Forms of polycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic disease can be primary or secondary:
- With primary polycystic disease, symptoms will appear already in adolescence. This happens when the girl turns 12-13 years old. Therapy will be difficult, the course of the disease will be severe.
- The secondary form of the disease develops in adult women who have undergone childbirth or entered menopause. The disease is accompanied by metabolic disruptions in the body, increased body weight, and insulin surges, which is caused by disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas.
Regardless of what form of the disease a woman has, she will not be able to give birth until she is cured. Therapy boils down to the prescription of hormonal drugs. Sometimes surgery is required.
Causes of polycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic disease can develop for the following reasons:
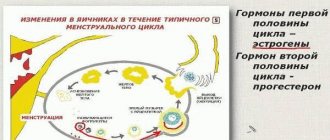
- Hormonal disbalance. In this case, the woman develops follicular cysts. They are a consequence of disruption of the endocrine glands. Moreover, the pancreas, thyroid or adrenal glands, pituitary gland, or hypothalamus can fail. Often, polycystic disease develops against the background of increased levels of insulin in the blood due to pathologies of the pancreas. When there is a lot of insulin in the body, this affects the functioning of the adrenal glands, which begin to produce androgen in excess quantities (male sex hormone). A shift in the balance between androgens and estrogens occurs in the body, which becomes the basis for the development of polycystic disease.
- Infectious diseases.
Frequent colds suffered in childhood, as well as severe infections in an adult woman, can become the basis for the development of polycystic disease. At a doctor's appointment, it is often possible to establish a connection between polycystic disease and tonsillitis, since the tonsils and ovaries have a certain dependence on each other.
- Hereditary factor.
It has been established that the disease can be transmitted at the genetic level.
- Emotional turmoil.
A number of experts are of the opinion that polycystic disease may be the result of stress.
Symptoms of polycystic disease
The main symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome:
- Menstrual irregularities.
Menstrual irregularities are observed in all women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Sometimes they are absent altogether, and sometimes they occur with a delay. There is no regularity of the cycle. If a woman has periods 9 times a year or less, then this is a reason for examination. When menstruation does not occur on time, this is the first sign that the egg in the body is not maturing. Although sometimes menstruation may be absent for other reasons. Among these: inflammation of the genital organs, polycystic uterus. Therefore, the patient requires a comprehensive examination to make the correct diagnosis.
- Lack of pregnancy.
A woman with polycystic disease cannot become pregnant. For conception to occur, long-term treatment will be required.
- Excess of male sex hormones.
Often, with polycystic disease, a woman has an increased level of androgens in her body. This causes the patient to begin to develop male sexual characteristics, for example, excess hair growth, acne on the face, back and chest, and male pattern alopecia.
- Overweight.
In women with polycystic disease, their body weight begins to increase. Moreover, the increase is quite noticeable. It is 10-15 kg. Therefore, treatment of polycystic disease is always aimed, among other things, at weight loss, since it is problematic for obese women to get pregnant.
- Pain in the ovaries.
Polycystic disease can manifest itself as nagging pain in the lower abdomen. However, most patients do not pay attention to this symptom.
The benefits of vitamins and diets
If you have excess weight, then you should lose it. Choose a diet for yourself. It is necessary that the diet in it be completely balanced. You can’t trust “fantastic star secrets for weight loss.” They often do not spare the body and exhaust it. Therefore, you will either lose weight quickly, but you will still immediately gain weight, and even gain something that was not there before. Or the achieved result will not be enough. Both options are not suitable. For success you need proper nutrition, which can help you lose weight with a balanced diet.
Polycystic disease and pregnancy
Women with polycystic disease cannot get pregnant because they have too many male sex hormones in their bodies. Therefore, in order for conception to occur, efforts must be made to reduce them.
If hormonal therapy does not achieve the desired results, the woman is referred for surgery. It is performed using laparoscopic equipment.
Provided that none of the listed methods succeeded in achieving conception, the patient is indicated for IVF.
Example from practice.
