CYTOLOGY smear is a method of microscopic examination of the cervical epithelium for the purpose of PREVENTION AND EARLY DIAGNOSIS OF CERVICAL CANCER.
A cytology smear primarily performed to detect atypical cells , which allows early diagnosis of dysplasia (CIN, LSIL, HSIL) or cervical cancer. It is an inexpensive and convenient method for reaching large numbers of women with preventative care. Of course, the sensitivity of a single study is low, but annual mass screening in developed countries has significantly reduced the mortality rate of women from cervical cancer.
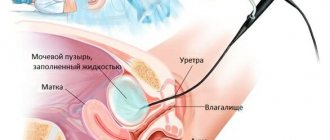
Due to the fact that atypical cells can be located in a relatively small area of the mucosa, it is very important that the material is obtained from the entire surface of the cervix, especially from the cervical canal ! For this purpose, special brushes have been created that make it possible to obtain material from areas inaccessible to inspection.
Particular attention is paid to the transformation zone, the cells of which most often undergo tumor degeneration. It is in the transformation zone that up to 80-90% of cervical cancer develops, the remaining 10-20% occur in the cervical canal.
When to take a smear for cytology? A smear for cytology should be taken starting from the 5th day of the menstrual cycle and 5 days before the expected start of menstruation. The analysis cannot be carried out within two days after sexual intercourse or insertion of suppositories into the vagina. Failure to follow these rules may lead to erroneous interpretation of the results. Also, the presence of a pronounced inflammatory process in the cervix and vagina seriously complicates diagnosis.
It should be noted that collecting material is a rather unpleasant procedure. The gynecologist must scrape the epithelium from the surface of the cervix and enter the cervical canal. The more epithelium from different zones gets in, the better the diagnosis. Sometimes bruising may remain after cytology, this is considered normal.
Thus, the main significance of a cytology smear is to determine qualitative changes in cells. To determine the infectious agent that caused the inflammation, it is better to use a smear on the flora or bacteriological culture . However, during a cytological examination, the doctor may note the presence of any microorganisms. Normal microflora includes rods (lactobacillus), single cocci, and in small quantities there may be opportunistic flora. The presence of specific infectious agents (Trichomonas, amoebas, fungi, gonococci, gardnerella, leptothrix, chlamydia, an abundance of cocci) is considered a pathology that needs to be treated.
Processing of smears. Cytology deadlines
After collecting the material, the sample is transferred to a glass slide, fixed and stained. When directly transferring a smear from a brush, partial loss of material and cell deformation are possible, which leads to a decrease in the sensitivity of the method and a large number of false results. The classical method was replaced by liquid cytology, which significantly increased the accuracy and quality of the study.
Liquid cytology is a new technology for processing smears, which involves placing samples in a container with a special stabilizing solution. In this case, the entire resulting epithelium enters the solution, which is then centrifuged and cleared of unwanted impurities (mucus, etc.). Today, liquid-based cytology is becoming the “gold standard” for examining smears from the cervical mucosa. But even in this case, the sensitivity of a single study does not exceed 60-70%. During reproductive age, false negative results are common, and in menopausal women, false positive results are common. Only triple cytological examination allows one to approach 100%.
There are various methods for staining preparations: according to Papanicolau (Pap test), according to Romanovsky, according to Wright-Diemsa, according to Gram. All methods are aimed at staining certain cellular structures, which makes it possible to differentiate different types of epithelium and distinguish between cells with keratinization and tumor transformation. The Pap test is widely accepted and is now used as the main standardized test.
How long does the test take? Depending on the organization of the process, the result can be obtained within 2-3 days.
Cytogram without features - what does this mean?
Cytological findings vary widely. As a variant of the norm, the following conclusions can be used: “ cytogram without features ”, “ cytogram within normal limits ”, “ cytogram without intraepithelial lesions ”, “ cytogram corresponds to age - atrophic type of smear ”, “ NILM - Negative for intraepithelial lesion or malignancy”, " proliferative type of smear ." All this is NORMAL!
The cervical mucosa is normally smooth, shiny, and moist. The squamous epithelium is pale pink, the glandular epithelium is bright red. The cellular composition that can be found in normal cytology is presented in the table.
| Exocervix | Well-preserved cells of squamous epithelium, mainly of the superficial, intermediate layers. |
| Endocervix | Cells of glandular (cylindrical) epithelium. |
| Transformation zone | Squamous epithelial cells, single cells or small clusters of metaplastic squamous epithelium, small clusters of glandular epithelium. |
Atrophic type of smear - what does it mean?
