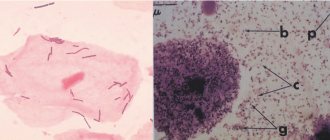
What is a polymorphic rod
Bacteria exist in various forms. Some are round or oval, they are called cocci. Others take on a rod-shaped form, these are bacilli. Still others exist in the form of a spiral, called spirochetes. Bacterial forms are not limited to just these 3 types. Some of them are polymorphic, meaning they exist in different states.
Such bacteria do not have a specific shape or differ from the three known stereotypical forms. Polymorphic bacteria change to adapt to the human genome. Polymorphic rod, which is often found in women's smears, refers to bacilli that change their shape and have different types.
Pathogenic effects of polymorphic rod
The normal microflora of the female body is a qualitative and quantitative ratio of microbial populations that have colonized a certain body system. Colonies of bacteria are involved in maintaining health. When pathogenic microorganisms begin to predominate, the microflora balance is disrupted. Among the pathogens there are both rod forms and cocci.
The article describes the reasons for the appearance of a polymorphic rod in a smear in women.
A woman's vagina is acidic because it contains a lot of lactic acid, produced under the influence of estrogen. About 97% of the bacteria inhabiting the microflora belong to lactic acid bacteria. At the same time, the microflora contains opportunistic organisms, cocci, rods, and bacilli.
Their number should not normally exceed 10.3 CFU/ml. Exceeding this parameter indicates the onset of a bacterial disease. The increase in cocci is accompanied by the growth of another conditionally pathogenic form - polymorphic bacillus.
Reasons for the appearance of a polymorphic rod
A polymorphic rod in a smear in women is a microscopic organism that creates a pathogenic environment in the vagina, cervix or cervical canal. Vaginal microflora refers to the cohabitation of different bacteria.
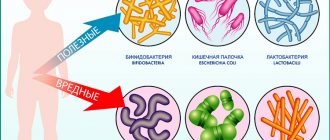
Some of them are present in the body normally, without causing any consequences. E. coli lives peacefully in the stomach and takes part in the process of food digestion. Likewise in the sexual sphere, many bacteria work for the benefit of health.
But this division is conditional; the microflora environment is divided into 3 categories:
- Normal microflora. Beneficial bacteria that perform a protective function predominate in the majority.
- Conditionally pathogenic. A certain number of bacteria present in the microflora do not bring any benefit to the body, but do not cause harm either. All this happens for the time being until a failure occurs in the system caused by stress, hypothermia, which weakens the immune system. Then the opportunistic forms of bacteria unite and begin to secrete waste products that inhibit the beneficial bacteria inhabiting the microflora. The functioning of the body is disrupted, and illness occurs.
- Pathogenic microflora. It is dominated by microorganisms that have a negative effect on humans. If the body is stable and the immune system is increased, then they do not cause much harm. But any failure increases the chances of getting an infectious disease, bacterial infection.
Dederlein's bacilli, which maintain an acidic environment, are responsible for the purity of the microflora.
They also take part in the creation of antibodies to various infections, maintain vaginal moisture, and inhibit the proliferation of pathogenic microbes within acceptable limits. The polymorphic bacillus is a pathogenic microbe that can attack a person at any time, affecting the cervix and cervical canal.
Dederlein's rods act as an antagonist to this microbe, preventing polymorphs from multiplying excessively. When the number of Dederlein bacilli decreases, their place is taken by a polymorphic bacilli, which indicates the formation of dysbacteriosis.
The number of leukocytes in the blood begins to increase, which are responsible for fighting bad microbes. Their increased reproduction signals that an infectious or inflammatory process has begun in the body.
Reasons why the number of polymorphs in the microflora increases:
- failure to comply with intimate hygiene rules;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- refusal of barrier contraceptives;
- frequent and unsystematic douching;
- uncontrolled long-term use of antibiotic drugs;
- hormonal changes during menopause, during pregnancy, and with menstrual irregularities;
- diseases caused by infections;
- long-term use of glucocorticosteroids that weaken the immune system;
- damage to the vaginal mucosa.
Diagnosis of polymorphic rod
A polymorphic rod in a woman’s smear is determined using bacteriological analysis. To carry out diagnostics, a smear is taken for microflora. Using a smear, it is difficult to determine the specific type of bacteria that predominates in the microflora.
For this purpose, bacteriological culture is carried out, on the basis of which not only the type of bacteria that has settled is determined, but also its sensitivity to antibiotics is determined. The results obtained enable the doctor to diagnose gynecological diseases: colpitis, vaginosis. Often a large accumulation of polymorphic rods indicates the development of vaginal dysbiosis.
The influence of microbes on microflora:
| State of microflora | Violations | Forms of disorders |
| Normal | Absence of negative microflora, predominance of lactobacilli | Normal state of the vaginal environment |
| Intermediate state | The number of lactobacilli is moderate, the presence of rods, gram-positive and gram-negative cocci. There are leukocytes and macrophages. | Normal condition in healthy women, teenage girls, without objective complaints. |
| Vaginal dysbiosis | There are few or no lactobacilli. Numerous colony of polymorphic rods and cocci. The white blood cell count fluctuates. |
Bacterial vaginosis
During pregnancy, the predominance of polymorphic rods negatively affects the health of the woman and the unborn child. Tests can be taken at clinics, where the cost of a smear does not exceed 300 rubles. Bacteriological culture costs from 600 to 800 rubles.
What is smear culture?
is a laboratory test in which the contents of the vagina are placed in a nutrient medium and optimal conditions are created for the growth of bacteria.
