Inflammation of the uterine appendages on the left, or left-sided adnexitis, develops much less frequently than the diffuse form of the pathology. Its clinical picture can be confused with diverticulitis, acute intestinal obstruction and renal colic. In order to recognize the disease in time and begin appropriate treatment, you need to know the main signs of left-sided adnexitis. This will help avoid serious complications in the form of suppuration, sepsis and reproductive dysfunction.
Definition
Adnexitis is an inflammatory process that occurs in the uterine appendages. Women under 30 years of age are more susceptible to the disease. Most often, left-sided adnexitis is diagnosed, which tends to progress rapidly. If left untreated, a chronic stage of the disease may develop, which often leads to infertility. The most common cause of pathology is infection. In the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10), left-sided adnexitis has a code of 70.1.
Causal factors of pathology
Regardless of the location of inflammation in the appendages (right or left), most often primary infection occurs when microbes enter the uterus from the vagina through the endocervical canal.
However, in addition to the ascending route, other options for the spread of infection are possible. Left-sided adnexitis can occur against the background of the following causative factors:
- absence or blockage of the right tube;
- congenital anomaly of the uterus (bicornuate, saddle-shaped, duplication);
- penetration of infection through blood or lymphatic vessels from neighboring organs (paraproctitis, colitis, hemorrhoids, rectal fissure);
- frequent and prolonged constipation;
- chronic pancreatitis with constant exacerbations;
- inflammation of the prolapsed left kidney (nephroptosis).
Acute or subacute left-sided salpingoophoritis manifests itself with vivid symptoms, and with chronic inflammation, a woman may have minimal signs of the disease.
Effective and timely treatment for initial manifestations will help prevent complications, so you should consult a doctor as quickly as possible.
Classification
Experts divide adnexitis into several stages, which depend on the severity of symptoms. Let's look at them in more detail:
- Acute stage. Occurs when the inflammatory process develops due to infection in the genitals and decreased immunity.
- Subacute left-sided adnexitis. It does not occur as often as other forms of the disease. The signs are similar to the acute course, but the symptoms are not so pronounced.
- Chronic stage. It usually occurs due to an untreated acute form of the disease. It is characterized by periods of exacerbation and subsidence of accompanying symptoms. The menstrual cycle is greatly disrupted. This stage of adnexitis can lead to infertility.
- Purulent form. Occurs due to the activity of various bacteria. A very dangerous stage of adnexitis that requires immediate treatment.
What is left-sided adnexitis
Left-sided adnexitis - description of the disease
Due to strange circumstances, for some reason doctors most often diagnose left-sided adnexitis, although this cannot be explained in any way.
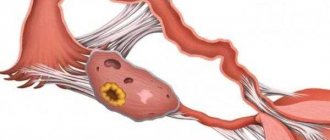
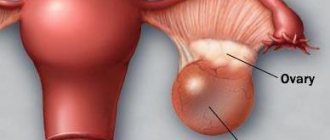
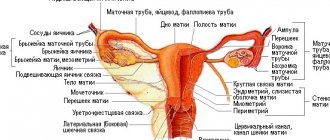
Left-sided adnexitis is inflammation of the fallopian tubes or ovaries on the left side. Everyone knows that the ovaries are located both on the right and on the left. Therefore, both inflammations are dangerous.
The symptoms of the problem are very obvious, and often a woman, going to the gynecologist, already approximately knows her diagnosis. Of course, hearing it for the first time, everyone gets scared, because, as you know, one of the most common complications regarding problems with the reproductive system is infertility. Therefore, when the very first and sometimes not the most obvious symptoms appear, it is necessary to visit a gynecologist, because only during the examination will he be able to make an accurate diagnosis and understand the stage of the inflammatory process, because the speed of recovery will depend on this, as well as the possibility of pregnancy in the future.
The second name for the disease, and a fairly common one, is salpingoophoritis.
