Dilation and curettage , or colloquially curettage , is a medical procedure performed to remove a portion of tissue from the uterine cavity as a way to diagnose or treat certain conditions. This method can be used in case of severe uterine bleeding, removal of the upper layer of the mucous membrane after a miscarriage, as a method of artificial termination of pregnancy (abortion), although in this case more modern and safe alternatives are currently recommended by WHO. During the procedure, the doctor uses instruments or drugs (as a more modern and safer approach) to dilate the cervix or lower part of the uterus, and then surgical instruments to remove any necessary tissue.
Traditionally, dilation and curettage refers to dilation of the cervix and curettage of the walls of the uterus using a special sharp instrument called a curette or surgical spoon. But some sources consider the procedure in a broader sense, also including additional cleaning of the uterus using tissue suction - vacuum aspiration using an electric or manual pump. The method is selected depending on the condition of the tissue.
A little about physiology: the structure of the uterus
The uterus is the main organ of the female reproductive system, with the help of which it becomes possible to bear a child. It is hollow inside and unpaired. The uniqueness of the uterus is that, thanks to its muscular structure, it stretches very much, and after childbirth it returns to its original state.
Due to the extensibility of the ligaments, the uterus can change its position in the woman’s body relative to neighboring organs. In the absence of pregnancy, it is located between the bladder and rectum, in the lower abdomen. Many people feel pain during menstruation, so they know exactly where it is located.
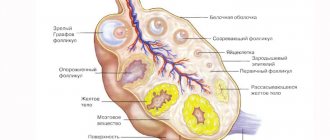
It is important to know the structure of the uterus. It consists of the body of this hollow organ and a narrow part - the neck. Doctors call the upper point of the uterus the fundus, and the isthmus is located between the cervix and the body. In its shape it resembles an inverted pear. The dimensions of the uterus outside pregnancy are small - length 7 cm, width 4 cm, and thickness 5 cm. In multiparous women, these parameters can be increased.
Possible diseases
But the origin and manifestation of precancerous conditions and cancer are similar. Many people call HPV one of the reasons. Thus, the presence of human papillomavirus in the body is not a guarantee that there will definitely be cancer. But those women who were diagnosed with precancerous conditions of the cervix were still diagnosed with HPV in 90% of cases. But it is necessary to understand that out of more than 60 types of this virus, about 20 affect the genitals, and 11 serotypes are considered highly oncogenic.
How the uterus changes during pregnancy in the first weeks
During early pregnancy, the uterus initially does not change much in size, it only changes its shape and density. You can notice a change in the size of the uterus only by the 6th week of pregnancy, that is, after 2 weeks of delay.
Structure of the uterus
The uterus consists of a body, an isthmus and a cervix, which directly passes into the vagina. The highest part of the uterine body is called the fundus. It is the location of the uterine fundus that is one of the mandatory indicators that the gynecologist monitors at every visit to a pregnant woman, starting from the second trimester, in order to determine how the uterus is growing.
The uterus consists of three layers: the inner layer is called the endometrium, the middle layer is the myometrium, and the outer layer is the perimeter. The condition of the endometrium changes depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle. If the egg is not fertilized, then menstruation occurs, and the endometrium is released from the uterus, the mucous membrane is renewed. If a fertilized egg is implanted in the uterine cavity, the endometrium undergoes changes and thickens to provide nutrition to the fetus.
The myometrium is the muscular layer of the uterus. In the early stages of pregnancy, the uterus enlarges due to the active division of muscle cells. The myometrium grows and thickens, and after the 20th week of pregnancy, the growth of the uterus occurs due to stretching of the muscle fibers. The walls of the uterus in the second half of pregnancy stretch, and their thickness naturally decreases. Therefore, it is dangerous to become pregnant with a scar on the uterus due to a recent cesarean section or other gynecological surgery, for example, removal of uterine fibroids. After all, the scar becomes thinner along with the entire wall of the uterus and can separate.
Size and shape of the uterus
The uterus is pear-shaped. In the early stages of pregnancy, some “loosening” of the structure and ligaments of the uterus occurs so that it can actively grow and stretch. First, the uterus acquires a spherical shape, and then begins to increase transversely.