Research objectives:
- identify the causative agent of genital infection;
- establish the degree of contamination - the number of bacteria in the vagina;
- monitor the state of microflora after long-term treatment with antibiotics and cytostatic drugs. It is carried out 7-10 days after discontinuation of the drug.
- to all pregnant women upon registration;
- with inflammatory processes in the genital organs;
- Gram-negative diplococci were found in the smear - to confirm gonococcal infection (gonorrhea);
- with vulvovaginitis, recurrent or chronic.
Vaginal discharge is placed in nutrient media - solutions or jelly-like masses that contain nutrients for bacteria. Test tubes and Petri dishes are placed in a thermostat for 3-5 days, where the temperature is constantly maintained at about 37 degrees, optimal for the proliferation of microorganisms.
After cultivation, the laboratory assistant evaluates the results. From each microorganism, during the process of division, a whole colony of bacteria grows. Based on its appearance, the laboratory technician determines the type of pathogen. And by the number of colonies one can judge the concentration of these microorganisms in the vagina. Next, the concentration is compared with normal values.
The conclusion issued by the laboratory states:
- the type of microorganism that predominates in the smear;
- pathogenicity of a microorganism – the ability to cause disease:
- Pathogenic – the presence of which can only be caused by disease.
- Opportunistic - bacteria that cause disease only when immunity is reduced, with a significant increase in their number.
- concentration of the microorganism in the vagina. In numerical terms and in the form of verbal characteristics: “meager”, “moderate growth”, “abundant growth”.
| Degree | Features of bacterial growth | |
| Liquid culture medium | Dense nutrient medium | |
| I | Growth is very poor. | There is no bacterial growth. |
| II | Moderate growth | Up to 10 bacterial colonies. |
| III | Abundant growth. | From 10 to 100 colonies. |
| IV | Massive growth. | Over 100 colonies. |
I degree is the norm. In degree II, they speak of a violation of the vaginal microflora. III-IV degrees indicate a disease caused by this type of bacteria.
Tags: pregnancy, woman, smear, rod, flora About the author: Admin4ik
« Previous entry
Prevention of the appearance of polymorphic rods
To avoid microflora disorder:
- You should not use scented intimate hygiene products or antibacterial soap.
- Try to change pads and tampons as often as possible, and do not leave them in the vagina all day.
- Sex should be protected, reduce the number of casual sexual contacts.
- When purchasing underwear, give preference to cotton products to allow air access to the external genitalia.
- Include fermented milk products, fresh fruits and vegetables in your diet. Limit sweets and sugar, because they do not contribute to the formation of normal vaginal microflora that is resistant to the development of vaginitis.
Treatment methods for polymorphic rod
To correct the microflora, the root cause of dysbiosis should be established. If pregnancy or gynecological surgery is not planned, then you can do without medications, waiting until the balance is restored on its own. If aggravated symptoms are present, drug treatment is required.
A polymorphic bacillus that has multiplied in the microflora, as evidenced by a smear taken from a woman, is treated in 2 stages.
Initially, it is assumed that antibacterial and antiseptic drugs are used that suppress the proliferation of pathogens. At stage 2, drugs are used that restore the microflora. Between stages 1 and 2 of treatment, medications are prescribed that destroy the biofilm that pathogens create to reduce the activity of cells that protect the body.
Therapy with antibacterial drugs has side effects in the form of death of natural flora and is not always effective, due to the fact that pathogenic organisms take various forms. Many bacteria have increased resistance to many drugs.
Medications
Antibacterial drugs:
- Metronidazole. The drug is taken after meals, twice a day, 2 tablets. Treatment is carried out for 10 days. It is recommended to use intravaginal suppositories simultaneously with the tablets. Use a suppository in the morning and evening. Candle therapy is carried out at the beginning of the menstrual cycle. Price of the drug: 10–30 rubles.
- Atrican. The tablets are taken orally with meals, 1 capsule 2 times a day, morning and evening. Treatment lasts 4 days. It is not recommended to increase doses. The price of the drug is 2—–300 rubles.
- Ornidazole. Vaginal tablets are used 1 pc. daily before bed, for 5 days, for trichomoniasis. To treat vaginitis, 1 piece is inserted deep into the vagina. before bedtime, for 7 days. The drug costs from 70 rubles.
- Clindamycin. It is used in the form of suppositories, the course of treatment is 3 days, suppositories are administered 1 pc. for the night. The drug has many side effects; use must be discussed with your doctor. The price of the drug is from 300 to 500 rubles.
Medicines based on lactobacilli improve the effect of antibacterial therapy:
- Vagilak. Take 1 capsule per day with meals. Improvement occurs after 2 weeks.
- Lactozhinal. For therapeutic purposes, it is used for 7 days, 1 vaginal suppository 2 times a day. For prevention, take 1 suppository once a day.
- Gynoflor. The drug is used during menopause, 1-2 tablets intravaginally, for 12 days.
- Trioginal. Take 1 capsule intravaginally in the morning and evening for 2 weeks.
A drug that destroys bacterial biofilm:
- Vaginorm-S. Vaginal tablets, taken daily, 1 piece, for two weeks.
Other methods
Treatment involves the use of biological products that restore the biocenosis of the vaginal microflora.
These are dental preparations:
Traditional methods
A polymorphic bacillus in a smear in women, discovered during a visit to the doctor, may be a sign of vaginal dysbiosis, which can be treated with home remedies.
Treatment with tampons:
- It is good to moisten the tampon in natural milk or yogurt.
- Insert it into the vagina, pushing it as far as possible and leave it for several hours.
