A polyp on the vaginal wall is a common occurrence, which does not pose a threat with timely and adequate treatment. The pathology is more often diagnosed in women over 40 years of age, but its development at a younger age is also not excluded. The formation of polyps in the vagina is considered a precancerous condition. The connection is caused by disruption of cell division processes due to the proliferation of the epithelium. The disease is serious and, if prolonged and left untreated, leads to cancer.
Causes of pathology
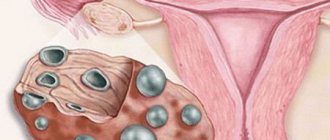
A polyp is a light pink formation with an irregular shape that tends to grow. Consists of stroma, stalk and body. Diameter - from a few millimeters to 1.5 cm. There are single and multiple polyps. Most of them are benign in nature.
Not a single woman is immune from the onset of the disease. It is diagnosed both at a young and adult age. There are many factors that lead to impaired regeneration of cells of epithelial and glandular structures. The formation of polyps on the vaginal mucosa can be caused by the following reasons:
- Hormonal imbalance due to stress, steroid use, pregnancy, lactation, menopause.
- Frequent vaginal injuries. Growths occur after childbirth, surgical interventions, diagnostic curettages, abortions.
- The presence of cervical erosion and foci of dysplasia.
- The progression of HPV (human papillomavirus), which greatly increases the risk of developing pathology.
- Unprotected intimacy, the presence of diseases that are sexually transmitted.
- Progressive endometriosis.
Polyps in the vagina occur due to the activation of a viral infection after chemotherapy, against the background of excess weight or obesity. The likelihood of polyps occurring on the walls of the vagina is higher in girls suffering from pathologies of the genitourinary system, hypertension, and vascular problems.
The formation of such growths is associated with a violation of the biocenosis, burdened by heredity, autoimmune processes, and age-related changes.
Examination of patients
First of all, the gynecologist simply talks with the woman, studying her complaints, medical history, and heredity. It is very important that the doctor knows that the patient has had abortions, undergone curettage of the uterine cavity, surgery on the genitals, and had complications during labor. Also no less important are such issues as the presence of infectious pathologies, infertility, and hormonal disorders.
Then the doctor conducts an examination on a chair, as a result of which he determines the parameters of the reproductive organ, its structure, the presence of pain during palpation and other changes. It is not always possible to make a diagnosis based only on a gynecological examination and women’s complaints, so additional examination methods are prescribed.
- Ultrasonography. It is carried out using a special sensor, which is inserted directly into the woman’s vagina. On the monitor, the doctor sees the cavity of the reproductive organ from the inside. Thus, he can determine the structure of the uterus, its parameters, and the location of the polyp.
- Dopplerography. It can be prescribed as an addition to ultrasound, which allows you to assess the blood flow in the polyp, as well as more accurately determine the location of the tumor’s stalk.
- Hysteroscopy. This is the most informative diagnostic method, allowing a detailed examination of the uterus by introducing an optical device into its cavity. The main advantage of this method is that during the verification process the polyp can be immediately removed.
- Curettage of the uterus. This can also be done for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. During this procedure, the affected endometrium of the uterus is removed, and part of it is sent to the laboratory for histology.
During the last two diagnostic measures, the doctor takes polyp cells for further histological examination. This allows us to determine the type of tumor and its malignancy.
Types of vaginal polyps
Based on their structure and nature, several types of formations are distinguished. It is these criteria that determine treatment tactics and prognosis. According to etiology, polyps are:
- Inflammatory. They arise due to a long ongoing inflammatory process.
- Hyperplastic. Characterized by disruption of normal cell division due to the constant influence of negative factors.
- Neoplastic. They develop due to the intensive proliferation of pathological cells. Predates the appearance of cancer.
The disease is also classified according to its structure. There are 4 types of polyps - granulation, fibrous, villous, cholesterol:
- The structure of the vaginal granulation polyp is dominated by glandular tissue. The neoplasm has a granular structure, the body is attached to the base by a thin stalk. The development of pathology occurs after difficult childbirth with ruptures, after abortions, operations, and inflammation of the reproductive system.
- Cholesterol or pseudopolyp. Occurs with active atherosclerosis. Over time, the plaques grow together with the mucous membranes and fill with capillaries. This type poses a threat of transformation into cancer.
- Villous. Consists of epithelial cells. The multiple form is more common. It differs from other types in increased bleeding due to the abundance of small vessels.
- Fibrous. Has a dense consistency. Its appearance is provoked by frequent injuries, diagnostic or therapeutic procedures, and chronic inflammation. The structure of the formation contains few cells, but many elastic fibers.
What's happened
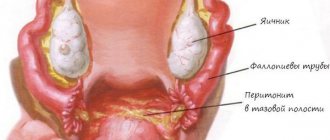
The vulva is a collection of female external genitalia. The location of polyps is most often the clitoris, labia or vestibule of the vagina.
A pathological neoplasm is a tubercle or growth affecting the mucous membrane. It is spherical in shape and prone to growth. In addition, with the development of pathology, the formation of lobular structures is possible, which in appearance are similar to cauliflower.
Due to the fact that polyps are located on an open surface, they are easiest to diagnose, which makes it possible to identify the disease at the initial stages of development, which makes it possible to begin therapeutic measures in a timely manner and significantly reduce the risk of malignancy.
