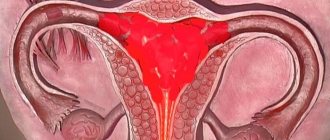
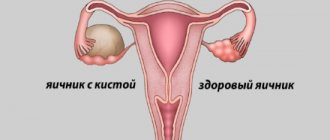
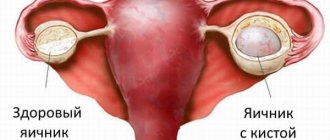
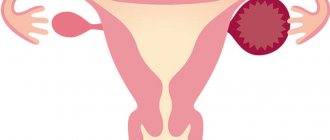
Ovarian diseases, such as cysts, cystomas and other neoplasms that can affect the functioning of these organs, are often encountered in gynecology. In such cases, ovarian laparoscopy is recommended.
Laparoscopic surgery is a more gentle type of surgery for the body compared to abdominal surgery, also known as laparotomy. With it, the doctor makes an incision ten centimeters long.
Healing after laparotomy is a long process, with many possible negative consequences.
Painfulness of the procedure
Although some patients experience ovarian pain after laparoscopy, the procedure itself is completely painless. The surgery takes place under general anesthesia. Anesthesia is administered intravenously. If general anesthesia is prohibited for any reason, local anesthesia is used. A pain relief method is often used in which the medication is injected between the discs of the spine. Therefore, during the removal of the cyst, the patient feels almost nothing, even if she is conscious. To perform laparoscopy, you only need to make small punctures in the abdominal cavity, so there is virtually no pain during and after the operation. In modern medical practice, the most effective methods of pain relief are used, so there will be no pain during the procedure.
We recommend you find out: If pain in the ovaries begins when sneezing
Progress of the operation
Laparoscopy of the cyst is performed under general anesthesia with intravenous administration of drugs. The intervention is carried out with the woman lying on her back, with her head down. A catheter is inserted into the bladder. The operation lasts about 60-120 minutes.
Three incisions measuring 3-6 cm are made, one of which is located in the area of the umbilical ring, the other two in the right and left iliac region.
The classic technique involves three incisions measuring 3-6 cm, one of which is located in the area of the umbilical ring, the other two in the right and left iliac region, in the area of the ovaries. Special devices - endoscopes with lighting and video equipment - are inserted into the abdominal cavity. Before this, the surgeon pumps it with carbon dioxide for a better view.
The formation is gradually enucleated and removed from the abdominal cavity.
The progress of the operation is monitored on a video screen. The blood vessels are cauterized using a coagulator. The ovarian tissue under the cyst capsule is carefully dissected and the space between them is expanded. Then the formation is gradually enucleated and removed from the abdominal cavity. Intact ovarian tissue is completely preserved. During laparoscopy of a paraovarian cyst, the organ is practically not affected. Then the specialist carefully examines the bed and coagulates the vessels, taking into account the anatomy of this area. The resulting biological material in a container is sent for histological examination.
The final stage is suturing the incisions, draining the wound if necessary, and applying bandages. The patient is taken out of anesthesia and transported to the ward.
Pain syndrome after surgery
Many patients are frightened not so much by the laparoscopy process itself, but by the pain syndrome in the postoperative period. In reality, there is no reason to be afraid of this. The fact is that pain in the lower abdomen after laparoscopy is quite rare. Unpleasant symptoms in this case are less intense than after surgical removal performed by the cavity method. Their nature and source after lapara may vary. So, unpleasant sensations arise:
- in the area of incisions;
- in the chest and shoulders;
- lower abdomen.
Pain in the operated area most often appears immediately after surgery, while the patient is recovering from anesthesia. Doctors call it postlaparoscopic syndrome. In this case, the nature of the pain after elimination of the cystic neoplasm is quite clear: it occurs due to injury to the soft tissues, genitals and abdominal cavity. It is especially acute at the puncture sites through which the endoscope was inserted. Sometimes after laparoscopy, pain is localized in the upper abdomen, although surgeons do not touch this area during the operation.
Please note: About 95 percent of patients after lapara complain of quite severe postoperative pain. According to research, their intensity on a 100-point scale often reaches sixty points. Most often, this is how patients feel in the first hours. Having completely recovered from anesthesia, women rated them at thirty points.
After laparoscopy, the right ovary or left appendage hurts severely, most often for one day. After the same amount of time, the discomfort in the area of the stitches disappears. In this case, pain may remain if the seam is injured or pressure is applied to its area.
After lapara, many women feel pain in the chest and shoulders. This is due to the fact that during surgical removal of the cyst, carbon dioxide is introduced into the abdominal cavity. This is necessary for its expansion. As a result, some internal organs and the diaphragm are compressed. Unpleasant sensations from this may occur for the first few days after surgery. This symptom is not very pronounced, so it is tolerated quite normally by patients. The introduction of carbon dioxide most often brings only discomfort and inconvenience.