- For moistening, you can prepare a mixture consisting of milk and turmeric powder at the rate of 1 tsp. powder per 200 ml of warm milk.
- Soak the tampon in a solution consisting of 3% hydrogen peroxide diluted in equal quantities with water. The tampon is inserted into the vagina for 30 minutes.
- Coconut oil has preventive and antibacterial properties. You can also moisten a tampon with it for a hygienic procedure and leave it in the vagina for 2 hours.
Apple cider vinegar is a good pH restorer. You can add it to a warm bath and sit in it for 30 minutes.
Herbs with medicinal properties:
Herbal infusions are used for douching, lotions, and baths.
Diagnostic methods
To diagnose bakvaginosis in women, a correctly collected anamnesis is important. Often the pathology is combined with menstrual cycle disorders, such as luteal phase deficiency and oligomenorrhea.
When examined in the mirrors, characteristic leucorrhoea is noticeable, while the vaginal mucosa does not look swollen and inflamed.
The discharge can be very copious and flow freely down the walls into the vestibule area. During the examination, the doctor can assess the nature of the discharge by color, smell and consistency.
The Amsel criteria are used to confirm the diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis. They include 4 points:
- 1 Copious vaginal discharge with a characteristic “fishy” odor.
- 2 “Key” cells were found in smears under microscopy.
- 3 pH of the vaginal environment is more than 4.5.
- 4Amine test is positive.
The presence of three of the four listed signs is taken into account, which speaks in favor of bacterial vaginosis.
The study of native smears is a mandatory stage of diagnosis. With bakvaginosis, characteristic signs are found in them:
- 1The number of leukocytes is minimal or absent.
- 2The flora is abundant, represented by coccobacilli, cocci, vibrios, covering most of the field of view.
- 3 Lactobacilli are practically absent.
- 4The presence of “key” cells is required - this is the epithelium, on the surface of which bacterial cells are adhered.
The acidity of vaginal contents is determined using a litmus indicator, which should show alkalization of the environment.
Additionally, an amine test is carried out: a few drops of 10% KOH are added to the secretions. At the same time, a strong smell of “rotten fish” appears. It occurs when alkali reacts with the waste products of anaerobic microbes, represented by compounds of volatile amines.
PCR is of auxiliary value and is not used to diagnose bakvaginosis. Detection of gardnerella in non-pregnant women or a child (girl) in the absence of complaints and symptoms is not an indication for treatment.
However, PCR is necessary to diagnose chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis and other STIs that disrupt the balance of flora in the vagina.
Possible complications
The formation of large colonies of pathogenic bacteria in the vagina threatens inflammation of the vaginal walls and cervix. Over time, bacteria will penetrate into the uterus itself, which will lead to the development of endometritis and adnexitis. Inflammation can affect the urethra and bladder.
The accumulation of bacteria, the body’s reduced readiness to resist, leads to sexually transmitted infections: herpes virus, gonococci, chlamydia.
Disruption of the normal microflora in women, one of the reasons for which is a polymorphic bacillus found in a smear, is not a harmless disease at all. You should not put off visiting a doctor, because vaginal dysbiosis leads to serious problems.
Author: Belyaeva Anna
Video about the causes and methods of treatment of polymorphic bacillus in women
About microflora disorders:
How to decipher the results of a smear on the flora:
At the first symptoms, you need to go to the doctor and get tests done. I once delayed it so much, the treatment was long and expensive. Any problem must be solved in the early stages by listening to your body.
As a result of diagnostic procedures, rod flora is often detected in a smear - what it is can be understood by specifying the type of microorganisms identified.
There are several types of sticks: some are a mandatory option for the norm, while others warn of the development of pathological processes.
The presence of which rods can be shown by decoding a smear?
After receiving test results, it can sometimes be very difficult to understand the numbers and letters written by the doctor. It's actually not that complicated. In order to understand whether you have gynecological diseases, you need to know the normal indicators when deciphering the smear analysis for flora. There are not many of them.
In smear tests in an adult woman, the normal indicators are as follows:
- Mucus – should be present, but only in small quantities.
- Leukocytes (L) – These cells are allowed to be present as they help fight infection. The normal number of leukocytes in the vagina and urethra is no more than ten, and in the cervical area - up to thirty.
- Flat epithelium (s.ep.) - normally its number should be within fifteen cells in the field of view. If the number is higher, then this is evidence of inflammatory diseases. If less is a sign of hormonal disorders.
- Dederlein sticks - a healthy woman should have a lot of them. A small number of lactobacilli indicates a disturbed vaginal microflora.
The presence of Candida fungi, small rods, gram(-) cocci, Trichomonas, gonococci and other microorganisms in the analysis results indicates the presence of a disease and requires a more in-depth study and treatment.
Rod flora is an integral sign of women's health, to measure which smears are taken from the mucous membranes of the vagina. With the help of cytological tests, it becomes possible to identify many ailments of the genitourinary system.
READ MORE: What does ascus mean on a cytological smear - LiveAcademy
Find out what rod-shaped flora in a smear means, why rod-shaped flora is tested in gynecology, what types of rods there are, and what the decoding of a gynecological examination is.
Rod flora in a smear
Special laboratory tests for flora are carried out to study the conditions of the microflora of the genital organs in women and men.
A flora smear is one of the most common and diagnostically effective types of research in gynecology and urology.
During the procedure of taking an analysis, biological material is taken from the patient’s genitals with special instruments for examination under a microscope.
The results of the smear become known within a couple of days. Based on the analysis, it is possible to determine the presence of infection (or traces thereof) in the genital organs of men and women, inflammatory processes, pathological imbalance of microflora and other deviations from the norm.
