Is it possible to do electrophoresis during pregnancy?
As you know, medications have side effects. Penetrating into the body, they affect the liver, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, as well as the composition of the blood. Therefore, during pregnancy it is important that their effect on the body is very low.
Physiotherapy is a widely used method of treatment. Electrophoresis is one of the means of physiotherapy. Under the influence of a low-power electric current, the drug is delivered to a specific organ through the pores or mucous membranes, bypassing the gastrointestinal tract.
Electrophoresis is prescribed to women in the following cases:
- Endometriosis.
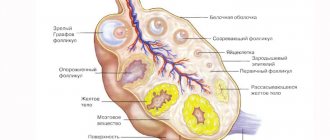
- Cysts.
- Uterine fibroids.
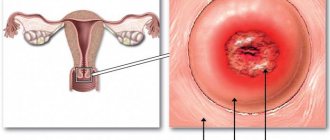
- Cervical erosion.
- Tonsil proliferation.
- Toxicosis.
- Increased muscle tone.
It should be noted that this method of treatment guarantees the concentration of the drug directly in the area of the affected organ. The therapeutic effect is achieved much faster.
Pregnant women are prescribed this procedure for more than 8 weeks. The reasons may be the following:
- Increased uterine tone.
- Threat of miscarriage.
- Placental insufficiency.
- Mild toxicosis.
- The formation of the placenta is disrupted.
To improve blood circulation during pregnancy and lactation, the use of electrophoresis is considered the most gentle and optimal option.
Carrying out electrophoresis at home
To carry out the procedure at home, you need to purchase a device with all the additional elements and a solvent (saline solution) to which certain medications will be added.
Before using the device, you should consult a doctor who is monitoring the condition of the pregnant woman. He must explain to the expectant mother how to properly carry out the procedure in order to minimize the harmful effects of current and medications on the child.
To summarize, we can say that pregnant women can receive a procedure such as electrophoresis. However, during all manipulations you should be careful and strictly follow the instructions so as not to harm the child.
Main contraindications
It should be taken into account in which cases the use of electrophoresis during pregnancy is contraindicated:
- The occurrence of toxicosis in the later stages of pregnancy with seizures.
- Impaired kidney function.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Blood clotting levels are below normal.
- Risk of bleeding.
- Damage to the skin at the site where the bandage was applied.
- Drug intolerance.
- The condition of the fetus is cause for concern.
The doctor takes into account contraindications when prescribing the procedure. It is also necessary to discuss possible side effects of treatment with the expectant mother.
The following undesirable effects may occur:
- Allergic reaction to a drug.
- Redness of the skin at the application site.
- Itching.
- Slight swelling at the site of contact of the electrode with the skin.
- A slight increase in body temperature of a local nature.
- Pinching or tingling during the procedure at the site where the electrodes are applied.
Upon completion of the course of treatment, side effects quickly disappear. Allergic manifestations are relieved with antihistamines. In case of severe reactions, the doctor may cancel the procedure.
Electrophoresis can be replaced with an even more gentle option - galvanophoresis. In this case, even less current is used. The possibility of side effects is zero.
How is the electrophoresis procedure performed in pregnant women?
The use of electrophoresis during pregnancy does not harm the fetus. How does the treatment process work? The algorithm is as follows:
- A device with two electrodes is used. One is negative and the other is positive.
- Fabric dressings are treated with a drug. It is prescribed by a doctor taking into account the patient’s diagnosis.
- The solution is preheated to body temperature.
- Apply to the place where the pathological process is localized.
- A pregnant woman has one electrode placed on her stomach and the other on the opposite side.
- The electrodes are placed over the bandage, secured with a weight and covered with a diaper.
- Pass a small electric current.
With this effect, the drug is retained in the subcutaneous layer. Long-term electrophoresis provides good penetration and therapeutic effect. The toxic effect on the body is minimal.
Electrophoresis with a bath in which electrodes are built-in is also popular. It is filled with a solution containing medications. Then the required part of the body is immersed in water. This could be a leg, elbow or hand.
The cavity electrophoresis method is carried out as follows. One electrode is inserted into the organ cavity, and the other is placed on the surface in the area of development of the pathological process. Before this, a medicinal solution is injected into the cavity.
What drugs are used for electrophoresis during pregnancy?
Mechanism of current action and method of conduction
Using this procedure, medications penetrate into the body of the expectant mother in the form of ionized particles with a positive or negative charge. More than half of the dose of the drug accumulates in the subcutaneous tissue area, and then, leaving this area, is distributed to organs and tissues. This explains the fact that during electrophoresis, the medicine does not reach the pregnant woman in its entire volume at once, but gradually, over a certain period of time. It has a milder effect on both the expectant mother’s body and the fetus.
The electrophoresis procedure can only be carried out using a specialized apparatus. It generates a current of a given power. The medication itself must be dissolved in a bath filled with an isotonic sodium chloride solution heated to human body temperature. A special pad is impregnated with this solution and attached to the desired area of the body. And the electrodes are attached directly on top. The gaskets are fixed and covered with a clean cloth. When the device is turned on, pulses of electric current transfer medicinal ions into the body through the skin.
There are four main methods:
- Galvanic.
- Cavity.
- Interstitial.
- Vannochkovy.
Before the procedure, the doctor must explain to the pregnant woman in detail what electrophoresis for pregnant women is, why it is needed and what contraindications it has.
