Vaginal mycosis is one of the most common, but also the most unpleasant side effects of antibiotic therapy. Why does a fungal infection develop when taking antibiotics and how to fight it?
To answer this question, you first need to know how antibiotics work. Antibiotics are substances that are produced by certain microorganisms - bacteria and fungi - that destroy other microorganisms. Their discovery is one of the greatest achievements of medicine, as it helps fight many dangerous diseases for which there was previously no known cure and which have caused damage for centuries.
Characteristics of the norm
The use of antibiotics does not leave a mark on the body; after taking it, the therapeutic effect that needed to be achieved occurs, and the functioning of some internal organs and systems also changes. The severity of side effects depends on the state of the immune system, the presence of chronic diseases, and the duration of treatment.
The use of antibiotics affects the functioning of the immune, nervous, digestive, and reproductive systems. The action of the drugs is aimed at destroying pathogenic microflora, which is a provocateur of illnesses. However, the active components affect not only pathogens, but also beneficial bacteria.
Due to the influence of antibiotics, the microflora of the intestines, stomach, and vagina is disrupted. Specific discharge appears, which is the norm for a particular situation:
- The situation with thick, mucous, white, yellowish discharge, not accompanied by pain or itching, does not require treatment. With normal vaginal flora, the condition returns to normal within a week.
- The appearance of a cheesy white discharge with a sour odor after taking antibiotics is also common and is regarded by experts as normal. They appear against the background of decreased local immunity and microflora disturbances. Accompanied by itching and an unpleasant burning sensation when using alkaline hygiene products. The condition is popularly called thrush, and in medicine – candidiasis. For therapy, folk remedies, vaginal suppositories, creams, and ointments are used.
- The absence of specific discharge after taking antibacterial drugs also happens. This happens if the course of antibiotics was no more than 3 days, the body is not weakened by chronic, long-term diseases.
Mucous discharge after antibiotics can be a consequence of natural physiological processes (ovulation) or indicate the development of inflammation of the genital organs - the uterus, appendages. An examination and consultation with a gynecologist are recommended.
If there is a latent infection in a sexual partner, the woman’s likelihood of developing diseases after a course of antibiotic therapy increases. Vaginal discharge changes color, smell, consistency, and is accompanied by painful sensations.
Types of atypical discharge in women when taking antibiotics
Antibiotics are drugs that are prescribed for complex infectious diseases associated with decay processes in the body. Such remedies can harm your health and cause uncharacteristic vaginal discharge.
In addition to mucus, immunity decreases, the functioning of internal organs and general well-being deteriorate. Particular attention is paid to gynecological problems. Discharge after antibiotics appears in women for several reasons.
If treatment is not timely, exacerbations and inflammatory processes may occur.
Causes
Against the background of antibacterial therapy, women's immunity weakens, opportunistic microorganisms are given the opportunity to actively develop. A reduced number of beneficial bacteria and an increased level of fungi and viral cells lead to an imbalance, and dysbiosis develops.
The cause of the appearance of specific discharge can be fungi of the genus Candida, Gardnerella. Candidiasis, or thrush, or bacterial vaginosis develops. These microorganisms become causative agents of gynecological diseases when the body’s protective functions decrease. Symptoms are changes in the color, consistency, and smell of the discharge.
Vaginal dysbiosis after antibiotics provokes relapses of herpes viral infection. Mucous discharge and rashes begin in one or several places on the external genitalia. The condition normalizes on its own within 14 days, with the use of local antiviral medications – within 5 days.
Discharge after antibiotics, complicated by chlamydia, gonococci, trichomonas, mycoplasmosis, becomes abundant, foamy or mucous, changes color, and smells unpleasant. The situation requires examination and complex therapy for both the woman and her sexual partner.
Bacterial vaginosis
Gynecological disease caused by a violation of the vaginal microflora. The number of lactic acid bacteria, which are responsible for the normal condition of the mucous membrane, decreases, and the number of gardnerella increases. The smears do not reveal yeast-like fungi, trichomonas, chlamydia, or other provocateurs of sexually transmitted infections.
A sign of the presence of gardnerella is copious discharge. Initially, they have a slimy consistency, transparent, like snot, and there is an unpleasant smell of rotten fish, which intensifies in the evening, before menstruation, and after sexual intercourse. Over time they become thicker, white, gray in color. In the absence of timely treatment, another disease may develop - thrush.
