Salpingoophoritis is an infectious and inflammatory disease of the uterine appendages, which can be complicated by purulent processes leading to surgical treatment tactics. Based on this compressed and dry concept, inflammation of the tubes and ovaries can already be understood. That self-medication and independent decision-making in this case simply cannot happen. That is why such a pathology requires etiotropic, pathogenetic treatment, which can only be prescribed by a qualified doctor.
However, as in the treatment of many pathological conditions of the female body, there are also methods of traditional medicine, which in most cases are used by patients in completely the wrong direction. They put traditional, drug therapy and traditional medicine methods on the scale, making a choice between such methods. Moreover, this choice stops precisely on traditional treatment recipes. Making such a decision can significantly undermine the health of a representative of the fair sex, and can also deprive her of functioning, important organs in the form of fallopian tubes and ovaries.
When diagnosed with salpingoophoritis, treatment with folk remedies should not be used as an alternative to drug therapy, but as a parallel, auxiliary treatment, which, as part of complex therapy, can have a beneficial effect on the overall picture of the pathological process of inflammation of the uterine appendages.
Treatment of salpingoophoritis at home is simply contraindicated, since the consequences of such self-therapy not only will not give any positive effect, but can also affect both the reproductive function of the woman and the woman’s health in general, posing a real threat.
Folk remedies against inflammation of the uterine appendages mostly have a physiotherapeutic focus. What does it mean? This means that traditional medicine uses combinations of different herbs used in different forms to treat this condition.
What antibiotics are prescribed for acute salpingoophoritis?
In general, the treatment regimen for andexitis is as follows:
- First stage: after determining the immune status, immunocorrectors are prescribed for three days and, at the same time, enzymes (drugs such as Wobenzym, Serta) for ten days.
- Second stage: antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, interferon inducers and correctors, continuation of enzyme therapy and agents that improve microcirculation.
- Third stage: antimycotics and eubiotics are applied locally (topically and orally).
After a course of treatment with all necessary drugs, a control study is carried out and, in case of a negative result, maintenance therapy is prescribed to prevent relapse of the disease.
The most important component of the overall treatment regimen for salpingoophoritis is taking antibiotics.
The problem in prescribing anti-inflammatory drugs is that many pathogenic microorganisms, in the process of evolution, have acquired resistance to most known active substances. Therefore, in modern clinical practice, mainly only the latest generation of antibiotics are used, and when diagnosing any infectious disease, an analysis is required to determine the resistance of identified bacterial strains to a specific drug.
A couple of decades ago, the most effective drugs for the treatment of salpingoophoritis were antibiotics of the tetracycline group. But now they are practically not used in gynecology precisely because of their high stability. In addition, the first generation of drugs give many side effects and have a negative impact on women's health.
The most safe and well-tolerated antibiotics today are considered to be antibacterial agents of the macrolide group. When treating andexitis, they are most often prescribed.
We recommend reading about acute adnexitis. You will learn about the causes and symptoms of adnexitis, diagnostic methods, treatment at home and in the hospital.
And here is more information about acute cervicitis.
Azithromycin (Sumamed)
This latest generation drug from the group of macrolides shows high effectiveness in the fight against gram-negative bacteria; in the treatment of salpingoophoritis, the course of therapy lasts up to one and a half weeks.
The action is aimed at disrupting the protein synthesis of pathogenic microorganism cells, which leads to their destruction and death. Currently, it is widely used in gynecological practice, since it affects various types of pathogens.
The benefits of Azithromycin are as follows:
- the drug has a strong effect on bacteria;
- practically does not cause side effects;
- has immunostimulating and anti-inflammatory effects;
- may be prescribed to pregnant women with some restrictions;
- works well in the treatment of salpingoophoritis caused by chlamydia and mycoplasma;
- the drug quickly reaches high concentrations in the body;
- does not have a negative effect on the gastrointestinal tract;
- the drug can accumulate in tissues, so it can be used in short courses.
Exceeding the permissible doses can cause nausea, diarrhea, and lymphocytopenia.
The advantages of the drug include a high rate of absorption into the blood and ease of penetration into the site of inflammation through cell membranes.
Sumamed has the following side effects: it negatively affects the nervous and digestive systems, and affects the functioning of the heart and liver.
In gynecological practice, a combination of antibacterial drugs is often prescribed, since monotherapy may be ineffective. This is due to the fact that salpingoophoritis is usually provoked by several pathogens.
