Uterine epithelium. What characteristics are normal?
The uterus consists of three layers: integumentary, muscular and internal mucosa (endometrium).
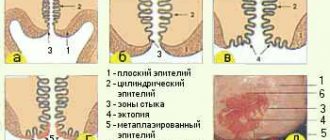
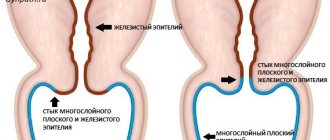
The lining of the uterus is formed by several epithelia. Several layers of squamous epithelium line the inside of the vagina (flat cervix). This stratified squamous epithelium (MSE) is sometimes called squamous epithelium and is layered. The cervical canal of the uterus is lined with a single layer of cylindrical cells. Among the cylindrical cells there is a special glandular epithelium that secretes mucus.
Between the two types of epithelium there is a transformation zone: here the MPE passes into the glandular one.
The surface of the cervix is normally smooth and pink, since it is lined with a uniform layer of epithelium, this is the basal epithelium. As a result of a gynecological examination, there should be no mucosal defects or pathological formations on the surface. The Schiller test indicator should be uniformly brown.
Cytological analysis of the mucous membrane on the fragment under study should reveal a single number of leukocytes, as well as flat epithelial cells. The number of white blood cells may vary depending on your menstrual cycle.
Normally, leukocytes are characterized by pure cytoplasm and intact nuclei. Signs of phagocytosis are not observed. A vaginal smear may contain mucus and individual cells with altered cytoplasm.
What are reactive changes?
Various infections enter the female body through unprotected sexual intercourse. Various fungi, bacteria and viruses cause vaginitis and reactive changes in the epithelial lining of the uterus. Most infectious lesions are caused by bacteriosis.
Changes caused by a lack of nutrients in the tissues of the uterus are called dystrophic. Such problems arise due to the fragility of blood vessels. They usually appear due to erosion. First, dystrophy occurs, and then desquamation (ulcer formation). In some cases, the upper epithelium of the uterus peels off.
Inflammation on the vaginal membranes can spread to the mucous membrane, and in some cases, even bacteria naturally present in the microflora can carry the infection. The spread of infection and the appearance of an inflammatory process indicate a decrease in the body's immunity.
Proliferation (hyperkeratosis) is a term meaning active cell division. With reactive changes, it usually affects the columnar epithelium of the uterus. The appearance of tumors entails a process of proliferation - cells continually divide, forming hyperplasia (neoplasm). Uncontrolled hyperplastic processes can be life-threatening.
Diffuse changes
Diffuse changes are not a disease, it is a diagnostic sign. They affect the muscular layer of the myometrium. They are usually detected by ultrasound.
Normally, the muscle layer is homogeneous and should not contain tumors. With diffuse changes, the muscle layer is heterogeneous, the integumentary tissues are evenly distributed throughout the myometrium. This deviation is called adenomyosis and is visible using ultrasound.
Note! Upon visual examination of the vagina, redness on the mucous membrane may be noticeable. They indicate the development of the inflammatory process. Cytological analysis of the smear reveals an increased number of leukocytes with a destroyed nucleus, as well as lymphoid elements and eosinophils. The microflora mixes.
Timely detection of pathological deviations helps to begin treatment on time. At the last stage of therapy, the vaginal microflora is normalized with the help of prebiotic drugs.
Other members of the vaginal microbiology community
Who else lives in the vagina? Who are these 5%?
In fact, there are about 40 species of other bacteria, including:
- Mycoplasmas;
- Corynebacteria;
- Bacteroides;
- Peptostreptococcus;
- Staphylococci.
Each of them also lives here for a reason. Their number is regulated by already known lactic acid bacteria. But when the latter are weakened, the minority does not wait, and begins a mortal struggle for primacy. And this ultimately results in cytolytic vaginosis.
Types of pathological changes
Depending on the results of cytological analysis from the vagina, the types of reactive changes are divided into several types.
With exudative changes, leukocytes-neutrophils are destroyed, and acute inflammation occurs on the mucous membrane of the uterus. The smear contains fragments of destroyed cells and leukocyte nuclei. The remaining intact cells are in the stage of phagocytosis.
Reparative changes are characterized by regeneration and epithelization of defects in the surface layers of the uterus. The smear contains relatively large cells; histology analysis shows tissue proliferation and repair of damaged areas. The nuclei of leukocytes also become larger, but their outline is clear and the chromatin is not cluttered. Chromatin has a fine granular structure.
Degenerative changes are changes in which the nuclei of cells shrink. The structure of the nucleus is disrupted and degeneration occurs: the shell and chromatin change their shape. Such changes are characteristic of a chronic inflammatory process.
