes.
- Standard blood and urine tests.
- Pregnancy test.
- Additional smears for the presence of sexually transmitted diseases, such as gonorrhea, syphilis, Trichomonas, HIV.
If any diseases are found that interfere with radio wave excision, then drug treatment is prescribed to eliminate them. Afterwards the diagnostics should be repeated.
Immediately before the operation, the woman will conduct self-preparation:
- Do not have sexual intercourse for a week;
- Have a light dinner before surgery;
- It is better not to have breakfast in the morning;
- Before going to the hospital, perform genital hygiene, but without using fragrances and dyes.
The operation is usually prescribed in the first half of the cycle, approximately 7-10 days, since tissue generation is increased during this period.
Preparation for the procedure
Loop excision of the cervix is performed in a one-day hospital setting. The operation is performed in the morning, after which the patient remains under the supervision of a doctor for two hours. If there are no complications, the woman can go home after 2-4 hours. If any problems arise, hospitalization in a 24-hour hospital is possible.
Before excision, it is necessary to undergo a complete examination:
- Blood tests: general, biochemical, coagulogram, determination of Rh factor and blood group;
- General urine analysis;
- Flora smear and bacteriological culture from the cervical canal;
- Oncocytology test;
- Screening for infections: HIV, viral hepatitis, syphilis;
- Tests for STIs (HPV and other microorganisms according to indications);
- Colposcopy;
- ECG and consultation with a therapist.
Oncocytology is a microscopic examination of a smear of cervical cells for the purpose of early detection of oncological pathology.
Two days before the procedure, you should avoid intimacy, do not use suppositories or douche. Taking any medications (primarily those affecting the blood coagulation system) should be discussed with your doctor.
It is important to know
Any manipulations can be carried out only after receiving the results of colposcopy and smear for oncocytology.
Types of excision methods
There are several options for excision:
- Radio wave (radio excision).
- Loop electroexcision (diathermoelectroexcision, diathermoexcision).
Among these varieties, laser and radio wave excision are considered the safest in medicine. Because with their help you do not have to resort to direct surgical intervention. This significantly reduces the risk of postoperative complications and shortens rehabilitation time.
Surgical technique: how cervical excision is performed
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. Lidocaine or other drugs are used to anesthetize the cervix. A mixture of anesthetic and vasoconstrictor drugs can be used. Injections are performed with a thin needle clockwise from the posterior lip of the cervix. This is usually enough to eliminate any discomfort. According to indications, the operation can be performed under general anesthesia.
On a note
Numerous reviews of women who have undergone loop excision indicate that the procedure is not too painful, but quite unpleasant. During tissue excision, you may feel a nagging pain in the lower abdomen, slight dizziness, and weakness. A small percentage of women indicate that the pain was quite severe. This is probably due to the individual sensitivity threshold or characteristics of pain relief. Much depends on the qualifications of the doctor who performed the operation.
Stages of cervical excision:
- The patient is in a gynecological chair. The doctor exposes the cervix in the speculum, fixes the instrument, and removes any secretions that interfere with the examination;
- A control colposcopy is performed, the boundaries of the lesion are established;
- A loop is selected - its shape and size will depend on the area of the lesion;
- The power of the device is set (the loop should not spark or get tied in the tissue);
- The cervix is fixed with bullet forceps beyond the border of the lesion;
- The doctor removes the affected tissue with a loop;
- The resulting material is sent for histological examination;
- Bleeding vessels coagulate;
- In case of severe dysplasia and suspected cancer, curettage of the cervical canal is performed.
Excision is a medical procedure that has both therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. The essence is to remove the epithelium affected by the disease on the cervix, and then conduct a histological analysis of the removed tissue to confirm or clarify the diagnosis.
In laboratory conditions, scraping of the cervical canal and removed tissues are examined under a microscope. Clean resection margins are a good sign, because in this case the doctor was able to remove the entire pathological focus. If altered cells are visible along the contour of the excised tissue, a new operation may be required. This means that the doctor has not captured the entire lesion, and there is a high probability of relapse.
On a note
Based on the results of histology of the cervix and cervical canal, re-treatment with an expansion of the scope of the operation may be recommended.
Indications and contraindications
Radio wave surgery is used in many branches of medicine. Gynecologists name the following indications for the use of radio wave excision of the cervix:
- benign tumors;
- dysplastic and other precancerous and background processes;
- scar deformity;
- initial stage of malignant tumors;
- complicated pseudo-erosion;
- lack of effect after using other treatment methods.
It is noteworthy that radio wave excision can be used for both therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. Despite the effectiveness and gentle effects of radioexcision, there are certain contraindications to the use of the treatment method.
Gynecologists note the following contraindications to radio wave excision:
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- infections of the reproductive organs;
- menstruation;
- diabetes;
- installed pacemaker;
- thrombocytopenia.
Most contraindications are relative and can be eliminated over time. In diabetes mellitus, prolonged healing of wounds of any size is observed. Radio wave excision is possible only after agreement with an endocrinologist and a preliminary examination.