I have been seeing a woman with polycystic disease for a long time. The diagnosis was confirmed by ultrasound and laboratory data. Until a certain time, she believed that she could get pregnant herself as soon as she wanted it. However, by the age of 30, she realized that her attempts to conceive were unsuccessful and sought help. After 3 months of hormonal therapy (she refused long-term treatment), I prescribed Clostilbegit. Pregnancy occurred in the first month. She took Duphaston for a long time, for 2 months. However, at the next examination it turned out that the pregnancy had stopped. I had to do a scraping. Then for 2 years the woman did not come to me for treatment. After this period, she appeared with the firm intention of undergoing laparoscopic intervention. She underwent surgery at a regional hospital. There she underwent laparoscopic ovarian resection. She became pregnant after 4 months. In general, the gestation period went well, and a healthy baby was born.
Laparoscopic examination
If there is a need to identify an additional cause of infertility (for example, obstruction of the fallopian tubes due to adhesions), as well as the advisability of surgery, laparoscopy is prescribed. This method involves inserting an optical endoscope with a microcamera into the abdominal cavity and examining the ovaries through it. Polycystic ovaries are large, and their capsule is dense and lumpy.
Using a laparoscope, simultaneously with diagnosis, the surgeon also performs a therapeutic intervention. The capsule of the glands is incised, which facilitates the exit of the follicle into the tubes, the adhesions are removed, and the growth of the internal uterine layer (endometrium) in the ovaries is cauterized.
Diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome
During the appointment, the doctor pays attention to such signs as:
- The patient's physique and excess weight.
- Type of hair growth.
- Skin pigmentation.
- The condition of the hair and dermis, their fat content.
- Condition of the mammary glands.
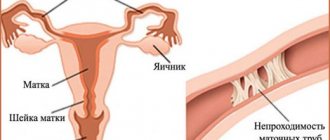
The doctor palpates the thyroid gland and abdomen and conducts a standard gynecological examination. The ovaries in women with polycystic disease are enlarged 2-3 times compared to the norm, and give off pain when pressed.
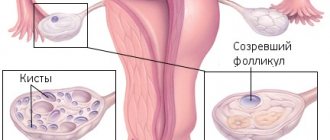
The diagnosis can be made based on ultrasound. Based on its results, it can be established that the ovaries in diameter exceed 9 cubic centimeters. In addition, several small cysts are always found. There may be more than 10 of them.
The ovaries are dense, surrounded by a white capsule. This can be visualized during laparoscopic examination.
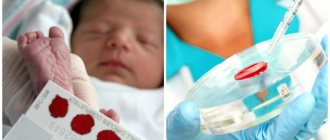
A woman suspected of having polycystic disease will definitely need to undergo a blood and urine test for hormones:
- The ratio of luteinizing hormone to follicle-stimulating hormone in polycystic disease is 3:1.
- Testosterone levels will be increased.
- Progesterone levels decrease in the second phase of the cycle.
- A high concentration of 17-KS is found in the urine.
Be sure to perform a study aimed at determining the level of insulin and glucose in the blood. Results may vary. In addition, with polycystic disease, high levels of fats in the blood are found.
Hyperplasia of the endometrium of the uterus is determined during diagnostic curettage, which is performed during uterine bleeding.
Some diseases have symptoms similar to polycystic disease. Such pathologies include: Cushing's disease, adrenogenital syndrome, excessive production of prolactin, androgen-producing tumors, etc. Therefore, it is so important to carry out a differential diagnosis with them.
Paraclinical methods
All abnormalities discovered by a doctor during a gynecological examination must be confirmed using ultrasound scanning and tomography.
Ultrasound for PCOS
To identify polycystic disease, the following criteria are taken into account:
- ovarian volume from 10 cm3 (both enlarged);
- follicles ranging in size from 2 to 9 mm, located closer to the outer layer;
- follicular formations (cysts) of at least 12 on both sides;
- dense capsule.
Polycystic ovary syndrome on ultrasound
A cyst is an enlarged follicle that initially grows, but at a certain stage of its development stops. It does not leave the ovary into the uterus, but remains under its dense capsule. Because of this, the glands are larger than usual, and their surface is lumpy.
Taking an MRI
The need for tomography arises if ultrasound cannot exclude a benign or malignant tumor formation. In all other cases, ultrasound scanning is usually sufficient.
Treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome
There is no quick way to get rid of polycystic ovary syndrome. A woman must prepare herself for long-term therapy. First, we need to focus our efforts on combating obesity.
Nutrition and physical activity
Adipose tissue produces both male and female sex hormones, which negatively affects the course of the disease.
Sometimes it happens that after stabilizing the weight, the menstrual cycle returns to normal. To get rid of excess weight, you will need to visit a nutritionist who will create a nutrition plan for a specific patient. It will be necessary to avoid spicy, spicy, fatty and salty foods. You cannot drink alcoholic beverages.
Sweets are completely excluded from the diet. It’s not enough to just follow a diet; you need to increase physical activity. Loads should not exhaust a woman; she needs to choose a sport that will bring her pleasure. This could be swimming, yoga, jogging, bodyflex.
Reversing Insulin Resistance
If a woman has insulin resistance, she is prescribed Metformin. This drug allows the body to process glucose and stabilize its level in the blood. At the same time, appetite decreases. Treatment lasts from 3 months to six months. Sometimes such therapy helps stabilize the menstrual cycle.
Normalization of the menstrual cycle
After the weight returns to normal, you need to focus your efforts on restoring your periods. For this, the patient is prescribed contraceptives, medications aimed at reducing the level of androgens in the body (Yarina, Zhanin, Diana-35, etc.). The course of treatment can last from six months or more.
To cope with hirsutism, use Veroshpiron or Flutamide.
It is important to remember that taking combined hormonal drugs doubles the risk of developing venous thromboembolism.
Ovulation stimulation
When the menstrual cycle is restored, you need to focus your efforts on stimulating ovulation. This is important for those women who want to conceive a child. For this purpose, the drug Clomiphene is prescribed, which has anti-estrogenic properties. When it is discontinued, the woman begins to actively produce FSH and LH, which stimulate follicle maturation and ovulation.
Clomiphene is prescribed from days 5 to 9 of the cycle. Its dosage is 0.05 g per day. The course of treatment should not last more than 3 months. If there is no effect, then the dose can be increased to 200 mg.
The danger of taking Clomiphene comes down to the risk of the formation of ovarian cysts, which can reach impressive sizes. When there is no effect of treatment, surgery is required.
Operation
In recent years, the operation has been performed using laparoscopic equipment. It is possible to perform wedge resection of the ovaries or electrical coagulation of ovarian cysts. The second option is a gentle intervention, since resection affects large areas of ovarian tissue.
It is necessary to take into account that the more time passes after the operation, the less chance of getting pregnant. The maximum ability to conceive is maintained in the first 3 months after the intervention. In a year it will be unlikely. The operation is indicated for women who suffer not only from polycystic ovary syndrome, but also from uterine endometrial hyperplasia.
Author of the article:
Lapikova Valentina Vladimirovna |
Gynecologist, reproductive specialist Education: Diploma in Obstetrics and Gynecology received from the Russian State Medical University of the Federal Agency for Health and Social Development (2010). In 2013, she completed her postgraduate studies at NIMU named after. N.I. Pirogova. Our authors
Preparing for a blood test for hormones
For the research results to be reliable, it is necessary:
- 3-5 days before blood tests, avoid taking hormones and medications that change their levels. To do this, you need to consult a gynecologist about treatment. You should also not use dietary supplements or herbal preparations. If a woman takes birth control pills, then blood is donated between the next cycles (menstrual break).
- Diet should not change significantly before the study. Therefore, the day before diagnosis, you should not overeat, drink alcohol, or start a new diet. In the evening, have a light dinner, and then drink only plain water before your visit to the laboratory. Break in meals – 8-12 hours.
- During the day it is not recommended: sports, sexual intercourse, stress loads. If there is an increase in temperature or a recent injury or surgery, then it is better to reschedule tests for polycystic disease to the next cycle.
The laboratory should be visited between 8 and 11 am. Before the visit, you should not smoke, engage in physical labor, or be nervous. This may affect the result. Since all repeated studies will be compared with the first indicators, they must be completed in one institution. Most often, the gynecologist prescribes an examination 3-4 days after the start of menstruation; in their absence, diagnosis is possible on any day.