Surgical treatment of cervical-cervical pathology requires preliminary preparation. Tests before cauterization of erosion on the cervix will help the doctor identify hidden infections that will lead to a complicated postoperative period. However, the main thing that needs to be done at the stage of preparation for cauterization is to exclude the possibility of malignant degeneration: precancerous changes in the cellular structures of the cervix and cervical canal cannot be treated with conventional methods. The doctor knows exactly what tests will be required. It is important to accurately follow the specialist’s recommendations in order to avoid postoperative problems and ensure rapid wound healing after cauterization of cervical erosion.
What tests need to be done before cauterization of cervical erosion and how to prepare for the procedure?
Before gynecological manipulations, including coagulation, it is necessary to undergo a series of examinations to exclude complications and identify contraindications to the procedure. If the examination reveals diseases for which cauterization cannot be performed, the procedure is postponed until recovery or replaced with another.
When is cauterization required?
Cervical erosion can be asymptomatic, so the doctor detects it during a visual examination or colposcopy. When diagnosing ectopia, the doctor prescribes a set of examinations and tests to decide on treatment methods.
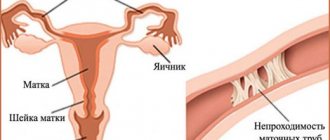
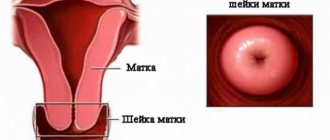
Erosion is the replacement of flat multilayered epithelium with cylindrical epithelium, which normally lines the cervical canal. In most cases, the squamous epithelium replaces the cylindrical epithelium without intervention, and the condition of the cervix is stabilized. If the pathology is asymptomatic and without complications, it can be left without treatment.
The following pathologies are called cervical erosion:
- ectopia - a round red spot, replacement of multilayer epithelium with cells of the cervical canal;
- ectropion - inversion of the cervix, violation of the anatomy of the organ, cicatricial deformity.
Erosive changes often cause sexually transmitted diseases, therefore, before cauterization of the cervix, a wide range of tests are taken to identify the infectious pathogen - which ones are chosen by the gynecologist depending on the symptoms.
In other cases, surgical reconstructive plastic surgery or cauterization is indicated:
- electrosurgical;
- cryosurgery;
- laser coagulation;
- chemical (pharmaceutical);
- thermocoagulation.
It is important to determine the causes of the development of the pathology and carefully examine the patient in order to determine more effective methods of therapy. Depending on the depth of the cervical lesion, conservative or surgical methods are chosen. For deep lesions and cancer, conization (surgical excision) is performed.
If there are indications for the procedure, it should not be postponed in order to prevent the development of complications and degeneration into a malignant formation.
Cauterization has the following characteristics:
- the process is painless, if necessary, the doctor will administer anesthesia;
- in 95% of cases the procedure eliminates the problem forever;
- no scars remain, reproductive function is not affected.
Contraindications to cauterization
If the defect progresses, becomes inflamed, or degenerates into neoplasms of a malignant or benign nature, in cases where conservative therapy does not help to cope with the problem, surgical or chemical coagulation is performed. In some cases, these manipulations are prohibited to avoid complications.
Cauterizing erosion is contraindicated if:
- inflammatory processes in the reproductive organs;
- infectious and fungal infections;
- bleeding;
- installed intrauterine device;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- blood clotting disorders;
- decompensated form of diabetes mellitus;
- psychological pathologies;
- pregnancy;
- oncology;
- installed pacemaker.
Before carrying out manipulations, it is important to conduct a full range of examinations in order to exclude a negative reaction and determine the need for preliminary treatment of existing diseases.
What studies are carried out before cauterization?
What tests and studies must be taken and completed before cauterization of erosion on the cervix:
- colposcopic examination with special devices;
- detailed biochemical blood test;
- determination of antibodies to HIV and hepatitis;
- urine analysis to detect inflammatory processes;
- a smear from the cervical canal for oncology or parts of the cervix for cytological examinations;
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs;
- taking anamnesis;
- bacteriological culture of vaginal and cervical mucus;
- testing for oncogenic HPV types;
- PCR method for detecting infections.
