Symptoms and signs of cervical dysplasia - nuances of the operation
Cervical dysplasia is a serious pathology of the female sphere, most often found in young girls aged 25 to 35 years. It is a disease that precedes the development of the oncological process, so untreated dysplasia eventually turns into cancer.
The disease is difficult to diagnose because it rarely provokes the appearance of pronounced symptoms; changes in the cervix are usually discovered during routine examinations by a gynecologist.
Treatment is carried out by two main methods - conservative therapy and surgical intervention.
The decision about the method of treatment should be made by an experienced doctor, since it is important to take into account many factors, for example, the degree of organ damage, the age of the patient, or the presence of concomitant pathologies.
What is dysplasia
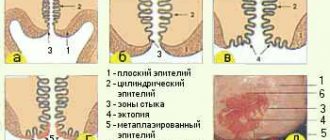
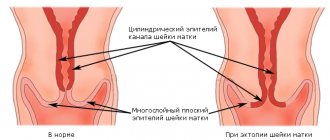
The cervix is a part of the uterus, consisting mainly of muscle tissue, which is covered on top with multilayered epithelium (mucous ball), and inside - cylindrical.
It is the structural changes in epithelial cells of the first type, leading to their atypical structure, that are called dysplasia (neoplasia).
In gynecology, several cellular layers of squamous epithelium are distinguished:
- basal - the deepest ball, it is located on the border of the mucous epithelium and muscle fibers. Here new cells appear, which, as they mature, move to the surface epithelium;
- parabasal - functionally no different from the basal ball, but parabasal cells are more mature and have a rounded shape;
- intermediate and intraepithelial - here the growth and development of cells completely ends;
- superficial - an outer ball that covers the younger epithelium, protecting it from negative effects, for example, from infections. Cells quickly die and peel off, giving way to new structural units.
Cervical dysplasia is a disease that is characterized by structural changes in the epithelium. The layers mix with each other, the cells increase in size and change structure - extra nuclei appear, the shape disappears.
Causes
The main reason leading to the development of cervical dysplasia is a special papillomavirus that attacks humans. There are more than 80 types of infection, but only 30 of them lead to diseases of the cervix or other genital organs.
13 types of HPV have a high risk of cancer, and when infected with virus 16 or 18, cancer develops in more than 80% of cases.
Not in all cases, infection with papillomavirus leads to cancer. For epithelial dysplasia to occur, which then develops into cancer, provoking factors are needed:
- the woman has parity, that is, a history of multiple births;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs as protection against unwanted pregnancy. When taking tablet forms of contraceptives for five years, the risk of atypical changes in the cervix doubles;
- the presence of cancerous changes in the partner’s penis;
- sharp hormonal surges - pregnancy, use of postcoital contraception, menopause;
- tobacco use – even passive smoking increases the risk of developing neoplasia;
- hypovitaminosis – the most dangerous is a lack of vitamins A and C;
- decrease in the body's defenses - AIDS, taking immunosuppressants, stress conditions, depletion of the immune system due to diffuse infections;
- the presence of infections in the genital tract, chronic inflammation.
Predisposing factors also include early pregnancies (before age 18), injuries during abortion or childbirth, and sexual activity that began at a young age. In addition, heredity plays a big role.
Important! Girls whose family members have suffered from cancer should closely monitor their health and regularly visit a gynecologist for preventive examinations.
Symptoms and signs
There are no characteristic symptoms of cervical dysplasia; only in advanced forms may minor discharge with blood or discomfort in the lower abdomen appear.
Typically, cell atypia is detected during preventive examinations, or when a girl turns to a gynecologist for help in treating other diseases.
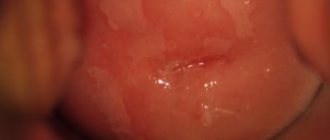
Erosion often appears against the background of cervical dysplasia, so if such a defect is present, it is important to conduct a detailed diagnosis.
Signs that may indicate the development of pathology:
- change in the nature or amount of vaginal discharge;
- the appearance of blood streaks in the vaginal mucus, especially after sexual intercourse;
- discomfort or pain during penetration during sex.
The presence of symptoms is an optional factor for making a diagnosis; usually signs appear already at grade 3 cervical dysplasia. In other cases, the disease can be recognized only by conducting an oncocytological study.
Treatment
Treatment of the cervix will be prescribed after a complete diagnosis. Only after the test results are known and the degree of pathology is determined, the gynecologist has the right to prescribe appropriate therapy. If a woman is carrying a child, treatment will have to wait, since the medications used can harm the baby.
Vaginal suppositories
In case of moderate or mild pathology, when the affected cells are single, the treatment is conservative. The woman will be treated at home. It is recommended to take immunomodulators, vitamin complexes, and a balanced and nutritious diet. Special vaginal suppositories are prescribed. They restore the vaginal microflora and enable tissues to recover as quickly as possible. Administration should be done in a lying position. After the procedure, it is not advisable to get up for half an hour. If a vaginal capsule or suppository was prescribed once a day, then it should be used before bedtime so as not to get up after its administration.