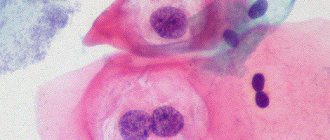
Atypia of epithelial cells during inflammatory processes leads to the appearance of all three types of reactive changes. In the preparation you can find cells with two or more nuclei, the nuclei themselves are greatly enlarged.
Cytological indicators resemble an oncological condition or dysplasia. Unlike formations of an oncological nature, with inflammatory atypia the chromatin is evenly distributed.
What pathologies do reactive changes indicate?
Accidental trauma to the epithelial surface, which occurs as a result of surgery, improper douching or sexual intercourse, can lead to erosion. The integrity and structure of the epithelial coating is disrupted. The infectious process in the acute phase is one of the main causes of erosion. Sometimes, as a result of a pathological process, rotting of the squamous epithelium of the uterus occurs.
Erosion is a temporary process. As a rule, after 2-3 weeks the damaged area is restored, covered with lining epithelium and healed. Erosion refers to secondary changes in the cervix, that is, those that are associated with a change in the shape of the cervix, as well as displacement of the mucous membrane. The structure of the tissues does not change.
In the scientific literature, pseudoerosion is referred to as ectopia of the cervix. This type of reactive changes in epithelial tissue does not require any therapeutic intervention. Pseudo-erosion occurs during embryogenesis during the formation of the reproductive system in the fetus. Visual examination reveals areas of redness that stand out against the pink and smooth surface of the uterus. A cluster of cylindrical cells forms around the os of the uterus.
False erosion can be detected using colposcopy. The reddened area is not stained with iodine solution. If ectopia occurs as a result of childbirth, the doctor may prescribe a cauterization procedure.
Leukoplakia is a condition in which a white spot appears on the cervix, that is, squamous acetowhite epithelium (ABE) appears. Leukoplakia is characterized by thickening of the uterine epithelium. The white epithelium arises from keratinization of cells; the mature metaplastic epithelium hardens into a keratosis. This process is not the norm. Such a reactive change in epithelial tissue is considered a precancerous condition. It needs to be diagnosed and treated in time to avoid the development of cancer.
Erythroplakia is a pathology during which dark red or burgundy areas without a specific shape form on the surface of the cervix. In the affected areas, the epithelial tissue begins to thin out. The affected area changes its color depending on the degree of atrophic changes.
The reason for the reactive change is a violation of the microflora of the genital tract. To study the inflammatory process in detail, a hormonal analysis is prescribed, because Problems in the endocrine system can lead to the development of thinning.
Cervical dysplasia is a pathological process in which atypical formations appear at the junction of single-layer and multilayer epithelial tissue. Another name for dysplasia is neoplasia of the cervical epithelium. The main reason for this reactive change is the herpes virus and human papillomavirus. Dysplastic processes occur in three stages (designated CIN1, CIN2, CIN3), complications of the latter are very dangerous.
A polyp of the cervical canal occurs as a result of abortion and improperly performed gynecological manipulations. Damage received after sexual intercourse leads to protrusion of uterine tissue into the cervical canal, and a polyp is formed. Persistent inflammation of the genital tract is one of the main causes of the appearance of polyps. Usually the pathology is removed through surgery.
Lesions caused by HPV
HPV is one of the most dangerous viruses for reproductive health; some of its varieties are oncogenic. A wart resembles a papilla in appearance. Usually the spread is focal.
Flat papilloma of the cervix is a small single or multiple tumor. It is formed by two types of tissues - connective and epithelial. The virus causes cells to proliferate after infection. The peculiarity of uterine papilloma is its flatness; in other localizations, papillomas may look different.
Cervical condyloma is one of the most dangerous lesions of the female reproductive system. It is caused by the human papillomavirus. The most serious complication of condylomas is infertility, the formation of cysts on the ovaries. Human papillomavirus infection (PVI) requires timely diagnosis and treatment. The main symptom of this disease is the abnormal proliferation of multilayer epithelial tissue, such as acanthosis. Acanthosis is a pathological condition in which the integumentary cells become rough; there are two types - malignant and benign.
It's unpleasant, but you can live
Of course, cytolytic vaginosis is an unpleasant thing and cannot be treated. Doctors advise eliminating the disease with a simple diet and patience. You can exclude lactic acid products, sweets, and various gels containing lactobacilli. The diet will help somehow regulate the microbiological balance, although the doctors are right that there is actually nothing to treat.
But medical science does not stand still, and this is encouraging. What today is a medical problem that has no solution will receive an adequate solution and appropriate treatment tomorrow.
The main thing is not to avoid the doctor, but to find a good gynecologist who can improve the woman’s physical condition as much as possible. And it most often depends on the lifestyle of a modern person, for whom low immunity, emotional overload, and hormonal imbalances are common things.
