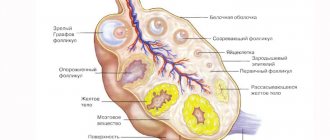
Using ultrasound diagnostics, the presence of a hypoechoic or hyperechoic neoplasm can be determined. In the first case listed, the patient has nodes that have a reduced level of density. Such a diagnosis can be either normal or a disease. Only a doctor can determine why a hypoechoic formation occurred. It is impossible to do this on your own. The presence of a disorder can only be determined using an ultrasound machine. All tissues and organs have a certain level of echogenicity. Hypoechogenicity is characterized by a reduced level of density. This can be clearly seen on the monitor during an ultrasound.
Hypoechoic and hyperechoic formations can be clearly seen on ultrasound
In this article you will learn:
What is a hypoechoic formation?
Hypoechoic formation is a formation localized in any organ and having echogenicity below the normal level. This area weakly reflects ultrasonic rays. The monitor is darker than other areas.
A hypoechogenic formation contains water or a cavity. On the monitor, the area is visualized as gray or black spots. With hyperechogenicity, the zones are light or even completely white.
To decipher the picture, a special scale with 6 categories of gray shade is used. The diagnosis is made by specialist doctors. Often hypoechoic formations are cysts. In this case, the patient is additionally referred for a biopsy.
You can decipher the image using a special scale
The root causes of hypoechogenicity
The formation can have any localization. Formations also have different underlying causes of development and symptoms.
The root causes of hypoechogenicity, depending on the location of the formation, are listed in the table below.
| Liver and gallbladder | The causes of hypoechogenicity include: • polyps; • lymphoma; • angiosarcomas. |
| Bladder | The following factors provoking the lesion are identified: • fibroids; • transitional cell malignant process. |
| Abdomen and pelvis | Among the root causes that contribute to the finding of hypoechogenicity on ultrasound are: • hernia; • abdominal hematomas; • phlegmon; • inflammatory process in the lymph nodes; • spread of metastases; • carcinoma of the cecum: • testicular cancer in men. |
| Subclavian zone | The violation is a consequence of: • benign neoplasms; • cysts; • thymomas of the thymus. |
With all of the above factors, an ultrasound examination will diagnose a neoplasm with a reduced level of echogenicity. The current disorder does not always require any specialized treatment.
Similar formations can be found in different organs
Locations of formation localization
The clinical picture and the main diagnosis depend on the localization of the formation with a low density index. Pathological changes may affect:
- thyroid gland;
- uterus;
- mammary gland;
- spleen;
- ovaries;
- kidneys;
- pancreas;
- liver.
Hypoechogenicity is not a diagnosis, but only the result of an examination. That is why in an area with low density you should not worry ahead of time.
If the pathological process has affected the thyroid gland, then the presence of cysts and nodules can be suspected. Cancer is diagnosed in only 5 patients out of 100. An altered structure of the uterus indicates an inflammatory process, fibroids or miscarriage. Often the symptom indicates neoplasms of a benign or malignant nature.
Hypoechogenicity in the mammary glands may indicate various pathologies
Most often, hypoechogenicity is observed in the mammary glands. The symptom indicates:
- cancer;
- adenosis;
- the presence of cystic formations.
In the kidneys, an area of low density indicates either cancer or cystic formations. With a malignant tumor, the boundaries of hypoechogenicity are erased and the structure is uneven. Additionally, the patient may be recommended a biopsy.
Changes in the pancreas may be explained by:
Hypoechogenicity can manifest itself in absolutely any human internal organ. Some of the underlying causes require drug therapy or urgent surgery. Ignoring any doctor’s orders is strictly prohibited. First of all, it is important to exclude the possible presence of a cancer process.
Such formations may indicate cancer and are observed in different organs
In some cases, hypoechogenicity does not cause any discomfort and does not provoke the appearance of negative symptoms. The reduced density will be discovered completely by accident.