Antibiotic therapy should continue until all acute symptoms disappear completely and the patient’s general condition significantly improves.
Doxycycline
Semi-synthetic antibiotic, belongs to the tetracycline group. This is one of the few drugs of this class to which andexitis pathogens show low resistance, but for greater effect it is usually prescribed in combination with Gentamicin. The medicine affects bacteria not only in the intercellular space, but also penetrates inside the affected cell.
The advantages of Doxycycline include:
- affordability;
- rapid and almost complete absorption;
- good therapeutic effect.
The disadvantages of the drug are: contraindication during pregnancy and lactation, side effects such as headaches, gastrointestinal problems, nausea, skin reactions, danger of simultaneous use with other drugs, for example, with Methoxyflurane or Retinol.
Augmentin
An antibiotic from the penicillin group, a drug with an extended spectrum of activity. It is a combination of two active ingredients – amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. The course of treatment with Augmentin is quite long, can reach three weeks.
Advantages of the drug:
- acts against both gram-negative and gram-positive pathogenic microorganisms;
- in the treatment of salpingoophoritis, various dosage forms are equally effective;
- can be used during lactation and for special indications in the last trimester of pregnancy;
- has a long-lasting effect after withdrawal.
This antibacterial agent is contraindicated for patients with liver problems; it also causes a number of negative consequences: nausea, diarrhea, thrush, water-salt imbalance, and disorders of the digestive system.
Tsiprolet
A drug from the group of fluoroquinols, it is prescribed for infection with gram-positive or gram-negative bacteria, and also shows high effectiveness in influencing opportunistic microflora. The course of treatment takes about two weeks.
Advantages of Tsiprolet:
- fights especially well against Trichomonas and anaerobic bacteria;
- has a high degree of absorption;
- does not affect the balance of vaginal microflora.
The negative properties of the drug include a ban on its use during pregnancy and lactation, a large list of side effects and contraindications, possible convulsions and problems with the functioning of the genitourinary system in case of overdose.
Nolitsin
The action of the drug is aimed at destroying the DNA of pathogenic microflora. This is a specific drug aimed at treating infectious diseases of the female genitourinary system.
Advantages of the drug:
- low price;
- prolonged action;
- fast absorption.
The main contraindication for use is pregnancy. Side effects may include cerebral atherosclerosis, kidney problems, and problems with the digestive system.
Gentamicin
An antibacterial agent from the group of aminoglycosides, aimed at the cytoplasm of pathogenic microflora, excluding protozoa, fungi and viruses. The drug is characterized by slowly developing resistance.
The disadvantages of Gentamicin include the impossibility of its use by pregnant women and during breastfeeding, nephrotoxicity and a number of side effects such as headaches, allergic reactions and others.
Is it possible during pregnancy?
There are no episodes of acute adnexitis during pregnancy. Persistent remission is facilitated by a special hormonal background. But foci of “dormant” chronic infection can affect the development of the baby. That is why, at the discretion of the doctor and based on the results of tests (at least smears for vaginal flora), prophylactic therapy can be prescribed.
During pregnancy, any antibiotics should be prescribed with caution, taking into account all contraindications. Thus, pregnant women are strictly prohibited from drugs from the tetracycline group, since they can easily penetrate the placenta and accumulate in the tissues of the fetus. This poses a threat to the formation of a normal skeleton of the unborn child.
Also, the results of clinical studies prove that certain macrolides, such as Clarithromycin, should not be taken during pregnancy.
Approved drugs include:
- Erythromycin,
- Spiramycin,
- Josamycin.
Only the attending physician can prescribe a suitable drug to a pregnant woman based on laboratory tests.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out on the basis of a study of the woman’s medical history, as well as the disease itself. A specialist can make a preliminary diagnosis of “acute salpingoophoritis” if he finds in the medical history information about previous abortions, difficult births, and the use of an IUD to prevent pregnancy. It is also important to take into account the presence of symptoms characteristic of bilateral salpingoophoritis - pain in the lower abdomen, increased body temperature, etc.
Also, during the diagnosis, research is carried out in the laboratory. These include a blood test that can detect an increased number of white blood cells (this is an indicator of inflammation in the body). The doctor also takes a swab from the vagina and cervical canal. Such an analysis makes it possible to identify the pathogen, as well as determine which medications it is sensitive to.
