Bacterial vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis develops when the normal ratio of microorganisms in the vagina is disrupted, which is clinically manifested by creamy discharge with a specific amine odor (the smell of “fish”). Partial or complete loss of lactic acid bacteria in the vagina leads to excessive proliferation of other microorganisms, such as Gardnerella vaginalis, Mycoplasma hominis, Ureaplasma urealyticum, as well as other anaerobes - Fusobacterium, Prevotella, Peptococcus, Bacteroides, Peptostreptococcus , Veilonella, Vulonella, Mobiluncus. However, Gardnerella vaginalis plays a leading role in the development of bacterial vaginosis.
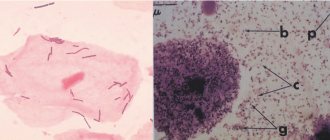
Changes in smear with bacterial vaginosis:
- White blood cells are usually normal or absent;
- A sharp decrease in the number of lactobacilli;
- A large number of small cocci;
- The presence of “key” cells are epithelial cells covered with a continuous layer of bacteria.
A flora smear is the method of choice for diagnosing bacterial vaginosis and there is no need for a PCR test. In some cases, bacterial vaginosis can occur in combination with other infections, which will be clinically manifested by swelling and redness of the mucous membrane, itching, and dysuric disorders. If a mixed infection is suspected, it is advisable to conduct additional research methods (PCR and flora culture with determination of sensitivity to antibiotics).
Treatment of bacterial vaginosis is indicated to eliminate symptoms and is aimed at suppressing excessive growth of conditionally pathogenic flora and normalizing the vaginal biocenosis. It has been proven that treatment of BV reduces the risk of contracting an STI, so a number of experts advocate antibacterial therapy in women with asymptomatic disease.
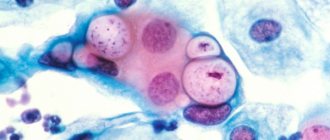
Candidiasis
Candidal vaginitis is a common disease in women of reproductive age. There is an asymptomatic carriage of yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida and a clinically developed disease with specific manifestations. The disease occurs due to hormonal imbalance, defects in general and local immunity, disturbances of the vaginal microflora, due to long-term use of broad-spectrum antibiotics, and psycho-emotional stress. The disease manifests itself with itching and whitish cheesy discharge, which is treated with a single dose of an antifungal drug. In cases of severe candidiasis with frequent relapses, long-term antifungal therapy regimens are used.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea appears as a yellowish-greenish discharge with swelling of the mucous membrane. The cause is diplococcus Neisseria gonorrhoeae. When a smear from the cervical canal reveals more than 15 leukocytes in the field of view, a subsequent in-depth examination for gonococcal and chlamydial infections is a mandatory step. The study is worth conducting, since gonococcal infection causes severe purulent adnexitis, which leads to infertility in the future.
The criteria for acute gonorrhea are:
- a sharp decrease in the number of lactobacilli;
- an abundance of leukocytes that phagocytose bacteria;
- abundance of diplococci;
- mixed flora.
Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis is an infection caused by protozoan microorganisms and manifests itself as a whitish, watery, foamy discharge. Trichomonas can carry other microorganisms (chlamydia, gonococci), thus causing a mixed severe infection. When trichomoniasis is detected in a smear, identification of the causative agents of gonorrhea and chlamydia becomes mandatory.
Nonspecific (bacterial) vulvovaginitis
Aerobic vaginitis is manifested by yellowish-greenish discharge with a sweetish odor. Nonspecific vulvovaginitis is caused by gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. The smears indicate the presence of leukocytes in large numbers, a large amount of desquamated epithelium and bacteria. It is treated with broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs or targeted antibiotics after determining sensitivity.
A correctly performed smear should contain cells of stratified squamous, cylindrical and glandular epithelium, vaginal flora, mucus, and a moderate amount of neutrophils. The ratio of components and the state of each type of cell allow the doctor to identify early pathology of the female and male genital tract.
Indications for prescribing analysis
Cell testing should be performed regularly on all women over 18 years of age. It is prescribed once a year and does not depend on the health status of the representative of the weaker half of society. If there are any pathological changes in the cervix, the doctor may order tests as long as necessary. Since recently diseases of the female genital organs have become younger, the environmental situation has worsened and people have become more susceptible to stress, experts prefer to prescribe a smear for cell examination at least 2 times a year.
Without this analysis, it is almost impossible to accurately determine the pathological processes occurring in the cervix. This test is popular because it allows you to quickly and safely identify inflammatory, precancerous and cancerous conditions in a woman. In addition to the fact that you can see squamous epithelial cells in a smear, it also displays the presence of leukocytes, bacteria, and fungus.
3.1
Leukoplakia of the bladder
Leukoplakia of the bladder and vesical triangle (squamous metaplasia) in many cases is practically asymptomatic for several years. In such patients, sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia, ureaplasma, gonococci, Trichomonas, herpes, mycoplasma, Escherichia, Gardnerella) are often detected in smears. In addition to high values of squamous epithelium and horny scales in the urine, there may be the following signs of the disease:
- the occurrence of a sudden strong urge to urinate;
- prolonged pain in the urethra or pelvis;
- frequent urination;
- abnormal location of the external urethral opening;
- increased symptoms upon initiation of sexual activity or change of sexual partner.
Often sick women are diagnosed with cystitis, although the cause of these disorders is the presence of another pathology. In 60-96% of patients, cystoscopy reveals leukoplakia located in the bladder neck and bladder triangle. This disease is a pathological process in the mucosa, characterized by dysfunction of the squamous epithelium and the occurrence of keratinization, which is absent normally. Many experts consider this condition as precancerous. The reasons for the development of leukoplakia are the following:
- chronic infectious process in the urogenital tract;
- prolonged irritation of the mucous membrane with chemicals, medications, catheters;
- lack of vitamin A;
- genitourinary schistosomiasis (irritation of the mucous membrane from contact with sharp spines on the eggs of a parasitic worm), a complication of which is bladder cancer.