In nulliparous women, the uterus before pregnancy has a length of about 7 cm, a width of 4 cm and a thickness of about 4-5 cm. In women who have given birth, these dimensions may be slightly increased, and the weight of the uterus is 20-30 g more. Also, the size of the uterus increases, and the shape changes if there are neoplasms in it.
How the uterus grows
In the first trimester of pregnancy, the uterus is located in the pelvis. By the 8th week of pregnancy, that is, by the 3-4th week of delay, the uterus doubles in size. At the beginning of pregnancy, asymmetrical enlargement of the uterus may be observed due to the fact that the attached fertilized egg is still very small compared to the entire volume of the reproductive organ.
If you imagine what the uterus looks like in the early stages of pregnancy, then in the second month it resembles a goose egg.
At the doctor
Before the 6th week of pregnancy, a doctor’s examination to diagnose an interesting position is practically useless, since changes in the size and shape of the uterus are too insignificant.
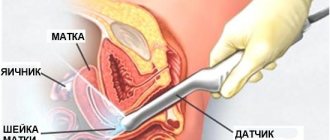
After 2 weeks of delay, the doctor can conduct an ultrasound examination of the uterus using a transvaginal sensor (at this time the heartbeat of the embryo will already be visible). In addition, changes in the uterus at this stage can be palpated. An experienced doctor can determine how enlarged the uterus is in the early stages of pregnancy by touch, and guess its duration.
In the early stages, the obstetrician-gynecologist conducts a bimanual examination. To do this, the doctor inserts the index and middle finger of the right hand into the vagina, and with his left hand he probes the uterus through the abdomen, gently pressing on the abdominal wall.
It is believed that it is better not to overuse frequent gynecological examinations during pregnancy, since the doctor’s actions can activate the contractile functions of the muscular layer of the uterus, which can threaten miscarriage. All the more harmful are frequent examinations for ICI, a pathology of the cervix that leads to its premature dilatation.
The notorious tone
Normally, the uterus should be soft during pregnancy. A woman should practically not feel the growth of the uterus or feel any discomfort.
If, in the early stages, nagging pain occurs, similar to the sensations at the beginning of menstruation, radiating to the lower back, uterine hypertonicity may have occurred. After the 12th week of gestation, if the uterus contracts, the woman herself may feel a hard ball in the lower abdomen.
A toned uterus during early pregnancy does not always mean a threat of miscarriage. Tissue growth and physical activity can cause natural tension in the muscles of the reproductive organ. It is always worth telling your doctor about how you feel. But only severe cramping pain, especially accompanied by bloody or brownish discharge, requires drug treatment.
We must remember that doctors love to play it safe and prescribe a lot of medications to avoid miscarriage. Moderate nagging pain can be relieved by the normal daily routine and rest of the pregnant woman. Therefore, you should focus on your well-being. If it is satisfactory, most likely the pregnancy is not in danger.
The uterus (womb) is a pear-shaped reproductive hollow organ consisting of smooth muscles. Thanks to muscle activity, it is able to stretch and contract. In the last month of pregnancy, the uterus increases 5 times. Its shape and size depend on how the pregnancy progresses. Based on the condition of the uterus, tone and position relative to other organs, one can judge the development of the baby, as well as the threat to his life and development. What should you pay attention to, what symptoms indicate pathology of fetal development, how does the uterus change throughout pregnancy? The answer is given in this article.
Causes of erosions
— infectious diseases, among which the most common are chlamydia, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, ureaplasmosis, genital herpes, papillomavirus;
- inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs;
- mechanical damage to the mucous membrane;
As a result of the changes, the multilayered epithelium, the layers of which are poorly cohesive and loosely laid, is damaged in places and sloughs off. It has been observed that this occurs 5 times more often in women with menstrual irregularities, they may even have greater cervical erosion. Instead of the desquamated layer, columnar epithelium is formed.
Provoking factors include disruptions in the cycle, frequent changes of partners, early onset of sexual activity and reduced immunity. Many of those who have discovered these problems are interested in whether there are any restrictions if cervical erosion has been diagnosed. What cannot be done with this disease? There are no strict restrictions. It is important to simply see a gynecologist regularly, undergo all the necessary examinations and not refuse the prescribed treatment.
What is the uterus like during pregnancy?