What diagnosis can a doctor make for abnormalities in the rod flora?
1) Cancer of the uterus and cervix. To diagnose malignant degeneration of the endometrium, histological material is needed, and in large quantities.
2) Pregnancy. To determine it, a smear is not needed and it does not matter what result it shows. It is necessary to take a blood test for hCG, undergo a gynecological examination by a doctor, or do an ultrasound of the uterus.
3) CC and other pathologies (erosion, leukoplakia, koilocytosis, HPV infection, atypical cells, etc.) are diagnosed based on the results of a cytological examination.
This analysis is taken directly from the cervix, from the transformation zone, using a certain method with Papanicolaou staining (hence the name of the analysis - PAP test). It is also called oncocytology.
4) Does not show infections (STDs) such as:
- herpes;
- chlamydia (chlamydia);
- mycoplasmas (mycoplasmosis);
- ureaplasma (ureaplasmosis);
- HIV.
The first four infections are diagnosed using the PCR method. And it is impossible to determine the presence of the immunodeficiency virus from a smear with high accuracy. You need to take a blood test.
Based on the decrease in Dederlein's lactic acid rods and the increase in the number of small rods with key cells (epithelial cells surrounded by small rods), bacterial vaginosis can be diagnosed.
This pathology may have symptoms similar to other vaginal pathologies. Its course may go completely unnoticed by a woman. This is why vaginosis is dangerous.
Signs of bacterial vaginosis:
- light (white-gray) vaginal discharge;
- sour smell, reminiscent of fish;
- itching in the genitals;
- pain during intimacy and when urinating.
Bacterial vaginosis is sometimes confused with thrush based on its symptoms. But these are different diseases that cause serious damage to women’s health; they require competent and adequate treatment.
If left untreated, bacterial vaginosis can plague a woman for a long time with a certain feeling of discomfort. And the chronic stage of the disease will require longer and more expensive treatment.
The rapid development of gardnerella completely suppresses the normal microflora. Visually, in a vagina inhabited by Gardnerella, a white coating is detected on its surface.
The diagnosis is made after confirmation by microscopy results. The diagnosis can be confirmed by determining the acidity of the vagina and performing colposcopy.
Treatment of bacterial vaginosis is carried out in two stages. The first shows antibacterial agents that suppress the activity of harmful bacteria: preparations of Clindamycin and Metronidazole in the form of vaginal suppositories, gels, or in the form of tablets for systemic use.
The second stage involves “populating” the vagina with beneficial lactic acid microflora. For this purpose, appropriate dietary nutrition is prescribed (including lactic acid products and sauerkraut), and auxiliary preparations of lactic acid bacteria.
A more serious disease of the female genital area caused by gardnerella is gardnerellosis. If gardnerellosis is not treated and the development of the disease is allowed to take its course, then in the future this situation threatens to result in unpleasant consequences - inflammation of the vagina (nonspecific vaginitis) or infection.
In women with a predominance of gardnerella, there is an increased tendency to various venereological diseases, which in the future will have to be quite difficult to treat.
And inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs, which can occur against the background of gardnerellosis, can cause female infertility. Due to the presence of gardnerella, there is a high risk of developing endometritis or adnexitis. This also negatively affects women's reproductive health.
The patient may not even suspect its presence. And in order not to miss the moment necessary for effective treatment, it is necessary to promptly see the deviations of the flora in the smear.
When is rod flora detected in a smear?
In a smear, women will normally always have rod flora, because it is the presence of Dederlein rods in large quantities that contributes to the health of the female body.
There is a special classification of smear purity for vaginal microflora:
- The first degree of purity indicates the woman’s complete health. The analysis reveals a large number of lactobacilli - normal vaginal microflora;
- the second degree implies a high content of Dederlein bacilli and allows a small number of leukocytes in the smear - no more than 10 per 1 cm 2 in the material being studied. This is also one of the norm options. In pregnant women, the white blood cell count may be slightly higher;
- with the third degree of purity of the smear, pathological changes in the vaginal microflora are detected - a very small number of gram-positive beneficial bacilli are observed, per 1 cm 2 there are from 10 to 30 leukocytes, and the flora is mixed, may contain cocci (spherical bacteria), and large and small bacilli ;
- The fourth degree of purity of the analysis is characterized by a large number of leukocytes (representing the main composition of the smear), the absence of normal flora, mucus, rods and cocci in the smear.
In women with regular sexual intercourse, tests may show mixed flora at the end or beginning of the menstrual cycle, during decreased estrogen production or under the influence of ovarian pathologies (with severe hyperfunction).
Mixed flora with rods and cocci can be a sign of gynecological diseases or sexually acquired infections, because the development of opportunistic microflora is often accompanied by other, more serious diseases.
In little girls and women during menopause, due to the characteristics of hormonal levels, analysis may also show a mixed flora.
What are they and are they all dangerous?
If necessary, different tests can be done to determine each specific type of rod.
But there are a few sticks that should be detected anyway. Small rod flora in a woman’s vagina is considered dangerous. It indicates that the smear may contain gram-negative harmful bacteria, which greatly reduce immunity and prevent the body from fighting even the most minor diseases.
If small rod flora is abundant, this is an alarming signal. The doctor must definitely prescribe complex treatment with special drugs that can restore normal microflora in the vagina.
Small rod flora may also indicate the presence of diseases such as gardnerellosis or dysbacteriosis. Then the treatment must follow a strict regimen, which is developed by the attending physician.
