The vagina has a unique structure, thanks to which it independently maintains an acidic environment inside and is renewed. Mucus released daily is intended to cleanse the body of pathogenic and dead cells. Depending on the period of the cycle, it acquires a characteristic color and consistency.
White discharge in women - causes
The type of vaginal mucous substance in question may represent a symptom of a certain set of diseases or indicate the normal functioning of the reproductive system. To find out why white discharge appears, it is important to consider several of its characteristics:
- time of occurrence;
- smell;
- thickness and structure;
- the presence of accompanying symptoms.
White discharge during pregnancy
The initial stages of gestation are accompanied by a sharp imbalance in the balance of hormones and suppression of the immune system. White discharge during early pregnancy often indicates the successful introduction of a fertilized egg into the uterine epithelium and associated changes in the body. The mucus has a thick consistency, as during ovulation, and may acquire a beige tint.
Sometimes white discharge in women planning to become mothers is a symptom of sexually transmitted infections. During conception, the activity of the immune system decreases slightly to prevent rejection of the fertilized egg, and low-grade inflammation may intensify, and pathogenic microorganisms (viruses, fungi, bacteria) begin to multiply intensively. To accurately determine the causes of the described phenomenon, a qualified examination is required.
White discharge before menstruation
On the eve of the start of a new cycle, the vagina prepares for renewal and gradually cleanses itself. During this period, mucus, even normally, may become cloudy due to the content of the following components:
- physiological transudate;
- single leukocytes;
- dead epithelial cells;
- cervical secretions and glandular secretions from the vaginal section of the uterus itself;
- lactobacilli;
- single microbes of the coccal group.
If a delay in menstruation and white discharge are observed in parallel, pregnancy is likely (in the absence of pathological symptoms). It is better to confirm or refute the fact of conception with the help of a doctor and a laboratory blood test for human chorionic gonadotropin. At the earliest stages, the sensitivity of pharmacy tests is too low to obtain accurate results.
White discharge after ovulation
From days 13-15 of the menstrual cycle, the volume and viscosity of vaginal secretions increase noticeably. This is the most favorable period for conception, so the body produces an increased amount of the corresponding hormones, which externally manifests itself as white vaginal discharge. This phenomenon indicates the normal physiological state of the reproductive system and readiness to become pregnant.
If fertilization does not occur, the body automatically cleanses the uterus and its cervix of the excess layer of basal cells. White discharge in women at this stage is a sign of renewal of the epithelial surface. When they are odorless and do not cause any discomfort or inconvenience, there is no reason to worry either. Intense secretion will stop after 30-45 hours.
White discharge after sex
Excitement is accompanied by a strong rush of blood to the genitals, which causes an increase in the amount of mucus. White discharge in women immediately or some time after sexual intercourse is normal. They are a mixture of vaginal lubricant and male ejaculate (sperm), if intimacy occurred without barrier contraception.
Reasons for appearance
Intimate secretions serve as a kind of indicator of the health of the female sphere.
With natural discharge that does not cause discomfort, we can conclude that the organs of the female reproductive system are healthy. However, regular examinations by a gynecologist at the beginning of the cycle are still necessary. Many pathological processes occur without symptoms; their presence can only be demonstrated by a gynecological examination and laboratory tests.
Several factors can influence the appearance of discharge in a healthy woman. These are stress, climate change, taking hormonal drugs, taking strong medications, allergic reactions. Personal hygiene can also affect the nature of the discharge.
A woman should be concerned when the discharge changes in consistency, acquires a strange color or smell, or changes in intensity. Often such discharge is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, itching, pain in the perineum, irritation of the external genital organs, and discomfort when urinating.
There are some symptoms that can be used to preliminarily identify the disease. Of course, an accurate diagnosis is only possible with a doctor after examination and laboratory diagnostics, but the appearance of some can give a more or less accurate picture of the disease.
White curdled discharge with a sweet or sour odor indicates candidiasis. Other symptoms of candidiasis are:
- burning, itching in the vagina and external genitalia;
- swelling of the vagina after sexual intercourse;
- pain when urinating and during sexual intercourse.
