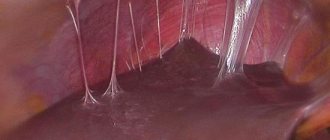
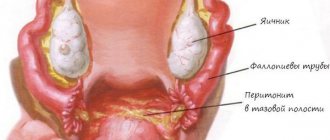
Among gynecological diseases, doctors identify adhesions in the fallopian tubes. This pathology is difficult to diagnose due to the lack of clear symptoms. Often, the disease can only be identified through an examination aimed at identifying the cause of infertility.
Causes and symptoms
The most basic reasons for the formation of adhesions are:
- Mechanical effects on the peritoneal area.
- Consequence of drying of the peritoneum and internal cavity during surgery.
- Development of infectious inflammation in the abdominal cavity.
- Bleeding or presence of blood clots in the abdominal cavity.
- The presence of foreign bodies in the area of the internal cavities of the body.
- Long-term paresis of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Ischemic organ damage.
- Consequence of inflammation on any organ.
- Congenital presence of adhesions.
Among the main signs of the presence of adhesions are:
- Disturbances in intestinal motor function.
- Development of pain syndrome , which can be permanent or periodic.
- Tendency to constipation.
Pain syndrome and the appearance of discomfort will be characteristic of the area where the predominant deposition of fibrin occurred. For women, this can be expressed by pain that occurs during sexual intercourse, menstruation, etc.
The principle of development of the adhesive process The formation of adhesions involves several successive natural stages. Among which:
- Development of the reactive phase . There are signs of shock in the body, which is associated with damage to the peritoneum.
- Exudative phase . In this case, vascular permeability increases and undifferentiated cells leave the vascular bed in combination with fibrinogen.
- Adhesive process . It is characterized by the fact that by the third day of the inflammatory state, fibrin is transformed into threads. Fibroblasts develop with the synthesis of collagen, which is part of the connective tissue component.
- Formation of a young commissure . The process lasts 1–2 weeks and represents the development of loose connective tissue, in which the vascular bed, nerve endings and smooth muscle cells begin to grow.
- Forming dense fibrous connective tissue mature adhesions . They can form over a period of up to two months. The development of fibers that are more dense in structure is underway.
What are adhesions in the fallopian tubes2
Adhesions or synechiae are the proliferation of connective tissue or fibrin that glues adjacent organs together. They arise from surgical interventions and inflammation. For example, after surgery on the pelvic region or peritoneum, the process of restoration of damaged tissue begins, and a certain pathological chain of events contributes to the growth of tissue and gluing of adjacent areas. In a previously uninjured body, the peritoneum can be likened to a slippery cellophane wrapper, with adjacent organs and structures sliding away from each other and not sticking together.
The development of synechiae is influenced by: the nature of the traumatic event, the duration of the injury, the number of interventions undergone, the method of surgical intervention, the addition of infection, the skill of the surgeon and the characteristics of each individual person.
Classification of adhesive disease
Adhesive disease is divided according to the type of clinical course:
- Acute course.
- Chronic process.
- Specific.
- Perivisceritic.
- Abnormal.
- Intermittent.
Zhenzhevsky divides adhesive disease into the following clinical course:
- The presence of pain syndrome with manifestations of organ dysfunction.
- Development of acute adhesive-dynamic obstruction .
- Recurrent course.
- Obstructive course.
- Formation of strangulation adhesive obstruction with signs of disturbances in the blood circulation of the intestinal wall.
Symptoms of tubal obstruction
Depending on the number of adhesions and the fallopian tubes affected by them, the clinical picture also differs. Obstetricians-gynecologists note the individual manifestation of symptoms of uterine adhesions and therefore recommend examination at least twice a year.
In some cases, the appearance of adhesions is asymptomatic, and the only thing that can indicate them is the inability to get pregnant. Sometimes women feel a nagging or aching pain in the lower abdomen, especially after physical activity. In addition, in some cases, the amount of vaginal discharge increases, sometimes with pus. A strong manifestation of pain or a sharp increase in body temperature indicates an acute form of the inflammatory process, therefore, in case of sharp pain in the iliac regions (as during contractions) and other similar ailments, try to promptly consult a doctor.
USEFUL INFORMATION: ARTICLE DK. KOMAROVSKY TO ALL YOUR WANTS
Diagnostics
The doctor may suspect the presence of adhesions during a conversation with the patient, focusing on typical complaints. The basis of diagnosis is additional methods, which will include:
- X-ray of the suspected affected area.
- Ultrasound examination , in which the pathological location of the organ, difficult displacement and adhesion to other organs is noted.
- Computed tomography with determination of a clear relationship between organs and visualization of possible fibrous strands.
- For the pelvic organs, this may be hysterosalpingography with the introduction of a contrast agent into the uterine cavity.