Anechoic avascular inclusions in the cervix
An anechoic object can be defined as a neoplasm caused by various diseases. Such elements can be detected using an ultrasound machine. When using the technology, the doctor can easily make the correct diagnosis using the data from the echo signal receiver.
Nature of formations
In accordance with ICD-10, formations of the low echogenicity type are a variant of the non-inflammatory process of female internal organs.
The phrase anechoic formation means that the ultrasound emitted by the equipment does not pass through the tissue of the object. Thus, only a dark echo structure with possible inhomogeneous inclusions will be visible on the screen. This may mean that the device is aimed at a fluid, a blood clot, or tissue that has undergone a structural change.
When detected, an anechoic structure is not put forward as a diagnosis, but only the fact of the presence of pathology in the organ is stated. Such neoplasms can be located in the cervical canal of the cervix, uterus, and ovaries. If a woman has given birth to children, inclusions up to 5 mm in size, an anechoic formation in the cervix, are considered within normal limits.
Reasons for changes due to anechoic single inclusions
A single anechoic variant of the formation may appear, in addition to the cervix, in the area of the ovaries, uterus, and the space surrounding the pelvis.
The main factor due to which such neoplasms appear is the cystic nature of the inclusion. The course of events is also affected by the proliferation of endometrial tissue.
Also the cause of the appearance is endometriosis. A special layer that covers the inside of the uterus creates foci that do not transmit the ultrasonic spectrum of the ultrasound machine. In this embodiment, such areas look like spots, the size of which does not exceed 1 cm, with a chaotic arrangement. On the monitor, such formations have a heterogeneous appearance. Therefore, to the question: “what is an anechoic formation in the cervix up to 5 mm?” a common answer is endometriosis. With this diagnosis, diathermocoagulation (melting tissue with electric current) can be effectively used.
Other factors in the formation of anechoic inclusions:
- The uterus contains cancer or another tumor. In this embodiment, the formation appears on the monitor as a heterogeneous shape, with varying degrees of echogenicity. In this case, the organ can change in shape, becoming more massive
- Uterine leiomyoma is a benign type of tumor that is dependent on secreted hormones. Such pathologies can be supplied through the bloodstream. Such formations are typical for older women.
- The corpus luteum is an anechoic body and is the gland that produces progesterone during the ovulation period. The absence of a separately isolated gland during the initial stages of pregnancy indicates an insufficiency of secreted hormones.
Clinical picture
The clinical picture varies depending on the underlying cause and location of the deviation. The main danger signs include:
- difficulty swallowing and eating;
- respiratory dysfunction;
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- pain and discomfort at or near the site of hypoechogenicity;
- hoarseness and hoarseness in the voice;
- unreasonable decrease or increase in body weight;
- improper functioning of the digestive organs;
- constant drowsiness and feeling of fatigue;
- sudden mood swings;
- change in body temperature;
- dullness of hair;
- brittleness of the nail plate.
Patients often complain of drowsiness and fatigue
All symptoms are common. The patient may have several symptoms or all at once. It all depends on the factor that provoked the decrease in density.
In the presence of serious illnesses, the patient’s well-being rapidly decreases. Every day a person has less and less strength. Usual things become a real test. The skin becomes drier.
Signs of general intoxication of the body appear. Aggression may occur without obvious reasons. High risk of underweight.
Diagnostic methods
The only way to detect a hypoechoic area is to resort to ultrasound diagnostics. In this case, the examination is carried out with a special device that emits ultrasonic waves.
Ultrasound is a painless and completely safe procedure
In contact with internal organs, ultrasonic waves are reflected and returned. Thanks to this, everything that happens is displayed on the monitor. Subsequently, the doctor deciphers the results obtained.
Ultrasound is harmless regardless of the patient's age. The method can be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding. The method does not require special preparation. An exception is abdominal ultrasound examination. In this case, sometimes you need to fill your bladder or follow a diet.
Before performing an ultrasound, an acoustic gel is applied to the area being examined. The product promotes better glide. Does not interfere with visualization and does not cause an allergic reaction.