Clinical manifestations
Due to the asymptomatic course of the pathology, at an early stage a woman learns about the presence of a formation during an ultrasound scan or when undergoing a preventive examination by a gynecologist. As the disease progresses, symptoms appear. A vaginal polyp is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- menstrual irregularities;
- spotting after intimacy;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- stomach ache;
- decreased libido;
- change in the nature of vaginal discharge.
Large growths are especially dangerous. When exposed to them, they bleed and hurt. Trauma to the mucosa increases the likelihood of penetration of pathogenic microflora and the development of inflammation.
If you sit on a hard surface for a long time, you may feel the presence of a foreign body in the groin. This is due to the pressure of a large polyp on the mucous membrane.
If such symptoms occur, you should consult a doctor.
Symptoms
Forming vaginal polyps are rarely accompanied by specific symptoms. Signs of neoplasms may resemble the course of various gynecological diseases.
Frequent symptoms are:
- changes in the menstrual cycle;
- infertility, inability to conceive for a long time;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- painful sexual intercourse;
- copious mucous discharge mixed with blood;
- the appearance of pus when infectious processes occur.
As the volume of the polyp increases, menstrual bleeding often increases. The smell of discharge changes only against the background of a fungal or bacterial infection.
Complications
Ignoring the manifestations of pathology is fraught with unpleasant consequences. The danger of vaginal polyps lies in the potential risk of developing a malignant tumor. Other possible complications of the pathology include:
- Infection. Inflammation of the polyp may be associated with the spread of the process to the cervix and endometrium of the organ, as well as other structures of the genitourinary system.
- Bleeding. Untreated polyps that grow in size often bleed. Because of this, the development of iron deficiency anemia is possible.
- Infertility. Large formations can lead to the inability to conceive or bear a baby.
To prevent such complications, you need to go to the hospital when the first alarming symptoms appear. Any delay will negatively affect the condition of the genitourinary and reproductive systems.
Methods of pain relief before the doctor arrives
If for some reason it is impossible to contact a doctor promptly, then it is necessary to relieve or dull the pain. For this purpose, there are some medications that temporarily relieve pain. It is necessary to make sure that there are no allergic reactions to them and other contraindications. Such drugs are:
- Medicines that relieve spasms in women (noshpa, drotaverine, papaverine, etc.).
- The use of rectal suppositories, which are anti-inflammatory drugs (ketoprofen, diclac).
- Drugs that are strong painkillers are used exclusively per os (ketanov, ketalgin).
But in any case, if it is possible to quickly visit a doctor, do not take any measures and do not use medications. The doctor will thoroughly examine you and prescribe the optimal treatment. If it is still a polyp, and it causes pain, then it must be removed. Most often, surgical treatment is performed.
Diagnostics
In addition to the survey, medical history and gynecological examination, the following is prescribed:
- Vaginal ultrasound - to identify echo signs of a neoplasm, assess the condition of the internal genital organs, and the abdominal cavity.
- Colposcopy - for a detailed study of the vaginal mucosa. The technique helps to identify even small polyps located near the cervix.
- Biopsies with histology - to determine the structure of growths and atypical cells.
- Bacteriological culture - to detect pathogenic microflora and malignant cells.
They may also prescribe a PCR blood test to detect different types of HPV.
Treatment
The method of therapy is selected after examination. For small polyps, a wait-and-see approach is used, which involves observation by a doctor. If the vaginal polyp is large, surgery is performed.
Drug therapy
Conservative treatment is carried out if the formation occurs due to inflammation, an infectious process or hormonal imbalance. This method is used for small, single growths.
Table - Drugs for vaginal polyps
| Drug group | Medicines used | Effect/properties |
| Antibacterial agents |
| Stops the activity of pathogenic flora |
| Antiviral |
| Destroy herpes, HPV |
| Antispasmodics |
| Eliminate pain |
| Immunostimulants |
| Increases defenses |
If a pathology of infectious origin is suspected, the use of vaginal suppositories is prescribed: Betadine, Terzhinan, Hexicon. To strengthen the immune system and improve the health of the female body, vitamins and lactobacilli are prescribed.
Surgical intervention
The operation is performed by excision of the polyp with a radioknife or scalpel. The first method is more effective and painless. The formation is removed at the base using a loop, then the wound is cauterized with high-frequency current. The formed scar heals quickly. The mucous membrane recovers in about a month.
The procedure is performed at the beginning of the menstrual cycle (on days 6–8). This will prevent blood from entering the wound, as well as the occurrence of an infectious or inflammatory process.
Cryodestruction
The technique is indicated for multiple vaginal polyps not exceeding 2 cm in diameter. Polyps are targeted with liquid nitrogen, which leads to cell destruction and death. The intervention is painless, so it is performed without anesthesia.
Traditional treatment
As an auxiliary method of therapy (after preliminary consultation with a doctor), you can use products made from natural ingredients. For polyps due to inflammation or infection, it is useful to do douching. To do this, use a decoction of one of the plants: chamomile, oak bark, calendula. The medicine is prepared in this way. Dried crushed raw materials in an amount of 30 g are brewed in 500 ml of boiling water. The product is used for douching. The procedure is carried out before bed every day.
It is also recommended to use honey and propolis. Medicines strengthen the immune system and speed up recovery:
- Chopped horseradish root (100 g) is mixed with honey (200 g). The container with the composition is left in a warm place for 3 days. Take 10 g of the drug three times a day.
- Propolis (20 g) is combined with butter (200 g). Take 15 g of the mixture 3 times a day.