Excessive yellow or bloody discharge with an unpleasant odor may indicate bacterial vaginitis. This is an inflammation of the vagina caused by a violation of the microflora. This means that local immunity cannot restrain the growth of pathogenic bacteria; they attack vaginal cells, and the inflammatory process begins. Characteristic symptoms of bacterial vaginitis:
- redness, itching and swelling of the genitals;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- painful intercourse;
- slight increase in body temperature;
- weakness and fatigue;
- frequent urination.
Excessive foamy leucorrhoea with an unpleasant odor may indicate trichomoniasis. The causative agent of the disease is Trichomonas. The following symptoms are also observed:
- irritation of the genitals and inner thighs;
- erosion of the mucous membranes of the intimate area;
- pain when urinating;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- pain during sexual intercourse.
Homogeneous yellow-green discharge with an unpleasant odor may be a sign of gonorrhea. This is an acute infectious disease caused by gonococcus and sexually transmitted. Symptoms of gonorrhea are:
- itching and pain in the urethra and vagina;
- increased body temperature;
- separation of pus from the vagina;
- frequent painful urination;
- enlarged and painful lymph nodes;
- weakness;
- nausea;
- loss of appetite.
Serous-purulent discharge with blood often indicates the presence of a cyst in the uterus or its appendages. Symptoms of a cyst, in addition to bloody discharge, are:
- discomfort in the vagina;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- increased menstrual flow;
- menstrual irregularities;
- painful menstruation.
Bright yellow and green discharge in copious amounts with a very unpleasant odor signal endometritis. This is an inflammation of the uterus caused by bacteria or injury. Symptoms of endometritis:
- acute pain in the abdomen, in its lower part;
- fever with chills;
- increased heart rate;
- painful urination;
- weakness;
- enlargement of the uterus caused by tissue inflammation;
- heavy and painful periods;
- infertility.
Brown discharge during delayed menstruation can indicate a pathological course of pregnancy, for example, an ectopic pregnancy. The likelihood of this pathology can be judged by the following symptoms:
- absence of menstruation;
- sharp or cramping pain in the lower abdomen, usually on the side;
- toxicosis and other signs of pregnancy.
This is a very dangerous condition that requires immediate medical attention. Even if the pregnancy is intrauterine, but there is spotting, you should immediately consult a doctor, as this is a sign of a threat of miscarriage.
White discharge without odor
Ideally, vaginal secretion should not have any aroma, clearly defined color and structure. Sometimes it can acquire turbidity and a light beige tint, and become thicker (during the ovulatory period), so white, odorless discharge in women is considered by gynecologists as a variant of the normal state of mucus. It is important that the change in color is not accompanied by itching or burning, or redness of the labia.
Rarely, abundant white odorless discharge indicates the occurrence of pathological processes associated with changes in the functioning of the hormonal system, the ratio of estrogens and androgens, the concentration of cortisol and prolactin. The cause of the imbalance can only be determined based on blood tests ordered by an endocrinologist or gynecologist.
When is clear discharge normal, and when is it a pathology? Film-like discharge in women
Film Film-like discharge in women
Many women consider vaginal discharge to be a sign of “uncleanness” or illness, not realizing that it is just a type of normal physiological secretion, such as stomach acid, tears or saliva.
On the other hand, the color and structure of female discharge is one of the factors for determining various sexually transmitted infections, says obstetrician-gynecologist, doctor of the highest category and candidate of medical sciences Alexander Voloshin.
“The appearance of any unusual changes in a woman’s sexual sphere should be a reason for a visit to the gynecologist.
Since in medical practice quite often one has to deal with a combination of various pathological processes with atypical manifestations for a particular disease, it is impossible to establish a reliable diagnosis based only on the color and nature of the discharge.
Of course, in this way one can assume the development of a certain pathological process. However, the final diagnosis, as well as individual selection of treatment, are possible only after laboratory and instrumental examinations,” Voloshin said.