With vitamin B1
B vitamins are essential during pregnancy. With a lack of vitamins of this group, there may be a delay in the development of the nervous system and the general condition of the unborn child.
Electrophoresis with vitamin B1 is prescribed if:
- There is a danger of miscarriage.
- There were early miscarriages.
- Mild toxicosis.
When treating toxicosis, vitamin B1 is administered through the nose. The course of treatment is 5-10 days. You can repeat the course after a break of 2 weeks.
If electrophoresis with vitamin B1 is used to reduce uterine tone, electrodes are placed on the uterine area. Use a 6% solution for a course of 10 days. The duration of treatment can be changed according to the doctor's recommendation.
In what cases is Magnesia contraindicated for pregnant women?
Despite all the benefits of the drug, it is necessary to say about contraindications for its use:
- An overdose of magnesium is dangerous; it can lead to respiratory problems.
- Magnesia during pregnancy is contraindicated for low blood pressure; it can lead to weakness, drowsiness, headache, vomiting, sweating, anxiety, and speech disorders.
- Magnesium sulfate is incompatible with calcium supplements, is not used in the early stages of pregnancy, and is discontinued in the prenatal state.
With magnesia
It is permissible to prescribe magnesia to a pregnant woman only in the later stages, but not before childbirth. If you have the following symptoms:
- The threat of not carrying a child to term.
- Preeclampsia.
- Cramps.
- Swelling.
- Impaired kidney function.
- Blood pressure increases.
- There is a predisposition to thrombophlebitis.
- Lack of magnesium in the body.
- Epileptic seizures.
- Eclampsia.
How does magnesium act on a woman’s body:
- Relieves spasm of blood vessels.
- Normalizes blood pressure.
- Helps relax muscles.
- Eliminates cramps.
- Helps relieve swelling.
- Improves the outflow of excess fluid from the body.
- Helps improve general condition.
- Reduces increased uterine tone.
- Calms and relieves tension.
Electrophoresis with magnesium during pregnancy is most often used to eliminate uterine hypertonicity. The procedure is carried out as follows:
- A special bandage is moistened in a magnesium solution.
- It is applied to the woman’s uterine area.
- Cover with protective cloth.
- An electrode is placed.
- Cover with a diaper.
Magnesia also reduces the sensitivity of the uterus to the hormone oxytocin, which can contribute to premature birth.
The procedure lasts at least 10 minutes. Sessions are repeated every day. The course of treatment can be 10-14 days.
Features of treatment
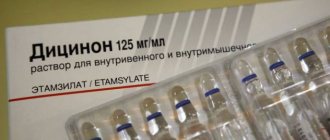
Magnesium sulfate during pregnancy is prescribed only by a doctor and only if there are direct indications for its use. It is worth noting that the drug is administered intravenously or intramuscularly, that is, droppers or injections are used.
Magnesia during pregnancy is prescribed intravenously in the form of droppers or injections, less often intramuscularly (due to the pain of the procedure)
Intravenously
Injections with magnesium are given when there is an urgent need to maintain a pregnancy. After intravenous administration, blood circulation increases, blood vessels dilate and, as a result, uterine hypertonicity is relieved (this is the diagnosis most often given to pregnant women).
The dosage of the drug is determined by the doctor based on the individual characteristics of the course of the disease and the body of the expectant mother, her age and weight. Magnesium sulfate is prescribed twice a day for early stages of nephropathy, four times a day for serious complications.
Intravenous magnesium is also administered using a dropper. A pregnant woman needs to be in a relaxed, reclining state. The procedure itself takes a long time, since the drug must enter the body in small doses and slowly.
The woman does not experience very pleasant sensations. With the rapid introduction of magnesium, the side effects only intensify. Increased heart rate, increased body temperature, shortness of breath, and sweating are observed.
Intramuscularly
Intramuscular injections of magnesium during pregnancy are quite rare. This is directly related to the peculiarities of the method of administration - it is quite painful. In addition, against the background of a general decrease in immunity, abscesses may form in expectant mothers after injections. Again, the dosage and duration of treatment will depend on the severity of the disease.
Magnesia injections during pregnancy have a number of features:
- the procedure is painful and unpleasant;
- incorrect administration of the drug is fraught with purulent processes;
- the solution for administration must be warm;
- syringes with a long needle are used;
- magnesium is introduced very slowly.
Pills
When tableted magnesium sulfate enters the intestines, it is not absorbed into the blood, so it only works in the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract) and has an exclusively laxative effect.
Magnesium sulfate is present in various vitamin preparations for pregnant women, but it has no effect on the smooth muscles of the uterus, and is useful only for replenishing magnesium deficiency, as well as as a sedative and laxative.
Powder
Magnesia is found quite often in powder form, but just like with magnesium sulfate tablets, only a laxative effect can be expected from the powder, since it is not absorbed by the intestines.
Magnesium sulfate powder is taken orally, dissolving it in a sufficient amount of water.
During pregnancy, the powder is prescribed in case of prolonged constipation, thereby enhancing intestinal motility and a mild laxative effect.
Electrophoresis
Sometimes, if it is necessary to influence a certain organ, expectant mothers are prescribed electrophoresis (simultaneous exposure to electric current and a substance) with magnesium. This treatment is practically painless, and the result is very noticeable.