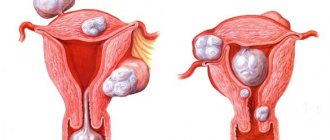
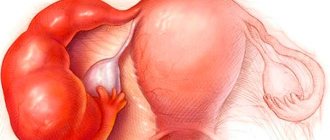
Submocotic fibroids are one of the most insidious manifestations of the disease. Located in the uterine cavity, such a node quickly makes itself felt with unpleasant symptoms. Even a small submucous fibroid disrupts the menstrual cycle and causes uterine bleeding and infertility. Without treatment, it significantly changes the usual course of life.
Sometimes submucous fibroids are born and fall into the cervical canal. This is a dangerous condition - it is accompanied by severe pain and bleeding. How and why a knot is born and whether it can be avoided - read the article.
Prerequisites for the development of the disease
The main reason for the growth of a nodular tumor is hormonal imbalance. Imbalance of the endocrine system in some women is accompanied by hyperestrogenism.
It is the receptors sensitive to this hormone that were discovered long ago in fibroid cells. Various prerequisites, in turn, can provoke hormonal imbalance:
- Independent use of oral contraceptives.
- Frequent stimulation of ovulation by hormonal agents.
- Taking medications to build up the endometrium.
- The use of herbs to obtain benefits from alternative medicine (sage especially enhances the production of estrogen).
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system that disrupt the functioning of the ovaries.
- Changes in the functioning of the thyroid gland.
- Distortion of the interconnected sequence of functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary system.
- Injuries to the mucous membrane of the reproductive organ received during childbirth or abortion.
- Unfulfilled reproductive function after the age of 40.
- Menopausal changes in the body.
- Neurological diseases, stress leading to menstrual dysfunction.
There is also a theory about the hereditary dependence of multinodular uterine fibroids. It is generally accepted that if a mother, grandmother and other female relatives had a benign hormone-dependent tumor, then it will certainly appear in the heiress. The question of when active cell division and the development of pathology will begin remains open.
Prevention
Even after complete recovery from submucous fibroids, it is necessary to regularly visit a gynecologist and undergo an annual ultrasound of the pelvic organs in order to prevent the disease. After all, there is always a risk of tumor recurrence.
Hypothermia and overheating of the body should be avoided. Therefore, you need to avoid visiting baths and saunas, as well as taking hot baths. It is also necessary to avoid tanning in solariums and in direct sunlight.
Nutrition should be healthy and balanced. It is important to eat a lot of vegetables and fruits, and you can also take pharmacy vitamin complexes. You should be very careful when taking any medications and folk remedies.
Medicines can only be taken as prescribed by a doctor. Before taking hormonal medications and homeopathic remedies containing phytoestrogens, it is necessary to take a blood test for hormones.
Classification
Identification of subtypes of nodular uterine fibroids allows you to choose the optimal treatment option for each of them. The classification of neoplasms is determined by the location of the nodes:
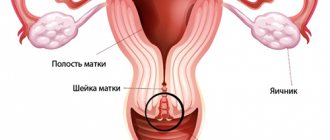
- submucosal - the tumor is located at the border of the myometrium with the endometrium in the area of the submucosal layer; when enlarged, the nodes can be found in the area of the internal pharynx and descend into the muscle tissue of the cervical canal;
- intermuscular - grows from the thickness of the muscle layer and is located in the cavity of the reproductive organ, usually has a stalk;
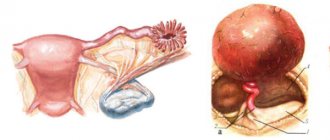
- subserous - the location of the myomatous node is external, the tumor is located in the abdominal cavity, protruding through the superficial lining of the uterus.
Based on the nature of their growth, benign formations - nodular fibroids - are divided into simple and proliferating. The first include tumors consisting of evenly dividing cells of the muscle layer. They usually do not exceed 70 mm in diameter, and there are less than 4 of them throughout the entire uterine cavity. Proliferating nodes include tumors that grow into the internal cavity of the reproductive organ. They are penetrated by numerous vessels and have a diameter of more than 80 mm. The number of benign neoplasms exceeds 5 pieces, so they contribute to an increase in the volume of the uterus and deformation of its cavity.
How does a submucosal tumor affect pregnancy?
Submucosal nodes have the greatest negative impact on pregnancy: they deform the uterine cavity, change the condition of the endometrium and thereby create unfavorable conditions for the implantation of a fertilized egg. And even if conception occurs, fibroids interfere with the normal development of the fetus. With an existing submucosal node, there is always a risk of premature termination of pregnancy due to abnormal blood supply to the uterine tissue in the tumor area. Cases of non-developing pregnancy are also common.
For your information
If you have been diagnosed with submucous uterine fibroids and are still planning to become a mother in the near future, you must begin treatment immediately after the diagnosis is made. Timely removal of internal nodes increases the likelihood of pregnancy.
In order to get pregnant, carry and give birth to a healthy baby, the pathology should be treated immediately after its discovery, before pregnancy.
