Detection of a cyst
When there is a certain discomfort and pain upon palpation, this indicates the presence of a neoplasm.
Before diagnosing an ovarian cyst, it is necessary to understand what it is. It is a formation that is filled with fluid and is located in the middle of the ovary. Before this procedure, it is necessary to fill the bladder by first drinking a large amount of liquid approximately one hour before the examination. On an ultrasound, the pathology will be visible, even if its size is very small.
Biopsy is a procedure for removing cells from formations for further examination.
After pathology is detected and the development of a malignant ovarian tumor is suspected, a histological examination can be performed. This procedure is necessary to obtain accurate information about the origin of the pathology. The study allows not only to recognize the cancer cells themselves, but some methods make it possible to determine the reasons for their appearance.
Histology of an ovarian cyst is carried out when the presence of cancer is suspected and consists of studying the structure of the tissue of the formation. The histology of an ovarian cyst consists of studying the structure of the tissue of the formation. On average, the procedure takes about 10 days. With its help, you can understand the nature of the pathology and whether it is malignant. Once the type of formation has been established, it is recommended to remove it. For this purpose, therapeutic and surgical methods are used.
Description
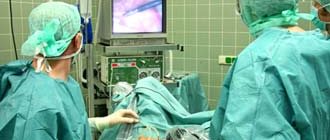
Ultrasound examination is one of the most informative types of diagnostics. Ultrasound allows you to assess the condition of the ovaries, their functionality, and possible pathologies. The procedure is carried out during population screening, routine medical examinations and when gynecological diseases are suspected.
A woman is examined with a sensor emitting ultrasonic waves in a hospital setting. During the procedure, the doctor determines the condition of the organs from the image obtained on the monitor screen. Using an ultrasound machine, measurements of all sizes and examination of individual tissue areas are taken. If necessary, the image is enlarged. The average time for an ultrasound is up to 15-20 minutes.
Changes in the appendages during the menstrual cycle
Folliculometry is a test to detect ovulation in the current cycle. When there are pregnancy plans, doctors recommend diagnosis at the beginning of the second half of the cycle. But there is also a certain dependence of time on the individual structural characteristics of each woman’s body.
Inflammation of the fallopian tubes is accompanied by exudation of fluid into the lumen - hydrosalpinx. An ultrasound examination reveals an elongated single- or multi-chamber anechoic formation with thin walls between the uterus and a normal ovary. In chronic salpingitis, the wall of the fallopian tubes is thickened, along the periphery there are hyperechoic small (2-3 mm) “bead”-type structures; in the lumen there is a heterogeneous suspension.
Drawing. A woman complained of nagging pain in the lower abdomen for several days. The uterus and right ovary were removed 4 years ago. On ultrasound, the left ovary is in contact with an anechoic tubular structure with incomplete septa. Conclusion: Hydrosalpinx on the left.
Drawing. An ultrasound reveals a multi-chamber anechoic structure between the uterus and ovary, the walls are thick with small hyperechoic inclusions like “beads”, there is a fine suspension and levels in the lumen. Conclusion: Chronic salpingitis.
The appendages themselves are always the same size. Changes occur in the follicles and corpus luteum necessary for conception. The first contain an egg that is released on days 14-16 of the cycle for fertilization, breaking the outer shell. The corpus luteum is formed at the site of the burst follicle - it is necessary for the production of the hormone progesterone, which promotes the movement of the egg through the fallopian tubes and the implantation of the fertilized egg into the walls of the uterus.
Changes in follicle size by day of the cycle:
- 5-7 days – formation of several dominant follicles up to 6 mm in diameter;
- 10-11 days – clear identification of a dominant follicle measuring 14-16 mm;
- 14-15 days - the follicle reaches its maximum size of 18-22 mm, after 1-2 days it will rupture and the egg will be released, i.e. ovulation.