The myometrium is the middle, muscular layer of the uterus, which consists of elastic fibers that can contract and stretch. It is this that changes throughout pregnancy, adapting to the size and position of the baby. The myometrium is heterogeneous in structure, which ensures contractility: a powerful vascular layer is responsible for feeding the organ, subserous muscle fibers are located lengthwise and in a circle, and the submucosal layer also consists of longitudinal fibrous formations. The hormones progesterone and estrogen contribute to the elasticity of the uterine walls and the stretching of the myometrium. It increases not only in length, but also in volume, due to which the uterus during pregnancy takes on a round shape instead of a pear-shaped one.
In addition to the myometrium, changes occur in the inner layer lining the uterine cavity - the endometrium. It is a loose mucous surface to which the embryo is attached. During the 1st trimester of pregnancy, the thickness of the endometrium changes from 8-10 mm to 20 mm. Until the placenta is formed, it protects and nourishes the embryo.
The perimeter, or layer made up of connective tissue, also changes. Being a continuation of the bladder, under the weight of the fetus it lowers slightly and moves forward. This causes frequent urination as well as problems with bowel movements.
Inspection
During pregnancy, the uterus is a “house” for the child, in which he lives from the moment of conception until birth. His condition depends on the course of pregnancy and the due date of the baby. Various uterine pathologies lead to premature birth or miscarriage. For this reason, the woman undergoes several visual examinations of the uterus.
- The first examination of the uterus during pregnancy is carried out at 8-14 weeks. Usually by this moment a woman knows that she is expecting a baby and decides exactly what she will give birth to and register. The first thing they do is send her for an ultrasound to make sure there is no ectopic pregnancy. The doctor examines the uterine cavity and makes sure that the embryo has implanted in the endometrial layer. The number of fetuses in a pregnant woman is also specified, because multiple births require a completely different type of support. Uterine pathologies are also detected. If there is uterine fibroid, the doctor determines how much it will affect the pregnancy and whether it needs to be removed. If there are significant problems, the woman is offered to terminate the pregnancy. At a later date, interruption has more serious consequences and complications.
- The second examination is done at 20-22 weeks. At this stage of pregnancy, the condition of the uterine walls, appendages and cervix is checked. A woman may be diagnosed with cervical insufficiency - a disorder consisting in its too short length. This means that it is impossible to cope with the increasing load caused by the increase in fetal weight. A pregnant woman's risk of spontaneous miscarriage increases. Also, due to hormonal changes, a woman may increase the thickness of the myometrium along the anterior or posterior wall.
- The third examination is done after 32 weeks of pregnancy. A child can be born at any moment. An ultrasound examination shows the amount of amniotic fluid, the condition of the placenta and uterine tone.
The uterus during pregnancy feels to the touch in the early stages
In case of pregnancy, when visiting the antenatal clinic, uterine pulpation is required. It helps to identify problems that are not always possible to see using an ultrasound machine. Using his fingers, the gynecologist identifies two important indicators: softness and mobility of the womb. In the absence of one or the other, we can talk about a problem that will become an obstacle to bearing a child. Also, feeling the uterus will help reveal the following picture:
- External changes in the uterus are observed from the 5th week of pregnancy. If before conception it was pear-shaped, then with the implantation of the embryo it takes on a rounded shape. The doctor can determine the shape and size of the uterus by touch;
- The structure of the tissue changes, it becomes more loose. It feels good when touched. The hormone progesterone, the amount of which increases noticeably during pregnancy, relaxes the muscles of the uterus, making its surface soft and pliable. It makes the endometrial layer looser so that the uterine muscles cannot push out the embryo. In the case when the womb is hard to the touch, we are talking about hypertonicity and the threat of miscarriage;
- in the early stages the uterus remains mobile. When palpated, it is able to deviate in different directions, which indicates its mobility. If there is none, the question arises about adhesions in the body during pregnancy, when for some reason the walls of the uterus fuse with neighboring organs;
- a special sign of pregnancy is the Horwitz-Gerard symptom: during manual examination, the fingers close smoothly at the isthmus;
- up to 10 weeks, Piskacek’s sign is observed: at the site of embryo implantation, the uterine wall protrudes slightly;
- Snegirev’s method is used: when pressing on the uterus, it reacts by hardening and contracting, and then becomes soft again, regaining its original size;
Information Pulpation of the uterus in the early stages of pregnancy is mandatory because it gives the doctor answers to many questions no worse than an examination with an ultrasound machine.