The greatest danger is that the flora mixed with a predominance of small rods can, over time, destroy the beneficial flora of the vagina. And then it will be quite difficult to avoid complications that can even lead to infertility.
Large gram-positive Dederlein rods are considered useful. They should be present in sufficient quantities in the smear of every healthy woman. These non-motile bacteria create an acidic environment in the vagina, which affects the fertilization process.
The bottom line is that weakened sperm die in an acidic environment, while active cells suitable for the formation of a zygote remain and pass further to the uterus.
Dederline's gram-positive bacilli are responsible for the cleanliness of the genital tract and can also destroy the causative agents of trichomoniasis and gonorrhea. They secrete a substance similar to hydrogen peroxide, which is a natural antiseptic in the female genital area.
The norm of such rods in the female body is determined by the doctor. A sufficient number of such bacteria indicates a woman’s health. But if there are very few rods, this may indicate pathological processes in the female body.
To determine the normative value of Dederline rods, not only their number is taken into account, but also the presence of leukocytes and lactobacilli.
- So, if from 10 to 30 leukocytes are observed, the flora contains both cocci and rods, but there are few Dederline rods, then the flora is considered mixed. It is observed in women who have regular sex life. Mixed flora can also occur in teenage girls. In other cases, mixed flora may indicate an inflammatory process in the vagina.
- If only single leukocytes are observed in the smear, but there are a large number of Dederline rods, then the microflora in the vagina is poor and favorable. It is observed in completely healthy women and girls, whose bodies cope well with pathogenic bacteria.
- If the number of Dederline rods is average, there are about 10 leukocytes, and there are a lot of lactobacilli, then this indicates an average flora in the vagina. Some women may have a large amount of mucus and many cocci in the vagina. Lactobacilli are absent in this case; a polymorphic rod may be detected in a smear on the flora.
Doderlein bacilli, or, as they are also called, lactobacilli and lactobacilli, are microorganisms that protect the vagina from pathogenic infections by producing lactic acid, which helps maintain an acidic environment and destroy pathogenic flora.
A decrease in the number of lactobacilli indicates a disturbed acid-base balance of microflora in the vagina and a shift towards the alkaline side, which often occurs in women who are sexually active.
Cytological studies of a vaginal smear help to determine in what quantities pathogenic and beneficial bacilli are present in the discharge.
Deviations in the state of the reproductive system can be indicated when small rod flora is detected in the smear, indicating the presence of gram-negative harmful bacteria in the vagina, which contribute to a significant decrease in immunity.
As a result of such changes, the immune system weakens and its resistance to the development of various diseases decreases.
Abundant small rod flora in a woman’s smear is an alarming signal indicating inflammatory processes.
A patient whose flora smear contains small rods is recommended to undergo complex treatment using special medications aimed at restoring normal microflora in the vagina.
The presence of small rod flora in a smear may also indicate gardnerellosis and dysbacteriosis, the treatment of which is impossible without prescribing an individual strict regimen.
The category of beneficial bacteria includes gram-positive Dederlein bacilli, a certain amount of which must be present in the smear.
Gram-positive bacilli are also responsible for ensuring the cleanliness of the genital tract and the destruction of pathogens of diseases such as gonorrhea and trichomoniasis, due to the release of a kind of “antiseptic”.
Polymorphic rod flora in a cytology smear - what does this mean? The active development of polymorphic rod flora occurs against the background of a decrease in the required rate of gram-positive Dederlein rods in the vagina.
vaginal dysbiosis, which most often develops against the background of dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract and nutritional problems.
There can be two types of rods in a smear: Dederlein rods or small rods. Both types may have some impact on the health of the female reproductive system. The main thing is to notice pathogenic deviations in time.
Doderlein's rods are named after the German obstetrician-gynecologist with the same name Doderlein A. These non-motile bacteria are quite large in size and do not form spores.
Due to the presence of Dederlein's rods, an acidic pH environment prevails in the female vagina, which plays the role of a kind of filter in the selection of sperm that are full in terms of viability.
In addition, beneficial bacillary flora is responsible for the cleanliness of the genital tract through the formation of hydrogen peroxide released into the vaginal cavity. Lysozyme (a kind of natural antibiotic) takes part in the control of cleanliness.
READ MORE: Cervical cytology - what is it, explanation
Also, gram-positive rods are initiators of macrophage activity. The latter, in turn, fight various foreign pathogenic microorganisms that have entered the body.
The involvement of Dederlein's rods in the synthesis of specific antibodies and biologically active substances has been established. In cooperation with leukocytes, beneficial bacillary flora takes part in strengthening the local and general immune defense of the body.
Dederlein's sticks, even in significant numbers, are considered an indicator of the health of the vagina and do not indicate the presence of any disease.
Another fact that may alert the doctor is a reduced number of gram-positive rods in the smear. This may mean the patient has bacterial vaginosis.
The appropriate content of Dederlein rods determines the degree of purity of the smear. There are 4 degrees in total:
- Many Dederlein rods, single leukocytes, poor and mostly beneficial bacillary flora.
- High content of lactobacilli, up to 10 leukocytes per field of view, average flora.
- From 10 to 30 leukocytes in the field of view, there are few gram-positive rods, the flora is represented by both rods and cocci (spherical bacteria), that is, mixed.
- Leukocytes mainly cover the flora, the rod flora in the smear is represented by cocci (lactobacillus are not noted), a large amount of mucus.
In women who have regular sexual relations, mixed flora is present in the smear at the end or beginning of the menstrual cycle, when estrogen production is reduced.
In addition, mixed flora is observed in girls before puberty, in women during menopause or in active reproductive age with ovarian pathology (hyperfunction).