After diagnosis, you need to remove the remaining gel. This can be done using dry wipes. The doctor will decipher the indicators and confirm or deny the likelihood of the presence of hypoechoic tissue.
From this video you can learn more about benign formations in the mammary gland:
Diagnosis after childbirth
Hypoechoic nodes in the uterus do not always indicate pathological formations.
The diagnosis should be clarified by a gynecologist after assessing the results of the ultrasound diagnostics. In some cases, it is recommended to drink drugs that help contract the smooth muscle layer of the uterus and reduce bleeding.
Regardless of the ultrasound results obtained, the patient should consult with her gynecologist. The doctor, having assessed the results of the study, may prescribe additional diagnostics to clarify the diagnosis.
If the doctor notes a hypoechoic formation in the uterus, what it is needs to be specifically clarified. Such lesions always require very close examination by a specialist. Only its detailed description allows the gynecologist to accurately and reliably make a diagnosis.
A hypoechoic formation appears on ultrasound during examination of the uterus not so rarely. This characteristic suggests that ultrasound travels much slower than in other areas, and the acoustic density of the affected tissue is noticeably reduced. Such lesions in the photographs appear as dark spots ranging from light gray to black in color.
Treatment measures
Treatment is selected by the doctor. Sometimes therapy is not necessary at all. Depending on the diagnosis, the patient may be recommended:
- vitamin therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- traditional therapy;
- homeopathic treatment;
- surgical intervention;
- taking medications.
There is no single treatment therapy. Self-medication is strictly contraindicated, since hypoechogenicity can be provoked by various provoking factors.
Possible risks
The most serious cause of hypoechogenicity is malignancy. Some tumors cannot be excised. The patient's condition is constantly deteriorating. Body weight rapidly decreases and appetite disappears.
Cancer is a serious disease, without treatment it always leads to death.
With cancer, the functioning of the body as a whole is disrupted. If left untreated, the patient may experience spontaneous death. Every day will begin with unbearable torment.
In order to avoid serious complications, preventive diagnosis is preferred. An ultrasound should be performed annually.
If the doctor notes a hypoechoic formation in the uterus, what it is needs to be specifically clarified. Such lesions always require very close examination by a specialist. Only its detailed description allows the gynecologist to accurately and reliably make a diagnosis.
A hypoechoic formation appears on ultrasound during examination of the uterus not so rarely. This characteristic suggests that ultrasound travels much slower than in other areas, and the acoustic density of the affected tissue is noticeably reduced. Such lesions in the photographs appear as dark spots ranging from light gray to black in color.
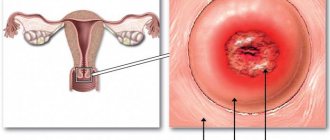
Dense formation on the cervix
A dense formation on the cervix most often appears as a benign polyp. The lump may be large or appear as a small, hard lump or lump. Such seals can be movable or remain static.
With 5% of variants, submucosal nodes may appear. It is also possible to register another type of disease - for example, fibroids.
To find out exactly what kind of dense object is in the cervix, you should undergo a test. Symptoms of neoplasms may include bleeding and the presence of other discharge from the genitals. It is especially worth focusing attention if there are inclusions of purulent formations.
To establish a diagnosis, the following steps are taken:
- Gynecological examination using speculum.
- Hysterography (x-ray of the uterine cavity).
- Examination of the pelvis using ultrasound.
The most common is a minimally invasive method - hysteroscopy. This method allows the doctor to quickly determine the exact location and type of tumor. The doctor can take biomaterial for analysis, which is also convenient in the presence of tumors.
Specialists resort to hysterography if it is necessary to detect an uneven surface of the cervix. Contrast is introduced into the pelvic cavity, the function of which is to create a high-quality image. The method can help in establishing the nature of the dense formation in the uterine cervix.
Prevention of the appearance of anechoic formations
A woman should adhere to simple rules of personal hygiene:
- organization of pregnancy planning.
