One of the most common reasons why women turn to a gynecologist is the appearance of vaginal discharge. But this phenomenon is not in all cases a sign of a disease. Vaginal discharge accompanies us every day through life, and, as a rule, it should not cause discomfort. Normally, the cells of the vaginal mucosa produce a certain amount of fluid. When should you worry? The cause for concern may be changes in vaginal secretion.
Normal discharge before puberty
A woman’s reproductive system matures at 12–15 years of age and functions until menopause, that is, until 50–55 years of age. All this time, the female body is influenced by hormonal cycles, and first of all this concerns the reproductive system.
Infancy
Sometimes a newborn girl may have mucous or bloody vaginal discharge. This is a response to the hormonal crisis that her mother is experiencing; this is how the body gets rid of a large concentration of estrogen in the baby’s blood. Such secretions do not require any intervention; they are scanty, painless and completely safe. Therefore, parents are only required to maintain hygiene.
Not everyone experiences discharge in the first week of life; their presence or absence does not mean anything. Normally, such discharge should last no longer than two days and end no later than two weeks of age.
Childhood
Girls should not have vaginal discharge at all. In the period up to ten to twelve years, any discharge is a sign of pathology.
Prepuberty
The onset of puberty in girls is quite easy to determine. The breasts begin to enlarge first, then hair appears under the arms and on the pubis. The easiest and surest way to put yourself and your child in a state of combat readiness for the appearance of the first menstruation is to monitor the beginning of hair growth under the arms. The first hair appears about a year before the onset of puberty.
Around this time, vaginal discharge begins. The body is being rebuilt, homones begin to be synthesized, and the condition of the endometrium and vaginal mucosa is rapidly changing. The mucus itself is secreted; it is transparent, whitish or yellowish, odorless. A slight sour smell is also normal. This discharge does not cause pain, is not accompanied by itching, but can frighten the girl, so she must be warned in advance.
Menses
A girl turns into a girl when she gets her first period. This, of course, is completely normal discharge: blood, clots and mucus. Usually menstruation lasts 3–4 days. It should not be accompanied by severe pain, only mild discomfort is acceptable. However, girls often experience significant pain during menstruation, this is called dysmenorrhea. Painful sensations are caused by contraction of the uterus, which tries to expel the sloughing endometrium and clots faster and more effectively. Dysmenorrhea may be
- normal until a teenager’s cycle is established;
- as a result of stress or overwork;
- a sign of a disease if it occurs suddenly and for no apparent reason.
Menstruation should begin immediately with the appearance of blood. Mucus mixed with blood, dark discharge a day or two before menstruation may be normal, or may indicate incipient endometriosis.
If menstruation becomes heavier, if bleeding occurs in the middle of the cycle, uterine fibroids can be suspected. Myoma is a benign tumor, but it often requires surgical treatment.
Discharge outside of menstruation
From the onset of puberty, vaginal discharge will be constant. They depend on the concentration of hormones in a woman’s blood, so throughout the cycle the nature and amount of discharge will change slightly.
The hormonal cycle of the female body can be divided into two halves. The first day of the cycle is the first day of menstruation, the last day is the last day before the next menstruation. Ovulation occurs around day 14 of a standard 28-day cycle. The first half of the cycle is considered the time from the beginning of menstrual bleeding to ovulation, the second half is from ovulation to the next menstruation.
In the first half of the cycle, the discharge is scanty, no more than 1 ml per day. A spot of no more than 1-2 cm appears on the panty liner. The discharge is usually mucous, watery, and odorless. Small colorless lumps of mucus or a sour smell of the discharge itself is normal.
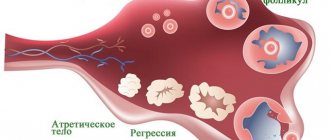
Ovulation is the release of an egg from an ovarian follicle. Ovulation and the egg's journey through the fallopian tubes is the optimal time for conception. At this time, the amount of discharge increases sharply (up to 5 ml per day) and its nature changes somewhat. The size of the stain on the pad is up to 5 cm. The discharge becomes viscous, more mucous, and sometimes darkens. There may be a particularly large amount of discharge during sexual arousal during this period.
Sometimes at the time of ovulation, the discharge becomes reddish. This is the norm.
In the second half of the cycle, the amount of discharge decreases. They become thicker, whiter, and have a jelly-like consistency. A few days before the start of a new cycle, the amount of discharge increases again.