Although discomfort after laparoscopy of ovarian cysts worries almost all women, the pain is usually mild. It goes away in a few days, so it shouldn't be a cause for concern. If the pain after removal of the cystic formation is too severe, the patient is prescribed painkillers.
IMPORTANT! If you have sharp or cutting pain that affects the lower abdomen and does not disappear for too long, you should visit a doctor, as this indicates the presence of a complication. In emergency cases, accompanied by ongoing severe pain in the ovaries, urgent hospitalization is carried out.
Causes of pain in the postoperative period
In some patients, after laparoscopy, the ovary is pulled, while in others, quite severe abdominal pain is observed. The reason that such sensations appear may be:
- adhesions;
- too rapid resumption of sexual activity during the period of recovery of the body (the first month after elimination of the ovarian cyst);
- the course of inflammatory processes in the genital organs;
- failure to maintain personal hygiene after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst;
- formation of internal bleeding due to suture divergence;
- infection during or after surgery;
- significant physical activity and lifting heavy objects;
- rupture of the ovarian membrane.
It is worth remembering that the larger the cyst and the more advanced the disease, the more difficult the operation is and, accordingly, the longer the recovery period. Pain caused by laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst is quite common. However, if the pain is accompanied by fever, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, or acute pain that radiates to the lower back or lower abdomen, it is recommended to immediately consult your doctor or call an ambulance. The stomach should not be pulled for longer than a few days.
Possible complications
Complications resulting from the operation are as follows:
Formation of adhesions, hematomas in different areas of the abdomen.
- internal bleeding (more often during laparoscopy of endometrioid ovarian cyst);
- failure of sutures;
- development of infection;
- thromboembolism;
- formation of postoperative hernias;
- formation of adhesions;
- hematomas in different areas of the abdomen.
Among the specific consequences inherent only to laparoscopy of ovarian cysts, the following are most often recorded:
- tissue emphysema (accumulation of gas used during intervention in the subcutaneous fat tissue), resolves in most cases on its own;
- violation of the integrity of hollow organs (intestines, bladder, ureter, retroperitoneal vessels).
There is also always the possibility of recurrence of a cyst of one or both ovaries, the pathogenesis of which has not been sufficiently studied.
How to relieve pain
In modern medical practice, after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, specialists tend not to use painkillers. The fact is that the unpleasant sensations are not too pronounced to require the use of anesthetics. They are prescribed only in rare cases when it is really necessary. As a rule, painkilling injections are administered once during the process of the patient coming out of anesthesia. Doctors are in no hurry to use pain-blocking medications because they interfere with the timely detection of complications that arise during the recovery period. This may be a relapse of cyst development after laparoscopy, organ rupture, inflammatory process and other pathological complications.
Patient reviews
Laparoscopy is a low-traumatic method of surgical intervention for various pathologies. It is most widely used in gynecological and gastroenterological practice: during surgery on an ovarian cyst, gall bladder if there are stones in it, to remove the appendix and eliminate adhesions. Despite the delicate effect on the body and tissues of individual organs and the lack of open access to the body cavity, complications after laparoscopy still occur, and they have much in common with the consequences of radical intervention.
Recommendations in the postoperative period
In most cases, surgical treatment of cystic neoplasms does not require long-term recovery. However, if the operation is not very successful, the patient may experience severe pain. Sometimes the cause of its appearance is an incorrect lifestyle: lifting weights, active sports, washing in the bathroom. Until the sutures heal, general hygiene should be observed and the operated area should be treated daily with antiseptics. To avoid unpleasant nagging pain in the lower abdomen, it is not recommended to resume sexual relations earlier than after three weeks. Complications caused by laparoscopic intervention are rare, however, if there is too much pain in the lower abdomen, fever, or the formation of purulent discharge on the surface of the suture, it is worth visiting a doctor.
Please note: On the first day after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, women often experience general fatigue and weakness, so it is advisable to maintain bed rest. You should return to your normal lifestyle, including sports, no earlier than after a month. To avoid complications and discomfort in the appendage area, it is recommended to gradually increase the load.
It is important to avoid sudden movements, lifting weights of more than three to five kilograms and long trips in the first month. It is worth doing everything possible to maintain the integrity of the stitches and prevent them from becoming infected. It is recommended to temporarily avoid tight and tight clothing. It is better to choose loose clothes that will not put pressure on the genitals. Do not panic if in the first month after laparoscopic treatment, menstruation is more painful and heavy than usual.
