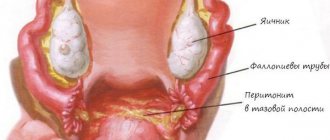
Chronic periadnexitis, inflammation of the peritoneum that develops against the background of adnexitis, which has been going on for a long time and its symptoms cannot be completely and completely cured. After suffering from this most dangerous disease, approximately every fifth woman cannot become pregnant. Even if conception occurs, the presence of an inflammatory process in the uterus, appendages and peritoneum increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy tenfold.
Causes
Many patients are frightened by this diagnosis. Therefore, it is important to understand what adnexitis is in women and what its symptoms are.
In medicine, adnexitis has another name - “salpingoophoritis”. Translated into Russian, salpingitis means inflammation of the fallopian tube, and oophoritis refers to the inflammatory process that occurs in the ovaries.
But what kind of disease is this? Adnexitis refers to diseases of the genital organs in women. The pathological process occurs in the uterine appendages, that is, in the ovaries and fallopian tubes. Purulent fluid accumulates in the lumen of the tubes.
The onset of inflammation during adnexitis in women begins with the penetration of bacteria into the mucous membrane of the fallopian tubes, where the muscular and serous layer is gradually involved. After this, the inflammatory process spreads to nearby tissues (ovaries and pelvic peritoneum). As a result of this, the ovary and fallopian tube are welded together and form a single inflammatory conglomerate (TOVO - tubo-ovarian formation). This leads to the development of adhesive processes that limit the patency of the fallopian tubes. The main causes of the development of the disease are generally considered to be:
- entry into the body of pathogenic microorganisms (gonococcus, tuberculosis bacillus, chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, etc.);
- activation of one’s own opportunistic flora (Escherichia coli, staphylococci, etc.);
- the presence of an intrauterine device;
- having sexual relations with several men;
- hypothermia of the body;
- previous diseases of the female genital organs (cervicitis, endometritis);
- decreased immunity;
- difficult childbirth;
- injury to the internal genital organs;
- failure to comply with hygiene standards.
Reasons for the development of periadnexitis
Pathology begins to develop if, with ordinary adnexitis, appropriate measures are not taken for a long time. Sometimes such a complication is possible after a long period of diagnosis or due to a medical error, the latter most often occurring due to the low qualifications of the specialist who was consulted. Unfortunately, the level of training of medical personnel in regional “on-site” clinics in Russia is constantly falling. The unsatisfactory quality of education, as well as the lack of personnel, has an impact. Therefore, if possible, it is better to contact specialized, preferably private, clinics, where you will be correctly diagnosed in a timely manner. The desire to save money in case of health can result in a lot of problems.
However, periadnexitis rarely appears due to the fault of doctors. Most often, the reason is self-medication, a blurred clinical picture due to the presence of other pathological processes in the body.
Some women interrupt treatment for adnexitis early, focusing more on their own feelings than on the gynecologist’s instructions. Some feel sorry for the money, others believe that taking medications can have a harmful effect on the condition of the liver, kidneys, and other internal organs.
Such amateur activity leads to the appearance of a chronic form of periadnexitis. It is dangerous because it can manifest itself in the later stages, when urgent surgical intervention may be required, for example, to remove pus. In addition, there is a risk of sepsis, a negative effect on the internal organs of both the pelvis and the abdominal cavity as a whole. Remember: experimenting with your health and trying to do something you don't understand can have consequences you may not be prepared for.
Symptoms
Adnexitis has two variants of its course: acute and chronic.
The main symptoms of acute adnexitis include:
- elevated body temperature up to thirty-nine degrees;
- manifestation of chills;
- pain in the groin area;
- enlargement of appendages on one or both sides;
- upon palpation, the patient may feel sharp pain;
- the occurrence of bloody or purulent discharge from the vagina;
- manifestation of nausea or vomiting;
- menstrual irregularities.
If you do not start timely treatment of acute adnexitis, the disease will become chronic or serious complications will begin. The treatment process involves taking medications and lasts quite a long time. The main symptoms of chronic adnexitis include:
- constant painful sensations of a dull nature in the lower abdomen, their intensification occurs when the body is hypothermic;
- menstrual irregularities,
- decreased libido.