As for thrombocytopenia, this pathology can be either symptomatic or permanent. With thrombocytopenia, there is a violation of blood clotting, a tendency to bleeding even with minor damage to the blood vessels.
If a pacemaker is installed, radioexcision is not performed due to possible disruption of the device. As a rule, alternative methods are used as treatment.
Complications after surgery
After excision of cervical tissue, the following complications may occur:
Bleeding
Occurs in 5% of cases. If bleeding is obvious, tamponade is performed. If the measures taken do not help, chemical or electrocoagulation of the bleeding vessels is performed.
It is important to know
Minor bleeding and bloody discharge within 3 weeks after surgery are not considered a complication and are a normal reaction of the healing mucous membrane.
Infection
A rare complication that occurs when the rules of asepsis and antisepsis are not followed, or the procedure is performed against the background of active inflammation (including in patients with reduced immunity, vaginal dysbiosis). Prevention of this condition is thorough sanitation of foci of infection before surgery. Inflammation of the postoperative wound is indicated by the appearance of copious purulent discharge from the genital tract, itching, discomfort, and pain in the lower abdomen. Without treatment, this condition can lead to endometritis and pelvioperitonitis.
Cervical stenosis and cervical scarring
A dangerous complication that occurs in 1-3% of women. Stenosis is observed mainly after electrical excision of the cervix. Severe narrowing of the cervical canal threatens infertility. The formation of scars is also possible, which in the future will lead to the development of isthmic-cervical insufficiency (ICI). During pregnancy, ICI provokes spontaneous miscarriage or premature birth of a child.
Undesirable consequences of cervical excision can be avoided by properly planning the procedure, taking into account certain aspects:
- The choice of a specific treatment method depending on the reproductive status and age of the woman;
- Preliminary colposcopic assessment of the lesion, its area and depth of the lesion;
- Compliance with all antiseptic rules;
- Taking into account possible contraindications;
- Competent management of the postoperative period;
- Monitoring the condition of the cervix after the procedure.
After the operation, you should undergo regular preventive examinations and follow all the gynecologist’s prescriptions in order to prevent possible deviations that will negatively affect reproductive health.
Procedure for electroexcision
The doctor must provide moral support to the patient during this procedure. He will tell her what he is going to do and how it will make her feel. Then it begins to act according to plan:
- A passive electrode is attached to the surface of the thigh.
- A gynecological speculum, which does not conduct current, is inserted. If there is none, then the metal mirror should be placed in a latex condom.
- Using a colposcope, the affected area of the cervix is determined. Treat it with vinegar solution or iodine. This way the doctor will see clear boundaries of the lesion.
- The woman is given anesthesia using a long needle. Due to this, the operation is painless for her.
- The doctor then prepares the excision apparatus. It would be better to choose an electrode that will immediately cover the entire affected area. If the girl has not given birth, then the maximum expansion of the electrode will be 0.5 cm. If the patient has given birth, then the expansion will be 0.8 cm.
- Then the excision itself occurs, with the smoke evacuator previously turned on.
- The excised material is placed in a container and sent for further examination for atypical cells. The operation itself lasts from 10-30 minutes.
An approximate image of electrical excision of the cervix is shown below.
Postoperative period and rehabilitation
Within 2-3 weeks after excision there will be bleeding - this is a normal stage of healing of the mucous membrane. In the first days, the discharge will be scarlet, then brown and bloody. At the end of the third week, bleeding should stop. Prolonged healing is observed after DEE with the formation of a scab. The epithelium recovers most quickly after radioexcision.
Nagging pain in the lower abdomen for 2-3 days is considered normal and does not require treatment. If necessary, you can take 1-2 tablets of No-shpa or ibuprofen (Nurofen). If the pain does not stop or gets worse, you should consult a doctor.
The general condition of the woman usually does not suffer. According to reviews, the procedure is well tolerated, no increase in body temperature is observed. Temperatures are allowed to rise to 37.5 °C during the first three days.
Important
Severe pain, persistent bleeding or prolonged fever indicate the development of complications.
In order for the restoration of the cervix to take place without consequences, you should follow the doctor’s recommendations:
- Sexual rest for 4 weeks until the postoperative wound is completely healed (up to 6 weeks after electroexcision);
- Prohibition on physical activity, lifting weights over 5 kg;
- You cannot use tampons - you should replace them with absorbent pads;
- Douching is not recommended;
- It is prohibited to take a bath, visit a sauna, bathhouse, swimming pool, or swim in open water.
Taking any medications must be agreed with your doctor. According to indications, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and other drugs for a speedy recovery. It is strictly not recommended to take blood thinning medications (aspirin, etc.).
Sexual activity can be resumed after 4-6 weeks. In practice, gynecologists recommend waiting until the first menstruation after excision. If everything goes well, the ban on intimate relationships is lifted. It would be a good idea to visit a doctor and make sure that the healing of the cervix is proceeding without complications.
Surgical treatment may affect the monthly cycle and cause a delay in menstruation. The first periods after excision are heavy and painful. Within 2-3 months the cycle should normalize. If this does not happen, you should definitely consult a doctor.