You should consult a doctor if:
- the temperature reaches 37.5 degrees and lasts more than one day, and there are no other diseases;
- the pain in the lower abdomen has become too intense and sharp;
- vomiting and nausea continue for several hours;
- the stitches are red or there is pain in their area;
- There is unusual and noticeable weakness, dizziness, and confusion.
If at least some unusual signs appear, it is better not to delay consultation with your doctor.
Answers on questions
Future patients have many questions, so we will answer some of them briefly:
- How long do they stay in the hospital when they are discharged? About a week, but the period can be extended.
- Does it hurt to remove stitches? It usually doesn't hurt, but it depends on the pain threshold, which is different for everyone.
- When does complete recovery occur and how long does the recovery period last? The body will fully recover in a month if there are no complications. But the duration of rehabilitation depends on the characteristics of the patient herself.
- How long does the operation last? The operation lasts from 15 minutes to one hour. But, on average, about forty minutes.
- When can you go to work? Usually, sick leave is given for seven days so that rehabilitation is completed. But it is possible to leave sick leave earlier, on the third or fourth day.
- Can I use regular tampons? Prohibited.
- Is pregnancy possible after cyst removal? Possible.
- Is it possible to swim after surgery? No, you cannot. Regardless of whether it is the sea or the pool. As already mentioned, physical activity should be limited.
- What antibiotics are prescribed? Each case is unique, so your doctor will prescribe an antibiotic, like other medications (for example, suppositories).
- Is it possible to sleep on your stomach? For the first week it is better to sleep on your back, especially if you have removed an endometroid cyst. Then, for about another week, on my side.
- My belly button is pulling, is this normal? If there are no other symptoms, then this is normal.
- Is it possible to do this operation during Pregnancy? Yes, if necessary.
- When to play sports? Not earlier than in a month.
- After the operation, I don’t have periods. This may be due to a psychological state, it’s worth waiting a little.
- Why should I go to the doctor again? There is no pain, I follow the recommendations. Perhaps the result of the histology of the removed cyst came back, and the histology showed that the cyst contains cancer cells.
- Can you have heavy periods? Very rarely - usually after the operation something hormonal is prescribed, for example, contraceptives. The hormones contained in them will help recovery, but can disrupt the menstrual cycle. The most likely option is that your periods will be insignificant.
- My right side tingles or hurts, and my stomach has also become enlarged. This is normal, and the tightness is caused by the gas that is pumped in before the operation or by a very tight bandage. If the pain is severe, consult a doctor; it may be an attack of appendicitis.
- Is it possible to visit a solarium? Just like sunbathing in the sun is not allowed.
- Why is drainage installed? So that ichor and blood clots can drain.
- What famous doctors are there in this field? For example, Oksana Vladimirovna Samsonova, a gynecologist. Although, gynecology is not the only option for using this method.
- How much does resection cost? Up to 50 thousand rubles.
Video: What to do if your stomach hurts after laparoscopy
Source
Everyone experiences pain after laparoscopic cyst removal surgery. Let's clarify right away: laparoscopy is a minimally invasive intervention, and in principle there should be no severe pain after it. With any acute pain, go straight to the surgeon. It happens that napkins are forgotten in the abdominal cavity during surgery.
During laparoscopy there is normally no pain, as anesthesia is used. In the first hours after surgery, it continues to act. And then discomfort inevitably appears. Its strength depends on:
- size of surgery - how big the cyst was;
- the individual sensitivity of the patient, his pain threshold;
- surgeon's skill.
Painkillers help relieve pain: lidocaine, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. But you shouldn't abuse them. Mild pain can be tolerated. And for a strong one, the cause must be eliminated. Powerful analgesics may prevent complications from being detected after surgery in time:
- bleeding;
- internal seam divergence;
- suppuration.
You especially need to rush to the doctor if after laparoscopy there is not only noticeable pain, but also:
- heat;
- hard, tense abdominal wall;
- a very red, bleeding, or running stitch;
- problems with urination;
- weakness, dizziness;
- near fainting;
- headache;
- heavy discharge after laparoscopy of ovarian or uterine cysts.
It happens that the laparoscope damages the intestines, stomach, and liver. A minor wound on an internal organ can cause a serious complication. Therefore, under no circumstances should you endure severe pain after laparoscopy of a cyst. Including if it appeared in a different place in the abdominal cavity, and not where the operation took place.
Features and advantages of laparoscopic removal of ovarian cysts
Treatment tactics for single or multiple ovarian cysts are determined based on their characteristics and the woman’s age. Conservative therapy is practiced only for functional tumors. In other cases, they are removed. As a rule, in modern conditions, ovarian cysts are excised by laparoscopy.