- systematic medical examinations with a doctor
- using a hormonal contraceptive according to your hormonal status.
- physical activity, healthy eating and lifestyle
- using condoms during sexual intercourse
Also, to prevent the formation of cysts, it is possible to use propolis tincture - up to 20 drops per 50 ml of water. This mixture can be drunk every day for 20 days with a 10-day break. A total of three such cycles are necessary.
Anechoic formations can be detected at any age. Only a qualified doctor can accurately indicate the pathological nature of the formations and make the correct diagnosis.
The hyperechoic nature of the formation suggests that a homogeneous area does not transmit ultrasound.
Possible complications and consequences
The main option for the development of pathology in the uterus is bleeding from an endometrioid cyst. If a cyst bursts in the cervical area, urgent medical and anti-inflammatory treatment is necessary. There are also cases of the appearance of a myomatous node. Such a solid case requires differential diagnosis. In addition, anechoic formations can be caused by adhesions or tubal resection. These phenomena may occur during medical operations.
Underneath an anechoic avascular neoplasm in the cervix, a uterine cyst most often appears. This formation has thin walls and contains a liquid solution inside. The diameter of such an object can reach from 3 mm to several centimeters. The term “avascular” should be understood as a neoplasm that is not supported by the body’s bloodstream. Such a symptom can serve as an excellent factor for determining pathology. Endometrioid cyst variants also acquire an avascular character.
As soon as a woman feels pain in the lower abdomen or other ailments, she should immediately contact a gynecologist. Some pathologies can develop quickly and progress to malignant stages. If an anechoic formation is detected in a person, the woman should be systematically checked to monitor the dynamics of the development of the pathology.
Video: endometrial polyp in postmenopause
Endometrial polyp in postmenopause
Video: polyp of the cervical canal of the cervical stump
Polyp of the cervical canal of the cervical stump
Hypoechoic formation in the uterus
A hypoechoic inclusion in the uterus, as a rule, is closely associated with the appearance of a cavity containing some kind of liquid or air. It is this that appears on the monitor screen of the ultrasound machine as a grayish or dark spot.
Any pathological focus should be examined in detail and its:
It should be taken into account that blood-filled vessels are also always hypoechogenic. But most often this inclusion turns out to be a cystic cavity or neoplasm.
Based on certain characteristics, the doctor assumes the presence of a disease or prescribes a number of differential diagnostic measures to identify pathology.
In order for a specialist to make his expert opinion with complete confidence, the patient often also needs to undergo angiography, duplex scanning, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Sometimes a biopsy is also recommended.
What does hypoechoic formation mean?
The essence of ultrasound examination is to send an echo signal to the uterus. It reaches its tissues, is reflected from them and allows you to see the organ on the monitor screen of a diagnostic device.
A sonologist usually knows exactly the features of various anatomical structures, so he quickly understands the essence of the appearance of a particular shade of color and the uniformity of the lesion.
A hypoechoic node in the uterus is very clearly differentiated from a hyperechoic area by its ability to reflect an ultrasound signal. The wave coming from the device’s sensor is not absorbed by the organs, but gives a weak echo.
As already mentioned, the doctor clearly sees it as a grayish, dark or completely black spot. Such differences sharply differentiate tissues from hyperechoic ones, which appear as lightish or even white areas.
In order to very clearly distribute the shades of the values obtained during the study, scientists have developed a special line of Gray Scale Imaging, according to which the specialist specifies six options for the darkness of the color of the images. Any slight change in tissue conductivity most often indicates a developed disease.
Possible causes and types of hypoechoic formations
Most often, hypoechoic contents in the uterus mean the development of:
- cystic cavity;
- polyposis;
- endometriosis;
- fibroids;
- adenomyosis;
- endometritis;
- carcinomas;
- cancer, etc.
During pregnancy, every woman worries about her health. Therefore, the identification of a hypoechoic structure most often indicates the occurrence of a cyst or hematoma.