True, not all doctors pronounce this particular term out loud in front of patients, because due to the large number of letters and the incomprehensible combination of several Latin words, it terrifies patients. Therefore, it is customary to use adnexitis. Although they mean the same thing.
If we talk about deciphering the term “salpingoophoritis”, then we must say that salpingitis means an inflammatory process in the fallopian tubes, and oophoritis - in the ovaries. Therefore, when there is inflammation of the tubes and ovaries, the term adnexitis is used. All gynecologists say the same thing: improper treatment and ignoring problems associated with inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries in the future leads to serious obstetric problems, which are often simply impossible to solve due to the advanced state of the disease.
Causes
The main reason for the development of left-sided adnexitis is the impact of pathogenic microflora on the genitals. The following routes of infection penetration into the female genitourinary system are distinguished:
- Surgical interventions.
- The ascending path is from the vagina and uterus (for example, with vaginitis).
- Descending - infection occurs from the abdominal organs (for example, with appendicitis).
- Through lymph and blood. Diseases that cause adnexitis when entering the female organs are syphilis, tuberculosis and others.
The reasons that provoked the development of left-sided adnexitis include:
- Abortion.
- C-section.
- Inflammatory processes occurring in a woman’s body.
- Hypothermia.
- Intrauterine device.
- Untreated diseases of the reproductive system.
- Decreased immunity.
- Promiscuous sexual intercourse without the use of protection.
- Venereal diseases.
- Prolonged stress.
- Surgical interventions.
- Colds.
- Exchange disorders.
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules.
How to treat inflammation of the appendages
Treatment of inflammation of the appendages in women depends on the strength of the inflammatory process and the nature of the infection. If the cause of the disease is a pathogenic microorganism (bacterium), then antibacterial drugs (antibiotics) are needed. If the cause of the infection is a virus, then antiviral measures and agents are needed - specific antiviral drugs and immunomodulators.
Acute stage: treating the causative agent infection
More often, the causative agent of the inflammatory process in the female genital organs is pathogenic bacteria (anaerobes), the reproduction and vital activity of which occurs in an oxygen-free environment. Antibacterial drugs are prescribed for their treatment. The choice of antibiotic is determined by the type of pathogen. Antibacterial agents have a wide spectrum of action, but are unable to equally counteract all pathogens. Therefore, for effective treatment, the pathogen is determined by taking a smear from the vaginal flora.
If it is impossible to inoculate the pathogen, then antibiotics of the widest and most general spectrum of action are prescribed. These are drugs of the cephalosporin and penicillin groups (Ceftriaxone, Amoxiclav). They may also prescribe milder antibacterial agents - Erythromycin, Metronidazole. For minor inflammation, they are prescribed in tablet form. For severe adnexitis - in the form of injections (shots), which are given under the supervision of a doctor in a hospital.
What antibiotics are prescribed for home treatment for inflammation of the appendages and ovaries:
- Macrolides - Azithromycins (Summamed), Erythromycins (international version - Clindamycins). These tablets for inflammation of the appendages are most often prescribed for the treatment of adnexitis. They are considered the least toxic antibacterial drugs with a minimum of side effects and contraindications.
- Fluoroquinalines – Norfloxacin, Ofloxocin, Lomefloxacin. They represent one of the latest generations of antibacterial drugs and are almost non-addictive.
- Nitromidazoles - Metronidazole, Ornidazole, Ternidazole. This group acts against nitro group pathogens.
_
Note: often two types of antibiotics are prescribed simultaneously for the treatment of genitourinary diseases. One is against anaerobic bacteria (those that reproduce in an oxygen-free environment). And the second is against aerobes (reproducing in the presence of oxygen).
Remission stage: treating the remnants of the inflammatory process
After limiting the growth and development of the pathogen, a period of remission begins. It is characterized by the presence of residual signs of inflammation in the mucosal epithelial cells. That is, there is still inflammation, but the causative agent is no longer there.