After ovulation occurs, the corpus luteum matures:
- 15-16 days - the corpus luteum is determined to be up to 20 mm in size, free fluid in the uterus from a burst follicle;
- Day 20 – the corpus luteum actively produces progesterone and reaches a size of 25-27 mm;
- 26-27 days - regression of the corpus luteum - its diameter is 1 cm, with the onset of menstruation it disappears.
These changes are considered normal - they are present in all women who do not have health problems.
On what day of the cycle is folliculometry done?
Folliculometry is a test to detect ovulation in the current cycle. When there are pregnancy plans, doctors recommend diagnosis at the beginning of the second half of the cycle. But there is also a certain dependence of time on the individual structural characteristics of each woman’s body. In cases where the average duration of the second phase lasts 2 weeks, then using basic calculations you can calculate the approximate day of ovulation.
Therefore, diagnosis must be carried out several days before its onset. In this case, it is carried out after menstruation, but during the period when bleeding has not yet begun. The final stage of this diagnosis is confirmation that ovulation has completed.
Contraindications
An examination is indicated for suspected infertility or lack of conception. To do this, you should check the ovaries and uterus. The latter are initially examined completely; later, if pathologies are detected or functions need to be monitored, only the affected organs are subject to examination.
Indications for ultrasound of the ovaries in women:
- suspicion of infertility;
- irregular menstrual cycle;
- lack of conception for more than a year with regular unprotected sexual intercourse;
- heavy or scanty menstruation;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- diseases of the mammary glands;
- hormonal imbalance;
- routine gynecological examination.
Regular consultations with a gynecologist will ensure timely detection of diseases of the ovaries and other genital organs. Early treatment is highly likely to preserve a woman’s reproductive function. Pathologies are often diagnosed in their final stages - this is due to the frequent asymptomatic course of diseases of the appendages.
Ultrasound diagnostics of the ovaries is called pelvic ultrasound (pelvic organs) or gynecological ultrasound. This type of diagnosis allows you to examine all female organs (uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes).
Determining the condition of follicles, their size, number, growth dynamics is called folliculometry. This method is used to monitor the growth and development of follicles before pregnancy.
Main indications for ultrasound examination of female organs:
- examination for preventive purposes;
- cycle disorders (small or large volume of blood released, intermenstrual bleeding, pain during menstruation, delay);
- complaints of nagging or sharp pain in the lower abdomen;
- suspicion of inflammation;
- suspicion of neoplasms (cysts, oncology);
- inability to get pregnant;
- research before artificial insemination;
- control of chronic gynecological diseases;
- assessment of age-related changes during menopause;
- assessment of the effectiveness of treatment of infertility and other gynecological pathologies;
- first screening of pregnant women;
- diseases of the mammary glands.
Relative contraindications to ultrasound are damage to the skin or mucous membranes at the site of contact with the sensor, as well as the inability to contact the woman due to mental illness.
Ultrasound after childbirth or abortion
In cases where we are talking about ultrasound of the pelvic organs after an abortion, then such a study must be carried out at least 5-7 days after curettage. If bleeding is observed, then this is normal, because it does not apply to menstruation. The cycle itself will gradually, over several months, be restored.
Therefore, after childbirth, this type of examination is carried out before the onset of menstruation.
Most often, an ovarian cyst on ultrasound is visible through the anterior abdominal wall. Using this safe diagnostic method, it is possible to assess its size, type and exact location.
General examination
To conduct standard ultrasound diagnostics, this procedure is prescribed in the first half of the cycle.
To perform an ultrasound of the pelvic organs, you should contact a specialist as soon as menstrual bleeding stops on the 5-7th day of the cycle. There is no point in performing it earlier, because at this time the uterus is filled with blood and the examination will not be able to show accurate results. If the menstrual cycle is short, then the optimal study is on the 5th day, and if it is long, from 5 to 10.
Doctors also do not recommend carrying out a study before the onset of menstruation. The reason for this is the active formation of progesterone. This hormone leads to thickening of the endometrium. Therefore, when contacting a specialist during this period, it is possible to do an ultrasound, but it will not be impossible to identify pathologies and defects in detail (for example, a cyst on the ovary). That is why it is necessary to perform an ultrasound of the pelvic organs in the first half of the cycle.