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out using cystoscopy (insertion of an endoscope into the bladder through the urethra) and biopsy of epithelial tissue. Cytological examination of urine sediment reveals degenerative squamous epithelial cells. In later stages, red blood cells and a significant number of leukocytes appear. Complications of leukoplakia are:
- malignancy of the process;
- the development of renal failure due to loss of elasticity of the bladder walls;
- formation of ulcers and polyps;
- development of chronic urethritis and cystitis.
Areas of stratified squamous epithelium without keratinization are also detected in healthy women (up to 80% of cases), especially during childbearing age. Cells in lesions with altered tissue resemble vaginal epithelium. This condition in medicine is considered a variant of the norm, and it is associated with hormonal changes. An acceleration of this process can occur in a pregnant woman due to the increased secretion of estrogen during gestation. Therefore, it is important to recognize this disease in time and carry out its treatment, which consists of the following:
- use of antibacterial and antiparasitic agents;
- antiviral therapy (if herpes is detected);
- local treatment by introducing natural or synthetic analogues of glycosaminoglycans into the bladder (Heparin, hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfate) to restore the mucin layer;
- transurethral surgery in the absence of effect from conservative therapy (electrovaporization or electroresection).
Can squamous epithelium be present in a smear?
Sometimes women, when receiving test results, are frightened by the presence of squamous epithelial cells in it. But don’t worry, because their presence is physiologically justified. The fact is that the cervix and vagina are lined with tissue called squamous epithelium. In a smear, the norm of these cells in the field of view is up to 15 pieces. Their absence or a significant deviation from the norm indicates the presence of local pathological processes. You should never draw a conclusion about your health status based only on this indicator in the analysis. A doctor can get a complete picture of a woman’s health (or lack thereof) only by comparing the indicators of squamous epithelium in a smear with other elements.
Normal epithelium in a smear
Epithelial cells are either cylindrical or flat in shape. The rate of columnar epithelium increases if cancer progresses in the female body. If the cells are not enlarged and cannot reach normal size, then this indicates that there is a hormonal imbalance in the patient’s body.
Normally, epithelial cells are present in numbers from 3 to 15 in the visible area. If there is a large amount of epithelium in the smear, this may indicate cervicitis, urethritis and other inflammatory diseases. Also, epithelial cells should be in the body not one at a time, but in groups. If a woman did not observe hygiene standards before taking the test or did not prepare properly, the results of the study may be false.
You should know that specialists cannot make a diagnosis based on the number of epithelium alone. The epithelial cells in the smear will increase along with the increase in mucus and white blood cells. In this case, several indicators are taken into account. If they are higher than normal, this indicates an inflammation process in the patient’s body. Most often, its cause is banal hypothermia or infectious diseases.
If the number of epithelial cells is higher than normal, it is customary to talk about the degree of purity of the smear of the fourth degree.
The shape of the epithelium is also very important. If the cylindrical epithelium is enlarged, this may indicate the probable development of cancer.
This situation requires additional examination, since based on this analysis alone it is difficult to say whether a woman has such a pathology or not.
Read: Hemostasiogram: what is it and why is it necessary
Squamous epithelium in a smear in small quantities
Low values of any element in analyzes do not always indicate normality. After all, any deviation from it can have a detrimental effect on our health. Flat epithelium in a smear (the norm of which is indicated above) may be in the field of view, but have values of 1,2,4. A small number of these cells may indicate a lack of estrogen production, and an increased amount of male hormones. If these cells are not visible at all upon careful examination, this indicates that they are atrophied. Their complete absence should alert a specialist, since the death of epithelial cells can lead to the development of a cancerous tumor. In order to confirm this assumption, several more analyzes and studies need to be done, so there is no need to panic with such results.
What to do if the squamous epithelium in the smear is higher than normal?
Experts immediately pay attention to the results of the analysis if squamous epithelial cells in the smear are contained in large numbers. Indicators above 15 are considered a deviation from the norm and may indicate the presence of pathological processes such as inflammation of cervical tissue, the development of a benign tumor (diffuse mastopathy). Also, a large number of epithelial cells may indicate primary infertility in young patients.
Nuclear-free “scales” (this is what squamous epithelium looks like) can grow without a focus. This is observed in benign tumors, as well as in the pathological process of hyperkeratosis. Hyperkeratosis is a keratinization disorder in which the responsible organs do not control how much and how squamous epithelium appears. There may also be a lot of it in the smear due to a significant excess of estrogen in the body. In this case, the woman is also at risk of miscarriage. Epithelial cells are carefully studied in order to prevent the development of cancer in the early stages.
Microscopic examination of smears (smear bacterioscopy, flora smear)
Swabs for microscopic examination are taken from the cervical canal (C), vagina (V), urethra (U), and sometimes from the rectum (R). The smear is taken with a spatula or spatula, which, without damaging the mucous membrane of these organs, collects the secretions accumulated in their lumen. Before taking smears, the gynecologist inserts a special instrument into the vagina - a gynecological speculum, which allows you to see the walls of the vagina and the cervix. For girls and virgins, regardless of age, a speculum is not used when taking smears. The taken material is applied to a glass slide (discharge from each part of the genitourinary system is allocated a specific place) and sent to the laboratory. The laboratory assistant stains the smear with special dyes, dries it and examines it under a microscope, assessing the amount of mucus, cells, number and type of microorganisms (bacteria, fungi, protozoa). The results of the study are entered into the analysis form: the characteristics of discharge from the cervical canal, vagina, urethra and rectum are under the letters C, V, U and R, respectively.
Epithelium – the norm is up to 15 cells in the field of view. A smear from the vagina reveals squamous epithelium at different stages of development, and a smear from the cervical canal shows columnar epithelium. An increase in the number of epithelial cells indicates acute or chronic inflammation of the organ. The indicator is interpreted only in conjunction with other data obtained from smear analysis.