As you know, normal vaginal discharge performs a protective barrier function in the female body. Let's first find out where they come from and what their composition is. So, the composition of female secretions includes:
- mucus that forms in the glands of the cervical canal;
- epithelial cells that are constantly exfoliated from the walls of the vagina and cervical canal;
- vaginal microflora, which can be represented by various microorganisms of 5-12 species.
Normal discharge
Discharges of this kind, as a rule, have no odor or have a slightly sour odor due to the lactic acid bacteria that are part of this secretion. Externally, the discharge has a mucus-like structure.
Normally, such discharge begins to be recorded no earlier than a year before the onset of menstruation.
Subsequently, with a regular menstrual cycle, the quantity and quality of discharge may change - from scanty and transparent to abundant, mucus-like, slightly beige in color (on the days of ovulation).
When releasing such a completely physiological secretion, a woman should not experience burning, pain or itching. If she experiences at least one of the above, then this is a cause for concern and see a doctor.
Dark gray discharge
A concentrated, very, very viscous secretion of dark gray or yellow color is characteristic of chlamydia. With this disease, a woman experiences discomfort in the form of burning and itching in the external genitalia.
Grayish-white discharge
Copious discharge of grayish-white secretion with an unpleasant odor of rotten fish against the background of mild itching in the external genitalia are signs accompanying bacterial vaginosis. After sexual intercourse, all symptoms may intensify. If left untreated, the secreted secretion becomes yellow-green in color and has a sticky structure.
Yellow discharge
In the acute phase of gonorrhea, the discharge also has a yellow color. However, unlike chlamydia, with gonorrhea the secretion is not so concentrated and dense. With this disease, a woman may experience pain in the lower abdomen and pain when urinating. Intermenstrual bleeding in this case is also not uncommon.
Greenish-yellow discharge
A cloudy secretion from yellow to yellowish-green, with a foamy structure and the smell of rotten meat is characteristic of trichomoniasis. The secretion is accompanied by a strong burning sensation and pain. When urinating, a woman also experiences pain.
Copious cloudy discharge
Very abundant secretion, clear or slightly cloudy in appearance, may indicate the presence of an infection such as ureaplasmosis. And although there are those among specialists who do not consider these manifestations to be a sign of illness, the majority classify ureaplasmosis as a sexually transmitted infection.
Yellowish cheesy discharge
A thick and abundant secretion, visually similar to pieces of white or yellowish cottage cheese, accompanied by unbearable itching, swelling and irritation of the external genitalia - these are signs of candidiasis or so-called thrush. Self-treatment with advertised medications is not always successful, since in this case, as in any other, only a qualified doctor can determine an effective method of curing this infection.
Associated diseases:
Source: https://sitytreid.ru/plenka/vydeleniya-v-vide-plenki-u-zhencshin.html
White discharge with odor
The main disease associated with the described symptoms is candidiasis. White discharge with a sour odor is a sign of active proliferation of opportunistic fungi (thrush). The secretion may be present constantly or occur periodically, combined with other unpleasant symptoms or not accompanied by a feeling of discomfort.
Candidal white discharge in women occurs for the following reasons:
- long-term use of oral contraception;
- hormonal surges;
- violations of hygiene rules;
- infection from outside;
- long-term antibiotic therapy;
- stress;
- changing of the climate;
- reaction to fragrances in toilet paper or sanitary pads;
- incorrect selection of cotton swabs;
- douching;
- wearing synthetic panties;
- passion for diets, errors in diet planning;
- independent use of vaginal tablets, suppositories and more.
Watery discharge during pregnancy
The dependence of vaginal secretions on hormonal changes is especially evident during pregnancy. After successful conception, the corpus luteum is formed from the remains of the follicle in the ovaries. Its main role is to take care of the fertilized egg. It is the corpus luteum that produces progesterone, which affects the nature of vaginal secretions.
In the first weeks, when the delay occurs, the woman has a white or colorless liquid secretion. If it passes without pain, you should not worry - this is the norm.
Discharges such as water are considered dangerous in the following situations:
- brown discharge with an odor in the first weeks of pregnancy,
- unpleasant itching sensation in the perineum,
- foamy nature of the secretion,
- nagging pain below the waist,
- weakness in the body and fever.