Shortened uterus during pregnancy
Poor pregnancy prognosis is made if some parameters of the uterus are less than expected. This pathology is uterine hypoplasia - insufficient development of the organ, as a result of which its size is reduced. However, the presence of hypoplasia does not mean that a woman will not be able to bear and give birth to a healthy child. A woman may not know about the disease until childbirth, if it does not affect the course of pregnancy. Hypoplasia occurs in adolescence as a result of hormonal imbalance, but is sometimes congenital.
Additionally, the problem of shortening the cervix during pregnancy is much more common. In a non-pregnant woman, it is 2.7-3 cm, but after conception the cervix stretches. The reduction in length leads to the fact that the neck is not able to withstand the increasing load. If measures are not taken, the cervix will open and spontaneous labor will begin (or miscarriage in the early stages).
Alternative medicine
Some are starting to look for alternative methods. The most popular are douching with a diluted infusion of calendula (1 tsp in ¼ glass of water), eucalyptus (1 tsp diluted in a glass of water), tampons with sea buckthorn oil or mummy.
But these are not all the options for how the cervix can be treated with folk remedies. Some healers recommend brewing St. John's wort for douching at the rate of 1 tbsp. l. for a half-liter jar of boiling water. The herb must be boiled for about 10 minutes and infused for at least half an hour.
If you decide to refuse qualified help and are treated with the indicated methods, then regularly visit a gynecologist in order to monitor the condition of the cervix. This is the only way to see the deterioration in time and try to correct the situation.
In the cervix
various processes arise that involve both its vaginal part and the mucous membrane of the cervical canal (cervical canal).
When making morphological diagnostics,
one should take into account the functional nature of changes in the epithelium and stroma that occur in connection with changing phases of the menstrual cycle. In the proliferative phase of the menstrual cycle, the stratified squamous epithelium of the ectocervix reaches its greatest thickness; the cells of the intermediate and functional layers are rich in glycogen. The prismatic epithelium of the endocervix is high, with a basal arrangement of nuclei; mucus is detected in the cytoplasm. Reserve cells are rare and are in a state of rest.
In the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle
rejection of the surface cells of the functional layer of the stratified squamous epithelium begins, especially above the high connective tissue papillae of the subepithelial tissue. Increased mitotic activity is noted in the basal layer. In the epithelium of the endocervix, a large number of proliferating reserve cells are found with the formation of 2-3-row and multilayer layers, intra-epithelial glandular structures. On the part of the prismatic epithelium, migration of nuclei to the center of cells and increased mucus formation are noted.
In the stroma of the mucous membrane
In the ecto- and endocervix there are accumulations of lymphoid cells, histiocytes, and “mast” cells. In the desquamative and regenerative phases of the menstrual cycle, desquamation of most of the cells of the functional and intermediate layers of multilayered squamous epithelium is observed; loosening of the basement membrane; infiltration of interstitial tissue with lymphoid and histiocytic elements. In the prismatic epithelium of the endocervix, the amount of mucus decreases, the cells decrease in size, and the nuclei are located basally. There is no hyperplasia of reserve cells.
Border of stratified squamous epithelium
The vaginal part and the prismatic epithelium of the endocervix is most often located at the external uterine os, but it can be shifted both towards the vaginal part and the endocervix. They judge the border of the so-called last cervical gland [Burghardt, 1984], which is, as it were, its marker. Multilayered squamous epithelium found in the area of ectopia and endocervicosis, according to Burghardt, is always metaplastic.
Cambial elements
The stratified squamous epithelium of the ectocervix, due to which its regeneration occurs, are the basal cells of the prismatic epithelium - reserve cells. Reserve cells are pluripotent and, in the process of proliferation, can form both glandular structures and metaplastic multilayered squamous epithelium. The latter, at the ultrastructural level, differs from true multilayered squamous epithelium in the nature of intercellular contacts and cytoskeleton. Reserve cells in the prismatic epithelium of the endocervix are found inconsistently; there are many of them in the cervix of newborns and infants.
In women during puberty
they appear in significant quantities in the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle, in the first half of pregnancy and with various dyshormonal disorders. All this must be taken into account when interpreting a particular pathological process.