A reduced echo signal can also come from a vessel damaged by the implanted fertilized egg. As the mass increases, there is a risk of spontaneous abortion, so constant ultrasound monitoring is an urgent need.
A hypoechoic focus observed in the patient’s uterus, clearly displayed on the screen of an ultrasound device after the birth of a newborn child, indicates a sharp decrease in the contractility of the organ. It looks excessively expanded, and sometimes an inflammatory process is also observed in it.
There are several types of formations:
- An anechoic area implies a complete absence of signal from the organs. In this case, a uniform black color is noted.
- A hyperechoic inclusion occurs when ultrasound gives an increased response from tissue and light or whitish inclusions appear on the screen.
- A hypoechoic focus is noted if the signal is reduced and appears in a dark shade.
- The isoechoic structure is characteristic of healthy organs and looks like a uniform gray formation.
Causes
It should be noted that hyperechoic inclusions in the uterus have a variety of causes. To identify the exact picture, in some cases it is recommended to carry out complex diagnostic measures. These are not only instrumental, but also laboratory methods.
The highest density that blocks the penetration of ultrasonic waves is the intrauterine device. This is not a pathology. However, the likelihood of complications occurring is quite high. Among them are uterine perforation, inflammatory processes, as well as an excessively long menstrual cycle.
The sonographic image of the most common T-shaped spiral on the screen is viewed as a linear formation if the longitudinal scanning method is used. The transverse position of the sensor gives an image of a round inclusion. It has smooth edges.
The loop-shaped Lipps spiral on the ultrasound screen produces an image of a continuous line under the condition of transverse scanning. The longitudinal position of the scanner is accompanied by individual intermittent inclusions.
In addition to clarifying the location and condition of the IUD, ultrasound makes it possible to identify the condition of the tissues surrounding it in the uterus.
Chronic form of endometritis
The disease is caused by endometrial hyperplasia. It is observed in patients of different age categories.
Ultrasound imaging of the process may indicate different types of pathology. This:
- hyperechoic formation in the uterus from 2 to 6 mm, characterized by clear boundaries;
- inclusion of the same size, but with blurred contours;
- deviations in volume (expansion).
The likelihood of thickening of the walls of the uterus during menstruation can be observed before the onset of menopause.
Polyps
A characteristic manifestation of endometrial polyps is an isoechoic structure. But the presence of fibrin threads in them increases the echo density of the inclusion. On the screen they look like endometrium. With the transverse scanning method, they differ from endometrial inclusions by smooth round contours.
Image of polyps on an ultrasound screen
Other factors
A hyperechoic inclusion in the uterus is detected in the following situations:
- Hematometra. Represents blood clots. These are often postoperative or postpartum manifestations. Inhomogeneous particles resemble the residual phenomena of chorions. In contrast, these clots are displaced relative to the walls of the organ and modified. This does not happen with chorion components.
- Air bubbles in the uterine lumen. They form after surgical curettage. Chronic endometritis also provokes their appearance. The detection of numerous small formations is typical. The boundaries of the inclusions are clear, reminiscent of the tails of a comet. They are visible behind the bubbles.
- Remains of the fruit. Variants of echo signs are characterized depending on the timing of termination of pregnancy. The presence of remnants of chorion tissue appears on the ultrasound screen as heterogeneous inclusions of increased echo density. If the pregnancy is terminated in the later stages, clear boundaries and the presence of a shadow are observed.
- Inflammation of sutures after surgery. Marked by thickening of the infiltrate. Plaque may appear, causing an increase in echo density.
- Perforation of the organ. A thick cord (about 6 mm) is visually traced without acoustic shadow manifestation. A long process provokes the development of endometritis with accompanying inclusions.
Less often, zones of hyperechogenicity are found in submucosal myomatous nodes, as well as lipomas.
As for myomatous nodes, they are usually hypoechoic. But the tendency of nodes to degenerate and the presence of calcium elements leads to the identification of high-density foci.