Such secretions provide signals of dangerous internal processes. Brown secretion mixed with blood may indicate a threat of fetal loss. Itching or burning warns of possible inflammation. Foamy secretion occurs due to fungal infections, from which no one is immune.
Important information.
Watery yellow discharge in women expecting a baby indicates that fluid from the membranes has entered the vagina. If this occurs in mid-pregnancy, premature birth may occur. If at the end - the first call of the beginning of labor.
Some people believe that pregnancy prevents the occurrence of fungal infections. Actually this is not true. Often, yellowish, foamy mucus indicates an infection. Timely treatment of the disease will certainly lead to success. Even for pregnant women, there are medications that spare the fetus. Therefore, you should not neglect communication with your doctor if you are in an interesting situation.
White liquid discharge
Vaginal secretions are normal and should not be too thick. It is well absorbed by panty liners or the surface of cotton underwear, even if there is heavy white discharge. An alarming sign is the presence of an odor in the mucus and an unreasonable increase in its volume. In such situations, you need to quickly see a gynecologist and take a vaginal smear for research. Provocateurs of liquid white discharge in women can be:
- Trichomonas;
- chlamydia;
- mycoplasmas or other microorganisms.
Leucorrhoea or vaginal discharge
Vaginal discharge to one degree or another is characteristic of all adult women. A small amount of mucous secretion helps to constantly cleanse the vagina of microorganisms that enter it.
In healthy women, the discharge contains bacterial flora, which provides the vagina with natural protection against pathogens. Secretory function indicates the normal functioning of the reproductive system, and also reflects cyclical changes in the body associated with the functioning of the ovaries.
It is important to distinguish normal discharge from pathological ones in order to promptly pay attention to possible signs of gynecological diseases.
Pathological discharge
Scarlet bloody.
When they appear a few days before menstruation, they indicate erosion of the cervix, after sexual intercourse - about injury to the vagina, and during pregnancy - about the threat of abortion. In some cases, such discharge is associated with endometriosis, uterine fibroids, and endometritis.
Smearing brown.
They are a sign of hormonal disorders and/or endometrial hyperplasia.
Foamy, abundant, yellow-green.
Indicate infection of the vagina, fallopian tubes, ovaries or other organs of the reproductive system. May be one of the symptoms of sexually transmitted diseases.
Thick purulent.
They are a sign of purulent cervicitis and can worsen with stress or during bowel movements. Unlike normal white discharge after menstruation, it has a more viscous consistency.
Pinkish with an unpleasant odor
. May indicate the development of endometritis. Usually appear before menstruation.
Watery, dirty gray
. This is a symptom of diseases such as endocervicitis, endometritis. They are observed both before and after menstruation. Dirty gray mucus with a strong fishy odor may indicate vaginal dysbiosis.
Curdled white.
Heavy white discharge after menstruation and during other phases of the cycle may be a sign of vaginal candidiasis (thrush). They may be accompanied by the appearance of a white coating on the external genitalia, itching, and burning.
White thick discharge in women
Increased viscosity and density of secretions is an ambiguous symptom, indicating either problems in the reproductive system or its normal state. White thick discharge, combined with itching, soreness, burning or a strong aroma, indicates the progression of diseases against the background of the following processes:
- bacterial infections;
- hormonal pathologies;
- viruses;
- inflammation;
- flora imbalance;
- venereal infections.
When white, thick discharge without odor or other pathological signs is present, it can be regarded as normal. If any aggravating factors or negative feelings arise, it is better to immediately go to see a specialist, take a vaginal smear and do a bacterial culture, check the state of hormonal levels and the functionality of the ovaries.
Physiological processes and watery secretion
The appearance of watery discharge in women, like water, indicates the following physiological processes:
- puberty in teenagers,
- ovulation period,
- hormonal changes
- sexual arousal,
- natural decline of the reproductive system,
- pregnancy.
As the reproductive system develops in adolescents, watery vaginal discharge comes out. The process begins at about 10 years of age. During this period, the ovaries actively produce estrogen, which prepares the young body for changes. Even before the onset of menstruation, girls secrete a clear secretion from their genitals. Even after the rhythm of menstruation stabilizes, liquid and transparent discharge will remain with the woman forever. Their number can change throughout the entire period of time without causing any side unpleasant sensations.