In classification
There is no clear division into background, pre-tumor and tumor processes. The dedicated heading “Tumor-like changes” essentially includes background processes. Moreover, it presents both nosological forms and fragments of pathological changes that occur in various background diseases and in normal conditions. For example, metaplasia into stratified squamous epithelium can be observed in the area of endocervicosis, polyps, and it also occurs in the cervical canal during pregnancy, with hormonal disorders and hormone therapy. Thus, this process has no independent meaning; it is always associated with something, being an expression of either a norm or part of a pathological process.
Occurring in the cervix
lesions are ambiguous regarding progression to malignancy, so they should be divided into background processes, premalignant changes and tumors.
Enlarged
In some cases, the uterus becomes enlarged during pregnancy. In the 2nd and 3rd trimesters this is not so important, and by the time of birth the situation returns to normal. At the initial stage of pregnancy, an enlarged uterus indicates some pathologies. These include:
- uterine fibroids. Myoma is a benign tumor that develops in the myometrium. It thickens the uterine wall, and even without being pregnant, the organ increases slightly in size. During pregnancy, fibroids can either grow or shrink. In the first case, the size of the uterus will exceed the standard indicators characteristic of the size of the organ at a given period.
- endometrial polyps. These are benign neoplasms on the inner surface of the uterine cavity. It is believed that with endometrial polyps or endometriosis, the embryo will not be able to attach to the wall, but sometimes this happens. In this case, the size of the uterus during pregnancy will be higher than normal.
- polyhydramnios. This phenomenon is typical for a later period, starting from the 20th week. The walls of the uterus stretch, the size of the organ increases. Polyhydramnios is dangerous due to placental abruption and the onset of premature labor.
- inflammatory process. With inflammation, the tissues swell and the uterus increases in size. Causes may include infections, trauma (scars from surgery or abortion), and autoimmune diseases.
Why is dilation and curettage performed?
Curettage can be performed for a number of reasons. They are prescribed to remove parts of the placenta after birth or to remove some tissue from the uterus during an abortion or after a miscarriage, thereby preventing heavy bleeding and infection.
This procedure is used to diagnose or treat abnormal bleeding or to diagnose conditions such as hormonal imbalances, polyps, fibroids, uterine cancer, or endometriosis. After the abnormal cells are removed, they are examined to determine the cause of the symptoms the patient is experiencing.
For artificial termination of pregnancy, curettage is used in the first and second trimester, which is permitted in Russia and still remains the main method of abortion. But today WHO recommends replacing this procedure with safer ones, such as vacuum aspiration or medical abortion.
Pregnant woman's tone
Increased uterine tone during pregnancy is the main cause of miscarriages and premature births. It is caused by various reasons, the most common of which are:
- hormonal deficiency. The lack of progesterone, which is responsible for muscle relaxation, leads to the fact that the uterus, being a muscle, does not relax during pregnancy. She perceives the attached embryo as a foreign body and pushes it out, causing muscle contractions. To preserve the fetus, the woman is prescribed special hormonal medications;
- stressful situations. During stress, adrenal hormones release adrenaline, which puts the body on alert. Blood flow increases, heart rate increases, muscle tone increases, including uterine tone. Adrenaline blocks the production of progesterone, which is responsible for relaxation. During pregnancy there is a risk of miscarriage. This is why a pregnant woman needs peace and only positive emotions;
- structural changes. Multiple uterine fibroids, detected in an advanced state, make the structure of the walls heterogeneous, causing involuntary contractions. With small node sizes, pregnancy proceeds safely;
- polyhydramnios and multiple pregnancies. After 20 weeks, the uterus increases in size only due to stretching of the wall. Despite the fact that muscle fibers can stretch several dozen times, they have a limited resource. Excessive load provokes overstrain of the uterus;
- past infections and viruses. During illness, the body works at an increased rate, body temperature increases, which leads to muscle spasms. Blood clotting increases, and blood supply to the uterus becomes difficult. All this leads to hypertonicity;
- After an abortion, a scar remains on the uterus , which does not completely dissolve. It causes uterine contractions, causing miscarriage;
Causes and signs of expansion
An enlarged uterine cavity often does not manifest itself at all. A similar phenomenon can be detected by a gynecologist or doctor during an ultrasound examination. When the uterus expands, a woman notes the following symptoms:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- urinary incontinence;
- bloating;
- constipation;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- painful menstruation;
- bleeding not associated with menstruation;
- rapid weight gain;
- engorgement of the mammary glands;
- headache.