During the diagnosis, hysterosalpingography is performed. This technique is very informative. A special contrast agent is injected into the uterine cavity, after which an X-ray is taken.
Such a disease may require additional consultation of the patient with specialists other than the gynecologist (surgeon and urologist).
Anti-inflammatory drugs
These drugs are prescribed simultaneously with antibiotics to relieve pain symptoms and alleviate the patient’s general condition.
Typically, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used in clinical practice, such as:
- Piroxicam - can be used in the form of tablets and rectal suppositories, the effect occurs within 30 minutes. Piroxicam is prescribed in a dosage of 0.02 g once a day in the morning;
- Diclofenac or its numerous analogues, you need to take it once a day in tablet form (50 mg), and for severe pain you can give it an intramuscular injection;
- Nimesulide – 2 times a day, 100 mg after meals;
- Naproxen, used at the time of exacerbation, 1 tablet 2 times a day.
Anti-inflammatory drugs have a negative effect on the gastrointestinal tract, so they should be taken with caution.
Empirical therapy
In some cases, when adnexitis is detected in women, antibiotics are prescribed, the choice of which is based on the experience of a specialist or his observations. Empirical therapy uses broad-spectrum drugs. If they do not give positive results within three days, other drugs are prescribed.
Recommended antibiotics in this case may be:
- combination of Amoxicycline with Doxycycline or Erythromycin,
- Ceftriaxone in combination with Doxycyline, Clarithromycin or Metronidazole.
As an alternative, a specialist may prescribe the combined use of Ofloxacin with Metronidazole, a combination of Lincomycin with Gentamicin or Doxycyline. In some cases, it may also be a combination of Doxycycline and Ciprofloxacin.
Vitamins and other ways to boost immunity
Any infectious inflammatory process significantly weakens the body’s defenses, therefore, when salpingoophoritis is diagnosed, immunocorrectors and strengthening agents are prescribed from the first days.
Usually a complex of vitamins is selected, which includes:
- vitamin E (tocopherol acetate) - 0.5 - 0.1 g twice a day;
- vitamin C (ascorbic acid) - 0.05 - 0.1 g 1 - 2 times a day;
- vitamin B complex (B1, B2, B6) - in average therapeutic doses.
Vitamin complexes are recommended throughout the course of treatment.
Classification
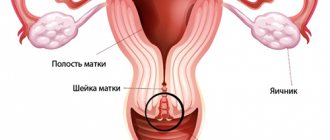
The ovaries and fallopian tubes in a woman are paired organs, therefore, depending on the localization of the inflammatory reaction, several types of pathological process in the appendages are distinguished:
- Right-sided salpingoophoritis is a long-term inflammation of the fallopian tube and ovary on the right.
- Left-sided - a disease that affects the fallopian tube and ovary on the left side.
- Bilateral - the pathological process affects the internal genital organs of a woman on both sides.
Depending on the activity of the disease, left-sided, right-sided or bilateral salpingo-oophoritis of the chronic form can be characterized by a stage of remission (improvement of condition) and relapse (exacerbation). Separation of the inflammatory pathological process into stages is necessary for the subsequent adequate selection of the most effective therapeutic measures.
Chronic treatment regimen
During the transition to this stage of the disease, therapy is carried out on an outpatient basis, and its tactics differ from those used in the acute form. At this stage, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are no longer prescribed, and the main emphasis is on restoring the body and the final elimination of symptoms.
Of particular relevance in the treatment of chronic salpingo-oophoritis are methods of physiotherapy, which are aimed at improving blood circulation, enhancing lymph outflow, and activating metabolism. The following procedures are especially indicated at this stage:
- impulse currents;
- blood plasmaphoresis;
- reflexology;
- Ural Federal District;
- hydrogen sulfide radon baths and others.
Spa treatment and restorative therapy are also recommended.
Watch this video about the benefits of physiotherapy in the treatment of gynecological diseases:
Symptoms
Clinical signs and symptoms of chronic salpingoophoritis depend on the activity of the inflammatory pathological process. In the remission stage (improvement of the condition with a decrease in the severity of the inflammatory reaction), manifestations of the disease may be absent or have minimal manifestations. In the stage of relapse (exacerbation), due to the influence of provoking causes, the activity of pathological processes increases, which leads to more pronounced clinical signs of the disease, which include:
- Painful sensations that are predominantly localized in the lower abdomen and have a pulling nature. The intensity of pain depends on the severity of the inflammatory reaction. It can be constant or periodic.