For the information of inquisitive ladies.
Vaginal discharge is considered normal if it is liquid in consistency, without a strong odor or other unpleasant symptoms. The daily natural volume is about one teaspoon.
Over time, vaginal secretions in girls acquire an individual character, which is not an anomaly. Depending on the level of hormones produced by the ovaries, the volume of secretion can be scanty or large.
During ovulation, when hormones are especially active, a woman experiences copious watery discharge. They continue to come out of the vagina for 5 days. Due to the large amount of progesterone, the secretion becomes watery. Over time, the situation will normalize.
If the discharge like water associated with ovulation does not stop, but continues for more than 7 days, it is advisable to consult a gynecologist.
Abundant transparent discharge occurs in a woman as a result of hormonal changes. As the amount of estrogen increases, a new egg matures in the ovaries. This affects the thickness of the secretion, and it takes on a new character.
Later, thick, watery discharge appears after menstruation, which indicates a decrease in estrogen levels.
After some time, the amount of hormones changes again, and the woman experiences heavy discharge. They often resemble egg whites.
Liquid vaginal secretion promotes the unhindered movement of sperm to the egg. If fertilization occurs, vaginal discharge and watery fluids will help the fertilized egg reach the uterus. During this period, estrogen levels decrease, and progesterone increases significantly. Its main task is to ensure the successful development of the fetus.
During strong sexual arousal, a woman experiences a large amount of discharge like water. They promote comfortable sexual intercourse, softening the movements of the male organ. After copulation is completed, the secretion may remain in the vagina for several hours. In some cases, it is released throughout the whole day. It all depends on the individuality of the female body. Typically, such discharge is odorless and itchy and is not dangerous to health.
During the period of decline of the reproductive system, women's hormonal levels change dramatically. After the cessation of menstruation, liquid vaginal secretions are considered normal.
When a lady is diagnosed with delay, she realizes that she has reached a new milestone in her life. In 9 months the baby will be born. Especially now, it is important to carefully monitor vaginal secretions. Often life depends on it.
Practice shows that during the first 12 weeks of pregnancy there is usually no watery secretion. At this time, the level of progesterone in the expectant mother’s body increases. Due to this, new eggs do not mature, and the embryo remains firmly in the uterus. Therefore, discharge, if any, is very scanty.
After the 13th week, the amount of estrogen rapidly increases, due to which new fetal cells are created. The appearance of strong liquid discharge is a natural process.
Immediately before childbirth, vaginal secretions melt like water due to the fact that they mix with urine. While in the uterus, the fetus puts pressure on the bladder, which cannot close completely.
After childbirth, milk appears in the breasts of the woman, so the consistency of the vaginal secretion becomes more liquid. In this case, the process is considered the norm.
White discharge and itching in women - causes
These clinical manifestations are characteristic of the proliferation of candidal fungus. Itching and white discharge are especially pronounced in women in the middle of the cycle and immediately before the onset of menstruation. A light coating is constantly observed on the underwear and labia, which easily rolls off like wet paper. At the same time, a sour, musty odor is felt, reminiscent of spoiled milk.
White discharge in women in combination with itching can also be caused by a cause such as vaginosis of bacterial origin or gardnerellosis. It is an inflammatory process caused by the spread of one or more types of opportunistic bacteria into the vagina. The secreted secretion smells sharp and very unpleasant, like rotten or rotting fish. Additionally, a burning sensation may be felt when visiting the toilet for minor needs.
Film-like discharge in women
Transparent, stretchy, mucous discharge, similar to egg white, often abundant - the period before ovulation, the norm.
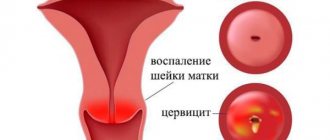
White mucous discharge or transparent mucous discharge with white streaks at the end of the cycle, before menstruation - cervical erosion, cervicitis (inflammation of the cervical canal). Mucous discharge is somehow connected with the cervix.