The essence and advantages of laparoscopy in the treatment of ovarian cysts
Laparoscopy is a surgical method in which manipulations of internal organs are performed through small incisions in the anterior abdominal wall. They insert medical instruments and a laparoscope - a thin tube with a lens system, a light source and digital matrices through which the image is transmitted to the screen. Thanks to this, the surgeon gets the opportunity to visualize the condition of the internal organs and clearly control all his actions: innovative equipment allows you to magnify the image 40 times and view it from different angles.
Laparoscopy is widely used in the treatment of gynecological diseases, including the diagnosis and removal of ovarian cysts. The main advantages of this method:
- low morbidity;
- short rehabilitation period;
- minimizing the likelihood of complications and pain after surgery;
- absence of scars after the intervention.
Indications and contraindications
The purpose of ovarian laparoscopy can be both to clarify the diagnosis (determine the type of neoplasm) and to directly remove the cyst. Main indications for surgery of cystic cavities:
- large dermoid and endometrioid cysts;
- tendency to rapid growth of tumors;
- risk of capsule rupture or ovarian deformation;
- the presence of a stalk in the cyst (it may become twisted);
- the danger of the neoplasm degenerating into malignant.
Laparoscopic surgery to remove an ovarian cyst is assessed by experts as relatively safe and gentle, but there are certain contraindications to it. The main ones:
- viral or bacterial diseases (surgery is possible 30 days after recovery);
- exacerbation of chronic pathologies - asthma, cardiovascular diseases, arterial hypertension;
- blood clotting disorder;
- exhaustion of the body;
- the presence of an abdominal hernia;
- severe obesity;
- the malignant nature of neoplasms in the ovaries or other organs;
- adhesive process in the abdominal cavity;
- purulent peritonitis;
- cerebrovascular accident;
- hemorrhagic shock.
Pregnancy is not a contraindication to laparoscopy.
Preparing for surgery
A mandatory stage of preparation for ovarian laparoscopy is a series of instrumental and laboratory tests, the exact list of which is determined by the doctor based on the woman’s medical history. Typically, the list of tests includes:
- clinical blood and urine tests;
- determination of blood group and Rh factor;
- coagulogram (assessment of the blood clotting system);
- biochemical blood test, which shows the level of bilirubin, urea, protein, glucose, and so on;
- tests for hepatitis B and C, syphilis, AIDS;
- vaginal smear for microflora;
- fluorography;
- ECG;
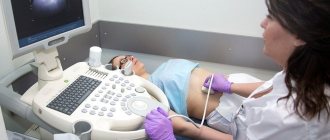
- examination of the pelvic organs using ultrasound, in some cases CT or MRI are prescribed.
When planning an operation, a woman should definitely consult an anesthesiologist, since laparoscopy is performed under general anesthesia. It is also important to clarify all the nuances of surgical intervention with the attending physician. After this, the patient signs consent for the operation.
Direct preparation for ovarian laparoscopy includes the following activities:
- Hair removal in the pubic area.
- Conducting cleansing enemas the day before and on the day of surgery.
- Compliance with a certain diet - the last meal is allowed the evening before the day of surgery at 18:00-19:00, and liquids - at 22:00, after which it is forbidden to drink or eat.
Progress of laparoscopy
Laparoscopy for cystic neoplasms is performed exclusively under sterile conditions in the operating room. Main stages of surgical intervention:
- The woman is placed on the operating table. She has an intravenous catheter installed to supply anesthesia solution and other medications, as well as a urinary catheter.
- The anterior abdominal wall is treated with a disinfectant solution.
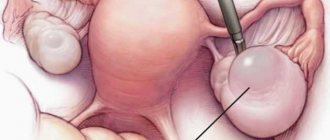
- The surgeon makes three incisions measuring 0.5-1.5 cm - one near the navel for the laparoscope, two in the lower abdomen for instruments. All devices are inserted into the abdominal cavity through trocars - special conductors that protect the skin from injury and make it easy to change instruments.
- The abdominal cavity is filled with carbon dioxide. This is necessary to create operational space. The abdominal wall rises like a dome, and the intestines shift. This makes access to the ovaries easier.
- Based on the image on the screen, the doctor removes the cyst.
- Carbon dioxide is removed from the abdominal cavity. Sutures and sterile dressings are applied to the incised tissue. In some cases, drainage is installed.
The operation without a preparatory stage lasts 15-60 minutes.
Types of operations
Removal of an ovarian cyst during laparoscopy can be performed by cystectomy, oophorectomy or adnexectomy.
Cystectomy is the “husking out” of an ovarian cyst. This method involves dissecting the ovarian cortex, removing the tumor without damaging the capsule, placing it in a sealed container and removing it from the abdominal cavity. At the moment of passing through the abdominal wall, the capsule is opened and emptied, due to which it freely exits through a small hole. Small vessels in damaged ovarian tissues coagulate. Thanks to this technique, the functions of the ovary are completely preserved.