Lipoma
The neoplasm is not malignant. Its composition is fat cells. The absence of pronounced symptoms, as well as the manifestation mainly after the age of 60-65 years, became the reason for its rare detection.
Hypoechoic formation in the uterus: examination using ultrasound
Indications for mandatory ultrasound scanning of gynecological organs are most often:
- severe pain in the lower abdominal cavity;
- disruption of the normal course of menstruation;
- uncharacteristic discharge;
- excessive leucorrhoea;
- severe disruption of the menstrual cycle;
- constant discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- inflammatory process in the uterus or ovaries;
- menopause symptoms;
- preventive examination, etc.
The procedure is often carried out when planning conception, preparing for in vitro fertilization, as well as during mandatory screenings during pregnancy.
Interstitial uterine fibroids
Manifestations of interstitial uterine fibroids correlate with the number, volume and location of nodes, the degree of inflammatory and degenerative changes that have developed in them. Interstitial-subserous uterine fibroids have a low risk of malnutrition and destruction; when small in size (up to 2-4 cm), they are not clinically detected for a long time. With multiple fibroids and large nodes (10-25 cm), the uterus noticeably increases in volume, causing compression of the intestines, bladder and nerve plexuses in the pelvis. Patients are concerned about discomfort and a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen, periodic or constant pain in the pelvic region, pain during menstruation (algomenorrhea). Acute pain and fever appear when blood circulation in large nodes is impaired.
Interstitial uterine fibroids may be accompanied by heavy uterine bleeding, usually during menstruation (menorrhagia), less often - acyclic (metrorrhagia). It is possible to deposit a certain amount of blood in the uterus enlarged due to myomatous nodes. Prolonged and frequent menstrual and intermenstrual blood loss is complicated by iron deficiency anemia, weakness, fatigue, headache, dizziness, and frequent fainting.
Compression of the inferior vena cava by bulky interstitial myomatous nodes (>20 weeks) is manifested by shortness of breath and tachycardia in a horizontal position. Myoma located on the anterior wall of the uterus causes dysuria - difficult or frequent urination, incomplete emptying of the bladder, obsessive urge to urinate, and sometimes acute urinary retention. Cervical uterine fibroids growing towards the rectum make defecation difficult, leading to constipation and hemorrhoids.
Small interstitial fibroids do not interfere with reproductive function; large nodes that severely deform the uterus can cause uterine infertility or spontaneous abortion at different stages. The location of fibroids in the area of the mouth of the fallopian tube with compression of the latter complicates the process of conception. The growth of interstitial fibroids into the uterine cavity can disrupt the normal development of the fetus, leading to spontaneous miscarriage and premature birth. Attachment of the placenta in the area of the node increases the risk of premature detachment and profuse bleeding. Interstitial uterine fibroids can cause complications during childbirth - weak labor and bleeding.
Useful video
Polyps are considered hypoechoic formations in the uterus. What is important to know about them can be found in this video.
Typically, the doctor will use one of three main options for performing sonography.
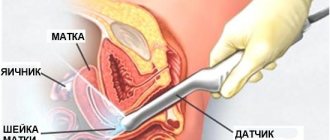
Transvaginal ultrasound allows you to thoroughly examine the uterus by inserting an ultrasound device into the vagina. This type of study provides the maximum amount of data about the condition of the organ.
A transabdominal ultrasound scan is done using a probe that examines the anterior abdominal wall.
Transrectal diagnosis is most often performed on virgins or patients who have direct contraindications to performing the two previous types of procedures. In this case, the sensor is passed into the woman's anus.
In order for the results of the uterine ultrasound protocol to be as reliable as possible, you need to thoroughly prepare for it.
- One day before, you should avoid foods that cause increased gas formation. These include peas, cabbage, liver, lemonade, baked goods, etc.
- To conduct a transabdominal ultrasound, you must come to an appointment with a specialist with a tightly filled bladder. An hour before the diagnosis, it is advisable to take at least one liter of liquid without gas.