Leukocytes - the norm for the urethra is up to 5 cells in the field of view, for the vagina - up to 10 cells in the field of view, for the cervical canal - up to 30 cells in the field of view. The presence of a small number of leukocytes provides support and protection of the organ from possible negative influences. An increase in the number of leukocytes always indicates the development of an inflammatory process - colpitis, urethritis, cervicitis. In acute inflammation, the number of leukocytes reaches 100 or more cells in the field of view; sometimes the laboratory assistant writes that the leukocytes “cover the entire field of view.”
Mucus is normally absent in the urethra, but is present in small (moderate) quantities in the vagina. The amount of mucus in the cervical canal varies during the menstrual cycle from moderate to heavy. The presence of mucus in the urethra indicates a possible inflammatory process.
Bacteria - normally, the vagina of girls who have not reached puberty and menopausal women has coccal flora; in women of reproductive age, the vagina is normally populated with gram-positive bacilli - lactobacilli. The number of microorganisms in the cervical canal is normally insignificant (less than in the vagina). There should be no normal microflora in the urethra. The appearance of pathogenic (harmful) or a large number of opportunistic bacteria in the smear indicates an inflammatory process or vaginal dysbiosis.
Gonococcus, Trichomonas, and key cells are absent in smears of healthy women. The appearance of these elements indicates the presence of gonorrhea, trichomoniasis and gardnerella, respectively.
Fungi of the genus Candida are very often found in the vagina and can take the form of spores and mycelium. Fungal spores indicate carriage of candida (this is a very common condition that often occurs in completely healthy women), while the appearance of mycelium is a sign of an active infectious process caused by fungi (candidiasis or thrush).
Using smear bacterioscopy, you can identify nonspecific inflammatory processes (vaginitis, colpitis, cervicitis) caused by the activation of opportunistic flora, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, candidiasis, gardnerellosis, and suspect bacterial vaginosis and chlamydia.
In order for the result of a smear on the flora to be informative, it is important to follow some rules for preparing for the study. You should not take antibiotics for two weeks before the test. For three days before taking a smear, drugs with antibacterial, antiseptic, and contraceptive effects should not be injected into the vagina. The day before the test, it is recommended to abstain from sexual intercourse. For three hours before a visit to the gynecologist, it is not recommended to wash your face or go to the toilet “small”.
Taking smears for flora carried out in accordance with all the rules is a completely painless and safe procedure. For healthy women, smear bacterioscopy is recommended to be performed at least once every 6 months.
Various changes in squamous epithelium in a smear
Flat epithelium in a smear can be combined with cylindrical epithelium. This is not a deviation from the norm if the smear was made in the transition zone (the cervical canal and its vaginal part). Given that the epithelium lines the canal and vagina in several layers, the analysis results may show cells from different layers. Stratified squamous epithelium may also appear in the smear; such results without additional abnormalities in cell structure or size are considered within normal limits.
Don't worry too much if you have modified epithelial cells. This is not reliable evidence that cancer is developing. Squamous epithelial cells that are abnormal in structure and structure may indicate ongoing inflammatory processes, the presence of human papillomavirus infection, benign lesions of the cervix, and dysplasia.
Flat epithelium in a smear: what does it mean, normal, causes of deviations
CYTOLOGY smear is a method of microscopic examination of the cervical epithelium for the purpose of PREVENTION AND EARLY DIAGNOSIS OF CERVICAL CANCER.
A cytology smear primarily performed to detect atypical cells , which allows early diagnosis of dysplasia (CIN, LSIL, HSIL) or cervical cancer.
It is an inexpensive and convenient method for reaching large numbers of women with preventative care.
Of course, the sensitivity of a single study is low, but annual mass screening in developed countries has significantly reduced the mortality rate of women from cervical cancer.
Due to the fact that atypical cells can be located in a relatively small area of the mucosa, it is very important that the material is obtained from the entire surface of the cervix, especially from the cervical canal ! For this purpose, special brushes have been created that make it possible to obtain material from areas inaccessible to inspection.
Particular attention is paid to the transformation zone, the cells of which most often undergo tumor degeneration. It is in the transformation zone that up to 80-90% of cervical cancer develops, the remaining 10-20% occur in the cervical canal.
When to take a smear for cytology? A smear for cytology should be taken starting from the 5th day of the menstrual cycle and 5 days before the expected start of menstruation.
The analysis cannot be carried out within two days after sexual intercourse or insertion of suppositories into the vagina. Failure to follow these rules may lead to erroneous interpretation of the results.
Also, the presence of a pronounced inflammatory process in the cervix and vagina seriously complicates diagnosis.
It should be noted that collecting material is a rather unpleasant procedure. The gynecologist must scrape the epithelium from the surface of the cervix and enter the cervical canal. The more epithelium from different zones gets in, the better the diagnosis. Sometimes bruising may remain after cytology, this is considered normal.
Thus, the main significance of a cytology smear is to determine qualitative changes in cells. To determine the infectious agent that caused the inflammation, it is better to use a smear on the flora or bacteriological culture .
However, during a cytological examination, the doctor may note the presence of any microorganisms. Normal microflora includes rods (lactobacillus), single cocci, and in small quantities there may be opportunistic flora.
The presence of specific infectious agents (Trichomonas, amoebas, fungi, gonococci, gardnerella, leptothrix, chlamydia, an abundance of cocci) is considered a pathology that needs to be treated.
Processing of smears. Cytology deadlines
After collecting the material, the sample is transferred to a glass slide, fixed and stained. When directly transferring a smear from a brush, partial loss of material and cell deformation are possible, which leads to a decrease in the sensitivity of the method and a large number of false results. The classical method was replaced by liquid cytology, which significantly increased the accuracy and quality of the study.
Liquid cytology is a new technology for processing smears, which involves placing samples in a container with a special stabilizing solution. In this case, the entire resulting epithelium enters the solution, which is then centrifuged and cleared of unwanted impurities (mucus, etc.).