Candidiasis
The growth of pathogenic fungi provokes disruption of the vaginal microflora, decreased immunity, and the influence of external and internal irritants. One of the most common side effects after a course of antibiotic therapy. At the initial stage of the disease, a change in discharge is observed, and in the absence of qualified treatment, other unpleasant symptoms appear: pain in the lower abdomen, frequent urination, discomfort during sexual intercourse, as well as weakness, headache, and decreased performance.
Initially, after antibiotics, discharge appears like snot, which indicates a violation of the microflora, then curdled.
Another name for candidiasis is thrush. The disease, caused by fungi of the genus Candida, increases the acidity of the vagina, resulting in the appearance of a curd-like discharge with a sour white odor. Thrush is accompanied by itching, burning, redness, and swelling of the genitals.
With self-treatment (in the case of strong immunity), the condition normalizes after using folk remedies, such as an alkaline solution, decoctions of medicinal herbs, medicinal tampons, tea tree oil, chlorhexidine, or it progresses and becomes a chronic relapsing form.
During pregnancy
Unpleasant sensations in the vagina in pregnant women often appear due to changes in hormonal levels. Thrush often develops in the first trimester, when major hormonal changes begin in the body and the immune system weakens. Treatment with antibiotics further aggravates the situation.
Healthy discharge during pregnancy is characterized by white color, thick consistency, and moderate amount. There is no itching, burning, no unpleasant odor. Discharge after taking antibiotics in women becomes mucous, thick, yellowish, gray in color. Treatment with antibiotics is prescribed in special cases if the therapeutic result significantly outweighs the risk of side effects.
Vaginal discharge after taking antibiotics, types and causes
Antibiotics are drugs that are prescribed for complex infectious diseases associated with decay processes in the body. Such remedies can harm your health and cause uncharacteristic vaginal discharge.
In addition to mucus, immunity decreases, the functioning of internal organs and general well-being deteriorate. Particular attention is paid to gynecological problems. Discharge after antibiotics appears in women for several reasons.
If treatment is not timely, exacerbations and inflammatory processes may occur.
Characteristics of the norm
Before using antibiotics, natural normal discharge should be transparent, mucous, light in color with a slightly sour odor. Their abundance depends on the period between critical days. With normal vaginal flora, mucus secreted during and after menstruation becomes more abundant. Afterwards the whites are again made more moderate.
After treatment with antibiotics, the nature of discharge in women may change somewhat. A sign of pathogenic microflora is a change in color and odor. Depending on the pathogen, mucus may be:
- yellowish, grayish, brownish, greenish-light green;
- curdled, similar to foam with pus;
- with stench;
- excessively abundant.
To identify which pathogen caused the pathology, it is necessary to take a smear. Both sexual partners should get checked.
Diseases that cause green menstruation
It happens that before menstruation and in its first days, green spotting appears. Should we be afraid of them?
- In this case, it is worth visiting a gynecologist, as this may indicate the presence of endometriosis, endometritis or adenomyosis.
- If during menstruation the color of the discharge changes to green, this may be a sign of colpitis, bacterial inflammation of the appendages or cervix. In such diseases, there is an excessive number of leukocytes and, due to their massive death, they stain menstrual blood this color. It is worth taking a smear for gardnerellosis. In this case, the discharge may be accompanied by an unpleasant rotten odor and itching.
Green discharge in girls under 8 years of age
If green discharge appears in a girl under 8 years of age, this may indicate inflammation of the vagina or vulva. This can be caused by mechanical trauma, rubbing by tight and uncomfortable panties.
It is also worth getting tested for worms, since green discharge can signal:
- about the presence of pinworms in the body and the development of enterobiasis.
- about the penetration of bacterial flora into the genitals - staphylococcus, enterococcus, E. coli. The cause may be: improper hygiene, an allergic reaction to detergent or laundry detergent, antibiotic treatment, vitamin deficiency, neglect of intimate hygiene, rare changes of underwear, masturbation with foreign objects.
Causes of discharge
Uncharacteristic discharge after antibacterial agents primarily appears as a result of infectious diseases, gynecological diseases, acute inflammatory processes, injuries and tumors of various locations.
After antibacterial therapy, mucus is accompanied by thick, curdled, granular impurities of blood or pus. The following diseases are caused by:
- inflammation of the vaginal mucosa;
- acute inflammatory process in the uterine appendages;
- inflammation of the genitals and vagina;
- gonococci, mycoplasma;
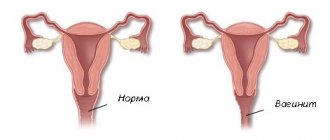
- vaginitis;
- bacterial vaginosis;
- trichomoniasis;
- cervicitis;
- vulvovaginitis and others.