In women in perimenopause and menopause, due to a decrease in the overall level of estrogen, many metabolic processes slow down, which results in atrophy of the squamous epithelium. These changes can be seen in the cytogram. The atrophic type of smear refers to a variant of the normal cytogram. You can often find in the conclusion the phrase “ cytogram corresponds to age ” or “ age-related changes nilm ”. All these are variants of the norm!
You need to understand that in menopausal women, false-positive cytogram results are very common - this is the case when it is difficult for a cytologist to distinguish atrophic squamous epithelium from dysplasia. This needs to be understood because subsequent cervical biopsies usually do not find any pathology. In addition, older women may have a tendency to keratinize the epithelium with the formation of hyperkeratosis (leukoplakia).
What should I do if I have a similar but different question?
If you did not find the information you need among the answers to this question, or your problem is slightly different from the one presented, try asking an additional question to the doctor on the same page, if it is on the topic of the main question. You can also ask a new question, and after a while our doctors will answer it. It's free. You can also search for the information you need in similar questions on this page or through the site search page. We will be very grateful if you recommend us to your friends on social networks.
Medical portal 03online.com
provides medical consultations via correspondence with doctors on the website. Here you get answers from real practitioners in your field. Currently, on the site you can get advice in 48 areas: allergist, anesthesiologist-resuscitator, venereologist, gastroenterologist, hematologist, geneticist, gynecologist, homeopath, dermatologist, pediatric gynecologist, pediatric neurologist, pediatric urologist, pediatric surgeon, pediatric endocrinologist, nutritionist, immunologist a , infectious disease specialist, cardiologist, cosmetologist, speech therapist, ENT specialist, mammologist, medical lawyer, narcologist, neurologist, neurosurgeon, nephrologist, oncologist, oncourologist, orthopedist-traumatologist, ophthalmologist, pediatrician, plastic surgeon, proctologist, psychiatrist, psychologist, pulmonologist, rheumatologist, radiologist , sexologist-andrologist, dentist, urologist, pharmacist, herbalist, phlebologist, surgeon, endocrinologist.
We answer 97.13% of questions.
The mucous membranes of the female genitourinary system consist of squamous epithelium. Columnar epithelium is also found and lines the cervical canal. Its cells secrete a certain secretion and help protect the mucous membrane of the organ from external damage. Columnar epithelium in a smear below or above normal may indicate a disruption in the woman’s hormonal background or the presence of inflammation.
The essence of columnar epithelium, possible deviations from the norm
The function of the columnar epithelium is to provide the necessary amount of mucus in the cervix for its lubrication. In the normal state, the cells of such epithelium are dispersed over the surface of the cervical canal in groups that have the shape of honeycombs, stripes or glasses. The latter depends on the stretching of the cytoplasm by mucus.
Deviations from the norm and consequences:
- displacement of the columnar epithelium and its replacement of flat cells indicates the presence of a pathology such as ectopia;
- a low number of columnar epithelial cells indicates hormonal imbalance;
- a lot of atypical columnar epithelium - this is the development of cancer pathologies in the cervix;
- an increase in atypical cylindrical cells may indicate infectious diseases of the woman’s genitourinary system, in particular the urethra, the presence of inflammatory processes (cervicitis, erosion);
- post-traumatic disorders - formation of fistulas in the vagina and cervix, ectropion, scar processes.
- the absence of columnar epithelium in the smear may indicate the death of its cells, which is a prerequisite for the development of cervical dysplasia.
Important! Intense proliferation of atypical cells of both cylindrical and squamous epithelium may indicate the development of benign mastopathy. Negative pathological processes in a woman’s mammary glands can provoke changes in the mucous membranes of the genitourinary system.
How is this pathology classified?
Based on the clinical form, this pathology is divided into:
Complications include colpitis and cervicitis caused by infection. However, in many cases, uncomplicated pathology occurs, according to which, in the colposcopic nomenclature adopted today, this form of pathology is regarded as a normal physiological state.
According to histological type, the following forms are distinguished:
- glandular (distinguished by the accumulation of glandular structures and inflammatory signs);
- papillary (characterized by the appearance of papillary growths, which are covered by cylindrical epithelium);
- pseudo-erosion, with the onset of squamous metaplasia.
Almost all cases of the phenomenon are acquired, but there are also some congenital ones. The former require mandatory treatment, the latter are considered a temporary phenomenon and do not require therapy.
Factors influencing the number of cells in the mucous layer of the reproductive organs
Basically, all organs in the human body are lined with squamous epithelial cells. Among them there is also cylindrical epithelium, which is mostly located in the cervical canal. Its main function is secretory. The presence of such a layer is responsible for the formation of a barrier to the negative influences of the external environment.