Ovariectomy is the complete removal of the ovary along with the cyst. If a resection of the corresponding fallopian tube is performed, the operation is called adnexectomy. Such interventions are carried out only in cases of high risk of oncological degeneration of tumors, significant damage to ovarian tissue, and also during menopause.
Condition after surgery
3-4 hours after ovarian laparoscopy, the woman is allowed to get up, but she cannot move a lot and eat. The next day, it is recommended to gradually increase physical activity. This is necessary to normalize intestinal motility. In addition, you should establish fractional meals in small portions. Basic dietary recommendations:
- limiting fatty, spicy, hard-to-digest foods for 1 month;
- abstinence from alcohol for 1.5 months;
- the predominance of vegetables, fruits, cereals, dairy products in the diet, that is, light dishes high in fiber and vitamins;
- drinking enough fluid.
In the first days after surgery, the following unpleasant symptoms may occur:
- Pain in the area of the incisions, the intensity of which may vary. To relieve them, analgesics are prescribed. Typically, the incisions will go away within 3-5 days as the incisions heal.
- Discomfort in all muscles and pain in the shoulder. They are associated with the introduction of carbon dioxide into the abdominal cavity, the remains of which are slowly absorbed into the blood and also irritate the phrenic nerve. Normally, discomfort disappears after 2-3 days.
- Temperature rises to 37 ºС. Slight hyperthermia indicates activation of the immune system. It can last 2-4 days.
- Vaginal discharge of a mucous nature for several weeks. They occur due to hormonal changes.
The development of an infectious process after surgery is indicated by:
- very severe pain lasting longer than 3-5 days;
- suppuration in the area of incisions;
- yellowish-green or bloody vaginal discharge;
- significant increase in temperature.
Rehabilitation period
Discharge from the hospital after laparoscopy to remove an ovarian cyst occurs on days 5-6. In case of a simple operation, a woman can go home within 2 days. You will be able to return to work in 7-14 days.
The entire rehabilitation process takes about a month. During this period it is recommended:
- treat the sutures with antiseptics prescribed by the doctor, bandage them (7 days);
- do not take a bath, do not visit the bathhouse, beach, solarium (1 month);
- maintain sexual rest (1 month);
- stop playing sports (1 month);
- Do not lift more than 3 kg (3 months).
If external sutures were applied using non-self-absorbing material, they are removed 7 days after surgery. After a few months, barely noticeable scars remain at the site of the incisions, which can be removed using laser skin resurfacing.
After surgery, a woman is usually prescribed hormonal therapy to normalize the background and prevent recurrence of cyst formation. If a cystectomy was performed, then menstrual function is not affected, but a minor disruption in the cycle may occur. It is recommended to plan pregnancy 3-6 months after the intervention. You must come to the doctor for a follow-up examination one month after laparoscopy.
Possible complications
In most cases, laparoscopy for ovarian cysts is successful. A small number of patients (5-10%) experience the following complications:
- bleeding;
- damage to the abdominal organs or large vessels adjacent to the ovaries;
- addition of bacterial infections;
- negative reaction to anesthesia;
- formation of adhesions.
Removal of an ovarian cyst using laparoscopic surgery is the “gold standard” of modern medicine. This method is characterized by low trauma, a short recovery period and a low risk of complications. The extent of the intervention and its consequences for a woman’s reproductive function are determined by the characteristics of the neoplasm and concomitant diseases. But in most cases, organ-preserving operations are carried out, which do not interfere with childbearing.
kistayaichnika.ru
Abdominal pain after laparoscopy of a cyst
Laparoscopic operations involve penetration into the abdominal cavity, so the stomach always hurts after them. But this feeling should not be acute. It begins after the anesthesia wears off, approximately 2 hours after the operation.
- Pain appears after laparoscopy at the puncture sites. But their size is only up to 1.5 cm; these holes should heal in 1-2 weeks. After laparoscopy, cyst puncture sites should be injected with painkillers.
- It may begin to hurt in the navel area because the gas used during laparoscopy stretches the umbilical ring.
- Pain occurs in the operated organ itself, but remember that it should not be very strong and cutting if the operation is done correctly: the ovary or testicle hurts after laparoscopy of a cyst in it;
- the lower abdomen hurts after laparoscopy of cysts of the uterus, ovary, prostate, bladder;
- The lumbar region hurts after laparoscopy of a kidney cyst.
Some operated patients cannot stand it and use painkillers. In this case, you need to consult with the surgeon in advance about what analgesics can be used and how compatible they are with the anesthesia used during the operation.