Vaginal dysbiosis after antibiotics can also progress due to cervical erosion, cervical polyps, and polycystic disease. Particularly light bleeding appears after intimate intercourse. In the case of an infectious disease, the causative agent of the disease is determined when taking a smear.
When you're on your period, you need to be aware of when your blood mucus is healthy and when it's not. A strong discharge of blood may indicate new bleeding. The main symptoms are:
- replacing gaskets every hour;
- the occurrence of lightheadedness, nausea, possible loss of consciousness.
When affected by pathogenic organisms and the progression of sexually transmitted diseases, the following symptoms appear:
- hyperemia of the labia;
- rash;
- yellow or light green mucus;
- itching and burning sensation.
After passing all the tests, the gynecologist will prescribe appropriate treatment.
Find out why discharge appears after using Hexicon - antimicrobial and antiseptic suppositories by following the link.
Bacterial vaginosis
Regardless of the reason for taking antibacterial agents, therapy may result from changes in the natural vaginal flora. After treatment, most of the beneficial bacteria die and the vagina is colonized by pathogenic organisms.
Most often, vaginal tissue is colonized by Gardnerella. By themselves, they are not dangerous or pathogenic and only in combination with other organisms cause unpleasant symptoms. Severe pain, bad odor and strong mucus are signs of an infectious process.
With bacterial vaginosis, the discharge has a fishy odor, a mucous consistency, a profuse nature and a yellowish tint. Such signs may also occur in other diseases. The natural biocenosis is brought back to normal not only in the vagina, but also in the intestines.
Inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes, inflammation after surgery
Sometimes the source of inflammation occurs in the very depths of the female body - the fallopian tubes or ovaries. The signs of such diseases are somewhat different from those listed above.
Thus, the serous discharge observed with this disease most often has a dirty green tint, while no manifestations in the form of itching, burning or pain during urination may be observed at all. However, pain in the lower abdomen with such discharge, on the contrary, is intense and sharp.
Another distinctive feature of mucopurulent discharge during inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes is that their discharge increases significantly with physical activity. Additionally, manifestations of intoxication are recorded.
Another reason for purulent discharge is the occurrence of inflammation after operations on the organs of the reproductive system, for example, after the removal of various tumors.
The development of internal inflammation is accompanied by intoxication, an increase in body temperature to critical values, sharp pain in the pelvic region, a reaction from the lymph nodes and intense discharge of a purulent mass that smells repulsive.
Most often, this type of inflammation is caused by E. coli, streptococci, and staphylococci. Ignoring the above symptoms can lead to dangerous consequences - infertility, blood poisoning, and severe intoxication.
How is it treated? Without antibiotics, purulent discharge during inflammation cannot be overcome.
In advanced stages of the disease, accompanied by clear signs of intoxication (vomiting, high fever, poor health), not only hospitalization, but also surgery may be necessary.
Additionally, the patient may be prescribed immunostimulants, vitamins, hormonal medications - it all depends on what caused the inflammation.
Candidiasis
All components of the intestinal flora are in close balance and create a biocenosis. With it, there is a constant ratio of different elements of the natural and pathogenic microflora of the vagina. Violation of one link causes an imbalance in the biocenosis.
When treated with antibacterial drugs, a number of elements are knocked out, and the immune system is also suppressed. This leads to an increase in yeast fungi. Most often, the Candida fungus becomes active. It provokes candidiasis.
With candidiasis, the discharge is like snot, a cheesy consistency of a light milky shade and flakes. Such symptoms manifest themselves along with burning and itching of the genitals and vagina, which causes a lot of discomfort.
With progressive candidiasis infection caused by fungi, not only the mucous layer can be affected. The submucosal layer is also affected. In this case, the blood vessels are damaged. The consistency and color of the mucus begins to change.
They may take on a brownish color. The shade varies from light to dark brown. Mucus is observed due to the fact that fungal spores corrode the capillaries over time, without provoking a strong outpouring of blood, and it has time to coagulate. This process is usually accompanied by severe pain and discomfort.
During pregnancy
Pregnant women are also susceptible to diseases that require antibacterial medications. Complications may occur when using this group of drugs.
During pregnancy, the mucus in the first three months is quite thick. Thanks to this, a traffic jam is formed, isolating the baby from the outside world.