If you take a blood test against the background of uterine bleeding, a sharp decrease in hemoglobin concentration will be recorded.
The described symptoms may indicate the presence of a serious pathology. To identify a gynecological disorder or another less dangerous cause, competent differential diagnosis is necessary. If several of the described signs appear, you should immediately contact a gynecologist.
Dilation of the uterine cavity is an ambiguous symptom that may indicate both pregnancy and the development of pathology.
After menstruation
Hormones affect the female reproductive system by regulating the menstrual cycle. Progesterone and estrogen are responsible for the cyclicity of menstruation. When blood is released, the endometrial layer of the uterus is rejected. When menstruation ends, the endometrium begins to grow, gradually loosening. This explains the slight expansion of the organ cavity.
Premenopausal
In the process of extinction of reproductive function, the functioning of the reproductive system ends. The concentration of estrogen decreases, a change in the regulation of the functioning of the uterine mucosa occurs, which sometimes leads to hyperplasia, serozometra. The uterine cavity can be expanded due to fibroids and endometriosis.
Endometriosis
An increase in uterine parameters may indicate a hormonal and immune disorder, which results in endometriosis. This disease is accompanied by the growth of the internal uterine layer onto the fallopian tubes, ovaries, and abdominal walls. When the process affects only the uterine cavity, adenomyosis is diagnosed.
Symptoms of endometriosis include:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- disruption of menstrual cycles;
- brown discharge;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- inability to conceive.
The disease can provoke the degeneration of cellular structures, which causes the growth of malignant tumors.
Myoma
The reason that affects the expansion of the uterine cavity may be a benign inclusion - fibroids. The pathology occurs due to hormonal imbalance and is often diagnosed during menopause.
According to research conducted by scientists from the USA, it was found that 80% of all fibroids are diagnosed in women under 50 years of age.
The tumor begins to grow in the muscle layer. Small formations do not affect the size of the uterus, while fibroids reaching 3 centimeters initiate expansion of the cavity.
Complications of the pathology include infertility and inability to carry a pregnancy to term. Although the tumor does not become malignant, large tumors must be removed.
Cancer
The reason for the enlargement of the uterus is the development of cancerous tumors, and the expansion of the cavity is one of the characteristic manifestations. Women with excess weight, polycystic disease, and nulliparous representatives of the fair sex are at risk.
Inflammatory processes
Inflammatory phenomena in the pelvis can cause expansion of the uterine cavity. The pathological process is manifested by menstrual dysfunction and increased body temperature.
With inflammation, the endometrial layer grows incorrectly, which causes the organ to enlarge. The consequences of the disease include:
- hormonal imbalance;
- bleeding;
- infertility;
- anemia.
Therapy of the inflammatory process is based on taking antibacterial drugs and immunomodulatory agents.
The uterus is displaced to the left or right during pregnancy
Lateroversion is a significant displacement of the uterus to the right or left. In the 2nd and 3rd trimesters, this can be caused by a change in the position of the fetus, and therefore does not pose a threat to the baby and the expectant mother. In the early stages of pregnancy, lateroversion in most cases indicates an inflammatory process in the pelvic organs. The womb deviates to the left if the right appendage is inflamed, there is a cyst on the right ovary. The organ tilts to the right when inflammation occurs in the ovary or fallopian tubes, located on the left side of the body.
Additionally, fibroids on the right or left wall of the uterus also lead to displacement of the organ to the side. The same thing happens during adhesions. As a result of inflammation, the wall of the uterus becomes fused with a nearby organ, for example, the intestines or bladder. The problem must be eliminated before pregnancy, because it will prevent the fetus from fully developing.
Any pain in the lower abdomen causes anxiety or even panic in a pregnant woman. Of course, there shouldn’t be any painful sensations, pregnancy is not a disease. But in some cases the pain is false. During normal pregnancy, the uterus moves slightly forward, putting pressure on the bladder. With cystitis, pain is observed, which a woman in labor may mistake for uterine pain. In later stages, when the bottom drops, the intestines are compressed. Considering that progesterone also relaxes its smooth muscles, its peristalsis is disrupted, which leads to gas formation. An expectant mother may be mistaken, mistaking abdominal bloating for gynecological pain in the uterus.