After receiving all, this gynecologist decides on the choice of coagulation method based on the patient’s age, birth history, pregnancies and stage of pathology.
Colposcopic examination of the cervix
Using a special device (colposcope), the doctor examines the cells on the cervix to determine their type and to identify pathological changes. Magnification of the examined area with a microscope by several tens of times allows the gynecologist to determine the course of the pathology.
Colposcopy lasts from 15 minutes to half an hour. Every patient must undergo this study before cauterizing erosion on the cervix in order to exclude pathological changes and oncology.
During an examination through a colposcope, the doctor may use vinegar and iodine to stain abnormal cells.
Bacterial culture
Opportunistic microorganisms can cause inflammatory processes on the cervix.
The PCR method is not able to detect such bacteria, so the gynecologist always prescribes bacterial culture as the most informative.
This analysis also determines the sensitivity of microorganisms to a class of antibiotics, which is important for determining the list of medications before cauterization of cervical erosion.
When diseases are detected, the gynecologist pre-treats them and prescribes repeat tests to confirm the success of therapy.
Additionally, a biopsy of a piece of the cervix is performed to exclude cancer. This procedure involves the collection of cells or tissues for diagnostic purposes. During the study, the cellular composition of the sample taken is determined.
There are two diagnostic methods:
- histological - examination of tissues under a microscope using chemical solutions;
- cytological - the study of cells, not tissues; in gynecology, a smear-imprint from the cervix is used.
An examination to identify pathological cells of precancerous and cancerous conditions is a mandatory analysis before cauterization of cervical erosion.
Blood analysis
The list of studies before treating a pathological area includes an extensive blood test in several areas:
- for AIDS;
- for syphilis;
- for hepatitis C and B.
A detailed blood test is also important for determining the general health of a woman and identifying inflammatory processes. An important nuance is not to donate blood for analysis during menstrual days.
PCR examination
Polymerase chain reaction is a research method for identifying sexually transmitted infections. If diseases are detected, it is necessary to undergo a course of treatment; the presence of untreated inflammatory processes is a contraindication to cauterization.
PCR tests before cauterization of erosion on the cervix can identify the following diseases:
- chlamydia;
- ureaplasmosis;
- gonorrhea;
- herpes;
- gardnerellosis;
- mycoplasmosis;
- human papillomavirus;
- violation of the vaginal microflora.
Ultrasonography
Ultrasound allows you to identify gynecological pathologies, confirm or refute the period of gestation. Pregnancy is a contraindication to the procedure, so ultrasound examination is an important and reliable method of determining it before treating cervical erosion using cauterization.
How to prepare for cauterization of cervical erosion
Before the procedure, gynecologists recommend adhering to the following rules:
- exclude sexual intercourse 2-3 days before surgery;
- It is better to carry out cauterization on an empty stomach;
- do not use tampons, vaginal products (douches, suppositories, creams) two weeks before the procedure;
- Avoid taking blood thinners;
- do not drink alcoholic beverages 3-5 days before cauterization;
- a week before your visit to the doctor, do not visit swimming pools or open water bodies.
If you follow the doctor's recommendations, the rehabilitation period is reduced and side effects are minimized.
The rehabilitation period after cauterization
The period for complete healing of the defect ranges from four to eight weeks. The shortest rehabilitation period is after radio wave or laser coagulation, it is one month. The recovery period depends on the patient’s health status and the individual characteristics of the body.
Discharge
During the first fourteen days after the procedure, natural discharge may increase. At first, there may be odorless bloody discharge, but after the cryoprocedure it is watery in nature.
Heavy bleeding is observed after treating the erosion with electric current, and after one to two weeks it gradually disappears.
Bloody discharge may be due to damage to healthy tissue, so this symptom requires a visit to a doctor and examination.
When to contact a gynecologist:
- bleeding is heavy or does not go away for more than two weeks;
- body temperature has risen;
- Fever or general deterioration in health appeared;
- the discharge changed color to serous, purulent, and an unpleasant odor appeared.
Painful sensations
Unpleasant pain in the lower abdomen after cauterization is normal. If the pain is pronounced or does not go away for more than a week after the procedure, you should consult a doctor. The presence or absence of painful sensations is individual and depends on the patient’s pain defect.