After the 12th week, when this plug forms, active production of estrogen by the placenta begins. The mucus secreted becomes thinner and stronger. The shade can vary from transparent to yellowish. This is healthy discharge.
It is normal to have clots no larger than 3 mm. There should be no other impurities.
Discharge after taking antibiotics in women carrying a fetus changes its consistency. This occurs due to a violation of the vaginal biocenosis. This provokes vaginal dysbiosis.
In girls who are not pregnant, the mucus may be identical. The problem is that there are frequent relapses.
The fungus can appear several times during pregnancy, which causes a lot of discomfort.
Highlights by color
Antibiotics are prescribed to cure infectious diseases, but they cause a severe blow to the body. This group of drugs causes uncharacteristic symptoms such as mucus.
Yellowish, red, green, brown and white discharge may appear after taking antibiotics. Some of them are accompanied by a stench.
But a woman should know in which cases there is a pathological process, and when underwear is the norm.
Source: https://gidroz.ru/matka/posle-antibiotikov-vydeleniya-v-intimnoj-zone.html
Highlights by color
Taking antibiotics affects the menstrual cycle, consistency, and number of periods. With a long course of therapy, there is a delay of menstruation of up to 2 weeks, the discharge is scanty or profuse.
Brown
The appearance of brown discharge in women indicates the rapid coagulation of blood droplets under the influence of oxygen. The situation arises against the background of hormonal imbalance, with impaired functioning of the nervous system.
Brown discharge after taking antibiotics appears during the period when menstruation should begin, or much earlier. They have no odor, but are accompanied by aching pain in the lower abdomen.
The appearance of a brown color indicates the development of neoplasms (cyst, fibroid, polyp). Taking antibiotics leads to disruption of microflora, a decrease in the body's protective functions, provoking an exacerbation of chronic diseases, disruption of processes in the reproductive system and, as a result, neoplasms. To prevent complications, you need to seek help from specialists if you have a specific color.
Reds
Excessive bleeding may be the cause of hormonal imbalance or indicate the development of an inflammatory process, endometriosis, fibroids, or cervical erosion.
In the absence of a pathological process, there is a delay of up to 2 weeks before the appearance of bleeding. Typically, bleeding begins on the second or third day, lasts up to four days, and menstruation lasts up to 8–10 days. In this case, the microflora in the vagina is not disturbed, the condition is normalized. In the next cycle, menstruation proceeds normally.
In the case of an inflammatory process or neoplasms, there is cramping pain in the lower abdomen of varying intensity. Blood flows for a long time, brown or mucous with pink streaks is constantly present. In the next cycle there is also a delay, menstruation is painful.
The development of endometriosis is characterized by severe pain in the lower abdomen, heavy bleeding, and spotting between periods.
Menstruation with a normal amount of discharge, which began earlier than expected while taking antibiotics, and is not accompanied by painful symptoms, is considered normal and is not a cause for concern.
Greens
Color alone is not a sufficient criterion for making a diagnosis. The cause of green discharge may be a banal violation of the microflora after antibiotics, as well as the development of STIs. The clinical picture of sexually transmitted diseases is almost the same: itching, burning, pain in the lower abdomen, discomfort during sex, problems with urination, frequent false urges, the foul smell of rotten fish, cycle disorders. A specialist can make an accurate diagnosis after a laboratory examination of a smear and an in-person examination.
Green color occurs with chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, bacterial vaginosis, as well as acute inflammatory process of the pelvic organs.
In the presence of inflammation, green discharge appears due to an increased number of leukocytes in the urethra. During antibiotic therapy, adnexitis, colpitis, urethritis, cervicitis, and adnexitis can develop. Inflammation is also caused by sexually transmitted diseases.
Yellow
The discharge changes in color, consistency, and quantity throughout the entire cycle. A yellowish tint unaccompanied by unpleasant symptoms is normal. Vaginal mucus contains many components; a pronounced yellow color is present after ovulation, at the beginning of the cycle it is replaced by white or transparent.
Increased yellow discharge indicates inflammation of the uterus. Other symptoms are initially absent or mild. As inflammation progresses, pain in the lower abdomen, weakness, temperature rises, decreased ability to work, and cycle disruption.
Yellow color can be the cause of banal vaginosis after antibiotics or indicates gynecological infectious diseases. Consultation with a gynecologist and examination are advisable.
Prevention
With long-term use of antibiotics, it is very difficult to prevent irregularities in the menstrual cycle and discharge, but every effort must be made:
- take probiotics;
- stick to a diet;
- give up sex for a while;
- exclude alcohol.