The detection of small rod flora in a smear is an alarming signal. After all, small sticks indicate an unfavorable clinical picture of the female vagina.
If, according to the results of the analysis, the predominance of small rods is noticeable, then the doctor may suspect diseases of the genital area - vaginal dysbiosis or gardnerellosis.
The abundance of small rod flora in a smear is always a health hazard, since the female body is weakened and unable to withstand the onslaught of infection and pathogens.
A smear taken by a gynecologist during an examination can help not only identify existing disorders in the functioning of the reproductive system.
Such an examination can prevent the development of infertility and endometritis, but only if pathogenic small rods, including polymorphic ones, are quickly and accurately detected.
Features of gardnerellosis
Gardnerellosis (unlike diseases such as trichomoniasis and gonorrhea) is a pathology of a non-venereal nature. As a rule, the root causes of the development of the disease are not related to the sex life of patients.
Thus, gardenelosis often occurs even in people who are not sexually active at all. The key factors that trigger the pathological process can be even ordinary stress, ARVI, chronic lack of sleep and an unbalanced diet.
The diagnosis of gardnerellosis is usually made in men. In women, the disease is diagnosed as bacterial vaginosis.
The gardnerella bacillus creates an environment favorable for the development of chlamydia, the growth of gonococci and trichomonas.
With the development of gardnerellosis, normal aerobic microflora can gradually be completely replaced by anaerobic organisms, which is accompanied by vivid clinical symptoms.
Like any opportunistic microflora, Gardnerella bacilli can live in the body in small quantities without provoking pathological changes.
In fact, it stimulates the active reproduction of Gardnerella:
- reduction in the amount of normal microflora that perform protective functions;
- general decrease in the functioning of the immune system;
- change in acidity level.
In men, this disease can occur only as a result of internal problems, including due to neglect of personal hygiene rules, but often patients, ignoring the minor discomfort that develops as a result of the onset of the pathology, infect women.
In women, bacterial vaginitis occurs both due to internal factors and as a result of transmission of active pathogenic microorganisms from a sexual partner. A man cannot become infected with gardnerellosis from a woman.
Symptoms of gardnerellosis include:
- sensations of itching in the genital area and burning sensation when emptying the bladder;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- copious gray mucus discharged from the urethra and having a strong fishy odor.
The burning sensation occurs due to the fact that, under the influence of opportunistic microflora, the urethral mucosa is damaged, and under the influence of urine, pain and pain appear.
In women, gardnerellosis is usually more severe than in men, whose symptoms are often intermittent in nature with declines and peaks of exacerbations.
Infection of a pregnant woman is dangerous because the pathology can affect the intrauterine development of the fetus.
The disease can be avoided by maintaining a high level of general and local immunity, following the rules of hygiene and monitoring your health.
Men and women should periodically undergo preventive examinations, taking smears for microflora.
It is better to responsibly treat gardnerellosis once under the guidance of a specialist than to periodically return to relapses of the pathology, which is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms and creates favorable conditions for the development of other diseases.
A woman who cares about her health should visit a gynecologist at least once a year, and ideally every three months. During the examination, the doctor must take material for examination from the cervical canal, cervix and vagina in order to determine the level of cleanliness of the vagina and identify the disease in time. Normally, the microbial flora is rod-shaped or mixed, where the bulk of the bacilli present are beneficial lactobacilli, which look like rods with a thick wall and are of the same size.
When and how is a smear taken?
- complaints of itching or vaginal discharge, other symptoms of inflammation;
- preventive examinations;
- control of the treatment;
- taking hormonal drugs and immunosuppressants;
- control of microflora during long-term use of antibiotics;
- pregnancy. It is carried out 3 times during pregnancy (at registration, at the 30th and 36th week).
This study has many names: smear for flora, general smear, bacterioscopy, smear for cleanliness. There are also smears on the flora from the urethra and cervical canal. Usually these three types of smears are performed together.
When the pregnancy proceeds without complications, a smear is taken when registering for pregnancy, then repeated at 30 weeks and before delivery. If a woman has previously had miscarriages or there was a threat of miscarriage, polyhydramnios, intrauterine infection of the fetus, chorioamnionitis, the study is carried out dynamically at the discretion of the doctor, in addition to other diagnostic methods.
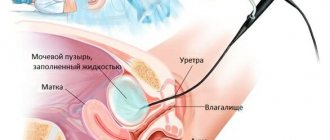
A smear is taken in a gynecological chair with a special instrument from the urethra, cervix and side wall of the vagina. Afterwards, the material is smeared onto numbered sterile glass and sent to the laboratory where the study takes place.
The color, quantity, smell of discharge, the condition of the cervix and vagina are assessed. The microbial composition of the smear is determined in the laboratory.
The first degree is given if a smear examination reveals an acidic environment in the vagina, a sufficient number of Dederlein bacilli, and facultative flora is found in small quantities. Red blood cells and white blood cells can be determined in single quantities.
The second degree of purity is assigned if in an acidic environment the number of lactobacilli predominates over the remaining microbial cells. White blood cells, as a rule, increase to 15; we recall that the permissible reading during pregnancy is 20, but only if there is no sign of an inflammatory process.
The third degree - dysbiosis, as a rule, is observed in women with bacterial vaginosis. The smear, in this case, contains a large number of gram-positive cocci, lactobacilli are practically absent, but there is a considerable amount of obligate anaerobic bacteria, gram-negative rods.
Vaginitis is the fourth degree of vaginal purity. In this case, the vaginal environment is alkaline, the smear contains a large number of red blood cells, leukocytes, and pathogenic microbes.