When is the best time to do an ultrasound of the ovaries and uterus?
The day of the examination is determined by the attending physician depending on medical indications. The first ultrasound examination can be performed on any day of the cycle, with the exception of the period of menstrual bleeding - in the presence of chronic or acute diseases, the disease is easily diagnosed in any phase of the cycle. Experts recommend doing an ultrasound of the ovaries on days 5-7 or 22-24 of the cycle - the exact time is determined individually.
To obtain a complete picture of the functionality of the ovaries, ultrasound is performed several times during the menstrual cycle. The first time it is done on days 5-7, then on days 8-9, 13-14 and 22-24. This study is called folliculometry and is necessary to monitor ovulation by monitoring the growth of follicles on ultrasound and their subsequent rupture in the ovaries for the release of the egg. This type of diagnosis is prescribed to women with suspected infertility.
The examination stages of the procedure itself do not differ from each other. The main differences lie in the area of the body through which the examination is carried out.
Transabdominal
The patient lies on the couch on her back with her legs straightened. A special gel that conducts ultrasonic waves is applied to the previously exposed lower abdomen. The sensor is moved over the lubricated area, assessing the condition of the internal genital organs. Visualization is difficult when the bladder is not full or when gases form in the intestines.
Transvaginal
The woman lies on the couch on her back, with her legs bent and slightly spread. A condom is put on the sensor, the latter is lubricated with a special gel. The device is inserted into the vagina and gently moved within it for a complete examination. This method is the most informative due to the absence of other organs that may interfere with the examination and the close proximity to the appendages.
Transrectal
The patient lies on the couch on her side, bending her knees and clasping them with her arms. The sensor with a pre-applied condom is inserted into the anus. This method is used very rarely and is relevant only when transvaginal scanning is impossible or examination through the abdominal wall is uninformative.
For girls and women who have not been sexually active, the transabdominal or transrectal method is used. Examination by inserting a probe into the vagina is not possible due to the risk of damaging the hymen. After the start of sexual activity, patients are recommended to undergo a transvaginal ultrasound for a more detailed examination of the organs.
Ultrasound examination of the ovaries is a mandatory diagnosis that is performed upon pregnancy. Usually it occurs at 11-12 weeks of obstetric time - simultaneously with the first screening. In the absence of pathologies and diseases of the appendages in the anamnesis, additional studies are not carried out.
The procedure, regardless of gestational age, can be performed transvaginally or transabdominally. Preparation for the study is carried out in the same way as for non-pregnant women. During the examination, the size of the organs, their location, the presence of cysts and the functioning of the corpus luteum are assessed.
How to do an ultrasound to identify an ovarian cyst and how different types look on the monitor
› Genitourinary system
17.01.2019
Ovarian cysts are the cause of women's health problems and infertility. An ovarian cyst can be detected by ultrasound; there are several types. Treatment is carried out using conservative and surgical methods.
Indications for examination
A gynecologist sends a woman for an ultrasound if she complains of pain in the lower abdomen, menstrual irregularities, or infertility.
For ovarian cysts, several types of ultrasound are performed:
- transabdominal - a classic method, but detects only large tumors;
- transvaginal - the most accurate method, allowing you to see the slightest changes, suitable only for women who are sexually active;
- transrectal - the sensor is inserted through the rectum, the method is used in virgins.
In addition to the direct diagnostic purpose, ultrasound is used to control some invasive procedures. For example, puncture of an ovarian cyst is done under mandatory ultrasound control, so as not to damage healthy tissue with the needle.
Watch a video about ovarian cysts and how to diagnose them, including ultrasound:
Preparation rules
On what day of the cycle to do an ultrasound is important for ovarian cysts. Neoplasms are hormone-dependent and change size depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle. The initial examination is carried out on days 5-7, that is, immediately after the end of menstruation. To assess the dynamics of the condition, the study is repeated on days 10, 15, 22.