Today, liquid-based cytology is becoming the “gold standard” for examining smears from the cervical mucosa. But even in this case, the sensitivity of a single study does not exceed 60-70%. During reproductive age, false negative results are common, and in menopausal women, false positive results are common.
Only triple cytological examination allows one to approach 100%.
There are various methods for staining preparations: according to Papanicolau (Pap test), according to Romanovsky, according to Wright-Diemsa, according to Gram.
All methods are aimed at staining certain cellular structures, which makes it possible to differentiate different types of epithelium and distinguish between cells with keratinization and tumor transformation.
The Pap test is widely accepted and is now used as the main standardized test.
How long does the test take? Depending on the organization of the process, the result can be obtained within 2-3 days.
Cytogram without features - what does this mean?
Cytological findings vary widely.
As a variant of the norm, the following conclusions can be used: “ cytogram without features ”, “ cytogram within normal limits ”, “ cytogram without intraepithelial lesions ”, “ cytogram corresponds to age - atrophic type of smear ”, “ NILM - Negative for intraepithelial lesion or malignancy”, " proliferative type of smear ." All this is NORMAL!
The cervical mucosa is normally smooth, shiny, and moist. The squamous epithelium is pale pink, the glandular epithelium is bright red. The cellular composition that can be found in normal cytology is presented in the table.
| Cytogram without features (NILM) in women of reproductive age | |
| Exocervix | Well-preserved cells of squamous epithelium, mainly of the superficial, intermediate layers. |
| Endocervix | Cells of glandular (cylindrical) epithelium. |
| Transformation zone | Squamous epithelial cells, single cells or small clusters of metaplastic squamous epithelium, small clusters of glandular epithelium. |
Atrophic type of smear - what does it mean?
In women in perimenopause and menopause, due to a decrease in the overall level of estrogen, many metabolic processes slow down, which results in atrophy of the squamous epithelium. These changes can be seen in the cytogram.
The atrophic type of smear refers to a variant of the normal cytogram. You can often find in the conclusion the phrase “ cytogram corresponds to age ” or “ age-related changes nilm ”.
All these are variants of the norm!
You need to understand that in menopausal women, false-positive cytogram results are very common - this is the case when it is difficult for a cytologist to distinguish atrophic squamous epithelium from dysplasia.
This needs to be understood because subsequent cervical biopsies usually do not find any pathology.
In addition, older women may have a tendency to keratinize the epithelium with the formation of hyperkeratosis (leukoplakia).
| Cytogram without features (NILM) in women in peri-menopause ( atrophic type of smear ) | |
| Exocervix | Well-preserved squamous epithelial cells, mainly of the parabasal and basal layers. More often there are smears of the atrophic type, but they can also be of proliferative or mixed types. |
| Endocervix | The absence of columnar (glandular) epithelial cells is not an indicator of poor quality of the smear, since during this period the transformation zone moves deep into the canal and to obtain glandular epithelium the brush must be inserted to a depth of more than 2-2.5 cm. |
| Transformation zone | Cells of squamous, metaplastic epithelium. |
The mucous membrane of the cervix in menopause is thinned, easily injured and damaged, which is a consequence of a decrease in estrogen.
Terminology
Dyskaryosis and dyskaryocytes are abnormal cells with hyperchromatic (dense and dark) nuclei and irregular nuclear chromatin. Dyskaryosis will be followed by the development of a malignant neoplasm. Used as a synonym for dysplasia, but as a more general term.
Atypia is any difference in cell structure from the norm. The meaning often depends on the context. But more often it is used to describe pre-tumor and tumor changes.
Inflammatory atypia is a combination of degenerative, reactive, proliferative changes in cells during inflammation. These changes can cause a false-positive diagnosis of dysplasia or cancer.
Source: https://MedLazaret.ru/ginekologiya/nilm-tbs-2014.html
How should you prepare for the analysis?
Since a woman lives on a cycle, she needs to know when it is best to do a vaginal smear. During reproductive age, it is important to calculate the days of menstruation, otherwise the squamous epithelium in the smear may be subject to changes. Women received many erroneous results precisely because of incorrect collection of biomaterial. For those representatives of the fair sex who menstruate, a smear should be taken no earlier than the 5th day of menstruation. In addition, the analysis should be done a maximum of 5 days before the start of menstruation, no later. If sexual intercourse took place, medications were introduced into the vagina, or sanitation was performed, the biomaterial will be ready for collection only after 24 hours.
The material is applied to two glasses with a soft brush or spatula. The results are ready in 5-10 days.
Cytology smear (Pap test) - what does the cytogram show?
CYTOLOGY smear is a method of microscopic examination of the cervical epithelium for the purpose of PREVENTION AND EARLY DIAGNOSIS OF CERVICAL CANCER.
A cytology smear primarily performed to detect atypical cells , which allows early diagnosis of dysplasia (CIN, LSIL, HSIL) or cervical cancer.
It is an inexpensive and convenient method for reaching large numbers of women with preventative care.
Of course, the sensitivity of a single study is low, but annual mass screening in developed countries has significantly reduced the mortality rate of women from cervical cancer.
Due to the fact that atypical cells can be located in a relatively small area of the mucosa, it is very important that the material is obtained from the entire surface of the cervix, especially from the cervical canal ! For this purpose, special brushes have been created that make it possible to obtain material from areas inaccessible to inspection.
Particular attention is paid to the transformation zone, the cells of which most often undergo tumor degeneration. It is in the transformation zone that up to 80-90% of cervical cancer develops, the remaining 10-20% occur in the cervical canal.
When to take a smear for cytology? A smear for cytology should be taken starting from the 5th day of the menstrual cycle and 5 days before the expected start of menstruation.
The analysis cannot be carried out within two days after sexual intercourse or insertion of suppositories into the vagina. Failure to follow these rules may lead to erroneous interpretation of the results.
Also, the presence of a pronounced inflammatory process in the cervix and vagina seriously complicates diagnosis.