What should I do if my period does not start 4-5 weeks after surgery? The cause may be either stress or hormonal imbalance, or more serious conditions. The doctor will be able to make an accurate diagnosis after examination. It is recommended to donate blood for hCG to exclude pregnancy, a blood test for hormones and undergo an ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
If all instructions are followed, the menstrual cycle is quickly restored, and all reproductive functions are preserved. If bleeding lasts more than two weeks, this is a reason to visit an antenatal clinic.
Recovery period
After electroexcision, the recovery period varies depending on what disease was treated and the degree of epithelial damage. During healing, you may experience pain in the lower abdomen. It can be eliminated with Ibuprofen and Paracetamol. Minor bleeding is also possible, which can last up to a month. In this regard, you should follow some rules and recommendations:
- Do not use tampons;
- Do not swim in ponds or bathtubs;
- Refrain from sexual intercourse;
- Do not lift heavy objects.
All this should be done within a month. Afterwards, the woman needs to come for an examination so that the doctor can evaluate the healing process of the cervix. Also at this appointment, the gynecologist will tell you the result of a histological examination of the tissue.
Prognosis: what awaits a woman after excision
The prognosis for life and health depends on the effectiveness of the therapy. Control colposcopy and cytological examination are indicated after 3-6 months. A general examination is required and tests are prescribed to detect STIs. If the cervix heals well, the prognosis is favorable and the risk of relapse is minimal.
It is important to understand: cervical pathology often occurs against the background of HPV infection. Removing the pathological focus does not rid the woman of the virus: it remains in the body and can be activated at any time. To eliminate HPV after treatment of erosion, antiviral and immunomodulatory agents are prescribed. This approach significantly increases the chances of a favorable outcome of the disease.
Is pregnancy possible after electroexcision?
In some cases, removal of damaged cervical epithelium may result in scarring. Or another difficulty is the large area of the removed area of the cervix.
In these cases, complications during pregnancy and childbirth are possible. Often, women are offered a caesarean section after cervical excision. The reason is that the cervix may either not open or be damaged during childbirth.
Another complication after electroexcision is premature pregnancy. Premature birth is a common occurrence after cervical manipulation.
Therefore, those girls who want to have children should consider, if possible, another method of cervical treatment. Laser conization is ideal.
Pregnancy and childbirth after the procedure
Modern methods of treating cervical pathology have virtually no effect on the course of gestation and the birth process. The use of radio waves, argon and laser allows all manipulations to be carried out almost bloodlessly, without causing infection. After this procedure, no scars remain, the cervix heals within 4 weeks, and in the future the woman can safely give birth to a child.
Certain complications arise when using electric current. DEE is not used in nulliparous women due to the high risk of complications. Scars on the cervix, stenosis of the cervical canal - these are what lead to undesirable consequences for a young woman. Pregnancy after DEE is accompanied by a high risk of developing ICI, miscarriage or premature birth due to cervical incompetence. If technically possible, doctors try not to use this method in women planning pregnancy.
Technique for loop conization of the cervix
In what cases is electroexcision of the cervix prescribed?
This operation is prescribed for various pathologies that cannot be cured with medication. The most common conditions that should be treated with electroexcision are:
- Dysplasia. This is the next stage after cervical erosion, which affects the epithelium of the cervix and looks like a white coating on the tissue. Usually the affected area is cut off so that the pathology does not spread over the entire surface.
- Malignant formations. Unlike other methods of surgical intervention, this method is suitable even in cases where preliminary diagnosis has determined the presence of cancer cells. Only the doctor will decide how appropriate this method will be. If the malignant tumor is not large, it will be removed using electroexcision, and then drug or radiation treatment will be used.
- Scarring. After various manipulations, scars may remain on the cervix. If a woman plans to have children in the future, scarring of the cervical tissue is completely inappropriate for her. Therefore, using electroexcision, doctors can remove scarred tissue.
- The formations on the cervix are benign. These can be polyps, condylomas, papillomas, etc. They are removed using loop electroexcision.
- Cervical erosion can also be treated with electroexcision. However, if a girl has slight erosion, then you can think about other more gentle methods. For example, laser cauterization.
Indications
Indications for this procedure are as follows:
- The presence of leukoplakia, dysplasia, recurrent erosion;
- Scars and deformities of the cervix as a result of past operations or injuries;
- Changes in the epithelium of an unknown nature;
- The presence of papillomas, cysts, polyps, multiple and untreatable;
- Oncological processes of weak development.
There may be other specific indications, but most often the intervention is carried out precisely for the reasons listed above.
Price
The price of this operation directly depends on the clinic where this procedure will be performed. Below are three centers in St. Petersburg.
| Medical Center | Price |
| Honey. | 6500 rub. |
| Orkley Hospital | 15300 rub. |
| Honey. Abia center | 6300 rub. |
So, the method of electroexcision of the cervix copes well with various pathologies and changes in the epithelial layer. The procedure is performed under anesthesia, so the patient feels almost no pain. However, if the girl has not yet given birth, then, if possible, she will be offered another type of elimination of the pathology.