Creamy or jelly-like scanty discharge - the second half of the cycle. Norm.
Creamy or jelly-like, increasing discharge - the last days of the cycle. Norm.
Transparent, white or slightly yellowish discharge in clots is normal in the first hours after unprotected intercourse, when sperm enters the vagina.
Copious white liquid discharge the morning after unprotected intercourse is normal.
Creamy white scanty discharge after sexual intercourse with a condom or without ejaculation in the vagina is normal vaginal lubrication.
Brown spotting at the end of the cycle before menstruation (spotting) is a pathological process in the uterus (endometriosis, polyp or endometrial hyperplasia, etc.)
Brown spotting (spotting), long after menstruation - a pathological process in the uterus (endometriosis, polyp or endometrial hyperplasia, etc.)
Brown spotting during pregnancy (daub) is an old detachment of the ovum or placenta, which happened a few days or even a week ago.
Cinnamon discharge (spotting) in the first months of taking hormonal contraceptives is normal.
Scarlet spotting a few days before menstruation - cervical erosion, endocervicitis.
Scarlet spotting, intensifying - the beginning of menstruation, the first day. Norm.
Scarlet bloody streaks in the middle of the cycle - happens shortly after ovulation, a variant of the norm.
Scarlet spotting during pregnancy - detachment of the ovum or placenta, threat of miscarriage.
Scarlet bloody discharge after sexual intercourse - microcracks in the vagina formed during sexual intercourse, cervical erosion, cervicitis.
White cheesy or kefir-like discharge, white films or plaque between the labia majora and minora, on the clitoris, usually in combination with a bready or sour-milk odor - thrush (candidiasis).
White or slightly greenish discharge that peels off in films, usually combined with a fishy odor - vaginal dysbiosis (gardnerellosis)
Yellow or green bubbling discharge - sexually transmitted infection (trichomoniasis, etc.)
Yellow or greenish copious discharge - acute bacterial infection in the vagina, acute adnexitis (inflammation of the ovaries), acute salpingitis (inflammation in the fallopian tubes).
Yellow or greenish scanty discharge - bacterial infection in the vagina, cervical erosion, chronic adnexitis (inflammation of the ovaries), chronic salpingitis (inflammation in the fallopian tubes)
Ichor, discharge like diluted blood, like “meat slop” - lochia after childbirth, normal
Ichor, discharge like diluted blood, like “meat slop”, but with an unpleasant odor, usually before and after menstruation - chronic endometritis, chronic endocervicitis.
Liquid watery discharge that takes on a dirty color on the pad, before and after menstruation - chronic endometritis, chronic endocervicitis.
Liquid whitish discharge, similar to milk, during pregnancy, usually intensifies with increasing pregnancy - the norm, if it does not irritate the external genitalia and does not have an unpleasant odor.
Constant discharge that does not change during the cycle, with the exception of the period of menstruation, occurs when a woman takes hormonal contraceptives or suffers from infertility and does not have inflammatory processes in the vagina.
Discharge in large clots during menstruation - bending of the cervix, bleeding disorders - tendency to form blood clots, hypovitaminosis of B vitamins, pathological process in the uterus (polyp, endometriosis, fibroids). Also, similar discharge occurs if a woman has an intrauterine device.
Green, thick, combined with mucus, aggravated by tension, after defecation - purulent cervicitis
And most importantly, the appearance of any pathological discharge that bothers you is a reason to consult a doctor who will determine the cause and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Source: https://prodyhanie.ru/vydelenie-v-vide-plenki-u-zhenshhin/
White curdled discharge
The described symptom is one of the variants of the course of thrush. Candidiasis, which has become chronic, manifests itself as a white, curd-like, odorless discharge. Signs of pathology are observed constantly, but with varying degrees of intensity. Exacerbations occur against the background of systemic infections, when the activity of the immune system decreases. Sometimes women even get used to such secretion, perceiving copious discharge of white color and thick consistency as normal. To clarify the reasons for their occurrence, it is necessary to analyze the smear and calculate the amount:
- leukocytes;
- representatives of bacterial flora;
- fungal colonies.