- If a transvaginal or transrectal procedure is to be performed, then it is necessary to give a cleansing enema and take carminatives Infacol, Smecta, Espumisan . It is also recommended to use Glycerin suppositories, Microlax, Norgalax, Senade .
- The bladder should be empty in the last two versions of sonography.
It is necessary to fully agree with the gynecologist to conduct an ultrasound for a certain period of the menstrual cycle.
In addition, you should inform your doctor about all medications, contraceptives, previous diseases or existing pathologies.
If there is a suspicion of pregnancy, it is better to take an hCG test in advance so that the specialist can choose the most appropriate type of ultrasound examination of the uterus.
All human organs have a certain echogenicity. The principle of ultrasound diagnostics is based on this: sound waves are sent from the sensor, which, like an echo, are reflected from the tissues, return to the sensor, and a picture is displayed on the screen. Depending on the homogeneity or heterogeneity of the structures, an ultrasound specialist can identify pathology.
Possible causes of formation
After the ultrasound specialist describes the formation and the gynecologist carries out all the necessary tests, a diagnosis can be made and treatment prescribed:
- Uterine carcinoma. Another name for this disease is uterine cancer or endometrial cancer. Usually a woman comes to the doctor with bleeding that does not go away even after the end of her period, the doctor sends the patient for an ultrasound, where a heterogeneous formation with various cystic inclusions and other pathologies is detected. The main method of treatment is surgical, if there are no contraindications to surgery. Radiation therapy is also used. The prognosis depends on the stage at which the disease was discovered.
- Cervical carcinoma. This is a malignant tumor in the cervix, which is closest to the vagina. The cause of cancer development is the human papillomavirus, but the presence of HPV in the body does not mean that a woman will necessarily develop cancer; there are other risk factors, such as promiscuity, frequent childbirth, smoking, and weak immunity. Quite often, such tumors occur in pregnant women, so every pregnant woman should undergo a thorough examination in the early stages.
- Cysts. A cyst is a benign formation that does not lead to cancer and does not affect reproductive function. Almost every woman encounters this concept. Cysts can develop for a variety of reasons: hormonal disorders, injuries during abortion and childbirth, diseases of the genital organs. Only large cysts can be removed. For this purpose, puncture, cauterization, laser removal, and radio waves are used.
- Internal endometriosis. The mucous membrane grows into muscle tissue, which causes pathology. This disease is more common in women over 35 years of age. It is accompanied by bloody discharge, abdominal and lower back pain, and infertility. There are several stages of the disease, from one or several lesions to complete fusion of organs, rectum, and vagina. Treatment can be either medicinal or surgical. For a small number of lesions, the doctor prescribes hormonal pills, which also increase the chances of pregnancy.
Hypoechoic formations
When performing an ultrasound analysis of the uterus, some people reveal hypoechoic inclusions. This means that in a certain area, ultrasonic waves move more slowly, and the identified formations are characterized by reduced acoustic density. On the screen, this area will be visualized as a darkening. Nodes with reduced echogenicity can be gray, dark gray or almost black.
Decoding is carried out after determining the shade of gray using a special Gray Scale Imaging scale. After all, each pixel displayed on the screen has its own specific shade of gray. It depends on the intensity of the ultrasonic signal that is returned to the sensors.
The physician should describe each hypoechoic nodule identified. Indicated:
But it is impossible to establish an accurate diagnosis based only on the conclusion of an ultrasound diagnostic specialist. After all, vascular formations, inside of which there is liquid, are distinguished by such a structure. There may also be an empty cavity inside hypoechoic inclusions. These may be cysts or tumors.
An accurate diagnosis is established only after clarifying studies: MRI, color Doppler sonography, angiography, CT. If possible, material is taken from the formations for histology.
If an ultrasound reveals a hypoechoic node, then there is no need to panic. The results obtained depend on:
- the doctor’s experience (the possibility of error and the influence of the human factor cannot be excluded);
- ultrasound device (on outdated equipment the picture may be unclear);
- preparation for the examination;
- individual structural features of tissues;
- presence of obesity.