Diagnostics
What is dangerous about nodular fibroids is their active growth and development of complications. Therefore, it is necessary to diagnose the pathological process as early as possible. At the initial stages of development of a nodular tumor of the uterus, a woman does not experience any disturbing signs. Therefore, pathological cells are discovered by chance during a routine examination.
Important! If you do not visit a doctor for a long time, nodular fibroids can be detected in the later stages, when cell growth is in the active stage, and it will no longer be possible to get rid of them using minimally invasive and conservative methods.
When a patient consults a doctor, special attention is paid to complaints indicating the growth of nodular fibroids:
- Painful sensations in the lower back, radiating to the legs and abdominal cavity.
- Increased menstruation time.
- Heavy uterine bleeding.
- Cycle disturbances, unstable periods and breakthrough spotting.
- Growth of the abdomen with active enlargement of nodular fibroids.
- Lack of pregnancy, infertility.
- Habitual miscarriage.
- Deterioration in general health.
The existing symptoms may indicate another gynecological pathology. Therefore, it is important to carry out differential diagnosis to confirm the tumor is benign.
For this purpose, hardware and instrumental studies are prescribed, including:
- Bimanual examination, palpation of the uterus with appendages - allows you to detect an enlargement of the reproductive organ.
- Ultrasound scanning - provides accurate information about where the multinodular fibroid is located and what size it is.
- Blood test - detects anemia, imbalance of hormones.
- A smear for the degree of vaginal cleanliness and oncocytology - shows the presence or absence of infectious processes, and also identifies atypical cells.
- Hysteroscopy - examination of the uterine cavity and nodular fibroids from the inside, provides a more accurate assessment of a benign tumor.
- Biopsy - a study involves taking a piece of a node for the purpose of further detailed diagnosis.
Diagnostic measures
Fibroids are detected during a standard gynecological examination with speculum.
As the disease develops, the uterus becomes enlarged and hardened. To confirm the initial diagnosis and determine the form of the disease, as well as the exact location of the nodes and their size, the gynecologist prescribes the woman a series of instrumental studies and tests:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs is performed in two ways: abdominal, which is also called external, and transvaginal - a special sensor is inserted into the vagina. Transvaginal ultrasound allows you to accurately determine the structure of the tumor, its size and location.
- A complete blood count can detect anemia.
- A smear for flora and atypical cells allows you to exclude malignant neoplasms of the cervix and associated infectious pathologies.
- Hysteroscopy - a gynecologist examines the uterine cavity using a hysteroscope - a special device equipped with a camera. The study allows you to determine the shape of the node, its size and exact location, as well as take a photograph in order to be able to observe it during drug treatment. If a malignant nature of the formation is suspected, during the examination the doctor takes tissue fragments for analysis in the laboratory.
- Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the pelvic organs. Both tests are performed using X-rays that are sensitive to soft tissue. During the study, layer-by-layer images are taken. Using a special computer program, the taken frames are combined and a three-dimensional image of the organs is obtained. During the study, it is possible to determine the exact number of nodes, their size and location, as well as the direction of growth.
Ultrasound and hysteroscopy are considered the gold standard in diagnosing uterine fibroids. CT and MRI are diagnostic diagnostic methods, but due to their high cost they are not often prescribed.
Treatment of nodular fibroids
Nodular fibroids are treated in two ways. The treatment method is selected in accordance with the shape and size of the node, as well as concomitant diseases of the uterus.
If the size of the tumor is small and there are no complaints, the patient takes a wait-and-see approach. For some time, doctors monitor the node and evaluate its activity.
If the fibroid grows and causes anxiety to its owner, it is recommended to begin conservative therapy. Lack of effectiveness is an indication for surgery to remove fibroids. This tactic is also recommended for patients with numerous nodes.
Surgery
Multinodular fibroids are treated surgically. Depending on the location of the tumor, fusel ablation, uterine artery emobilization, node resection, ultrasound, or radical surgery to remove the entire uterine cavity are performed.
Indications for surgical treatment are:
- Active growth of nodes with a size of 12 weeks or more.
- Heavy bleeding that poses a threat to the patient's life.
- Infertility.
- Death of node tissue.
- Spread of fibroids into the cervical cavity.
- Malignancy of benign cells.
When choosing a method of surgery to remove fibroids, the patient’s age, the need for reproductive function, as well as the individual characteristics of the body are taken into account.
Conservative treatment
In the presence of small fibroids, the nodes may respond well to conservative treatment. To correct bleeding, the patient is prescribed blood thickening drugs. Among a wide range of drugs, tranexamic acid is actively used.
It is important to take the medicine with caution, as it promotes blood clots.
To normalize the menstrual cycle and reduce the intensity of bleeding, oral contraceptives that have an antiandrogenic effect are prescribed. The drugs are selected individually, taking into account the patient’s hormonal background, previous births and ease of use. Intrauterine devices with a therapeutic effect can replace oral contraceptives. The use of the Mirena coil to reduce nodular fibroids shows good results.
A more complex treatment is the method of blocking estrogen synthesis. This effect is achieved as a result of the use of gonadotropin-releasing hormones. Medicines are used in the form of injections once every 3-4 weeks. During the entire treatment period, the woman does not have menstruation and does not produce estrogens. This suppresses the proliferative function of the endometrium and slows down (and in some cases reverses) the growth of nodes.