Recommendations for the rehabilitation period
For a month and a half after cauterization, gynecologists recommend adhering to the following rules:
- refrain from physical activity, do not lift weights exceeding 3 kg;
- During menstruation, the use of pads and tampons is prohibited;
- do not visit the bathhouse, swimming pools, jacuzzi, open reservoirs;
- do not have sexual intercourse without examination and permission from a doctor;
- don't get pregnant.
If you follow all the necessary recommendations of the gynecologist, the erosion will scar without complications.
Complications after cauterization of cervical erosion
Possible negative consequences after the procedure:
- cicatricial deformation, more often after high-frequency current;
- stenosis (narrowing) of the cervix after exposure to electric current;
- relapse occurs mainly when the patient does not follow the doctor’s recommendations or the human papillomavirus is activated;
- menstrual irregularities, more often after excision.
Complications often occur when personal hygiene and doctor’s recommendations are not followed.
A favorable outcome and the absence of complications during the rehabilitation period depend on high-quality preparation for surgery and a comprehensive examination to identify concomitant diseases.
The more thoroughly the patient is examined, the lower the risk of complications. 1-1.5 months after the procedure, gynecologists recommend coming to an appointment for a follow-up examination.
If signs of inflammation and complications are detected, the doctor prescribes repeat tests. The list of studies depends on the symptoms.
Source:
What tests need to be taken before cauterization of erosion?
Before starting treatment using one method or another, a woman will need to undergo a comprehensive diagnosis. It includes taking tests, among which the following are mandatory:
- Blood test for HIV.
- Clinical blood test.
- Blood chemistry.
- Clinical urine analysis.
- Blood test for hepatitis.
- Blood test to detect urogenital infections, including HPV. The most reliable in this regard is PCR analysis.
- Taking a smear for oncocytology (Papanicolaou test) and flora.
- Undergoing an extended colposcopy and, if indicated, a biopsy.
If no deviations from the norm are detected from the results of these tests, then the woman will be sent to undergo a cauterization procedure. If any genital or other infections are detected, preliminary treatment is necessary.
Consequences of cauterization of cervical erosion
Although medicine has made great strides in terms of treating erosion, an ideal procedure that would not have any consequences for the woman’s body has not been found. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, it is so important to make not only the right choice regarding the cauterization method, but also to find a qualified specialist.
Among the possible consequences of cauterization of erosion, both immediate and long-term symptoms are distinguished.
The immediate ones, that is, those that may occur in the first 8 weeks after the procedure, include:
- Exacerbation of inflammation of the fallopian tube or simultaneously the fallopian tube and ovaries. Most often the process is one-sided, although it can develop on both sides.
- Bleeding with significant blood loss (this complication does not include minor bleeding, which is normal).
- Menstrual irregularities, in particular the development of amenorrhea.
Source: https://cmsch71.ru/mammologiya/kakie-analizy-nuzhno-sdat-pered-prizhiganiem-erozii-shejki-matki-kak-podgotovitsya-k-protsedure.html
Common tests for cervical erosion before and after treatment
Cervical erosion requires a serious examination, based on the results of which treatment is prescribed.
This is the only way to get rid of this disease most effectively and without any consequences by choosing conservative tactics or more serious methods.
What tests should be taken for cervical erosion are determined by the doctor, taking into account the clinical situation, but there is a certain list of the most commonly used ones. What should you pay attention to?
Reasons for testing
The concept of “cervical erosion” often includes any changes in the cervical epithelium that are visible when examined in mirrors. Therefore, it is sometimes quite difficult to judge the choice of a particular treatment without seeing the entire clinical picture.
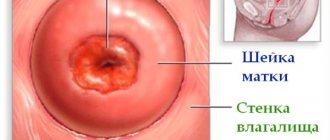
True cervical erosion is a tissue defect of 1 - 2 cm. This is an “ulcer”, which is a consequence of an acute inflammatory process. But over a short period of time, its surface becomes epithelialized, and it gradually disappears. Therefore, true erosion can be recorded quite rarely; more often you have to deal with its consequences.