Also, when chronic adnexitis occurs, there is a disturbance in the digestive function and functioning of the urinary system. If the patient ignores the signs of the disease, then chronic adnexitis leads to serious complications in the form of:
- infertility;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- spontaneous miscarriage;
- disruption of the ovaries, which leads to disruption of the menstrual cycle;
- occurrence of periadnexitis;
- formation of adhesive processes;
- obstruction of pipes;
- manifestations of chronic colitis, cholecystitis or pyelonephritis.
General information
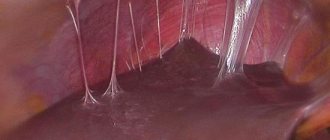
Often the disease leads to the development of many other negative consequences for the entire body. Firstly, there is a risk of pus accumulation and the development of sepsis. In addition, there is a tendency for periadnexitis to spread over a large area and for the inflammatory process to extend beyond the peritoneum. Many women experience disorders of the gastrointestinal tract or diseases of the urinary system. An adhesive process may also develop. As the exudate accumulates, it becomes thick and viscous. Strands are formed that change the location and functioning of organs. In addition, the appearance of adhesions is the main cause of pain in the pelvic area.
In most cases, patients are diagnosed with a chronic inflammatory process developing on the right side. Periadnexitis on the left is much less common. This is due to better blood supply to the right side of the pelvic cavity. However, the pathological process is not always one-sided. Without timely, effective treatment and properly selected medications, it affects the ovaries, fallopian tubes and peritoneum on both sides.
Most often, bilateral periadnexitis is provoked by pathogenic or opportunistic microorganisms. These can be staphylococci or streptococci, E. coli, enterococci, chlamydia. In addition, this disease is often accompanied by inflammation of the endometrium, and sometimes the muscular lining of the uterus. The prolonged presence of pathogenic microflora in the uterine cavity provides the opportunity for it to penetrate both fallopian tubes at once.
Types of adnexitis
The disease is divided into several types:
- Right-sided adnexitis. The inflammatory process occurs in the ovaries and fallopian tube on the right side. The pain is similar to appendicitis.
- Left-sided adnexitis. It is characterized by the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the left ovary and fallopian tube. In this situation, the symptoms are similar to colitis.
- Bilateral adnexitis. The inflammatory process occurs in two appendages at once. In this case, the patient feels pain in the abdomen, which radiates to the anus and vagina. If a woman experiences bilateral adnexitis, then this condition is considered dangerous. When the first symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Bilateral adnexitis
Bilateral adnexitis affects the appendages on both sides. It begins to develop in the fallopian tubes, then moves to the ovaries.
The main symptoms of acute bilateral adnexitis include:
- Increased body temperature.
- Pain in the groin area.
- Severe deterioration in general condition. There is fatigue and dizziness. Nausea and vomiting may occur.
- Failure of the menstrual cycle. During menstruation, a woman feels severe discomfort.
In medicine, it is customary to distinguish three main forms of bilateral adnexitis:
- Spicy. At this stage, the symptoms are very pronounced.
- I'll sharpen it up.
- Chronic. Possibly asymptomatic.
Features of treatment
To cure chronic periadnexitis, simply eliminating the infection is not enough. Therapy for the disease should also eliminate the consequences of a long-term inflammatory process. Therefore, the patient is selected drugs that:
- strengthen the body's immune function;
- eliminate inflammation;
- normalize the functioning of the endocrine system;
- will help restore the normal menstrual cycle;
- relieve pain;
- eliminate other foci of infection.
Chronic periadnexitis: symptoms
Chronic periadnexitis is considered one of the complications of untreated adnexitis. The risk group includes those patients who:
- are exposed to frequent hypothermia;
- suffer from other diseases of the genital organs;
- underwent surgery on the appendages.
The main features include:
- periodic increase in body temperature to subfebrile levels;
- the occurrence of dizziness;
- the appearance of general weakness and loss of strength;
- lower abdominal pain;
- heavy menstruation.