Information It is important for a pregnant woman to eat right, limiting herself to sweets (causes constipation), starchy foods (promotes gas formation), spicy and salty foods (provokes dysbacteriosis). You should also give up previous physical activity, because tension in the ligaments that hold the uterus in an upright position leads to pain.
If a woman has sexual relations during pregnancy, uterine pain that occurs after it suggests that she should limit herself in lovemaking and be sure to consult a doctor. The uterus hurts with hypertonicity, it is relieved with hormonal drugs. Of particular danger are pains accompanied by bleeding and cramps in the lower abdomen. If the pain resembles menstrual pain in nature and intensity, this indicates a serious problem.
When is the uterus sutured during pregnancy?
If the expectant mother has a too short cervix (isthmic-cervical insufficiency), hypertonicity or organ injury, then she undergoes the procedure of suturing the cervix. Surgery is performed only if the risk of miscarriage is too high. It is usually performed from 12 to 25 weeks of pregnancy.
Information The operation to suture the neck with lavsan or nylon thread is performed under general anesthesia in the hospital; it lasts no more than 15 minutes. A pregnant patient spends the day under the supervision of doctors, then goes home. After the operation, she takes antibiotics, and any exercise is contraindicated for her. Before giving birth at 37 weeks, the sutures are removed completely without anesthesia.
Diagnostics of background processes
On examination, pseudo-erosion looks like a red spot of irregular shape. It stands out against the background of pale mucous membrane. When performing a colposcopy, it becomes clear that the problem areas are covered with red papillae of a round or oblong shape, because of which the surface looks like velvet. You shouldn’t be afraid of colposcopy, it’s just an examination using a special device that can enlarge the area 30-40 times.
Diagnosis of a disease such as leukoplakia is also not difficult. In some patients, the keratinized layers of cells are visible to the naked eye; they appear as white plaques that rise on the ectocervix (the part of the cervix that protrudes into the vagina). In others, they can only be detected during colposcopy. To clarify the diagnosis, cervical tissue can be treated with iodine solution. The affected keratinized areas do not turn brown; they look like a surface covered with a whitish film. To determine the nature of leukoplakia (simple or with atypical cells), a biopsy is necessary.
Also, during examination, the gynecologist may see cysts on the cervix. The reasons for their appearance are as follows:
- sexually transmitted infections that provoke the development of inflammatory diseases;
- injury to the cervix during childbirth, abortion, diagnostic curettage;
Cysts look like sacs filled with mucus. They arise from the nabothian glands, which appear as small white swellings. If there are malfunctions in their work, the ducts close. In the case when only one sac is visible upon examination, it is called an endometriotic cyst. But there are times when there are several of them. In such situations, the doctor says that these are Nabothian cysts on the cervix. It is advisable to find out the reasons for their occurrence. After all, their appearance can be caused by infections that need to be treated. As a rule, doctors recommend only one treatment method - removal of cysts. This is done by puncturing the sac, removing viscous mucus and treating the place where it appears.
Tingling in the uterus during pregnancy
Tingling in the uterine area is observed throughout pregnancy. In general, this is normal if the tingling is not too intense and its duration does not exceed 1 minute. Each trimester has specific reasons for the occurrence of unusual sensations.
- In the 1st trimester, tingling is associated with physiological changes associated with implantation of the embryo into the uterine cavity. In the first month, tingling occurs when a pregnant woman sneezes, coughs, or lifts her bag. Muscles relax under the influence of progesterone, and any tension causes unusual sensations. If they are not intense and long lasting, you should not pay attention to them. The uterus changes shape, becomes rounded, and moves forward. Girls with a weak muscle corset feel stretching of the peritoneum, which is also accompanied by a slight tingling sensation.
- In the 2nd trimester of pregnancy, tingling in the uterus is usually associated with the fact that the rapidly growing womb begins to put pressure on neighboring organs, intestines and stomach. This is normal, but quite unpleasant. The only way to avoid discomfort is a special diet for expectant mothers, containing fiber, which helps prevent food stagnation and timely bowel movements.
- In the 3rd semester, tingling is caused by natural hypertonicity of the uterus, which begins at the 35th week of pregnancy and prepares the body of the expectant mother for childbirth. The gradually softening and shortening of the cervix may also tingle. Over a long period of time, the discomfort is especially pronounced.