Painkillers like Nimesil or Ibuprofen help well with pain of moderate intensity, but they also act as anti-inflammatory, they can be good to take at night to get enough sleep after a hard day. But you need to clarify how compatible they are with the other drugs that you took on the operating day, and there will inevitably be several of them. Stronger drugs from this group are Ketotifen and Ketanov.
Restrictions and contraindications
Contraindications to surgery are rare. These include viral diseases, heart disease, blood clotting disorders and others similar to the standard ones.
There are restrictions that will have to be adhered to until full recovery, that is, the next month.
A sample list of what not to do:
One of the most common questions that arise in connection with this operation is whether it is possible to get pregnant after such operations? Yes, this is possible, although if we are talking about removing one of the ovaries, it will be more difficult. If the operation involved simple removal of a cyst, then the chances of this are reduced very slightly.
If we talk about timing, then you should wait 2-3 months before trying to get pregnant. This is necessary for the hormonal levels to return to normal, and for the doctors to make sure that the recovery is completed successfully.
Pain in the back, side and other places
- During manipulations, gas is injected into it to expand the intra-abdominal space: carbon dioxide or argon, up to 4 liters. The gas presses on the diaphragm, which presses on the organs of the chest cavity. Therefore, after laparoscopy, pain may appear in the side, back, chest, under the ribs, and even significantly above the operation site, in the area of the shoulders or collarbones.
- Also, because of this, some people find it difficult to breathe at first or experience pain when straightening because the diaphragm has been compressed. The neck and chest may hurt for several days because the carbon dioxide introduced during laparoscopy of the cyst escapes through the lungs.
- Generally, general anesthesia with a tracheal tube is used during laparoscopy. Because of this, you may have a sore throat and discomfort in the chest - the delicate mucous membranes of the respiratory tract may be slightly damaged during installation or removal.
- If general anesthesia is contraindicated for the patient, an epidural is used - an injection into the spinal membranes. Below the injection site, sensitivity is lost during the operation. This injection may damage nerves or a section of the spinal cord. And this causes pain until the damage is repaired, or may develop into a serious complication. Therefore, it is very important that the injection into the spine is given by an experienced specialist.
- Even after successful epidural anesthesia, pain in the lumbar region is typical for 10-12 hours. Sometimes mild pain persists for several months. In this case, you need to contact a neurologist.
- If a surgical instrument during laparoscopy of a cyst damages a small nerve, an area of the skin may hurt or lose sensitivity.
- After anesthesia, which was injected into a vein, the forearms of the hands may hurt, and after 2 days pain may appear in the legs.
If the seam hurts
Healing of laparoscopic sutures can last from 7 to 14 days. The rate at which wounds heal depends on:
- the age and state of the patient’s immunity;
- correct suture placement and care;
- puncture sites.
It is more difficult for sutures to heal after laparoscopy of a cyst if they are made in the umbilical region. In this place there is often suppuration. Therefore, punctures in this place are done only when absolutely necessary.
Normally, the stitch hurts for the first 7 days. The pain is aching, and the seam may be slightly inflamed and red. The abdomen is usually swollen, and aching pain is also felt inside. During the second week after laparoscopy, the cyst discomfort should subside, at which time the sutures are removed. Suture removal should be painless if:
- it is not done ahead of schedule;
- no suppuration or other complications;
- the threads have not grown into the skin.
If self-absorbing threads were used during laparoscopic surgery, their “tails” will fall off 6-7 days after surgery.
Complete healing of the sutures should occur 4 weeks after laparoscopy of the cyst.
Features of the event
The laparoscopic method of removing a cyst is a cavity intervention, but access is through incisions that are minimal in length.
The main advantages of the operation over traditional techniques are the minimal invasiveness of the method, a more pronounced cosmetic effect, a reduction in hospital stay, and an acceleration of the recovery period. Complications such as the formation of adhesions, hernias, and intestinal paresis are recorded with significantly lower frequency than with open approaches.
Ovarian laparoscopy requires special equipment and trained personnel. It is carried out for urgent and planned reasons. Tactics depend on the patient’s age, location of the cystic formation, and desire to become pregnant in the future.
Pain after months or years
If it begins to hurt in the place where the cyst was laparoscopyed after a few months, a year, or even a few years later, this indicates the development of an adhesive process. Another reason may be the growth of a cystic structure in the same place, especially if the patient did not undergo hormone therapy or other restorative treatment after removal of the cyst.
Sometimes pain appears a month or two after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst or other abdominal organ. This may indicate that the patient began active physical activity or a vigorous sex life too early, without giving herself enough time to recover.
The reason for the resumption of pain some time after laparoscopy of the cyst may be:
- taking a bath instead of a shower;
- premature visit to the bathhouse, swimming pool or sauna;
- wearing clothes that are too tight;
- violation of the diet recommended by the doctor;
- lifting weights;
- refusal of rehabilitation therapy prescribed by a doctor.