Sexual intercourse with chronic periadnexitis may be accompanied by painful sensations. It becomes difficult to engage in physical exercise. The menstrual cycle is disrupted, and the nature of the discharge periodically changes.
Adhesive periadnexitis
Adhesive periadnexitis is a very unpleasant and very dangerous disease for a woman’s health. Firstly, an infection can get into the ovarian tissue, and purulent contents often accumulate in these female organs. Secondly, many internal organs malfunction.
Possible complications of chronic adnexitis
- uterine displacement;
- infertility;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- dysfunction of the menstrual cycle;
- intestinal obstruction.
Quite often, periadnexitis becomes chronic as a result of improper or interrupted treatment. Ultimately, this leads to the fact that chronic periadnexitis requires surgical intervention to remove the pus accumulated in the pelvic organs. The consequences may be the most unexpected and most disastrous, so the disease will not tolerate self-treatment.
Diagnosis of the disease
To avoid unpleasant consequences, you should immediately consult a doctor. Based on complaints, the doctor conducts a gynecological examination and prescribes an examination. It includes:
- General blood analysis. Allows you to identify signs of inflammation.
- Bacteriological culture from the cervical canal. Allows you to identify the causative agent of the disease.
- Carrying out ultrasound diagnostics. Using this method, the doctor can determine the size and condition of the ovaries.
- Carrying out laparoscopy. This method of research is carried out in situations where there are difficulties in making an accurate diagnosis, as well as when a tumor of the appendages is suspected.
- Carrying out hysterosalpingography. Allows you to determine the patency of the fallopian tubes.
Signs of left-sided adnexitis
Signs of left-sided adnexitis are as follows:
- Pain in the left abdomen and lower back, with varying degrees of intensity and severity. The pain can be cutting or aching, occurs periodically or is constantly present.
- Various stool disorders (constipation, frequent watery bowel movements).
- Dysuric manifestations (impaired urination function).
- Body temperature rises.
- Inflammatory fluid leaks from the vagina.
Treatment of adnexitis
For adnexitis, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed, taking into account the susceptibility of the identified microorganisms to the drugs. Usually, for adnexitis, antibacterial agents are prescribed, which belong to the group:
- Penicillins;
- Tetracyclines;
- Fluoroquinolones;
- Macrolides;
- Imidazoles;
- Aminoglycosides.
If severe intoxication of the body is observed, the patient is prescribed the administration of rheopolyglucin and a five percent glucose solution. The main treatment necessarily includes the use of vitamin complexes, immunostimulating agents, antihistamines and painkillers. In case of acute adnexitis, it is recommended to apply cold to the suprapubic area.
Using laparoscopy, you can not only detect the location of the inflammatory process, but also carry out therapeutic measures: irrigation of the fallopian tubes with an antibiotic solution, separation of adhesions, elimination of pus from the abdominal cavity.
Local treatment is also carried out by introducing suppositories with antibacterial components into the vagina. Diclofenac or Voltaren rectal suppositories have excellent anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties.
The patient is recommended to insert tampons with honey, aloe juice, tea tree oil, and infusion of medicinal herbs into the vagina. They should stay inside for no more than six hours. Calendula or juniper creams and oils can be used as compresses.
Treatment of chronic adnexitis
If a woman has chronic adnexitis, then treatment consists of:
- in eliminating the inflammatory process;
- eliminating pain;
- strengthening immune function;
- restoration of genital function;
- normalization of the endocrine and nervous systems.
Also, for chronic adnexitis, physiotherapy in the form of UHF, ultrasound, electrophoresis, mud therapy, the use of paraffin and mineral water baths are indicated. Additionally, vaginal irrigation and therapeutic tampons are used.
Surgical intervention
In some situations with adnexitis, surgical intervention is indicated. The procedure is prescribed in cases where:
- there is a rupture of the pyosalpinx;
- there is no effect from drug treatment and laparoscopic intervention;
- There is diffuse inflammation in the abdominal cavity.
If, as the pathological process progresses, the appendages are deformed or changed, then they are removed.
Treatment
The treatment regimen largely depends on the pathogen and the number of infections (one microorganism, several). Doctors also take into account the state of the immune system, since a weakened body needs not only highly targeted assistance, but also significant support. Balneological procedures are often quite effective in the chronic form. Gynecologists can also prescribe physical therapy, but only after a thorough examination of the patient.