Contact your doctor immediately if:
- There are visible blood spots on the underwear, and the tingling sensation is quite intense and prolonged
- During pregnancy, the uterus is in good shape and even contracts slightly
- it hurts to go to the toilet (perhaps a genitourinary infection has worsened)
- diarrhea, vomiting, dizziness began
- tingling turns into severe cutting pain
How to determine whether the uterine cavity is dilated?
Dilatation of the cervix or the uterus itself is diagnosed through several studies. As part of a preventive or diagnostic examination, the following may be prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- Ultrasound of the ovaries;
- Ultrasound of the uterus and fallopian tubes;
- CT organ.
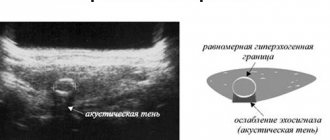
Uterus on ultrasound
Using an ultrasound, it is easy to determine whether there are problems with the reproductive organ or whether the cause of enlargement is the monthly menstruation period. But not only ultrasound is prescribed to patients; if indicated, the gynecologist can prescribe a CT scan of the organ.
Enlargement of the reproductive organ should not be considered a pathology, since there are a number of reasons that have no connection with diseases, but are a consequence of the natural state of the woman’s body.
But dilation of the uterine cavity can be asymptomatic; signs of the disease appear only when the phenomenon has a certain connection with the pathology and is diagnosed against its background.
What to do if dilation is visible on ultrasound:
- Contact a gynecologist.
- Carry out a number of additional diagnostic procedures.
- Do an ultrasound on another day of the cycle.
All this will help confirm or refute the accuracy of the diagnosis and identify the pathology that caused this phenomenon.
Pulls the uterus during pregnancy
Many pregnant women complain of a pulling sensation in the lower abdomen, similar to what occurs before the onset of menstruation. If this does not last long and does not cause pain radiating to the lower back, then there is no need to worry. Only jerky sensations during pregnancy, accompanied by bleeding, should cause alarm. To relieve discomfort, doctors prescribe medications with magnesium, which reduce muscle contractility.
Information The fact is that a fertilized egg, a zygote, is perceived by the body as a foreign body and is pushed out in every possible way. But at the same time, hormonal levels and reduced immunity do not allow one to get rid of the emerging life. It is the “struggle” for existence that causes short-term nagging unpleasant sensations just above the pubis. In addition, the epithelium at the site of attachment of the embryo is cleared, which also does not go unnoticed. If the uterus is slightly pulled, then this is normal, but if it contracts strongly, this means a threat of miscarriage.
Possible complications
One of the factors leading to pregnancy complications is cesarean section. Or rather, not so much the operation itself, but the insufficient recovery time from the moment it was performed. It is believed that at least three years must pass for the sutures on the uterus to completely dissolve. If a woman becomes pregnant within 1 year after the operation, the sutures will not heal and the walls will simply separate under the weight of the fetus. Uterine rupture will lead to the death of not only the fetus, but also the mother.
After surgery on the uterus (removal of fibroids), the woman is also given a recovery period. But usually the myomatous node is removed by enucleation without cutting the organ, and after surgery the patient undergoes a course of hormonal therapy. She artificially stops ovulation, which promotes rapid fusion of tissues and resorption of sutures. If the outcome of the operation is favorable, after six months the ultrasound machine will show virtually no traces on the walls of the uterus. But even in this case, in order to avoid organ rupture, it is not recommended to become pregnant for 1.5-2 years.
Additionally, uterine fibroids also complicate pregnancy. Particularly dangerous is a node located inside the uterine cavity. In this case, the likelihood of placental abruption increases, as well as premature birth due to lack of space for the development of the child. This also applies to tumors located on the outer wall. The larger the node, the higher the likelihood of an unfavorable course of pregnancy. But do not forget that each case is unique, and the outcome depends on many factors.
A common problem is instico-cervical insufficiency, when the length of the cervix poses a threat to pregnancy and must be sutured. Otherwise, it may be revealed.
Possible ways to get rid of the problem
Treatment tactics directly depend on the degree of dysplasia that was diagnosed. Thus, in the first stage, it is often recommended to simply observe the tissues over time and carry out conservative treatment, which is aimed at eliminating the possible cause of the disease. As a rule, antiviral or antibacterial therapy is carried out to eliminate infectious agents. In the absence of positive dynamics, as well as in cases where dysplasia of the 2nd or 3rd degree was immediately diagnosed, surgical treatment is recommended.