The term “cervical erosion” also in most cases includes the following:
- Ectopia is a condition that is diagnosed in young and often nulliparous girls. It is associated with the still incomplete growth of the cervix, as a result of which the part of it that should be inside the cervical canal (cylindrical epithelium) peeks out. Visually, this is defined as regular rounded redness. Gynecologists, claiming that this is erosion, often mislead and scare young girls. In reality, most often you should simply observe such a state.
- Ectropion is a violation of the anatomy of the cervix, its inversion outward. A similar condition develops as a result of injuries, ruptures, including after childbirth. Erosion may appear on the ectropion. Gradually healing, they form Nabothian cysts - glands covered with epithelium on top. They do not pose any particular danger, but if they are large, it is still better to remove them. Ectropion is often equated to cicatricial deformities of the cervix.
We recommend reading the article about the treatment of cervical erosion without cauterization. From it you will learn about the effectiveness of non-surgical therapy, drug treatment, and the drugs used.
Thus, several diseases of the cervix are visually identified in the same way, while having different treatment tactics. By conducting a full examination of “erosion,” the doctor determines its true causes, which helps determine the most effective ways to combat it. Also, when performing comprehensive research, the following goals are pursued:
- It is established whether changes in the cervix are a consequence of sexually transmitted infection, postpartum trauma, etc. This fundamentally affects treatment tactics.
- Are there dysplastic changes in pathological lesions? CIN 1, 2 and 3 are precancerous conditions that require a specific approach and further monitoring. If dysplasia is not detected in time, it can be “healed” to cancer already at the initial stage.
- During the examination, it is clarified whether the woman is a carrier of viruses that can cause cancer - these are different types of HPV. If they are present, she is at risk and must undergo special treatment to combat these pathogens. This analysis after cauterization of erosion is also carried out in dynamics.
- It is clarified how deeply the pathological process affects the cervical tissue. This is necessary to choose between conservative and surgical treatment (cauterization, laser treatment, etc.).
Thus, the quality of treatment depends on how thoroughly and competently the examination is carried out.
Types of tests and their significance in pathology
The entire examination can take place in several stages. It includes general research, in-depth and special research using special techniques and tools.
It is not always necessary to go through the entire complex.
What tests are needed to treat erosion in a particular case can only be determined by a gynecologist, taking into account the clinical picture, duration of the disease, complaints and the presence of concomitant pathology.
General examination
It is performed during the initial appointment at the time of examination on the gynecological chair. It includes the following:
| Survey | Purpose of the event |
| Flora smear from the vagina and urethra | This is a routine test that gives a general idea of the presence of inflammation in the vagina and cervix. It also allows you to identify some pathogens of STIs (Trichomonas, gonococci and others). It is important to determine whether there are any manifestations of candidiasis or gardnerellosis. But even an ideal smear does not provide a 100% chance of excluding sexually transmitted infections and other serious conditions. |
| Smear for oncocytology, which can be performed using different methods | It is considered the most optimal to conduct a Papanicolaou test in a liquid medium, then the material from the test tube can be taken for further research without conducting a second examination. The purpose of such smears is to detect cervical cancer, as well as dysplasia of varying degrees. All this significantly changes management tactics. Thus, CIN 1 is treated conservatively and resolves in 80% of cases. CIN 2 requires 60% surgical treatment in the form of cauterization or something similar (liquid nitrogen, laser radiation, etc.). CIN 3 is almost always an operation; when combined with endometrial pathology or the presence of fibroids, it can even be removal of the uterus. |
What additional tests are taken for erosion? This includes general blood and urine testing, testing for HIV, syphilis and hepatitis. If any diseases are detected, treatment is carried out not by a gynecologist, but by an infectious disease specialist or venereologist. At the same time, cervical erosion in these cases is no longer a prerogative; therapy for the underlying disease is carried out.
Watch the video about cervical erosion:
In-depth examination
These tests are required before cauterization of erosion, as well as in most cases of conservative treatment. These include the following:
- PCR for sexually transmitted infections, namely mycoplasma, chlamydia, ureaplasma, trichomonas, gonococci. Identification of these pathogens requires initial antibacterial treatment, during which erosion may also resolve if it is small in size. It is better to use the real-time PCR method for examination, which allows you to most accurately identify pathogens.