Often, many women end treatment at this stage, believing that the residual effects will go away on their own. This is indeed possible, but only in a healthy female body with a strong immune system. Often the opposite happens. Residual inflammation becomes the basis for re-infection and relapse (recurrence) of the disease. Therefore, treatment must be completed. What is prescribed during the remission stage?
For final recovery, measures are prescribed to resolve the source of inflammation. They speed up the elimination of toxins. As a rule, those agents are used that stimulate blood circulation inside the abdominal cavity and accelerate local blood flow in the area where the ovaries and fallopian tubes (appendages) are located.
These include:
- Physiotherapy (magnetic therapy, electrophoresis).
- Warming and compresses.
- Paraffin treatment.
- Mud therapy.
- Massage – special gynecological, on the lower back and lower abdomen.
Treatment with mineral waters at a balneological resort is also prescribed.
Remedies to boost immunity
In addition to “direct action” drugs, which are directed directly against the causative agent of the infection, the treatment of adnexitis uses means and drugs to boost immunity. They are also necessarily used in the treatment of viral inflammation caused by foreign particles (for example, in the treatment of genital herpes). Immunity boosters include:
- Vitamin-mineral complexes are necessary to ensure active protective reactions. They are prescribed for any diseases, infections, inflammations.
- Prebiotics are drugs for normalizing the bacterial flora, providing local immunity to the internal cavity of the vagina and intestines. Must be prescribed during treatment with antibacterial substances.
- Specific drugs to stimulate the immune system - antiviral drugs, immunomodulators. They are necessarily prescribed for a viral infection. For example, against herpes - tablets and ointments with acyclovir, famvir, panavir. And for any viral infections - suppositories with interferon.
Often, treatment with absorbable drugs and medications for immunity are prescribed from the first days of illness. If the inflammation is caused by a bacterial pathogen, then immunity agents are an additional treatment that shortens the duration of antibacterial therapy. In case of a viral pathogen, immunostimulants provide the main treatment for the disease.
Treatment with antibiotics lasts from 7 to 10 days. The duration of treatment with vitamins, prebiotics, as well as the use of physiotherapy is 3-4 weeks (almost a month).
_
Note: analgesics are also prescribed for severe pain.
Treatment of chronic inflammation of the appendages varies in duration and uses various drugs - tablets, injections, vaginal suppositories, as well as physiotherapy. Vaginal suppositories are the most convenient for treatment at home and are very effective.
Symptoms
Symptoms of left-sided adnexitis are very diverse and depend on the stage of development of the disease. But in almost all cases, their manifestations will be observed on the left side.
Acute left-sided adnexitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Increase in temperature to high values.
- Chills.
- Cramping pain localized in the lower abdomen. They can radiate to the sacrum area.
- Difficulty urinating.
- Increased sweating.
- Poor health, manifested by headaches and muscle pain.
- Pain is felt when pressing on the abdomen.
- The presence of pathological discharge.
The chronic stage of the disease is characterized by the development of the following manifestations:
- Painful sensations during sexual intercourse and during bowel movements.
- Menstrual irregularities.
- Purulent discharge.
- Aching pain in the lower abdomen.
- Painful menstruation.
- Stool disorders.
- The stomach is tense.
- Inability to get pregnant.
- Depressive states.
Exacerbation of chronic left-sided adnexitis is manifested by a slight increase in pain and deterioration in well-being.
Symptoms of the disease
Left-sided salpingoophoritis can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- slight, throbbing pain in the lower abdomen on the left (onset of the disease, pre-acute stage)
– pain intensifies during sexual intercourse, defecation, fast walking
- acute, short-term, frequent pain radiating to the sacrum
- long-term, constant pain, subsiding only in a lying position, which does not allow you to move or move (acute stage)
- increased body temperature (not always), chills, depression, increased vaginal discharge
- the formation and accumulation of pus leads to high fever, very severe pain, and the danger of inflammation of the peritoneum.