Justified use:
- "McMirror." Prescribe one suppository once a day. The course of treatment is a week.
- "Lactonorma". Administration is carried out using an applicator or manually. Depending on the situation, a capsule is prescribed once or twice a day. Duration of use is 1-2 weeks. If necessary, the course is increased.
- "Acylacta". Inserted into the vagina twice a day. The first administration is carried out in the morning, after which you need to not get up for half an hour so that the composition can dissolve. The course of treatment is a week.
- "Lactozhinalya". The capsule is moistened before use so that it quickly dissolves in the vagina. It is recommended to use it once a day for two weeks, or twice a day for a week.
Mild changes in squamous epithelial cells
please help me figure it out.
There are 5 oncocytologies
1. August. Laboratory - State Health Institution GP 218 Institution of Health of the North-Eastern Administrative District Scraping obtained: vagina, exocervix, endocervix The cytogram corresponds to the inflammatory process of the mucous membrane (vaginitis, exocervicitis, endocervicitis); changes characteristic of human papillomavirus infection?; pronounced changes in squamous epithelial cells: moderate dysplasia (D II)
2. Beginning of October. Laboratory – Interdistrict Cytological Laboratory at GP No. 120 Scraping taken: canal Endocervicosis (and glandular erosion), HPV, dysplasia II-III degree
Diagnostic methods
Biopsy results
The clinical picture has no characteristic signs and, as a rule, is asymptomatic. The complaints are due to concomitant gynecological diseases. When examined in the mirrors, you can observe ectopia of the cervix of various sizes, white spots of leukoplakia, papillomas, and even a visually unchanged cervix.
One of the diagnostic methods is colposcopy (examination of the cervix using a microscope), in which the picture can also be very diverse - from ordinary ectopia to leukoplakia, silent iodine-negative areas, areas of atypical transformations of squamous epithelium.
Discaryosis
A mandatory study is to take a cytological smear from the cervix, where cells with dikaryosis are detected. Dyskaryosis is a borderline condition in which cell atypia is expressed mainly in the cell nuclei, while in cancerous conditions changes are found in both the nuclei and the cytoplasm.
If dyskaryosis is detected, a histological examination is indicated, which allows a final diagnosis. To do this, a targeted biopsy of the cervix and diagnostic curettage of the mucous membrane of the cervical (cervical) canal are performed. The results of histological examination make it possible to determine the degree of changes in the cervical epithelium and outline the nature of treatment measures.
Larisa Skopina
Hello Nika! Reactive changes in the epithelium in the smear means that there is low-grade inflammation in the vagina, and the detection of leukocytes in increased numbers confirms the fact of inflammation. Key cells are vaginal cells associated (glued) with coccobacteria and are a diagnostic sign of gardnerellosis. In another way, gardnerellosis is also called bacterial vaginosis, in which the normal microflora of the vagina (lactobacillus, milk sticks) is replaced by pathological anaerobic flora, the normal acidic environment of the vagina is disrupted. With bakvaginosis, discharge with a characteristic “fishy” odor is often detected. This is a common non-inflammatory disease in women and is not an STI. More often it occurs against the background of the use of douching and the use of an intrauterine device, when changing a sexual partner. The disease is not dangerous, but it needs to be treated, since it will predispose to the occurrence of other inflammatory diseases (genital infections), fungal diseases, and negatively affects the course of pregnancy. Men rarely become infected with bakvaginosis, only with a severe decrease in immunity, especially if they previously had urological problems (prostatitis). If a man does not have any symptoms, then there is no need to treat him. The woman is treated with antibiotics.
I want to say that bakvaginosis itself is not an inflammatory reaction; with it, leukocytes should not increase in the smear, and if they are present (as well as reactive changes in the epithelium), then this indicates the possible presence of other pathological flora (against the background of bakvaginosis) , it needs to be identified by examining a smear using PCR for all sexually transmitted infections (ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis), trichomoniasis.
| 31.03.13 |
Classification
After cytological analysis, the following reactive changes in the squamous epithelium are revealed:
- Exudative. The woman is found to have destroyed neutrophilic leukocytes. The smear contains fragments of cells and nuclei. The preserved, intact ones are in a state of phagocytosis.
- Reparative. The name for this type of change was given by the repair and subsequent epithelization occurring in the defective surface of the layers. Based on the results of the analysis, cells of increased size are detected. It is because of them that tissue grows, which replenishes the affected areas. The nuclei become larger, but do not lose their clear contours. No chromatin accumulation is observed. By the way, it has a soft-grained structure.
- Degenerative. Manifested by shrinkage of the cell nucleus. Disturbances in the structure of the nuclear membrane and chromatin are also observed. Proliferation of the epithelium indicates a chronic inflammatory process.
When talking about reactive changes in the squamous epithelium, it is necessary to note that cytological analysis also often reveals a combination of inflammatory changes. Often reparative ones are combined with degenerative and proliferative ones.
In such cases, multinucleate cells with large nuclei are detected. The cytological picture strongly resembles dysplasia or cancerous conditions. If we talk about inflammatory atypia, it is characterized by a uniform distribution of chromatin. The lumps have unclear contours.