It should be noted that collecting material is a rather unpleasant procedure. The gynecologist must scrape the epithelium from the surface of the cervix and enter the cervical canal. The more epithelium from different zones gets in, the better the diagnosis. Sometimes bruising may remain after cytology, this is considered normal.
Thus, the main significance of a cytology smear is to determine qualitative changes in cells. To determine the infectious agent that caused the inflammation, it is better to use a smear on the flora or bacteriological culture .
However, during a cytological examination, the doctor may note the presence of any microorganisms. Normal microflora includes rods (lactobacillus), single cocci, and in small quantities there may be opportunistic flora.
The presence of specific infectious agents (Trichomonas, amoebas, fungi, gonococci, gardnerella, leptothrix, chlamydia, an abundance of cocci) is considered a pathology that needs to be treated.
What additional studies are prescribed if the squamous epithelium does not correspond to the norm?
If a single squamous epithelium is detected in the smear, but there are no changes in the cervix, then the analysis is considered normal and does not require any additional examinations or studies. But there are some situations when it is necessary to carefully look at the epithelial cells in an enlarged form. This happens when there is suspicion of cervical erosion, dysplasia, or the development of cancer. In this case, colposcopy or cervical biopsy is prescribed. Such studies are carried out by a highly professional specialist, since the patient’s life may depend on the diagnosis as a result of the examination. If moderate to severe damage to the cervix is detected, treatment methods such as cauterization or removal of the affected area are prescribed.
Prevention, regular examination and examination, timely treatment of pathological processes can prolong your life for a long time. Take care of yourself and don't get sick!
When visiting a gynecologist, it is always necessary to take a smear for flora. It can be used to determine the condition of the vaginal mucosa and the presence of infections. Only a doctor who knows the norms of all indicators can decipher a smear correctly. The epithelium in the smear may indicate the presence of an inflammatory process, which may be associated with various reasons.
What does a large amount of epithelium in a smear mean?
A normal cytogram in a smear for flora contains 12-20 epithelial cells per field of view. Excessive content of the squamous cell component indicates irritation and accelerated rejection of the integumentary layer. The cause may be inflammatory processes of various etiologies, then the doctor will see a significant number of leukocytes in the drug (normally no more than five). Often the pathogen is detected: Trichomonas, gonococci, viral inclusions.
In the absence of inflammatory elements, one should think about leukoplakia and other types of dyskeratosis. Allergic reactions to local medications (contraceptive drugs, medicinal ointments, suppositories) show a similar picture. Moderate irritation is often caused by hygiene products. The epithelium of the cervix during pregnancy may be somewhat more abundant, the cellular cytoplasm has signs of decidual metamorphosis, this is a normal variant.
The cytological picture in men varies; with age, the squamous cell component can be increased, but its number should not exceed 15 units in one visual field. The abundance of epithelial masses, mucus impurities, and leukocytes indicate an inflammatory process. You should not attempt treatment on your own, as this may lead to the symptoms subside without eliminating the cause of the disease.
When visiting a gynecologist, it is always necessary to take a smear for flora. It can be used to determine the condition of the vaginal mucosa and the presence of infections. Only a doctor who knows the norms of all indicators can decipher a smear correctly. The epithelium in the smear may indicate the presence of an inflammatory process, which may be associated with various reasons.
Indications for the purpose of analysis
There are certain reasons that require a smear test from the vagina or urethra to determine the presence of infections or inflammation in the reproductive system:
- pain localized in the lower abdomen;
- taking antibiotics for a long time;
- the presence of suspicious vaginal discharge that causes discomfort;
- sensation of itching and burning in the genital area;
- pregnancy planning;
- carrying out a preventive examination.
If you have unpleasant symptoms, you should immediately visit a doctor and get a smear and test for the presence of sexually transmitted infections. What epithelium means in a smear depends on the characteristics of its cells and their structure and quantity.
Rules for preparing for analysis
To get a reliable result, you must:
- two days before the smear test, avoid sexual contact;
- do not use vaginal contraceptives (including condoms, ointments, lubricants and creams) and suppositories;
- stop douching two days before the test;
- do not conduct examinations during menstruation, since menstrual blood significantly distorts the test results and may show that the epithelium in the smear is increased; the most correct option would be to take a smear in the first days after the end of menstruation;
- You should not use intimate hygiene products the day before; genital hygiene procedures should be carried out simply with warm water without using any detergents;
- You cannot go to the toilet two hours before taking the test.
Proper preparation for a smear will allow you to most accurately determine the number of cells in it and assess the health of the reproductive system. The epithelium in the smear indicates the condition of the vaginal and cervical mucosa. If the norm changes, one can conclude that there is inflammation or atrophy of the epithelial layer.
Smear technique
A smear for cytology is taken using a special spatula, which is available in a standard gynecological kit intended for examination. It is necessary to take the analysis at the site of transformation (where the squamous epithelium turns into columnar epithelium); after taking the material, it is distributed over a glass slide.
The transformation zone is located in the area of the external pharynx, but in some cases (depending on hormonal balance and age) it can change its position. Taking a smear from the area of transitional epithelium is necessary to accurately determine the presence of malignant cells. Since they appear from the lower layers, taking a smear from the location of the surface epithelium, it will be possible to diagnose cancer only at the last stage.
That is why the epithelium in the smear plays a very important role. The norm in women ranges from 3-15 units in the field of view. If their number is higher, additional examinations need to be carried out to detect a malignant tumor.
What is squamous epithelium and its significance in a smear
The squamous epithelium is the mucous membrane of the vagina. Depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle, cells may undergo minor changes. The surface epithelium is divided into keratinizing and non-keratinizing, the ratio of cells changes in different phases, so it is necessary to take this fact into account in order to determine whether the obtained indicators are normal.
Epithelium in a smear is normal only if its number does not exceed 15 units in the field of view. Exceeding the norm indicates the presence of inflammation or a recent infection. When the structure of cells changes, suspicions arise about the development of a benign or malignant tumor.