Important! Hormonal treatment of nodular fibroids can be used before surgery. Therapy allows you to reduce the size of the tumor and reduce the scope of surgical treatment.
What is the danger of the disease
For women of reproductive age, the development of myomatous nodes is dangerous due to the development of infertility. Depending on the location of the tumor, a woman will not be able to get pregnant or carry a child to term - there will be miscarriages.
Nodular uterine fibroids provoke various disorders of the menstrual cycle, an increase in the number of critical days and the abundance of menstrual flow, which leads to the development of iron deficiency anemia.
With a certain localization of the nodes, hematometra can develop - menstrual flow does not flow out, but remains in the uterus. When the uterus is filled with menstrual blood, urgent surgery is required.
Myomatous nodes can become inflamed, which leads to the development of peritonitis or sepsis. Torsion of the leg of the node leads to necrosis of myomatous cells, and in case of untimely medical care, to the development of peritonitis.
Submucous, internal and subserous fibroids.
If the myomatous node grows towards the bladder, then a frequent urge to go to the toilet begins, and then problems with urination. When a fibroid nodule grows towards the rectum, problems with defecation begin, frequent constipation appears and, as a result, hemorrhoids may develop. Myomatous nodes can degenerate into a malignant tumor.
To avoid the dangerous and irreversible consequences of the development of myomatous nodes, it is necessary to regularly undergo a preventive examination by a gynecologist every six months and promptly treat gynecological diseases, adhering to all the doctor’s recommendations.
Complications
Despite the fact that nodular fibroids are a benign tumor, they often lead to complications. Malignancy of cells occurs in isolated cases, but it cannot be completely excluded. Typically, complications occur due to the patient’s fault and due to refusal of observation and subsequent treatment. Adverse consequences of myomatous nodes include:
- bleeding from the uterus causing anemia;
- changes in the functioning of the pelvic organs (intestines, ovaries, kidneys and adrenal glands);
- twisting of the leg on which the node is located (requires emergency surgical removal of pathological tissue);
- suppuration of benign cells, necrosis of fibroids;
- inability to conceive and bear a child.
The cause of complications is often self-medication and the use of herbal medicine without prior consultation with a doctor.
The concept of a nascent myomatous node
A nascent myomatous node is the release of a submucosal (submucous) neoplasm on a stalk and its exit into the vaginal cavity. The pathological process develops quickly, and its onset can be triggered by lifting heavy objects or performing physical work. The complication requires immediate treatment.
Symptoms of a complicated condition:
- intense pain in the lower abdomen, reminiscent of labor pains;
- feeling of heaviness and fullness in the genital area;
- heavy bleeding;
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- the appearance of cold sweat, pale skin;
- cardiopalmus;
- general weakness.
If left untreated, complications may develop, such as infectious inflammation, peritonitis, and uterine inversion. Long-term complications may include infertility, severe anemia, and sarcoma.
The most common complication of a nascent myomatous node is necrosis of tissue that dies due to insufficient blood supply. This pathology is accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen, vomiting, nausea, dizziness, and fainting.
Consequences
The unpleasant consequences of nodular fibroids can be avoided if you are regularly examined by a gynecologist. Women of reproductive age are advised to visit a doctor at least once every 12 months.
Patients during menopause, when menstruation becomes rare, need to be examined every six months. Often, it is at this age that active growth of nodes begins due to hormonal changes.
By performing timely treatment, adverse consequences can be avoided.
It is important to follow the doctor’s prescriptions recommended for implementation during the recovery period. In the future, the patient should especially carefully monitor her health.
There is no specific prevention of nodular fibroids, but the likelihood of developing pathology can be reduced by the following methods:
- implementation of childbearing function up to the age of 35;
- conducting regular medical examinations in accordance with age;
- maintaining a correct lifestyle;
- balanced diet;
- eliminating bad habits;
- maintaining proper body weight;
- prevention of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the intimate area.
Pathogenesis
The formation of submucosal myomatous nodes is associated with damage to the genetic material of the muscle cells of the uterus. First there is a change in their functions, and then increased division. As a result, the appearance of small nodes is noted. The disease progresses and small elements combine into a tumor. The growth of fibroids in the uterus is ensured by increased recharge (blood supply) from the arteries of the reproductive organ. Submucosal formations with submucosal growth reduce the contractile function of the uterus, provoke an increase in the duration of menstruation, bleeding, and also pain in the abdomen and lower back.
Is it possible to cure with alternative medicine compounds?
The use of folk remedies for uterine fibroids is allowed, but such therapy must be agreed with a doctor. Herbal medicines cannot eliminate the formation of drugs, but they help in increasing the body’s protective properties and stopping tumor growth.
For uterine pathology, decoctions, infusions, and tampons soaked in medications are used. Doctors recommend the use of formulations from the following plants:
- Sabelnik and celandine have antitumor properties.
- Ginseng, lemongrass - have a protective effect.
- Upland uterus, burdock - regulate the production of hormones.
- Nettle, yarrow - stop bleeding.