No special preparation for ultrasound is required. The doctor recommends not to eat foods that promote gas formation three days before the procedure:
- cabbage;
- black bread;
- peas;
- dairy products.
They come for the study on an empty stomach.
How an ultrasound examination is done
The woman comes prepared; it is advisable to take a disposable sheet and towel with her. During the transabdominal procedure, the doctor lubricates the abdomen with gel and examines the site of projection of the ovaries with a sensor.
Transvaginal and transrectal techniques use a special sensor that is inserted into the vagina and rectum, respectively. If this type of examination is prescribed, you need to take a nozzle or a regular condom with you.
The entire ovarian ultrasound procedure takes 15-20 minutes, then the doctor makes a description. The conclusion is given to the patient along with the image.
Normal result
Healthy ovaries in the image have certain criteria:
- homogeneity of structure;
- density equal to the uterus;
- rounded follicles are located in the cortex;
- One dominant follicle is clearly visible.
The normal size of the gland is 2x3 cm, its contours are clear and even.
Possible mistakes
Ovarian cysts are clearly visible on ultrasound, but sometimes they are disguised as other diseases:
- corpus luteum - for ectopic pregnancy;
- hemorrhagic - under a malignant tumor.
An error in making a diagnosis may be due to insufficient qualifications of the doctor, equipment malfunctions, or an incorrectly chosen time for the examination. The error rate is low.
Other features noticeable during ultrasound
During the examination, not only the size and structure of the organs are determined, but also the degree of their functionality. Sometimes quite rare pathologies are diagnosed.
Most often, the appendage is not clearly displayed on the monitor screen during a rectal or transabdominal ultrasound. In this case, visualization is hampered by an overproduced bowel or an unfilled bladder. The study should be repeated in compliance with all preparation rules.
An ultrasound does not show the ovary even when it is depleted or there are adhesions. If it is difficult to make a diagnosis, magnetic resonance imaging of the organs should be performed - this type of diagnosis is considered much more informative than ultrasound.
Increase in size
A slight increase in appendages is noted when the follicles reach large sizes. If there is a strong deviation from the norm, an inflammatory process or cystic formation is diagnosed.
Indicates a violation of the reproductive function of the ovaries. The study must also be carried out for the next menstrual cycle - most women do not ovulate 1-2 times a year for natural reasons.
Stroma is the lining of the appendage containing many blood vessels. Its high echogenicity indicates the course of polycystic disease or an inflammatory process.
Oncology in the ovaries is determined by ultrasound in the form of a multilocular cancerous tumor and papillary growths. Such formations have thick walls; in the final stages they can reach enormous sizes.
Other violations
Other types of diseases that can be detected by ultrasound of the ovaries:
- endometriosis – adhesions of the uterus, fallopian tubes, formation of endometrioid cysts on the appendages;
- ovarian pregnancy - attachment of the embryo near the appendage or to its walls;
- calcifications in the ovaries by ultrasound are defined as the deposition of calcium salts in the organ;
- rupture of the appendage or its cyst is accompanied by acute pain, which forces an examination.
Ultrasound of the ovaries is necessary for every woman to undergo regularly to prevent the development of gynecological diseases. Carrying it out 1-2 times a year ensures timely diagnosis of pathologies, and early treatment accelerates the recovery process. The ultrasound examination method is considered completely safe and does not harm health.
| Name of ultrasound | Features of the event |
| Transrectal | It is highly informative. Involves inserting a sensor into the rectum. This study is carried out mainly in virgins. |
| Transabdominal | It is performed through the anterior wall of the peritoneum. For a small cyst, the method is ineffective |
| Transvaginal | The pelvic organs are viewed through the vagina. This research method is characterized by maximum information content. With its help, it is possible to view even small pathological processes on the appendages |
The standard duration of each of these manipulations is 5-10 minutes. During this time, the doctor will determine or deny the presence of an ovarian cyst on the body.
The information collected during the study is printed on a special form. It is interpreted by a gynecologist.