Flat epithelium in a smear for flora and cytology - what does this mean?
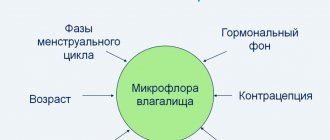
Flat epithelium in a smear for flora and cytology is determined in all women. Those who are of reproductive age and are not breastfeeding have more of it than those who are lactating, in the absence or depletion of ovaries, menopause (menopause) - in general, than in those who do not have a menstrual cycle.
For reference: estrogens continue to be produced in women during menopause and with the ovaries removed, since they are also produced by the adrenal glands.
The epithelium has a protective function. Thanks to it, the vaginal microflora remains rod-like, the environment is acidic, unacceptable for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. The epithelial layer may decrease somewhat when taking hormonal contraceptives and glucocorticosteroids.
What types of smears reveal the presence of squamous epithelium? You can see these words in the results of a smear on the flora (the so-called general smear) and a cytogram. In this case, only the amount of epithelium will be indicated in the first one. But the conclusion of a cytological examination (Pap test) contains more information; the description will contain qualitative characteristics.
Back to contents
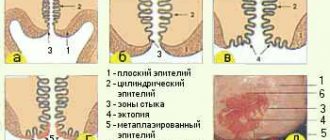
Types of epithelial cells and estrogen dependence
Squamous or stratified epithelium are the cells that line the vaginal part of the cervix. In the cervical canal, another type of epithelium is cylindrical. The flat layer consists of four types of cells - superficial, intermediate and basal-parabasal layer.
Which cells the doctor will take for analysis depends on the concentration of the main female hormone - estrogen. Flat epithelium in layers, fragments, clusters in a smear - these are all variants of the norm, if without anaplasia.
Superficial, largest cells, but with a small nucleus, are characteristic of days 9-14 of the menstrual cycle. If the analysis says that there is a large amount of epithelium, and you took it right in the middle of the cycle, then this is the reason.
Intermediate cells are found in any phase of the cycle. Their difference is their slightly smaller size, irregular shape, and larger core size.
While estrogen is at its lowest point, during menstruation, parabasal cells appear in the smear. In general, during menstruation a woman “loses” a third of her epithelium. Also, this type of squamous epithelial cells is characteristic of the period of amenorrhea (hormonal disorders)
Basal cells with a very large nucleus are characteristic of the atrophic type of smear (ATM). Diagnosed in menopausal women with at least 5 years of inactive ovaries. Also, a similar situation is observed in women with prolonged postpartum amenorrhea, if active breastfeeding continues for more than a year.
With ATM, the amount of epithelium is scanty, but there are a lot of leukocytes - there is inflammation. To avoid this, women undergoing menopause are prescribed hormone replacement therapy (HRT) in the form of tablets, vaginal suppositories or cream. We think many have heard about Ovestin and Femoston.
These drugs compensate for the lack of estrogen and significantly improve the quality of life of women, their well-being, sexual desire appears, and sex becomes less painful, thanks to a well-moisturized mucous membrane without wounds and cracks.
We wrote more about this in the article about atrophic colpitis.
Back to contents
Medical terms that scare you
Dystrophy or dystrophic epithelium - occurs with true erosion of the cervix or pseudo-erosion, which is also called ectopia. In a word, when there is a wound on the cervix. When it heals, cell degeneration will no longer be detected.
The medical term “metaplastic” is often present in the cytogram. Many people think that this indicates a malignant process. But no - metaplastic epithelium is a good smear result.
This indicates that the cells were taken exactly from the desired zone - the junction of two types of epithelium - from the endocervix (cylindrical) and exocervix (flat).
These are the cells of the transformation zone, where atypia, precancerous or cancerous changes are most often found.
Acetowhite epithelium (ABE) is not an indicator that can be displayed on smears. ABE is visible during extended colposcopy after exposure of the cervix to acetic acid. If there are pathological areas on it, the epithelium will begin to turn pale.
Next, the doctor makes conclusions based on how quickly the whitening occurred, how bright it was, how long it lasted, whether it had boundaries, whether there was a sign of a ridge, etc.
If the reaction was not pronounced, most likely the women have chronic cervicitis (inflammation), HPV or LSIL (mild dysplasia). In case of severe ABE, HSIL is diagnosed - severe dysplasia.
In appearance, the cervix, even with severe dysplasia, can be quite healthy. And only the vinegar test shows what is not visible to the eye.
Not every gynecologist is a good colposcopist.
An experienced specialist monitors the cervix during extended colposcopy after treatment with vinegar and iodine, literally without taking his eyes off, and makes very accurate diagnoses.
By the way, in some countries it is the vinegar test, and not the PAP test, that is a screening method for diagnosing precancer. If coarse acetic-white epithelium is detected, the woman is taken under control and treated.
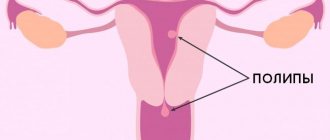
Hyperplastic epithelium is usually synonymous with cervical canal polyp. Needs removal and histological examination.
Cells with signs of keratosis, keratinization - most often these words can be seen in the reports of women with suspected leukoplakia. But the same signs (features of epithelial cells) occur in precancer and cancer.
Pronounced reactive changes are an inflammatory process in the cervix.
Signs of mild dysplasia - lsil. If there are pronounced, deep changes, we are usually talking about HSIL - severe neoplasia, in which surgical intervention is necessary - conization of the cervix.
Koilocytosis is a feature of epithelial cells most characteristic of PVI (human papillomavirus, HPV). Viral infection.
Reparative changes in the epithelium are benign changes in cells, a variant of reactive changes (see above).
Degenerative changes are not cancer; they occur during a chronic or acute inflammatory process. In the same category, reactive changes include the following concepts: inflammatory atypia, squamous metaplasia, hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis.
Atypia, atypical changes - dysplasia (precancer) or malignant neoplasm.