Maybe we need to be more selective in our approach to the modern delights of civilization and make more use of the gifts of nature. Fortunately, she has plenty of them.
Reasons for reactive changes
The reasons for the appearance of such pathologies are the entry into the body of various pathogens transmitted through unprotected sexual contact. Sometimes the changes are caused by representatives of the natural vaginal microflora, whose reproduction becomes excessive when immunity declines. Endocervicitis occurs.
Main reasons:
- The presence of papillomavirus in the body;
- Herpes virus;
- Weakening of the body's defenses;
- Early onset of sexual activity, premature birth;
- Disruption of the endocrine system;
- Sexually transmitted diseases (chlamydia, trichomoniasis, syphilis, etc.);
- Injuries to the uterine cavity due to improper gynecological manipulations;
- Infectious processes;
- Frequent change of sexual partners;
- Long-term use of hormonal contraceptives.
Experiments have confirmed that protein-based oral contraceptives do not have a pathological effect on uterine tissue.
Important! Any pathologies leading to a possible change in the structure of the epithelial tissue layer can lead to the appearance of cervical dysplasia.
Signs
Some symptoms will help identify reactive changes. Firstly, redness appears on the mucous membrane, causing discomfort.
Secondly, cytological analysis will help identify deviations from the norm in the composition of the smear - the number of leukocytes is usually increased, and epithelial cells may have structural changes.
A woman may notice the appearance of an unpleasant smell of discharge and an increase in its volume. The pathological condition is indicated by bloody discharge not associated with menstruation.
Diagnostics
Any changes in the menstrual cycle should be paid attention to. If the discharge becomes more numerous and its structure changes, then you should go to the hospital for help. A defect on the cervix can be detected during a full examination in the gynecologist’s office. Such a study should be carried out twice a year, regardless of the woman’s condition. The examination is very important, as it allows us to identify the development of pathologies in the early stages. The Schiller test and scraping for oncocytology help to make a final diagnosis.
Colposcopy is a study in which special dyes are applied to the surface of the cervix. This is a three percent solution of acetic acid and iodine. Substances allow you to identify damaged areas. If an abnormal reaction is detected, a biopsy is ordered. Iodine-negative uterine epithelium is an affected area that is not properly affected by iodine. During a colposcopic examination, normally the tissue is uniformly stained, but in pathological cases, light areas are revealed. The transcript of the analysis is usually ready in a few days.
Detection of atypical cells and cancerous formations is carried out using oncocytological scraping. This analysis allows us to assess the nature of inflammation and its nature.
The tumor can be analyzed through a biopsy. Material is taken from the affected area for analysis. The tissue is taken using a special electric loop.
If changes in epithelial tissue were caused by highly oncogenic infections, then doctors prescribe tests for HPV. A similar test recognizes the DNA of the virus.
Preparation and procedure for taking tests
It is optimal to do a smear for cytology after the end of menstruation and before the middle of the next menstrual cycle.
— Refrain from sexual contact. — Do not use vaginal products (suppositories, creams, gels, etc.). — Do not douche.
- Biomaterial is collected using sterile disposable instruments.
1. The patient undresses to the waist and lies down in the gynecological chair.
2. To visualize the cervix, the doctor uses a Speculum speculum.
It is rational to take scrapings for histology under colposcopy control.
3. The doctor inserts a cervical brush into the cervical canal to a depth of 1.5-2 cm, takes a sample of endocervix tissue and places (imprints) it on a prepared glass slide with appropriate markings.
4. Then, using an Eyre spatula, scrape from the junction (from the transformation zone) of the epithelium and place it on the designated part of the first slide or on the second glass.
5. If necessary, with another spatula, the doctor makes a targeted scraping from the suspicious area of the ectocervix and places the taken biomaterial on another glass with the appropriate marking.
6. Smears are immediately treated with a fixative, dried and sent for examination.
7. In the laboratory, first of all, the adequacy of the cytological smear is assessed: - are there enough cells on the glass for analysis; — is the biomaterial applied too thin/thick; - how well the fixation is done; — whether the smear is contaminated with mucus, blood, semen or inflammatory exudate.
- Satisfactory quality of the biomaterial (adequacy of the smear) is a key factor in the effectiveness of smear analysis for cytology for decoding.
If your doctor asks you to retake the PAP test, don’t be alarmed. Practice shows that up to 20% of smears are not performed adequately and must be repeated.
The procedure for taking a smear is short-term, low-traumatic, safe and in most cases painless. Sometimes the patient may feel mild, transient discomfort.
How to behave after the procedure: - Refrain from sexual contact for 1-2 days. — Otherwise, lead a normal life. — If necessary, the doctor gives individual recommendations.