Throughout the treatment, the woman should maintain complete sexual rest. Otherwise, the infection may re-infect, which is especially dangerous when the body is generally weakened.
Preventive actions
To prevent the disease from bothering a woman, you need to follow a few simple recommendations. These include:
- compliance with hygiene measures;
- wearing underwear made from natural materials;
- refusal of casual sex;
- conducting annual preventive examinations with a gynecologist;
- using condoms to avoid infection.
Adnexitis is not a fatal disease, but can lead to serious complications. To prevent this from happening, you should immediately consult a doctor when the first signs appear. With timely treatment, the outcome of the disease is favorable. But there are also advanced situations when the appendages and uterus are removed. This can lead to complete infertility and the need for hormone therapy.
Read
Also:
- Fallopian tube laparoscopy
- What is metroendometritis: causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention
- Acute cystitis with blood in women: signs and treatment
- Amenorrhea in women, what is it?
- What are adhesions in gynecology, treatment of adhesions in women
- Hydrosalpinx, what is it and how to treat it?
Left-sided adnexitis
Left-sided (left) adnexitis (salpingoophoritis) is inflammation of the uterine appendages on the left side. According to medical statistics, the diagnosis of “left-sided salpingoophoritis” is made more often than right-sided and bilateral.
Left-sided adnexitis - what is it?
Adnexitis on the left is accompanied by well-defined symptoms. The most common complication with this form of inflammation is infertility. Diseases that occur most often against the background of acute or chronic left-sided adnexitis are colpitis, left ovarian cyst, adhesions in the left fallopian tube, endometriosis (endometritis), chronic inflammation of the appendages and ovaries, the development of bilateral adnexitis (inflammation on the left side spreads to the appendages and fallopian tubes , located on the right).
Left-sided adnexitis of the left ovary or fallopian tube in acute form is characterized by rapid progression. Women with this diagnosis often end up in hospital and undergo complex inpatient treatment. inflammation of the uterus and appendages on the left develops in the following situations:
- pathogens of sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia, mycoplasma, gonococci) have entered the body;
- the patient wore clothes that were not appropriate for the season or swam in cold water, as a result of which she developed hypothermia;
- the woman has a history of childbirth and abortion (during gynecological manipulations, an infection could enter the left fallopian tube or ovary);
- the patient has previously suffered from an infectious disease (for example, tonsillitis, pyelonephritis, tonsillitis);
- a woman neglects the rules of intimate hygiene, washes her hands irregularly, does not wash herself).
Pathogenic bacteria, after entering the left ovary or left fallopian tube, begin to actively develop there. This leads to infection of the organ and the formation of purulent contents in it. If the pathological process is not stopped in time, pus from a localized area can break out into the abdominal cavity. The infection, which entered the left ovary along the ascending tract from the vagina, first affects the fallopian tube. Then, through small ducts it enters the ovary, disrupts its functioning, and provokes severe pain.
An infectious disease called “left-sided adnexitis” has an individual code in ICD 10.
Left-sided adnexitis according to ICD 10 has the code N70. There is also an alphanumeric coding of this disease in accordance with its form. For example, left-sided acute adnexitis is assigned the number N70.0. left chronic adnexitis has code N70.1. If the etiology of the disease is not clear, it is assigned code N70.9.
Left-sided adnexitis with code N70, regardless of its form, is included in a broader category of the classification medical reference book - “diseases of the female genitourinary system.”
Adnexitis and pregnancy
Chronic adnexitis and pregnancy are two concepts that are not recommended to be combined. That is why pregnancy planning is an important stage, which allows us to identify all diseases that impede this process. When diagnosing adnexitis, especially its chronic form, pregnancy should be postponed for the period of treatment, since the process of chronic adnexitis is accompanied by exacerbations, which, among other things, can be caused by hormonal changes in the body of a pregnant woman.