- Screening for oncogenic viruses is also of fundamental importance. It is necessary to carry out PCR for HPV types 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 52, 58, 59, 67, as well as for HSV (herpes simplex virus) classes 1 and 2. Identification of these microorganisms immediately puts a woman at increased risk for developing cervical cancer, so treatment will be more radical in some cases.
- Bacteriological culture for genital infections of the vaginal and cervical contents. This study is necessary in order to identify the quantitative content of bacteria in the material. Sowing is also needed in cases where the inflammatory process is caused by opportunistic microbes. PCR and smear are not informative for them. When identifying pathogens, this study involves determining sensitivity to groups of antibiotics.
And this is extremely important for drawing up a treatment regimen in the future, especially given the fact that there are many drug-resistant microbes. It is necessary to perform bacteriological culture for myco- and ureaplasmas, as well as for the general flora of the vagina and cervix.
Special examination
It is carried out using special equipment (colposcopes), instruments (for example, conchotome), and the material obtained during the procedures is often sent for further histological examination. As a result, the doctor receives a conclusion indicating the degree and nature of the change in the pathological area.
A special examination is almost always carried out, but at the second or subsequent appointments. These tests are especially important for cauterization of the cervix.
Colposcopy
This is a study using a special microscope (colposcope), where you can magnify the resulting image tens of times. This is a painless procedure, practically indistinguishable from a regular mirror examination, but longer.
There are simple and extended colposcopy. In the first case, an examination is simply carried out under magnification. During extended colposcopy, additional tests are made (with acetic acid and iodine solution), which help make pathological areas even more obvious.
Cervical biopsy
A cervical biopsy involves excision of a small area of tissue for further histological examination.
This analysis is always taken from the most changed area in order to identify the maximum existing changes in the cervix.
After all, at the same time, for example, mild and severe dysplasia can exist. In this case, the final diagnosis of erosion is established based on the poorest analysis.
Biopsy can be of several types. Namely:
- Loop. In this case, a small area of tissue is excised using a device that supplies an electric current.
- Using a conchotome , special “scissors-nippers” that allow you to grab the cervix and take the necessary material for research.
- Knife using a scalpel is the most informative, but often requires stationary, method of taking cervical tissue. In this case, it is necessary to apply stitches, which requires certain conditions and skills of the doctor.
We recommend reading the article about menstruation during erosion and after its treatment. From it you will learn about the impact of the disease on the menstrual cycle and the nature of discharge, the causes of heavy and scanty periods, delays, and possible complications after cauterization.
Thus, the range of studies for cervical pathology is quite large.
Therefore, if erosion is detected, only a gynecologist can determine which tests need to be taken in a particular situation.
Moreover, the next study may entail several subsequent ones, for example, when an STI is detected, etc. In any case, it is necessary to treat this disease in order to prevent more serious diseases.
Source: https://ProMesyachnye.ru/analizy-pri-erozii-shejki-matki/
Causes of cervical pathologies
Sometimes it is not possible to definitively find out why the neck is “sick.” However, most often the following factors contribute to this:
1. Infectious processes in the vagina. Pathogenic microorganisms (chlamydia, gonorrhea) make the vaginal environment more alkaline. This is also reflected in the cervix - under such conditions, the location of the epithelium changes.
2. Rapid labor, delivery of a large fetus, 3 or more births, late-term abortions lead to cervical deformation. It turns outward - this condition is called ectropion.
3. Damage to the epithelium by chemical agents during douching and the use of spermicides lead to changes in the cervix.
Testing before cauterization of cervical erosion
Surgical treatment of cervical-cervical pathology requires preliminary preparation. Tests before cauterization of erosion on the cervix will help the doctor identify hidden infections that will lead to a complicated postoperative period.
However, the main thing that needs to be done at the stage of preparation for cauterization is to exclude the possibility of malignant degeneration: precancerous changes in the cellular structures of the cervix and cervical canal cannot be treated with conventional methods. The doctor knows exactly what tests will be required.
It is important to accurately follow the specialist’s recommendations in order to avoid postoperative problems and ensure rapid wound healing after cauterization of cervical erosion.