Contraindications to cytology: - Acute genital infection (itching, profuse, purulent, with a strong odor, foamy vaginal discharge). - Pregnancy. - Virginity. - Menstruation.
For minor patients who are sexually active, cervical scraping is done in the presence of their parents (guardian).
After childbirth, you can take a cervical smear no earlier than 3 months later.
Biomaterial is collected for analysis using a special brush or spatula. The procedure itself is simple, taking 5-10 minutes. One type of smear is not enough for this. It is necessary to examine not only the vagina, but also the upper layer of the cervical canal. A competent doctor will never use the same glass for both samples during an examination.
An important step before taking a smear is preparation. For a couple of days, the use of any intimate cosmetics, ointments, candles, tampons is excluded. It is also necessary to abstain from sexual intercourse for 2-3 days before taking tests. Douching and other gynecological procedures are also prohibited. According to doctors, the best time to submit the material is before and after menstruation. It is also not recommended to take a bath, only shower during the preparation period.
An experienced doctor knows that a woman's smear is different at the beginning, middle and end of the menstrual cycle. Women will also have other indicators during pregnancy. Therefore, when conducting the study, the following factors are taken into account:
- Age;
- Gestational age, cycle time;
- Having an IUD or taking contraceptives;
- Treatment of other diseases.
The doctor often prescribes a repeat examination to obtain more accurate indicators.
We hasten to say that the procedure for collecting cells for oncocytology is absolutely painless and will not cause injury to the patient.
Treatment
Before starting any treatment measures, you first need to familiarize yourself with the clinical picture of the disease. Depending on the factors, different treatment methods will be prescribed:
- Origin of inflammation;
- Type of pathological condition;
- Pregnancy planning;
- Woman's age.
Sanitation is a set of measures to cleanse a damaged organ and remove non-viable tissue. The first stage in treatment is the sanitation of the genital tract. If the patient has cervical dysplasia, then surgical intervention is necessary.
The most popular treatments for reactive changes
Depending on the type of pathological changes, doctors can use various therapeutic techniques:
- Diathermocogulation. The essence of this method is the effect of electric current on the epithelial tissue of the uterus. The damaged areas are burned and destroyed, then a scar is formed and the tissue heals.
- Cryodestruction. The treatment process is carried out using a flow of liquid nitrogen.
- Treatment with radio waves. The shock wave destroys damaged tissue; after using this method, scar tissue does not appear.
- Chemical coagulation. The surface of the cervix is treated with special chemicals so that the damaged area heals faster.
Before starting a specific treatment method, the doctor must familiarize himself with the test results and take into account all the individual characteristics of the patient.
Fixing and staining the sample
After transferring the material onto a glass slide, it is important to “fix” it. To do this, the sample is dried. Fixation is carried out using various substances (for example, ethyl alcohol). This depends on the method of further staining.
The most commonly chosen staining methods are:
- by Papanicolaou;
- using hematoxylin-eosin;
- according to the Romanovsky method.
After applying the dye, the slide is placed in a sterile package and sent to the laboratory. The finished sample is examined under a high-resolution microscope.
If the smear is taken according to all the rules, cells of cylindrical, flat and metaplastic epithelium are found in the sample.
Preventive measures
To avoid the appearance of various reactive changes in the epithelium of the cervix, you must adhere to several rules. The choice of sexual partners should be treated very carefully; sexual intercourse itself should be protected. Sexually transmitted infections very often lead to reactive changes. The human papillomavirus is most dangerous for the tissues of the uterus and vagina. During pregnancy, exposure to negative factors should be avoided, especially during the third trimester. When infections occur, it is important to monitor the state of your immunity.
Particular attention should be paid to oral contraceptives. They can only be taken with the permission of a doctor; a monthly visit to a gynecologist will be required.
Important! Under no circumstances should you use oral contraceptives on your own, as there is a high risk of causing irreparable harm to your health.
As soon as a girl becomes sexually active, she should undergo mandatory gynecological examinations 1-2 times a year, as well as undergo tests for oncological cytology. As soon as pathological changes are identified in the early stages, it is necessary to follow all the doctor’s recommendations and not self-medicate.
Indications for cytology
- In 90% of cases, cervical smear cytology is done to ensure the woman’s health.
- In terms of cervical screening, a PAP test should be performed on all women aged 18–65 years.
Repeatedly, in case of negative (normal) results of the first study, cytology is done every 1-3-5 years.
- Preparing for pregnancy.
- Diagnosis of viral infections (HPV, genital herpes).
- Infertility.
- Metabolic syndrome, obesity, diabetes.
- Preparing for the insertion of an intrauterine device.
- Hormonal contraception.
Read everything about the HPV test in detail in the article: HPV-16 type in women