However, it happens that diagnosis occurs after pregnancy. There are two options here: either the onset of an exacerbation (which is most often characterized by pain in the lower abdomen and characteristic discharge), or the non-occurrence of an exacerbation (this is dangerous because the woman may not know her diagnosis, and the infection will begin to spread more and more throughout the body).
Lack of treatment for adnexitis during pregnancy can lead to infection of the fetus, which can happen both intrauterine and during childbirth, when the child is no longer protected by any amniotic membranes. All this boils down to the fact that you should think carefully before conceiving a child if you are diagnosed with chronic adnexitis, and it is best not to take risks and refuse until the doctor suggests a favorable period.
Treatment during pregnancy
Treatment of adnexitis in a pregnant woman is complicated by the fact that many drugs have a negative effect on the fetus. The situation in which infection only occurs during pregnancy deserves special attention, since this threatens intrauterine infection of the child. The inflammatory process itself, which already exists during pregnancy, threatens to infect the birth canal, which can lead to infection of the child during childbirth. In such cases, a caesarean section is usually recommended.
In cases where adnexitis was the result of infection with a sexually transmitted disease, the woman is strongly recommended to terminate the pregnancy. But if the inflammatory process began due to the presence of microorganisms natural to the woman’s body (candida, gardnerella), then the doctor prescribes the usual drug treatment based on the type of bacteria, their sensitivity to certain antibiotics, as well as the duration of pregnancy.
What is left-sided adnexitis
Left-sided adnexitis - description of the disease
Due to strange circumstances, for some reason doctors most often diagnose left-sided adnexitis, although this cannot be explained in any way.
Left-sided adnexitis is inflammation of the fallopian tubes or ovaries on the left side. Everyone knows that the ovaries are located both on the right and on the left. Therefore, both inflammations are dangerous.
The symptoms of the problem are very obvious, and often a woman, going to the gynecologist, already approximately knows her diagnosis. Of course, hearing it for the first time, everyone gets scared, because, as you know, one of the most common complications regarding problems with the reproductive system is infertility. Therefore, when the very first and sometimes not the most obvious symptoms appear, it is necessary to visit a gynecologist, because only during the examination will he be able to make an accurate diagnosis and understand the stage of the inflammatory process, because the speed of recovery will depend on this, as well as the possibility of pregnancy in the future.
The second name for the disease, and a fairly common one, is salpingoophoritis.
True, not all doctors pronounce this particular term out loud in front of patients, because due to the large number of letters and the incomprehensible combination of several Latin words, it terrifies patients. Therefore, it is customary to use adnexitis. Although they mean the same thing.
If we talk about deciphering the term “salpingoophoritis”, then we must say that salpingitis means an inflammatory process in the fallopian tubes, and oophoritis - in the ovaries. Therefore, when there is inflammation of the tubes and ovaries, the term adnexitis is used. All gynecologists say the same thing: improper treatment and ignoring problems associated with inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries in the future leads to serious obstetric problems, which are often simply impossible to solve due to the advanced state of the disease.
Symptoms of left-sided adnexitis
If left-sided adnexitis develops in a female body, the symptoms and external manifestations of the disease are important for developing the correct treatment regimen. The disease can be recognized by such manifestations.
- Sharp pain in the left side of the abdomen.
- High temperature (readings on the thermometer can reach 38-39 °C).
- Itching, burning in the vagina.
- Pathological discharge from the external genitalia.
- Weakness caused by intoxication of the body.
- Disturbed heart rhythm.
- Bloating.
Proper treatment, carried out on time, will help avoid chronicity of the inflammatory process in the uterus.
Causes of bilateral adnexitis
- Infection through unprotected sexual intercourse, as well as through household methods when using towels or in common areas (saunas, swimming pools).
- Uterine spiral. It can cause inflammation only when it is installed or removed.
- Hypothermia. Activates the growth of pathogenic microflora, which “lived” in the body in a latent form.
- Decreased immunity. It works the same way as hypothermia.
- Surgical interventions, for example, removal of an ovarian cyst. They increase the risk of bilateral adnexitis due to possible tissue infection.
- Previously suffered inflammatory diseases, as well as their improper treatment.
All of the above factors can not only provoke the development of the disease, but also cause an exacerbation of chronic bilateral adnexitis.