Standard list of tests before cauterization
Having seen an eroded cervical surface during a gynecological examination, the doctor will prescribe the following studies and tests:
- vaginal smears for degree of purity;
- cytology smear;
- bacterial culture of secretions for bacterial microflora;
- special culture for gonorrhea with provocation;
- detection of hidden infections using polymerase chain reaction (PCR);
- blood test for socially significant infections;
- colposcopy;
- taking a biopsy from the cervix.
If during the examination the doctor discovers the presence of viruses or bacteria, then a course of treatment will be required. A mandatory study before cauterization is to exclude oncological changes in the cells, determined by biopsy material taken from the erosion.
Strokes
Vaginal smears are routinely taken during any gynecological examination. Based on this analysis, we can guess what infectious problems there may be and what microbes to look for.
If the answer from the laboratory shows that there is inflammation in the smears (many leukocytes, pathogenic microflora, 4th degree of purity), then we need to continue the examination and look for the source of infection.
Sometimes smears reveal diseases transmitted during sexual activity (trichomoniasis, gonorrhea).
Cytology
A smear taken from cervical erosion with a special cytobrush can identify atypical cells.
The study is carried out in a special cytological laboratory, whose specialists are able to determine precancerous changes in the cellular structures of the endocervix and the outer part of the cervix.
If cytological atypia or dysplasia is detected, the doctor will conduct an examination taking into account the high risk of oncological pathology.
Bacterial cultures
Discharges taken from the vagina are transferred to a special nutrient medium, which can be used to determine the type of microbes and the sensitivity of the infection to certain medications.
Before testing for gonorrhea, a provocation must be done (an injection of a drug that causes an exacerbation of the infection and increases the likelihood of detecting the pathogen).
If any microbial pathology is detected, treatment with antibiotics is carried out.
PCR
Hidden and chronic infections in smears are extremely difficult to detect. PCR should be done for cervical erosion to detect the following microbes:
- papillomavirus;
- causative agent of genital herpes;
- chlamydia;
- mycoplasma;
- ureaplasma.
In case of cervical erosion, before cauterization, it is necessary to know exactly whether there is a human papillomavirus infection in the cervical canal and what the activity of this virus is.
Often, the combination of erosion, cervicitis and highly active human papillomavirus is a precancerous condition.
Therefore, when a viral pathology is detected, a specialist will prescribe special treatment, consisting of tablets and vaginal suppositories.
Detection of chlamydia and ureamicoplasmosis requires a course of antibacterial therapy followed by control PCR within the time frame specified by the doctor.
Blood tests
A prerequisite for examination before cauterization of cervical erosion is testing for socially significant infections, which include:
- Wasserman reaction to determine syphilis;
- donating blood for AIDS;
- tests for viral hepatitis B and C.
In addition to the fact that undetected infections can lead to dangerous complications in a woman, one should remember to protect medical personnel from infection during the cauterization procedure for cervical erosion.
Biopsy
Without taking a biopsy and obtaining a histological result that eliminates the risk of oncological pathology, no operations are performed for erosion.
The optimal type of biopsy is loop excision using the Surgitron device. Usually after 1 week the result of the study in the histology laboratory is ready.
If all tests are normal and there is no risk of malignant degeneration, then the doctor will prescribe a day for cauterization of cervical erosion.
A positive and uncomplicated outcome of therapy depends on high-quality and complete preparation for surgery to treat erosion on the cervix. It is necessary to follow all the doctor’s instructions in order to forget about gynecological problems 1 month after cauterization.
Source: https://gynecologyhelp.ru/eroziya-shejki-matki/analizy-pered-prizhiganiem.html
Possible complications
Although this disease is not life-threatening, it must be identified and treated promptly. After all, it favors the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria and the occurrence of serious diseases - chlamydia, trichomoniasis. Also among the complications of cervical erosion are infertility and cervical cancer.
Chronic cervical erosion
In the chronic form, symptoms are practically absent.
Sometimes scanty bleeding appears, accompanied by pain during sex. Treatment of chronic pathology involves: eliminating the infection that provoked the disease, relieving inflammation and cauterizing erosion.