Reasons for changes in the amount of columnar epithelium in a woman’s smear:
- The presence of infections in the genital organs that cause inflammatory processes. This can be the entry into the body of gardnerella, streptococci, chlamydia. The formation of atypical columnar epithelial cells can also be affected by the human papillomavirus.
- Trauma to the cervix as a result of difficult childbirth, curettage during abortion and other disorders of the epithelial layer.
- Hormonal imbalances are triggered by an increase in the level of estrogen in the blood. At this time, the replacement of squamous epithelium with cylindrical epithelium is provoked by the occurrence of diseases such as papillomas, endometriosis, fibroma, ovarian dysfunction, and disturbances in the menstrual cycle.
- A woman's weakened immune system.
- Early sexual activity. The pathological proliferation of cylindrical cells can be provoked by early sexual acts, during which the unformed epithelial layer could be damaged.
- An active sex life, which is accompanied by a constant change of sexual partners.
Note! Pathological changes in the columnar epithelium are almost always accompanied by some signs. Their presence should encourage women to consult a specialist.
Causes
Hyperplasia of the cervical canal (proliferation), according to experts, occurs as a result of hormonal imbalance. But the exact reasons have not been established. Scientists, based on the results of studies, have found that certain factors can increase the risk of developing the disease.
First of all, bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol have a negative impact on the state of hormonal levels.
The process of growth of the endometrium can be provoked by diseases of the urinary system and internal genital organs that have a long course and last for a long time. When inflammation is relieved, the process of epithelial cell division stops.
On this topic
Can an ovarian cyst resolve on its own?
- Editorial board of Oncology.ru
- October 16, 2021
Experts have found that women's health is negatively affected by early or promiscuous sexual intercourse, sexually transmitted diseases, the HIV virus or herpes.
The condition of the mucous membrane is negatively affected by curettage or abortion, the presence of immunodeficiency syndrome, fibroids or endometriosis.
Symptoms of the development of pathological changes in the mucous membranes
An increase in the amount of columnar epithelium in the flesh, until it replaces flat cells, in an advanced form causes a certain discomfort in the genitourinary system, which a woman cannot help but notice. Any more negative manifestations indicate the presence of pathological changes in the reproductive organs.
The main symptoms of changes in the columnar epithelium:
- The presence of copious discharge with the appearance of an odor, which is accompanied by itching or burning.
- The appearance of pain during intimate relationships, as well as the presence of bloody leucorrhoea after.
- Disturbances in the menstrual cycle that provoke long-term infertility.
Diagnosis of the disease and methods of treatment
Detection of a particular disease of the genitourinary system begins with a gynecological examination and taking a smear. Such an analysis makes it possible to identify the presence and quantity of both squamous and columnar epithelium, detect leukocytes that indicate inflammatory processes and prescribe further clarifying examination.
Normally, the cylindrical epithelium in a woman’s smear should contain no more than 4–15 cells that fall into the field of view. Exceeding the norm indicates the presence of pathology in the cervical canal and uterus. If there are very few cells, then we are talking about hormonal imbalances. The complete absence of epithelial cells may indicate cervical dystrophy and cause infertility.
Carrying out an analysis by taking a smear from the uterus and its canal makes it possible to determine the presence of atypical cells in the mucous membranes of the reproductive organs. Their presence indicates that malignant pathologies are developing in the cervical canal. A smear in which a large number of atypical columnar epithelial cells indicates a precancerous or cancerous condition.
If, after examining the smear, a significant replacement of the squamous epithelium with cylindrical epithelium was revealed, then the patient may be prescribed other methods of examination - cytological studies, bacterial cultures based on the smear, hormonal background, immunogram.
Important! After a special examination of the affected area and identification of atypical columnar epithelial cells, a biopsy may be prescribed.
After a woman has been diagnosed and the cause of the abnormal columnar epithelium in the smear has been identified, the woman is prescribed appropriate treatment. Therapy is based on drug treatment, which includes anti-inflammatory drugs, drugs that eliminate infection in the genitals. At this time, doctors try to normalize hormonal levels and strengthen the body's defenses.
The presence of cylindrical or squamous epithelium in a smear above or below the norm always indicates the development of negative abnormalities in the genitourinary system. If a woman experiences discomfort in the form of pain, burning, itching and pathological discharge, then diagnosis and treatment are urgently needed. Otherwise, untimely detection of pathology can lead to serious consequences, and self-medication will only aggravate the condition of the body.
What are epithelial cells and types of epithelium in a smear?