Depending on the complexity of laparoscopy of the cyst, the rehabilitation period can last 1-3 months, and you cannot take on the same loads before this period. The body must be given the opportunity to recover, and for this it cannot be overloaded. Especially if the lower abdomen or other area where the cyst was removed continues to hurt.
You need to understand that normally there should be no acute pain in any part of the body:
- during the first 12 hours after laparoscopy of the cyst, because analgesics are still effective;
- after 12 hours, since the intervention is minimally invasive and does not involve long-term use of painkillers.
Any severe and cutting pain after laparoscopy of a cyst requires immediate consultation with a doctor or calling an ambulance.
Source
Cysts on the internal genital organs are often found in women of reproductive age. This neoplasm has different etymology and classification. Some types of lumps can dissolve spontaneously during menstruation and come out during menstruation. However, sometimes a benign tumor increases in size and provokes pain. If an ovarian cyst hurts, the nature of the discomfort will be different, as well as the reasons.
Why does an ovarian cyst hurt?
Ovarian neoplasm most often occurs due to any disturbances in the functioning of internal organs. Until an increase in size occurs, symptoms do not manifest themselves. In the future, painful sensations force the woman to see a doctor. In most cases, cyst pain occurs for the following reasons:
With the rapid growth of pathology.
- excessive physical activity, overload of the body;
- the thickening quickly increases in diameter;
- there are disturbances in the functioning of the circulatory system, which provokes a lack of blood flow to the pelvic organs;
- with a tumor there are accompanying inflammatory processes;
- the cyst on the ovary begins to hurt due to the thinning of the membrane and the threat of internal rupture;
- the tumor has twisted around the ovary;
- compression of the vessels by the neoplasm occurred.
In addition to pain, there are other symptoms. The patient feels bloated in the abdomen, menstruation becomes irregular, and the urge to urinate becomes more frequent.
Contraindications
The following are absolute contraindications to surgery for ovarian cysts:
Contraindications include high obesity.
- diseases of the respiratory system, cardiovascular system in the stage of decompensation;
- period of exacerbation of an infectious-inflammatory disease of any localization;
- acute liver or kidney failure;
- shock of any etiology;
- diffuse peritonitis;
- adhesive disease of the pelvic organs;
- last trimester of pregnancy;
- various types of uncontrolled coagulopathies.
Relative contraindications include high obesity, previous invasive interventions on the ovaries, and large sizes of the pathological formation. In such cases, the decision is made individually, after a thorough assessment of all risks.
Laparoscopy for polycystic ovary syndrome is practically not used.
Where does the pain occur?
Pain is localized with an ovarian cyst in the lower region of the right or left side. It depends on where exactly the tumor has formed. Most often, the unpleasant sensations are aching in nature. Acute attacks are less common. If the tumor is large, the pain may radiate to other parts of the body. Where exactly depends on the type of cyst and its size:
- if there is pain in the chest, this is a sign that the thickening has formed due to pathologies of the corpus luteum. An ovarian cyst causes discomfort;
- if the discomfort is localized in the back, for example, lower back pain, this warns of significant growth of the tumor and the risk of its spontaneous opening;
If you have lower back pain, there is a risk of tumor rupture.
- pain is felt below and the lower abdomen hurts - this may be a sign of any complications;
Complications are possible with pain from below.
- if discomfort appears in the anus, it means that the cyst has reached a large size and is pressing on the rectum.
How does a cyst on an ovary hurt?
It is not always the side that hurts with an ovarian cyst simply because of the presence of a tumor on the internal organ. Often the appearance of discomfort is accompanied by complications. The most common causes are twisting of the tumor around the ovary and spontaneous rupture of the membrane.
In case of cyst torsion
If the seal becomes twisted, the functioning of the circulatory system is disrupted. As a result, necrotic processes develop.
Twisted ovarian tumor.
The woman experiences the following symptoms:
Nausea and vomiting occur.
- acute attacks of pain in the very bottom of the abdominal cavity;
- nausea, even vomiting occurs;
- general health worsens, pressure changes occur;
- often breaks into a cold sweat or fever;
- There may be some slight bleeding between cycles.
Twisting of the tumor can be caused by excessive physical activity, intimacy, pregnancy, as well as untimely emptying of the bladder.
What to do if the pain from an ovarian cyst has become unbearable? You must consult a doctor immediately. If the tumor is twisted, surgery will be required. Otherwise, cell death will continue, the membrane will rupture and bleeding will continue.
In the absence of timely treatment, reproductive function may be impaired. In this case, you can completely forget about pregnancy.