Atypical squamous epithelial cells of unknown significance - asc-us. These are cells of unknown significance. The cytologist sees that they look unusual, changed, but cannot accurately determine what was the cause - inflammation, dysplasia, infection or irritation.
There is no need to be afraid of this formulation. It does not raise the doctor's suspicion of cancer. However, it is a reason to take smears from the cervix for HPV of high oncogenic risk (required types 16 and 18).
And if they are detected, you need to undergo an extended colposcopy.
Proliferation of squamous epithelium - that is, proliferation or in medical terms - mitosis. Normally, this process proceeds slowly. Its purpose is to renew the upper layer of the cervical mucosa. During pregnancy, the process is more active, but normally moderate.
If, according to the results of scraping, proliferation is pronounced, then this happened for one of the following reasons:
- cervicitis (inflammatory process on the cervix);
- tissue trauma resulting from diagnostic curettage, abortion, difficult childbirth, conization;
- tumor growth - benign or malignant (cervical canal polyp, mild or severe dysplasia, cancer, papilloma).
That is, proliferation can be hyperplastic, inflammatory or post-traumatic.
Dyskaryosis is an enlargement of the cell nucleus. The cause is gynecological diseases (colpitis, cervicitis, vaginitis) or dysplasia.
Back to contents
When is treatment required?
- For mild dysplasia (CIN I, lsil), observation by a gynecologist, cytological smears and colposcopy are sufficient. For severe dysplasia (HSIL, CIN II, CIN III), conization is performed - surgical removal of the affected tissue. In some cases, doctors decide to amputate the cervix.
- With reactive changes. Often, a woman is diagnosed with the first degree of neoplasia (dysplasia) based on a cytogram. Questionable because the cells can become “normal” again after antibacterial treatment.
- If keratinization of the epithelium is detected - leukoplakia .
We wrote about this in detail in the article about hyperkeratosis. “Cauterization” of a tissue area is carried out if the presence of leukoplakia is proven by biopsy. - If, according to the results of a general smear on the flora, not only a large amount of flat epithelium is noticed, but also a lot of mucus, leukocytes , and the woman herself complains of unusual discharge, itching, unpleasant odor, etc.
Back to contents
The number of leukocytes in the visual field. to squamous epithelial cells
The number of leukocytes largely depends on the individual characteristics of the body and the day of the menstrual cycle (during the period of ovulation there are more of them), the presence or absence of sexual activity, and possible chronic cervicitis - inflammation of the cervix.
For this reason, doctors do not identify a specific norm for leukocytes. They only look at their ratio to the cells of the vaginal epithelium. The ratio of leukocytes to squamous epithelial cells should be up to 1:1.
If the number of leukocytes to squamous epithelial cells increases to a ratio of 2:1, 3:1, 4:1 or more, this indicates an infection, more often candidiasis (thrush) or trichomoniasis. 1:1 is a borderline ratio. This is not necessarily an incipient disease. Perhaps the result was influenced by some chemical or mechanical factor.
The same sexual intercourse if it happened a few hours before the smear test. That is, 15-20 leukocytes with 15-20 epithelial cells in the field of view may be a normal variant. This is especially common in pregnant women.
We bring to your attention a table from the guidelines for attending physicians. They can see that the number of leukocytes is greater than the number of epithelial cells in nonspecific vaginitis, candidiasis, and trichomoniasis. But with bacterial vaginosis, on the contrary, it is less.
Cytologists also pay attention to the structure of epithelial cells, their changes, and the ratio of their nucleus to cytoplasm. In disease, the cell nucleus is large. This is explained by the fact that the scraping contains cells from the lower layers of the epithelium. And the reason for this is the active desquamation of the surface epithelium due to an inflammatory reaction.
Back to contents
Source: https://viskablivanie.ru/ploskij-epitelij-v-mazke-na-floru-i-citologiyu.html
The value of columnar epithelium in a smear
The epithelium in the smear, which has a cylindrical shape, is functional, as it ensures the secretion of mucus on the cervix. Normally, the cylindrical epithelium in a smear is represented by groups of cells that have a honeycomb-like or linear structure.
In addition, goblet-shaped cells can be found, their difference is in the cytoplasm stretched with mucus. In some cases, such cells may contain secretion granules. A common pathology, ectopia, is a displacement of the columnar epithelium and its replacement of flat surface epithelium.
Further diagnostic measures
If epithelium is found in the smear, the norm of which is violated, the doctor can diagnose vaginitis. In addition to the high concentration of epithelial cells in the analysis, the woman should have an uncomfortable discharge with an unpleasant odor, itching and pain in the vagina, and redness of the vulva.
The development of the disease can be triggered by infections (bacteria, fungi, parasites), damage to the mucous membrane under the influence of chemicals, or hormonal imbalance, for example, during early menopause.
Vaginitis is treated with antibiotics, which are combined with antifungal or other drugs, depending on the type of pathogen.
Treatment of non-infectious vaginitis
If the epithelium in the flora smear is increased, and no infections were detected, we can conclude that a non-infectious pathogen is present. These may be hygiene products containing chemicals that cause irritation of the mucous membrane, contraceptives, or with increased sensitivity of the vagina to spermicides.
In these cases, it is enough to stop using the products, and after some time the concentration of epithelium in the smear will itself restore to normal levels. To speed up the effect, you can use suppositories or tablets that normalize the vaginal microflora and allow normal cells to recover faster.
Epithelium in a smear in men
A high content of epithelial cells in the smear can be observed not only in women, but also in men. The most common disease accompanied by an increased amount of epithelium is urethritis. In men, urethritis is accompanied by pain and burning when urinating, a feeling of discomfort and swelling in the genital area and groin, and the appearance of discharge from the penis or blood in the urine and semen.
Female urethritis is accompanied by chills, pain in the lower abdomen, frequent urge to urinate, burning and pain, as well as the presence of atypical vaginal discharge.
Urethritis can be caused by:
- cytomegalovirus;
- herpes simplex virus;
- chlamydia;
- gonococci.