Changes in discharge for various reasons
Beginning of sexual activity.
The change in discharge is easily explained:
- the first sexual intercourse is a great stress for the body, it changes the hormonal background of a woman;
- The microflora of the vagina changes due to the entry of new bacteria that are not characteristic of the body. The flora may be normal, but the new biocenosis comes into balance for some time and during this time the discharge may become different.
Sexual intercourse
Sexual intercourse increases the amount of discharge, as the cells of the vagina and cervix react to arousal. If during sexual intercourse sperm does not enter the vagina (condom, interrupted intercourse), the liquid discharge in the first minutes is followed by a thick white secretion. These are remnants of vaginal lubrication.
Sperm in the vagina causes a special reaction: transparent whitish-yellowish clots with an unpleasant odor are released.
Hormonal contraceptives
Hormonal contraceptives change the correct alternation of hormones in the female cycle, introduce the body into artificial menopause, and inhibit ovulation. As a result, the discharge becomes scanty, as in the first half of the cycle.
Change of partner
Changing a sexual partner leads to the colonization of new microflora in the vagina. Its flora is most likely different from the microbes living in the vagina, so the color of the discharge may change, its consistency may become different for a while. Changing a sexual partner can cause dysbiosis if a woman is inclined towards him.
If the soap brand changes
There are sensitive women who react to hygiene products or the composition of underwear. At the same time, the volume of secretions increases, they become liquid and transparent.
Pregnancy
Vaginal discharge changes during pregnancy for several reasons.
- The state of a woman’s hormones changes: the menstrual cycle stops with ovulation, the corpus luteum of pregnancy acts.
- The blood supply to the genital organs increases sharply.
In the first trimester there is more discharge than usual. If they are more liquid, transparent, colorless and odorless, with a slightly acidic odor, this is normal. The appearance of blood streaks in the discharge may indicate
- threat of miscarriage;
- ectopic pregnancy.
If in the first trimester the vaginal discharge becomes brown or mixed with blood, you should immediately do an ultrasound of the pelvic organs and consult a doctor.
At the end of pregnancy, more mucus appears in the vagina. You should also be wary of darkening of the discharge. This may indicate slight bleeding from small vessels of the cervix. It is especially important to monitor the passage of the mucus plug from the cervical canal. This is a symptom of the imminent onset of labor.
Postpartum period
After childbirth, blood and mucus come out through the vagina. Postpartum discharge is called lochia. The first week they are very similar to normal menstrual bleeding, only slightly heavier. But the wound surface from which the placenta was separated is gradually covered with new epithelium and the amount of discharge decreases. They become lighter, the last streaks of blood gradually disappear.
Lochia goes away in four to eight weeks.
Lactation
Usually there is no ovulation during breastfeeding; the body is not designed for conception. Discharge during this period is scanty, similar to the first half of the cycle.
Menopause
Several months before the last ovulation, the amount of discharge gradually decreases. The cycle becomes irregular again, and the intervals between menstruation increase. After menopause, discharge becomes very scanty.
If, after several months or years of absence of menstrual bleeding, they resume, this can serve as a very alarming sign: there is a high probability of an oncological process. Such a symptom (unexpected bleeding after menopause) should cause a woman to immediately consult a doctor.
Discharge is pathological if it becomes
- yellow, green, brown;
- have an unpleasant odor;
- irritate the genitals;
- accompanied by itching or pain.
In this case, you need to consult a doctor. It is impossible to conduct a full diagnosis at home.
Compound
Everyone knows well that during unprotected sexual intercourse, many sperm enter the female body together as part of semen. One of them must meet the egg and fertilize it. But many are surprised to learn that the sperm content in seminal fluid is only a little more than a tenth of its volume.
What does sperm consist of:
- Male reproductive cells.
- Prostate secret.
- Discharge of seminal vesicles.
And at the same time, each component part is very important. If you analyze the chemical composition of the mixture that is ultimately obtained and leaves the male body during ejaculation, you can see a whole complex of nutrients. It contains vitamins, minerals, a considerable amount of glucose and other carbohydrates, protein, fats, free amines, enzymes, and hormones.
This composition is necessary for sperm to be viable. Fertilization will not occur if they are not resistant to the acidity of the female genital organs or are not active enough to reach the egg.
Nutrients are used to create optimal conditions for movement and as an energy boost.