When it breaks
The bleeding becomes profuse and the pain intensifies.
If spontaneous opening of the membrane occurs, this causes even more unpleasant symptoms than twisting. In this case, the bleeding becomes profuse and the pain will be more severe. Discomfort is felt not only in the abdomen, but also in the lower back and pelvis. When moving, the painful syndrome becomes more acute.
The woman feels that the abdominal cavity has become larger and is constantly tense. Victims often lose consciousness. In addition, tachycardia and pressure surges are noted. If the patient is not hospitalized in time, purulent peritonitis develops. In case of spontaneous rupture of the membrane, surgical intervention is required.
When is laparoscopy performed?
If the ovarian cyst is small, does not cause symptoms and does not look cancerous, it can be left alone. No surgery needed. The gynecologist will prescribe periodic examinations and control ultrasounds. Moreover, postmenopausal women will have to do this more often, because they have a higher risk of malignant tumors.
Are there effective medications?
In some cases, hormonal contraceptives may be helpful. They help prevent the formation of new cysts in the ovaries, but do not affect the growth of existing ones. If a woman is bothered by pain, the doctor may prescribe drugs from the group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). But this is only symptomatic treatment. The only way to get rid of the formation is surgery.
If the cyst is “problematic,” then the doctor will definitely say that it needs to be removed. Indications for surgery:
- Large size of formation. In most cases, ovarian cysts have a diameter of 1–3 cm. Very rarely they reach 15–30 cm.
- Presence of symptoms: abdominal pain, pelvic pain, bloating, feeling of heaviness in the abdomen, heavy periods, vaginal bleeding not associated with the menstrual cycle. A large cyst can compress the intestines and bladder. This leads to problems with stool and urination.
- Suspicion of a malignant nature of the cyst - the risks are increased in postmenopausal women.
- Continued growth over 2–3 menstrual cycles.
- Pathological ovarian cyst.
What happens if the cyst is not removed?
If the doctor said that the cyst needs to be removed, then delaying the operation is primarily dangerous for postmenopausal women. They, as we have already mentioned, have a higher risk that the formation may turn out to be malignant. And with cancer, time is critical. The later treatment is started, the lower the chances that it will be successful and that remission will be achieved. The prognosis worsens and survival rate decreases.
In the European clinic you can receive treatment for ovarian cancer according to modern standards. Our doctors perform operations of any complexity; we have access to all the latest generation antitumor drugs registered in Russia. We work according to modern European, American, Israeli treatment protocols. For ovarian cancer complicated by peritoneal carcinomatosis, we use an innovative technique - hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC).
Diagnosis of causes
To find out the exact cause of pain due to follicular or other ovarian formation, the following types of examination are prescribed:
Analysis for tumor markers.
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity, which looks at the location of the tumor and also determines its size. When performing an ultrasound, you can find out whether it is twisted or burst;
- blood and urine tests can reveal the presence of hidden infectious processes;
- the contents of the thickening are transferred for analysis for tumor markers. This will exclude the malignant nature of the tumor;
- Laparoscopy is a procedure in which pathology can be examined in more detail. A small puncture is made, during which a biopsy is performed. The method is effective if ultrasound turns out to be uninformative.
To exclude pregnancy, it is worth conducting a test in advance.
Preparing for surgery
Before laparoscopy, a number of tests are taken from the patient and examinations of the pelvic organs are performed to determine the general condition of the body, as well as to localize the place that will need to be operated on.
Full list of these studies:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
- Fluorography of the lungs.
- ECG.
- Tests for HIV, hepatitis, syphilis and blood typing.
- General analysis of urine and blood.
- Vaginal flora smear.
- Coagulogram - blood test for clotting
- Biochemical blood test - glucose, urea, bilirubin and total protein.
Preparation for laparoscopy is not limited to tests. Written consent for the operation is given, a conversation is held with the anesthesiologist, who describes in detail what type of anesthesia will be used and what needs to be done to ensure that the operation takes place without complications.
The general list of recommendations for preparation is as follows:
- Cleansing enema, the evening before the operation and in the morning.
- The last time before the operation you can eat until six o’clock in the evening, the day before the operation. Drinking is prohibited after ten o'clock in the evening.
- It is necessary to shave the hair in the crotch and lower abdomen.
- Before the operation, you need to put on anti-varicose stockings on your legs. They will need to be worn for another week or two to avoid the formation of microthrombi in the veins of the legs.
Patients often have questions about what to take with them to the hospital. The list is quite ordinary, the same for everyone for any hospital visit. You should have a robe, a cup, a spoon, a pair of diapers, a book and hygiene items. It is worth taking a change of underwear, based on the fact that discharge from the hospital takes place 3-5 days after the operation.