If any virus or bacteria is detected, additional examinations and effective treatment are required.
Flat epithelium in a smear in women - norm and pathology
The result of an analysis of the vaginal microflora provides a complete picture of some of the processes occurring in a woman’s body. Timely diagnosis allows you to assess the stage of the disease and resort to a comprehensive solution to the issue. A smear should be taken in the following situations:
- Pregnancy planning;
- Periodic pain in the lower abdomen not associated with the menstrual cycle;
- Changes in the nature of discharge from the genitals;
- Itching in the genital area;
- Long-term treatment with antibiotics;
- The appearance of an unpleasant odor from the vagina;
- Preventive examination;
The smear is taken in the gynecologist's office. First, a visual examination of the genital organs is carried out, then secretions are scraped from the surface of the cervix and vaginal walls, using a special tool. Beforehand, a woman must follow the following rules:
- For several days before taking a smear, hygiene procedures are carried out using warm water, without detergents.
- You cannot have sexual intercourse the day before;
- Any type of douching should be avoided;
- It is necessary to stop using vaginal medications (suppositories and ointments), as well as vaginal lubricants or creams. This can significantly change the vaginal microflora.
- The analysis is taken on any day of the cycle, in addition to the menstrual period. It is advisable if these are the first days after its completion.
Treatment of hyperplasia with traditional methods
The choice of treatment tactics depends on many factors, such as:
- patient's age;
- duration and degree of development of pathology;
- possible relapses;
- histological examination.
In the initial stages of identifying signs of hyperplasia, especially in young girls or women, treatment is carried out conservatively, without curettage of the uterine cavity. Drug treatment is conventionally divided into 4 stages.
- First stage. The task during this period is to stop bleeding. For this, patients are prescribed oral combined contraceptives. To prevent anemia, blood substitutes, vitamin therapy, and drugs to restore the body's water-salt balance are prescribed.
- Second phase. Hormonal drugs, Buserelin, Goserelin, are prescribed to suppress the pathological growth of the endometrium. For each patient, the doctor selects an individual treatment regimen, taking into account the course of the pathology, age, and concomitant diseases. The duration of treatment is from three months to six months.
- Third stage. Treatment is aimed at restoring the menstrual cycle and ovulation in women of childbearing age, normalizing hormonal balance. Clomiphene and Gonadotropin are prescribed. During menopause, it is recommended to take Orgametril.
- Fourth stage. The longest (at least 5 years) consists of complex therapy, systematic monitoring, and mandatory examinations.
In the treatment of uterine hyperplasia, combined oral contraceptives (COCs) such as Zhanin, Logest, Marvelon, Yarina are used. These drugs contain estrogens and progestins, normalize hormonal balance, and reduce estrogen levels.
- Janine. It has a minimum of contraindications and side effects. Effective for simple hyperplasia.
- Logest. Reduces the likelihood of developing endometrial cancer, restores the female cycle, and relieves inflammation of the female organs.
- Marvelon. Regulates hormonal levels, recommended for heavy, irregular cycles.
- Yarina. It is prescribed for any stage of pathology, but has serious contraindications. The drug should not be taken if you have diabetes, thrombosis, pregnancy, or lactation. The treatment is long-term, at least six months.
Prescribed to replenish the deficiency of its own hormone. Release forms - tablets, injection solutions, are prescribed based on the woman’s condition and the source of inflammation.
Synthetic drugs have a small list of contraindications and side effects, do not increase blood clotting, and do not affect the functioning of the liver and gastrointestinal tract.
The components of synthetic progesterone analogues have a therapeutic effect by penetrating directly into the cells of the affected tissues. This group of drugs includes Duphaston, Norkolut.
Duphaston
The active component of the drug is a progesterone analogue. It has a small range of contraindications and does not affect ovulation or fetal development. Available in tablet form.
Used for simple, typical forms of hyperplasia. Like any hormonal drug, it is sold in pharmacies only with a doctor's prescription. The course of treatment is from 3 to 6 months.
If hyperplasia begins to develop at a young age, then the likelihood of malignant tumors is minimal. But in older women, hyperplasia can progress and lead to cancer.
Therefore, without waiting for obvious symptoms of the disease, you need to urgently contact a gynecologist for effective treatment.
One of the hormonal drugs recommended for this pathology is Norkolut. Before treatment, the patient is prescribed endometrial histology, a full examination to establish the stage and form of the pathology.
Mirena
Mirena is an intrauterine device used not only as a means of contraception. Due to the content of a gestagen (levonorgestrel), it can be prescribed for hyperplastic processes of the endometrium.
Agonist drugs have the same effect on the pituitary gland as their own hormone. Easy to use, injection solutions can be administered once a month.
Doctors warn that women may feel unwell for the first two weeks due to increased estrogen levels, but then the condition returns to normal. The course of treatment is up to 4 weeks.
Drugs such as Gonapeptil, Lucrin-depot, Sinarel are prescribed before and after surgical treatment of endometriosis, before removal of the uterus (hysterectomy), to reduce its size.
When treated with these drugs, a decrease in blood circulation, atrophy, and a decrease in areas of inflammation are observed.
Treatment of any form or stage of hyperplasia with traditional medicine recipes should only be carried out under the supervision of a physician.
Source: https://PlastikaPlus.ru/diagnostika/ploskij-epitelij-v-mazke-u-zhenshchin.html
Atypical epithelial cells in a smear
In some cases, atypical epithelium may be detected in the smear. What does it mean? An altered structure of squamous epithelial cells lining the vagina and cervix may indicate the development of cancerous tumors or dysplasia.
Cervical dysplasia causes cancer in only one percent of women. In other cases, with regular monitoring and treatment, it goes away within a few years. If the disease continues to develop and there is a danger of cancer cells developing, the doctor may recommend a hyperectomy - removal of the uterus and cervix.
Most often, this procedure is performed on women who have reached menopause or women who no longer plan to give birth.