Normally, a pregnant woman should have the first type of smear, sometimes the second type is allowed, everything else is outside the norm.
Pregnant women should know that before taking a smear to check the cleanliness of the vagina, it is better to abstain from sexual intercourse for a couple of days. You should not douche, or use vaginal tablets, suppositories, or local disinfectants. On the day of taking a smear, genital hygiene should be performed without using soap.
With a normal smear, leukocytes may be contained in the vagina, urethra, cervix in small quantities or absent altogether. Flat epithelium should be between 5-10. The microflora in the vagina should contain a large number of gram-positive lactobacilli. Microflora in the urethra and cervix should not be detected.
Mucus in the vagina and cervix should be in moderation. Gonococci, Trichomonas, and key cells should normally be absent. Yeast may only be present in the vagina in very small quantities.
Deviations from the norm
If squamous epithelium is not present in a smear on the microflora of a pregnant woman, this is an indication that the body is experiencing a lack of estrogen. An increase in the amount of squamous epithelium indicates the development of an inflammatory process in the body of the expectant mother.
If a large number of leukocytes are found in the smear, this is a sure sign of inflammation. A large amount of mucus can also indicate possible inflammation.
Gonococci, key cells, trichomonas and yeast-like fungi are found in the case of certain diseases. In case of any deviation from normal values, the gynecologist prescribes additional studies to find out the cause of the disease and select the appropriate treatment. An analysis for sexually transmitted infections is also required, and if they are detected, a course of treatment is prescribed.
During pregnancy, as a rule, women choose suppositories, vaginal tablets, and special creams for treatment. Preference is given to drugs that do not contain antibiotics. But in case of urgent need, a course of antibacterial therapy can be prescribed, taking into account the duration of pregnancy.
Many infections are hidden, but can significantly affect pregnancy and the development of the child, which is why, if you are planning a pregnancy, you need to be tested to determine the presence of sexually transmitted infections even before conception.
Even if you were diagnosed with some disturbances in the vaginal microflora during pregnancy, this is not a reason to panic. Follow your doctor's instructions strictly - do not interrupt the course of treatment, especially when it comes to suppositories, and also take special care of your personal hygiene.
Linen is only cotton, and it is better to iron it with a hot iron, even if you usually don’t do this. In general, normalizing the vaginal microflora is not so difficult, even during pregnancy, just treat this issue with due attention.
What does a smear test for flora show?
A smear is taken for analysis using a disposable special spatula. The resulting scrapings are applied to a glass slide and sent to the laboratory, where they are stained with the desired dye, dried, and then examined under a microscope. This is a microbiological analytical method.
It allows you to see:
- in a woman’s smear there is rod flora , which means the presence of lactobacilli, gram-positive bacilli that maintain an acidic environment and suppress the proliferation of harmful bacteria;
- squamous epithelium, which lines the mucous membranes, and its amount varies depending on the day of the menstrual cycle;
- leukocytes involved in the destruction of pathogenic microbes;
- mucus is observed as a product of the glands, it is necessary to maintain normal humidity;
- the appearance of polymorphic rod flora ; we will consider what this means for the body below.
The smear is analyzed in the laboratory under a microscope using special dyes
Polymorphic rod flora
The group of polymorphic rod flora includes bacilli that have different sizes and shapes of rods that differ in thickness from useful samples. Such microbes are much smaller and are called gram-negative.
This provokes the occurrence of diseases, from dysbiosis to inflammatory and infectious processes.
Symptoms
Polymorphic rod flora found in a smear in large quantities is accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the cervix and cervical canal. Accompanied by the following symptoms:
- there is a large amount of discharge of a light, gray or greenish color, sometimes even purulent;
- an unpleasant sour smell appears;
- worries about itching and discomfort;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- unpleasant sensation during bowel movements;
- pain in the lower abdomen and perineum.
Self-medication mistakes
Very often, women mistake the above signs for thrush and begin to treat themselves, driving the situation into a dead end. This absolutely cannot be done. If the slightest deviations in the functioning of the reproductive system appear, you need to visit an antenatal clinic to establish the cause and properly get rid of it.
The need for bacterioscopy
Representatives of the polymorphic rod flora can settle on the walls of the vagina in the form of a white coating, which is detected by the gynecologist during examination. It is difficult to determine exactly what kind of bacillus it is, therefore, as a rule, bacterioscopy is prescribed. After collection, the test material is placed in a special environment where microbes germinate. This helps to identify all their varieties and identify not only the type of pathogen, but also its sensitivity to antibiotics that can destroy it.
How is it surrendered?
Usually a vaginal smear is part of a woman's routine medical check-up. It is performed by a specialist during a gynecological examination. Biological material is also collected from the urethra and cervix.
This diagnosis allows you to detect possible problems with women's health, such as an inflammatory process or a disease caused by an infection.
A gynecological smear is taken if the following diseases are suspected:
- Vaginosis or vaginitis;
- Thrush
- Trichomoniasis
- Gonorrhea
Specialists can prescribe a smear if the patient has the following complaints:
- Burning and itching sensation in the vagina.
- Pain during sexual intercourse.
- Unpleasant-smelling copious discharge with discoloration.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
A smear is taken when planning pregnancy and after antibiotic therapy. In addition, the smear allows you to monitor the effectiveness of therapy in the treatment of gynecological diseases.
Advantages of the method:
- Painless procedure.
- Simple rules for preparing for a smear test.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of treatment of female diseases.
- Possibility of identifying many diseases of the genitourinary system.