Diagnostics
If signs of left-sided adnexitis are detected, the diagnosis will be aimed at confirming the diagnosis and identifying the provoking factor. Timely diagnosis is very important, because the symptoms of adnexitis are similar to the manifestations of many diseases of the female genitourinary system.
First of all, you need to contact a gynecologist who will collect an anamnesis of the disease, conduct an examination and give recommendations on further diagnostic measures.
To clarify the diagnosis and severity of the disease, a complex of laboratory and diagnostic tests is used. These include:
- A gynecological examination, with the help of which the doctor determines the size and sensitivity of the appendages.
- A general analysis of urine and blood will determine the presence of an inflammatory process.
- Taking a smear for bacteriological examination.
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity and pelvic organs.
- Laparoscopic diagnosis.
- MRI or computed tomography.
- Radiography.
The doctor makes an accurate diagnosis only after receiving the results of all prescribed tests. After this, an effective treatment plan is drawn up.
Types of diagnostic tests
Mandatory diagnostic methods are:
- microscopic examination of vaginal smears;
- culture of vaginal discharge for infections;
- special studies (PCR) to identify sexually transmitted microorganisms (viruses, chlamydia, mycoplasma);
- transvaginal ultrasound scanning;
- advisory assistance from a therapist, surgeon, proctologist and urologist;
- tomography and laparoscopy for suspected cystic ovarian tumors, acute life-threatening diseases and any doubts about the diagnosis.
The importance of all diagnostic methods is to necessarily detect the cause of inflammation and assess the condition of the uterine appendages on the left. If complications occur, effective treatment must be started immediately.
Treatment
First of all, treatment of left-sided adnexitis will be aimed at suppressing infection, eliminating complications and restoring the woman’s reproductive function.
Therapy is prescribed taking into account the characteristics of the course of the disease and the general condition of the patient. The most effective treatment is considered to be complex treatment, which includes taking medications, traditional medicine and surgery. With left-sided adnexitis, symptoms and treatment will be interrelated.
Drug treatment
Treatment in the early stages of the disease can be carried out on an outpatient basis, but acute adnexitis is treated in a hospital setting. Let's consider the most common categories of drugs used in the treatment of pathological conditions.
- The most effective drugs are antibiotics. They are prescribed individually by the attending physician, taking into account the severity of the disease and the type of infection that contributed to the inflammation.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Antihistamines, which help relieve swelling and prevent side effects when taking antibiotics.
- In case of severe pain, the use of painkillers is allowed. But since it is not recommended to take them for more than three days, cold is used as an alternative. To do this, ice is wrapped in a towel and applied to the site of inflammation. It is recommended to take a ten-minute break every half hour.
In the chronic stage of adnexitis, the following medications may be added to the above medications:
- Antiviral drugs.
- Antifungal agents.
- Vitamin complexes.
- Immunostimulants.
It is worth noting that the doctor may recommend the use of medications in the form of suppositories as therapy. After completing the course of treatment, physical procedures are indicated - vibration massage, ultrasound and others.
Doctors do not recommend becoming pregnant until the end of treatment. After a course of prescribed procedures, you need to undergo a re-examination to clarify the effectiveness of therapy.
Anti-inflammatory suppositories for inflammation of the appendages
The introduction of drugs into the vaginal cavity ensures rapid penetration of the drug into the inflammation zone and a high therapeutic effect of its use. What anti-inflammatory suppositories are used in gynecology for inflammation of the appendages?
Suppositories with NSAIDs
NSAIDs or non-steroidal suppositories for inflammation of the appendages with an anti-inflammatory effect:
- Indomethacin.
- Diclofenac.
- Voltaren.
Also, for adnexitis, hemorrhoidal suppositories with belladonna are prescribed. They are an anti-inflammatory and analgesic at the same time.
The listed drugs are classified as drugs for the treatment of joint diseases and inflammation. They are also successfully used in the treatment of any internal inflammatory processes.