Pathological discharge
Pathological discharge is called leucorrhoea. They can vary in color, consistency and smell. Pathological discharge is the most common symptom of genital disease. Based on the nature of the discharge, one can assume the pathology that caused it, but diagnosis must still be carried out using all possible diagnostic tools: ultrasound, laboratory tests.
The source of leucorrhoea can be not only the vagina. The pathological process can be in the cervix and uterus, in the appendages. Diseases are not necessarily inflammatory in nature; they can be trauma, chemical irritation, prolapse of the vaginal walls, and much more.
Red discharge
An admixture of red in vaginal discharge indicates an admixture of blood. Normally, such discharge appears a few days before menstruation, but it should not have an odor. Sometimes the color of premenstrual discharge is not red or pink, but brown or even black. This is not scary, and only means that the blood has managed to oxidize in the vagina.
Streaks of blood may also appear in the middle of the cycle, at the time of ovulation. This happens normally, but more often happens to women who wear an intrauterine device or are protected using contraception. In this case, consultation with a gynecologist is necessary.
Bloody leucorrhoea should be a reason to see a doctor, because it may be caused by
- cervical erosion (pink discharge after intercourse, pain during intercourse);
- endometriosis;
- cycle disruption (which indicates a disturbance in the secretion of sex hormones in general);
Bloody discharge is especially dangerous during pregnancy. They always indicate trouble and are an indication for emergency hospitalization.
White and yellow vaginal discharge
Most often, the cause of such discharge is a large number of microbes, that is, a violation of the normal biocenosis of the vagina. In some cases, it is possible to detect pus in such discharge, and this is a clear sign of infection.
This symptom occurs when
- gonorrhea,
- trichomoniasis,
- thrush,
- chlamydia
- and other infections.
It is not possible to more accurately determine the infection and prescribe adequate treatment simply by the nature of the discharge, because it mainly consists of leukocytes. Leukocytes are cells of the immune system that appear when attacked by a foreign agent, regardless of its nature. Their presence only indicates that there is inflammation, and its cause must be further clarified.
Sometimes the discharge becomes foamy or cheesy, this is also a sign of pathology.
Unpleasant smell
The cause of unusual, unpleasant odors is microbes. They decompose nutrients, resulting in the release of gases. An unpleasant smell of discharge is an indication for examination by a gynecologist.
Basic postures after intercourse
| Horizontal position | If a woman remains in a lying position after intercourse for some time or all night, then sperm may not flow out of her for long enough and then be released in minimal quantities |
| Vertical position (sitting, standing) | By adopting a vertical body position immediately after intercourse, the likelihood of sperm leaking out in large quantities increases significantly |
| Birch stand | A similar body position, in which a woman takes a headstand and supports her shoulder blades with her hands, is used specifically to increase the likelihood of conception. In this position, sperm flows out in minimal quantities. |
Leucorrhoea, characteristic of various pathologies
Trichomoniasis
This is the most common sexually transmitted infection, affecting up to 10% of people on the planet. The causative agent is Trichomonas vaginalis. Infection occurs through sexual contact with a sick person. Since the infection is often asymptomatic, he may not even know that he is infected.
The incubation period of the disease lasts from one week to one month. Immediately after infection, a woman begins to experience urethritis. The combination of symptoms of acute urethritis (pain during urination, leukocytes in the urine) with characteristic foamy whitish discharge from the vagina indicates the most likely causative agent of the infection - Trichomonas.
In this case, the woman experiences pain not only during urination, but also during sexual intercourse, and is bothered by itching and burning. Upon examination, the doctor will see a very reddened, swollen vaginal mucosa covered with purulent discharge.
If the disease is not treated, inflammation of the vulva, swelling of the labia, and bartholinitis may begin.
The diagnosis is made after laboratory testing of a vaginal smear. It is easier to detect microbes in a smear when stained with methylene blue. PCR is also used, its result is the most accurate.
Vaginal dysbiosis
In the vagina there are not only Doderlein bacilli, but also a certain amount of opportunistic flora. These are streptococci, gardanella, bacteroides. If there is little such flora in the vagina, this is completely normal. But if this flora multiplies excessively, the biocenosis is disrupted, and vaginal dysbiosis occurs.
Women suffering from vaginal dysbiosis have discharge with an unpleasant odor. But a diagnosis cannot be made based on this symptom alone. A vaginal smear, laboratory testing, and determination of the acidity of the discharge are required.
Normally, the environment in the vagina is slightly acidic.
Restoring normal vaginal flora is a long, complex process. Vaginal suppositories clindamecin and metronidazole gel are used. If local therapy fails to restore normal bacterial growth of the vagina, systemic drugs are used.