For preventive purposes, women periodically need to undergo this diagnosis. This will help prevent possible undesirable consequences.
The analysis is most often taken by a doctor when you come to him for a regular appointment at the clinic or when you simply go to a paid laboratory, where obstetricians and medical staff take biomaterial from you.
In men, a urologist or another doctor inserts a special disposable probe into the urethra, turns it around its axis several times and takes an analysis. It is believed that the examination does not cause pain, however, this does not exclude the carelessness of the doctor, as well as individual sensitivity or the presence of a particular disease, which can cause discomfort.
Doctors do not use full names, but abbreviations - the first letters of each of the analysis parameters. To understand the normal microflora of the vagina, knowledge of the letter designations will be very helpful.
READ MORE: Leukocytes during pregnancy in smear cytology
So, what are these letters:
- abbreviations of the areas from which the material is taken are designated by the letters V (vagina), C (cervical area of the cervix) and U (urethra or urinary canal);
- L - leukocytes, the value of which may not be the same in normal conditions and in pathology;
- Ep - epithelium or Pl.Ep - squamous epithelium;
- GN - gonococcus (the “culprit” of gonorrhea);
- Trich - Trichomonas (the causative agent of trichomoniasis).
In the smear, mucus may be detected, indicating a normal internal environment (PH), beneficial Doderlein bacilli (or lactobacilli), the value of which is equal to 95% of all beneficial bacteria.
Some laboratories make it a rule to mark the content of a specific type of bacteria. For example, somewhere they use the “ ” sign for this.
If there is no flora in the smear, the abbreviation “abs” is indicated (Latin, this type of flora does not exist).
State of the flora
In practice, the most often used is to evaluate the analytical results of the material under study microbiologically, according to which the following stages of purity are distinguished:
- Grade 1 characterizes a completely healthy woman, when rod flora is visually detected in a smear in large quantities with an admixture of single epithelium and a small amount of mucus;
- Grade 2 is also inherent in healthy women, but here, in addition to the lactobacilli and epithelium present in sufficient quantities, single cocci are added. This situation should not cause concern, since it is considered the norm and is observed in a sufficient number of girls who are sexually active;
- 3rd degree does not have a very favorable picture. The smear is dominated by cocci, a small number of rods, the number of leukocytes increases (more than 10 in the field of view), the performance of the rod flora decreases, what this means is not difficult to guess: an inflammatory process develops;
- Grade 4 is marked by the presence of only cocci, no rods at all, a large amount of cervical epithelium, a growing number of white blood cells, and an increase in discharge. This indicates the occurrence of bacterial colpitis.
In the latter case, to clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may recommend colposcopy in order to form an opinion about the level of damage to the cervix and cervical canal.
Doctors distinguish 4 stages of flora purity
Treatment based on tests
When conducting a smear examination, the tests are sent to the doctor, and after reading the results, he draws a conclusion about the state of the flora and decides whether there is a pathology, which microorganisms are interested in it, and how to bring the lactobacilli to a normal state. In this case, treatment with suppositories or tablets is recommended, and antibiotics are used if necessary.
Rod flora during pregnancy
It is more difficult for a pregnant woman to overcome such a problem. From the moment of conception, hormonal levels change. Its fluctuations lead to changes in the ratio of microflora in the vagina. The environment changes, which makes it possible for the development of bacteria that cause inflammation or some kind of infection.
Good rod flora during pregnancy is the key to the health of the child
Therefore, there is no need to explain what rod flora is in a smear of the expectant mother. This is an indicator of the health of her and the future baby. The first examination of a woman is done when she is registered, and then repeated twice, at 30 and 36-37 weeks. All these measures help to identify and treat pathological processes in a timely manner in order to prevent the child from becoming infected with pathogenic bacilli when passing through the birth canal during birth.
What symptoms might a woman have?
The symptoms of bacterial vaginosis are difficult to confuse with manifestations of other pathologies. Its course can be asymptomatic or with pronounced clinical signs.
The second option is associated with the appearance of heavy discharge, which corresponds to the following parameters:
- Liquid, abundant;
- White or with a grayish tint;
- Homogeneous;
- With a sharp, unpleasant, “fishy” odor.
Sometimes discharge appears or gets worse before menstruation, after sex or after a change of sexual partner. The disease can exist for a long time, with periods of relative remission.
The discharge may change its character: the color becomes yellowish-green, the consistency becomes viscous, viscous, but at the same time it can foam. Their number can be moderate or significant.
Bacterial vaginosis is not characterized by inflammatory changes in the genital tract. But against this background, salpingitis and endometritis can develop. Most often they are provoked by invasive intrauterine manipulations.
Tips and tricks for maintaining flora
To ensure the reliability of the smear before going to the doctor, there are several points that every woman should take note of:
- three days before visiting the antenatal clinic, abstain from sexual intercourse;
- do not douche;
- Do not get tested during your period.
In order for rod flora to live in large quantities in the vagina, you must adhere to the following rules:
- keep the genitals clean, wash yourself at least once a day;
- use special intimate hygiene products that do not disturb the acidic environment of the vagina;
- douching should only be done as prescribed by a doctor, since it also washes out beneficial microbes;
- do not get carried away with thongs and panty liners;
- when changing partners, use protective equipment;
- establish a regime of work and proper rest;
- strengthen the immune system in all available ways;
- develop a balanced diet;
- Avoid stressful situations whenever possible.
| Vaginitis | An increased number of macrophages, leukocytes is visible, there are gonococci, spores, and mycelium. | Nonspecific or mycotic vaginitis, gonorrhea. |