Epithelial cells or epithelial cells are cells of epithelial tissue that cover internal organs and line their cavities. The epithelium is separated from the underlying tissue by a fibrous basement membrane and consists of several types of cells.
What does epithelium mean in a smear from the urethra, vagina, cervical canal, nose, and what types of epithelium can there be in a smear?
When turning to a urologist with complaints about problems with urination, the patient undergoes an examination to determine their causes; One of the diagnostic procedures is a smear from the urethra (urethra). As in women, the epithelium found in a smear in men is most often: single-layer squamous, transitional or intermediate epithelium lining the urethra, as well as multi-row single-layer epithelium with goblet cells, stratified (multilayered) epithelium with signs of keratinization and glandular epithelium with glandulocytes (secretion-producing cells) . Increased surface epithelium in a smear in men in most cases indicates chronic inflammation of the urethra, less often the cause is urethral leukoplakia. More information from the material – Analysis of smears from the urethra
Epithelium in a smear in women is detected during examination of the urogenital area and organs of the reproductive system, in particular the vagina (vagina) and the cervical canal (cervical canal).
Stratified squamous epithelium is present in a smear from the vaginal mucosa; Often in the transcript of the analysis it is indicated as a single epithelium in a smear or a normal surface epithelium in a smear.
In addition, during cytological studies of vaginal discharge, columnar epithelial cells can be detected: single-layer columnar epithelium in the smear and single-layer prismatic epithelium in the smear, since these are the types of epithelium that line the vaginal walls.
What can a cervical smear show? First of all, the cylindrical epithelium lining the cervical canal is determined in the smear, as well as the transitional and glandular epithelium in the smear.
When metaplastic epithelium appears in a smear, this means that as a result of a pathological process (associated with infection, hormonal or endocrine disorders), differentiated epithelial cells of one type are replaced by cells of a different type.
The epithelium in the nasal smear is mainly single-layer multirow and columnar epithelium with goblet and intercalary cells. Scales of squamous epithelium in a smear, as well as cylindrical epithelium in a smear, appear in large numbers in a child if the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity is inflamed.
The difference between HPV and cervical erosion
Have you been fighting thrush for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure thrush by taking it every day.
Cervical erosion and HPV (human papillomavirus) significantly increase the risk of developing cancer. This fact terrifies women, because both pathologies are quite common. Fortunately, not all types of papillomaviruses are capable of causing cancer and not all cervical erosion is true. In fact, 15-28% of women with HPV types 16 and 18 face cancer, and erosion or, more accurately, squamous intraepithelial lesions in these cases is a consequence of increased infection. With this diagnosis, the woman is strongly recommended to undergo treatment with antiviral drugs, immunostimulants, and cauterize the erosion with liquid nitrogen, radio waves, laser or other methods. It is also important to consider that HPV often occurs in combination with other infections. All of them must be treated.
What you need to know about cervical erosion?
According to statistics, every third woman is diagnosed with cervical erosion. But what is this common disease? Cervical erosion (CEM) is a defect of the mucous membrane. There are 2 types:
Our readers successfully use Candiston to treat thrush. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
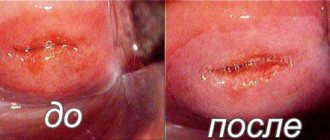
- True erosion is an acquired benign pathology, manifested by a change in the integrity of the cervical mucosa. Visually defined as a reddened area on the pink surface of healthy tissue. On palpation, the eroded area bleeds. Bleeding is also observed after sexual intercourse; the lower abdomen in women with this diagnosis periodically pulls and hurts. The most common causes of the disease: inflammation (most often caused by infectious diseases), damage to the cervix during childbirth, abortion or surgery, hormonal imbalance. Also, the development of true erosion can be affected by vaginal dysbiosis, frequent changes of partners, irregular sexual intercourse, and immune disorders.
- Pseudo-erosion (ectopia). It is characterized by a non-standard arrangement of the cylindrical epithelium, its growth from the cervical canal to its vaginal part. Simply put, ectopia is an “inversion” of the cervical canal outward. Visually, it is also defined as redness, but unlike true erosion, it does not bleed upon palpation and does not cause any discomfort to the woman. Most often, ectopia occurs during puberty, during pregnancy. It often appears when taking hormonal drugs or oral contraceptives.
It is impossible to determine with the naked eye whether this is ulceration or ectopia. To do this, the woman should undergo additional examinations. Now attention! Neither true erosions, nor even more so ectopias, are a precancerous condition and do not turn into cancer. What is really scary about true cervical erosion is its “readiness” for infections, menstrual irregularities, and infertility.