It is important to notify your doctor about existing diseases, suspected pregnancy, or the estimated duration of pregnancy. The phase of a woman’s menstrual cycle is important for examining the uterus. Most often, it is recommended to do an ultrasound after the end of menstruation, but sometimes a dynamic examination is necessary to clarify the diagnosis.
Encyclopedia of Ultrasound and MRI
Recently, ultrasound diagnostics has taken a leading position among diagnostic methods in gynecology. This is due to the accessibility, information content and safety of the method. However, ultrasound in gynecology has a number of difficulties due to the variability of the ultrasound picture depending on the day of the menstrual cycle, the number of previous pregnancies, and the duration of menopause.
In this regard, high professionalism and clinical thinking are required from the doctor conducting the study.
It should be understood that the sensitivity of the method is variable and depends on the pathology being diagnosed. Even conducting a study using an expert-class device does not guarantee an unambiguous diagnosis.
There are groups of pathological processes that have a similar ultrasound picture. Therefore, a high-quality examination should be comprehensive and include laboratory, instrumental research methods, as well as examination and medical history data.
The uterus is the largest organ of the female reproductive system, which is well differentiated by transabdominal and transvaginal ultrasound.
Organs of the female reproductive system
This allows you to diagnose space-occupying formations of even small sizes. Based on the visualized picture, all formations can be divided into three groups: hypoechoic, isoechoic and hyperechoic.
Isoechogenic formations have the same acoustic density as the surrounding uterine tissue.
Hypoechoic formations have a lower acoustic density and, during ultrasound examination, appear darker against the background of the main tissue of the organ. Hyperechoic inclusions have a high acoustic density and are visualized lighter against the background of uterine tissue.
To describe focal pathology of the uterus, the terms inclusion and formation are used. There is no fundamental difference in their use and the use of both terms is legal and acceptable in relation to any focal process.
Hyperechoic formations in the uterus have a different nature. The main reasons for their appearance are:
Intrauterine contraceptives . One of the most common types of contraception today, although complications of use are common (inflammatory processes, perforation of the uterine walls, menstrual irregularities). The ultrasound picture is different and depends on the type of intrauterine contraceptive device. The most commonly used is the T-shape. When placed correctly, it is visualized as a linear hyperechoic structure during longitudinal scanning and as a rounded formation with rough contours when the transducer is positioned transversely.
Intrauterine contraceptives, cysts – Uterus and appendages – Ultrasound
When positioned correctly, the hyperechoic inclusion reaches the bottom of the uterine cavity and does not protrude beyond the internal os. When using a Lipps loop as an intrauterine contraceptive, the ultrasound picture is characterized during transverse scanning by the detection of a solid hyperechoic line and individual inclusions of increased echogenicity during longitudinal scanning. When the uterus is perforated by an intrauterine contraceptive, a hyperechoic inclusion is determined, partially located in the thickness of the myometrium. Most often this occurs in the fundus of the uterus.
Chronic endometritis . This process is caused by endometrial hyperplasia and can occur in any age group. The ultrasound picture of hyperplasia is variable, most often it looks like hyperechoic inclusions of small size (2-7 mm) with clear contours, irregular shape, and possible expansion of the uterine cavity. In women of reproductive age, endometrial thickening and hyperechoic inclusions persist during all phases of the menstrual cycle.
Chronic endometritis. B-mode. Dilation of the uterine cavity
Endometrial polyps. In most cases, polyps have an isoechoic structure, but if there are a large number of fibrin strands in the structure of the polyp, this leads to an increase in the echogenicity of the formation. Fibrous polyps have a similar ultrasound picture to endometritis. Distinctive features are the presence of clear, even contours and a round shape during transverse scanning. There is a violation of the closure of the mucous membranes, its contours become wavy and intermittent. Color Doppler sonography reveals the vascular pedicle of the polyp, which consists of newly formed vessels that feed the formation.