- Diagnostic laparoscopy of fallopian tube adhesion . This method is an extreme measure in diagnosing such conditions; in addition, it can lead to activation of the process towards greater formation of fibrin threads.
Structure of the fallopian tubes
The uterine or fallopian tubes are a paired muscular hollow organ with a length of 13 to 20 centimeters and a diameter of 0.4-0.5 cm. They connect the uterine cavity with the abdominal cavity in the ovarian region, where it ends in a funnel. The task of these organs is to capture a mature egg with a funnel and deliver it to the uterus. It is logical that if there is an obstruction, then the egg does not reach its target. Also in their cavity there are sperm and an egg for fertilization. Because of adhesions that block their path, they may never meet.
The adhesion process can affect either one pipe or both. With a bilateral process, conception tends to zero, and the risk of infertility is very high. In this case, they resort to artificial insemination using the ICSI method and removal of both tubes. If only one side is blocked, there is a chance of getting pregnant.
The fallopian tube may be blocked by adhesions from the inside or damaged from the outside.
The tubes consist of muscle tissue on the outside and mucous tissue with cilia on the inside.
Partitions arise from the inside, and fluid accumulates between them, stretching the organ (this process is called hydrosalpinx). Also, due to fibrin strands, eyelashes may stop functioning.
Methods for treating adhesions
How to treat fallopian tube adhesions? The basis of therapy for adhesive conditions is:
- Fibrinolytic drugs . The mechanism of their action is aimed at dissolving fibrin threads, around which adhesions are formed. These include local forms in the form of candles, such as Longidaza or Lidaza.
- Antihistamines . Drugs such as suprastin or diphenhydramine help reduce the severity of edema and further inflammation, which will also be accompanied by excessive production of the fibrinous component.
- Anticoagulant drugs . Their mechanism of action is aimed at dissolving blood clots and preventing the formation of blood clots.
- Antibacterial agents , the most common of which are tetracyclines, biseptol, and other components aimed at destroying pathogenic flora and relieving inflammation.
- Folic acid and medications that contain vitamin E. These components are aimed at rapid tissue restoration.
- Painkillers . Their mechanism of action is aimed at faster activation of the patient and destruction of newly formed adhesions.
We recommend reading - histology of the uterus and fallopian tubes: what does this mean in gynecology?
Hysteroscopy of the uterus: is the procedure safe for a woman’s health and what is it like? See all information here.
What does the term “anechoic formation” mean and what danger does it pose for a woman: https://venerolog-ginekolog.ru/gynecology/diseases/anehogennoe-obrazovanie.html
Features of the disease
A feature of adhesions (intrauterine synechiae) is the fusion of connective tissue between the fallopian tubes and the ovaries (uterus), which leads to partial or complete obstruction in the fallopian and fallopian tubes.
Adhesions form against the background of an inflammatory process and prevent the natural release of the egg, which manifests itself in the form of infertility and ectopic pregnancy. Since synechiae provoke displacement of the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes and contact between them is lost, and the egg does not enter the lumen of the tube and cannot be fertilized. Also, the adhesive process contributes to atypical transformation in the endometrium of the uterus, provoking changes and functioning of the reproductive system and its organs.
ethnoscience
Traditional medicine is given great importance, since by acting in a complex manner, they help improve the condition. These include:
- Aloe infusion . Juicy aloe leaves obtained from a mature plant are finely crushed and mixed with honey at a rate of one to six, as well as an amount of ghee that is equal to the volume of honey. The resulting mixture is mixed with milk in the amount of one tablespoon per 200 ml of hot temperature milk. The course of therapy is carried out over two months.
- Plantain decoction . To do this, one tablespoon of seeds is boiled for 10 minutes in 200 ml of water. The drug is taken in the amount of one tablespoon three times a day.
- Sabelnik in the form of tincture . Sabelnik in the volume of one spoon is infused in vodka with a volume of 300 ml. The drug is used for forty-five days.
It is not recommended to use herbal remedies as the main method of treatment, as this may lead to a weaker effect.
Video: adhesions in the fallopian tubes in women - treatment.
Causes of the adhesive process
Adhesions in the abdominal cavity are formed when the peritoneum is damaged. These could be injuries, inflammatory diseases of the abdominal organs, surgical interventions. They are more often formed in people who have a genetic predisposition to adhesions.
The reasons for the formation of synechiae in the uterus differ:
- Injuries to the inner layer of the uterus. Occur during surgical and diagnostic interventions (curettage, removal of fibroids), miscarriages, childbirth, injuries associated with the installation of an intrauterine device;
- Frozen pregnancy. The fruit dies and is destroyed, this increases the activity of fibroblasts, which are involved in the formation of connective tissue;
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the uterus. They are caused by E. coli, chlamydia, trichomonas, gonococci, or opportunistic microorganisms. A common cause of synechia formation is genital tuberculosis.
An adhesive process can be detected in the cervical canal if its epithelium is damaged.