Candidiasis
Fungi of the genus Candida live in the vagina normally, but usually there are not many of them there. With a pathological increase in their number, candidiasis begins, also called thrush due to the specific type of discharge.
Vaginal discharge is similar to cottage cheese; it is thick, white, yellowish with a sour odor. Such discharge irritates the mucous membrane, causing itching in the vulva and vagina. The tissues are inflamed and swollen.
Vaginal candidiasis can occur when the immune system is suppressed during pregnancy.
There are traditional methods of treating thrush: tampons with soda solution, herbal decoctions. But they often turn out to be insufficient.
Candidiasis is treated by taking pills, but local treatment with vaginal suppositories is also possible.
Chlamydia
This infection does not always cause an increase in vaginal discharge. With chlamydia, the discharge comes from the cervix and flows down the vaginal wall, so it is not always clearly visible. But when viewed in mirrors, they are usually clearly visible. Often, pain in the lower abdomen and pain when urinating occur simultaneously. Bartholinitis often occurs.
Diagnosis of chlamydia is carried out using PCR and culture.
Cultural examination is the inoculation of a smear on a nutrient medium, in which colonies of microbes that are present in the smear grow. Therapy is selected individually.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea discharge is moderate, yellowish and white. Pain is felt in the lower abdomen, sometimes when urinating. Bloody discharge in the middle of the cycle is typical.
Other infections
Other sexually transmitted infections often begin with vaginitis, which is inflammation of the vagina. The main symptom of vaginitis is abnormal vaginal discharge. Each disease has different manifestations and a different incubation period, but almost every disease begins with an acute stage.
Often there is inflammation not only in the vagina, but also in the urethra. Pain, itching, burning, frequent urge to urinate with a half-empty bladder, pathological vaginal discharge are symptoms of a urogenital infection that requires immediate diagnosis and treatment.
If treatment does not begin, over time the manifestations and severity of the process subsides, the infectious disease becomes chronic. In the chronic stage of the disease, there may be no symptoms at all. But the disease continues, complications will arise over time, so treatment is necessary in any case.
Almost all diseases of the genital area in women manifest themselves as one or another type of pathological discharge.
Interaction between seminal fluid and the female reproductive system
Sperm, ejaculate or seminal fluid (synonyms), coming out of the head of the penis at the time of orgasm, contains:
- healthy germ cells (antherozoids, viper, male gametes, sperm or spermatozoa).
- liquid blood plasma;
- secretion of the prostate and bulbourethral (Cooper) glands;
- grease or mucus.
Everyone knows that male sperm freely penetrates into the vagina during each sexual intercourse if contraception is not used. Inside this cavity, which receives the main portion of ejaculate, there is an acidic environment, the pH level is about 4 units, that is, close to neutral.
Alkalization (douching with soda solution) helps reduce acidity, which is harmful to most sperm when there are problems with fertilization. Due to natural acidity, most of the active sperm dies after 2-3 hours. Hundreds of “live ones” out of millions launched into the female perineum during sexual intercourse manage to break through all the obstacles into the fallopian tubes to the egg.
Inexperienced women are worried that sperm leaks out after sex, is it possible to get pregnant? “Traces of love” on the bed and legs are physiological. Judge for yourself, all that volume of unused sperm has to go somewhere. Moreover, cervical mucus, male lubricant from the passages and a natural lubricant from the vagina are added to it.
Western andrology experts have repeatedly conducted experiments to study the amount of sperm needed for fertilization. This question interests men who have sexual problems. Scientists argue that the very formulation of the question is incorrect - is it possible to get pregnant if sperm has leaked out.
What is much more important is not the volume of ejaculate itself, but the number of active male cells. Couples who have been evaluated for infertility will confirm that men with inactive sperm can have a decent volume when ejaculating. And the shape of the vagina in many women is such that part of the sperm spills out only on the way to the bathroom. And the desire to get pregnant is not compensated by restless sleep until the morning after intercourse (sexual intercourse) with turning over on the stomach, as is often recommended.
You should not pay attention to myths, speculation and unverified information if something does not work out with conception. It is better to go for an examination to find out the quality of the man’s seed material, and also to find out if the woman has any pathologies. It is the quality, not the volume, of sperm that determines the ability to have healthy heirs. This is where the “rule of one” comes into play. It means that one active and tenacious sperm is enough to prolong the race.