- A cycle disorder characterized by a delay or premature appearance of menstrual bleeding or a change in its duration (menstruation against the background of changes in the functional state usually exceeds 7 days).
- A disorder of the organs of the reproductive system, which is characterized by female infertility (the inability to conceive a child subject to systematic unprotected sex with one sexual partner, as well as the exclusion of male infertility).
The clinical symptoms of salpingoophoritis are nonspecific. It is practically no different from the signs of isolated salpingitis or oophoritis, which is important to differentiate during diagnosis, since treatment may have fundamental differences. Most clinical manifestations of prolonged inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries are associated with a complicated course of the disease.
In what cases is a surgical solution to the problem necessary?
Surgery for salpingoophoritis may be necessary in some emergency cases when the patient’s life is threatened:
- pelvioperitonitis;
- ovarian abscess;
- hydro- or pyosalpings.
Most often, if the source of infection is in the fallopian tubes, they are subject to resection. In case of severe damage to the ovaries, all doctors adhere to gentle principles, since their removal means complete infertility and condemns the woman to lifelong use of hormonal drugs.
The ovaries are removed only in particularly advanced cases, when there is no healthy tissue left in them and they are completely filled with pus. Sometimes, if HIV or other immunodeficiencies are detected, the uterus is resected.
If salpingoophoritis provokes the formation of adhesions in the fallopian tubes, their dissection or partial removal of the tube followed by plasty is indicated. The operation is performed laparoscopically.
We recommend reading about acute endometritis. You will learn about the causes and symptoms of the pathology, types of endometritis and characteristics of the course, methods of diagnosis, therapy and preventive measures.
And here is more information about the treatment of gonorrhea in women.
Effective treatment of salpingoophoritis involves the complex use of various medicinal methods. Only the attending physician can develop a treatment regimen, taking into account the nature of the disease, its causative agent and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
What kind of disease is this?
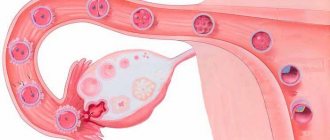
In women, the internal genital organs are represented by the ovaries, fallopian tubes and uterus. They serve different biological purposes, but in general have a close physiological and anatomical relationship to each other. This leads to the fact that the development of a pathological process (disease) in one structure of the reproductive system spreads to nearby organs. Typically, the development of the disease in the ovary or fallopian tubes does not occur in isolation, but spreads to both organs. In this case, with the development of inflammation, salpingoophoritis occurs.
If the disease lasts more than several months, then a conclusion is made about a chronic pathological process. The pathophysiological mechanism of the development of the disease lies in the characteristic tissue reaction. It is the result of tissue damage caused by various reasons. In this case, immunocompetent cells (various types of leukocytes) accumulate in tissues, where they produce biologically active compounds that mediate the inflammatory response. The compounds initiate increased blood supply to tissues (hyperemia), release of the liquid part of the blood into the intercellular substance (edema), as well as irritation of sensitive nerve endings (appearance of pain).
Salpingoophoritis is also called adnexitis, which means inflammation of the uterine appendages. Isolated inflammation of the fallopian tubes is called salpingitis, and of the ovaries - oophoritis.
Useful video
For information about the surgical treatment of complications of adnexitis, watch this video:
Similar articles
- Acute adnexitis (unilateral, bilateral)...
Acute adnexitis develops due to hypothermia, bacteria and other reasons. Symptoms can be either hidden or manifest as severe pain. Treatment can be carried out in a hospital or at home. Read more - Acute vaginitis (specific, nonspecific...)
Acute vaginitis occurs even in little girls. Symptoms of specific or nonspecific bacterial vaginitis include discomfort, itching, and discharge. Treatment involves the use of suppositories and antibiotics. Read more
- Acute cervicitis: causes, symptoms, treatment...
Almost invisible, acute cervicitis can cause a lot of trouble. The reasons lie in infections, weakened immunity, and poor hygiene. Symptoms appear if cervicitis is a reflection of another disease. The treatment is complex. Read more
- Acute endometritis (purulent, catarrhal...)
Acute endometritis develops due to infections. It can be purulent, catarrhal. The reasons may lie in abortion, examination procedures, and sometimes postpartum. Symptoms: fever, chills, pain. The treatment is long-term, antibacterial. Read more