Absorbable suppositories
These drugs prevent the formation of adhesions. They stop adhesions during inflammation and resolve adhesions after treatment of adnexitis.
- Terrylitin suppositories - dilute blood clots and pus, break down necrotic (dead) tissue.
- Longidaza also promotes the resorption of adhesions and stops the adhesive process.
Candles with antiseptics
Vaginal suppositories with antiseptics of antifungal and antibacterial action for the treatment of appendages are ineffective. They are prescribed if, in addition to adnexal inflammation, there is inflammation of the vaginal cavity (colpitis).
Antifungal suppositories:
- Gainomax.
- Myconalosis.
- Gyno-Pevaril.
- Nystatin.
- Primafungin.
- Terzhinan.
Candles with antibacterial action:
- Dalatsin.
- Clindacin.
- Metrovagin.
- Betadine.
- Hexicon.
- Iodoxide.
- Fluomizin.
- Terzhinan (complex drug with antibacterial and antifungal effects and hormonal prednisolone).
Treatment with suppositories, the introduction of medicinal substances into the vaginal or rectal cavity is indicated for various diseases. Medicinal substances enter the bloodstream, bypassing the digestive tract, without partial destruction in the liver. This reduces the incidence of allergic reactions and increases the effectiveness of treatment.
Rectal suppositories with immunomodulatory effects
Preparations with interferon exhibit an antiviral effect. They are broad-spectrum immunomodulators. The most famous of them are Viferon, Genferon, Kipferon.
Note: the drugs listed are rectal suppositories, that is, they are introduced into the rectum through the anus.
Suppositories for normalizing vaginal microflora
Also, during and after treatment with andexide, suppositories are used to normalize the vaginal flora - Acylact, Lactobacterin. They are absolutely necessary during antibiotic treatment. Desirable – in the treatment of viral forms of infections.
Surgical intervention
Surgery may be indicated in cases where other treatment methods have not brought a positive effect, or when a woman’s condition worsens with the development of a purulent process.
The purpose of surgical treatment will be to preserve reproductive function, remove purulent lesions and adhesions, and restore tubal patency. In most cases, laparoscopic surgery is used, which is more gentle. In advanced cases, the doctor may decide to remove the affected organ or part of it.
Traditional medicine and diet
In addition to traditional methods of treatment, it is possible to use traditional medicine that can help relieve inflammation and speed up recovery.
Medicinal herbs used in the treatment of adnexitis are used in the form of infusions and decoctions. The following plants have proven themselves well:
- Borovaya uterus.
- Rosemary.
- Rose hip.
- Chamomile.
- Dandelion.
- St. John's wort.
- Calendula.
- Oak bark.
It is important to remember that you can use any medicinal herbs only after consulting your doctor.
In addition to the above treatment methods, it is necessary to adhere to a certain diet that excludes allergenic, fatty, and spicy foods. It is recommended to consume vegetables and fruits rich in vitamin C and fermented milk products. In this case, you need to give up sweets and salty foods and limit the consumption of coffee, carbonated drinks and baked goods.
Complications
First of all, left-sided adnexitis has a negative impact on a woman’s reproductive function. More advanced stages of the disease can lead to infertility. If pregnancy occurs, there is a high probability of its pathological course. Complications include ectopic pregnancies or early miscarriages.
With the development of purulent adnexitis, infection may spread into the abdominal cavity.
Prevention and prognosis
To exclude the development of pathology, it is necessary to adhere to a number of recommendations:
- Systematic visit to the gynecologist.
- Timely treatment of all diseases.
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules.
- Elimination of stress and hypothermia.
- Use of contraception.
- Prevention of abortion.
- Refusal to wear tight underwear. Give preference to cotton fabrics.
If you contact a medical facility in a timely manner and treatment is started on time, the prognosis for left-sided adnexitis will be favorable. Therefore, you need to listen to your body and, if signs of the disease appear, undergo all the necessary tests.