A violation of the vaginal microflora can be diagnosed while taking antibiotics or after some time. To help the body recover, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle and eat right for a month. After sex for the first time, it is recommended to wash yourself with a soda solution or soap.
At the first manifestations of thrush, you should douche with a folk remedy: for 1 liter of boiled water, 1 teaspoon of baking soda, salt, 10 drops of iodine.
Antibiotics must be taken strictly according to instructions. An untreated disease is dangerous for relapses, pathological microorganisms develop with renewed vigor, and drug resistance may develop. Specific secretions can be the cause of both long-term therapy and insufficient therapy.
Antibiotics are drugs that are prescribed for the treatment of complicated infectious diseases or diseases accompanied by purulent processes in the body. However, such drugs have a strong impact on the body and can easily disable its functioning. A sign of this is atypical vaginal discharge after taking antibiotics. They can be different - white, brown, bloody, yellow, scanty or abundant, with or without odor. But why does this happen? How does taking antibacterial drugs affect the functioning of the female reproductive organs? And what complications can their use lead to? You will now learn about this and much more.
Treatment
After taking antibiotics, special therapy for other diseases caused by these medications is required. Medicines are selected depending on the diagnosis. It is imperative to follow a diet excluding sweets, spicy foods, alcohol, coffee, and fatty foods. The diet includes fermented milk products, cereals, vegetables, fruits, and mineral water.
As a result of treatment with antibiotics, intoxication occurs in the body, which can be eliminated with the help of a proper lifestyle, nutrition, and certain medications. As the immune system is restored, the menstrual cycle and discharge normalize.
Antibacterial drugs
For the treatment of bacterial vaginosis and candidiasis, traditional medicine and special topical preparations are used. The course of therapy depends on the complexity of the symptoms, on average 7 days.
Vaginal dysbiosis must be treated and eliminated in order to prevent complications and the development of a pronounced inflammatory process in the genital organs. For this purpose:
- Pimafucin. Indications for use are fungal infections of the intestines and genitals. Vaginal dysbiosis is treated with Pimafucin suppositories. To treat thrush and vaginitis, one vaginal suppository per day is prescribed. Administered before bedtime. The duration of therapy is from 3 to 10 days. To increase the effectiveness of the drug in the absence of positive dynamics for several days, oral tablets are recommended.
- Oflocid. It is produced in the form of tablets for oral administration. The use of Oflocid after a course of antibiotics requires serious reasons, since this drug is also a broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent. It is advisable to familiarize yourself with the side effects after using Oflocid, as well as the list of contraindications. Prescribed for the treatment of STIs, inflammation of the uterus, appendages, bladder, and excretory tract. The course of therapy is determined individually in each case.
- Zalain . Vaginal capsules are prescribed for thrush and vaginitis. Insert into the vagina once before bedtime. If necessary, repeat the procedure after 5 days.
- Klion-D. Vaginal suppositories for thrush are used one per day for 6 days. The advantage is the rapid effect, selective effect on pathogens. The vaginal microflora is not disturbed. The drug is effective for frequent relapses of candidiasis.
Antibiotics should be taken in parallel with probiotics. The products prevent the development of thrush, vaginitis, intestinal and vaginal dysbiosis, and increase immunity. Effective drugs - Linex, Laktiale, Hilak Forte, Bifidumbacterin, Laktovit, Turbiotic. It is recommended to take it for another 3 weeks after finishing the course of antibiotic therapy.
Prevention
To prevent dysbiosis in the female half, you should not take antibacterial agents without good reason. Initially, a specialist must diagnose the pathology. Not all medications have the same effect. Each medicine has its own pathogenic organism that it affects. But the drug can very easily suppress beneficial microorganisms.
Long-term and unsystematic use of this group of medications changes the balance of the entire body. Pathogenic bacteria affect those places that are the most unprotected - the mucous membranes. The female half begins to have problems with the reproductive system. Mucus appears, which causes burning and itching.
You should take antibiotics only as prescribed by a specialist. Only he can prescribe the correct dosage and duration of use. If necessary, the specialist prescribes antifungal agents along with an antibacterial drug.
Discharge after taking antibiotics in women changes from the first days of therapy, regardless of which organ is being treated. The drugs enter the blood, spread throughout the body, are localized in affected areas, and at the same time change the functioning of internal organs and systems. The effect of the medication is reflected in the state of the intestinal microflora, genital organs, vaginal discharge becomes thick or, conversely, liquid and mucous.