Options for ultrasound examination and features of its implementation
In gynecological practice, three types of ultrasound of the pelvic organs are used:
- Transvaginal ultrasound involves examining the reproductive organs through the vagina. The method is considered the most informative, since the distance to the internal organs is reduced. Allows you to identify small cysts. Not used in virgins;
- Transabdominal ultrasound is performed through the anterior abdominal wall. The distance to the pelvic organs is quite large, so the method is not very informative for small cysts;
- Transrectal ultrasound. The sensor is inserted into the rectum. In terms of information content, it is comparable to a transvaginal examination. It is used in virgins in cases where the transabdominal method did not produce results.
Types of examination
Types of ultrasound of the ovaries in women have different information content and differ in the process of conducting:
- transabdominal - examination of organs through the anterior abdominal wall, for this the doctor smoothly moves the sensor over the skin, previously lubricated with gel;
- transvaginal - the most informative method, carried out by inserting a sensor into the vagina to a depth of 12 cm;
- transrectal - rarely used for diagnosing ovaries; for examination, the sensor is inserted into the rectum to a depth of 6 cm.
Preparing for an ultrasound scan of the ovaries and uterus does not take much time. When prescribing a diagnosis, gynecologists inform the patient about all the rules of procedures that must be followed before the study.
To obtain the most reliable results, it is necessary to prepare the internal organs of the pelvis for the procedure. To do this, you need to follow a special diet for 2-3 days, excluding gas-forming foods - legumes, cabbage, white bread, etc. Before visiting a doctor, you should empty your bowels naturally or with the help of a microenema.
The bladder should be full. An hour and a half before the ultrasound, a woman needs to drink up to one and a half liters of non-carbonated liquid. Tea, water or juice are suitable for this purpose. Insufficient fullness of the bladder makes it difficult to examine the appendages.
Transvaginal
To perform such an ultrasound of the ovaries and uterus, no preparation is required from the woman. First, you should thoroughly rinse the perineum using intimate hygiene products.
Infections during examination are excluded - to protect the patient, doctors use a disposable condom made for sensors. Some clinics ask clients to bring their own protective product, which can be purchased at the pharmacy.
Transrectal
To carry it out, it is necessary to clear the rectum of feces. To do this, before visiting a doctor, you should empty your bowels naturally or with the help of a microenema. A few days before the procedure, gas-forming products should be eliminated.
Preparation for the procedure
First, a woman must determine the date of the onset of menstruation. Speaking about which day of the cycle to diagnose an ovarian cyst using ultrasound, experts note that the best time for this is 1-2 days after the completion of desquamation. That is, approximately 6-8 days of the cycle.
You need to go for this procedure with a referral from a gynecologist. Sometimes it prescribes a preliminary diagnosis. This is done with the aim of quickly orienting a specialist in the field of ultrasound examination, because, knowing about the suspicions of the patient’s attending physician, he will be able to quickly determine her pathology.
The patient should take with her:
- A disposable clean diaper.
- Shoe covers.
- A paper towel to remove gel from the body.
You must also have any identification document with you.
Preparatory measures depend on the type of ultrasound. For example, if a woman is having a transabdominal exam, she should fill her bladder first. This need is explained by the displacement of the intestines from the visual analysis zone. If this is not done, it will block the ovary affected by the cyst and the desired image will not be obtained.
Therefore, before performing a transabdominal ultrasound, the patient should drink at least 1.5 liters of mineral water, preferably without gas. This must be done 1 hour before the procedure.
If a woman is prescribed a transrectal examination of the ovaries, it is recommended to first do an enema to cleanse the intestines of feces.
You can undergo a transvaginal examination without prior preparation. However, hygiene measures will not be superfluous.
Carrying out gynecological diagnosis of cysts
This procedure is carried out in a special room equipped with diagnostic equipment. The method of conducting depends on the type of study:
- Transrectal. The sensor is lubricated with gel and inserted through the patient's anus. At the same time, she lies with her knees bent, on her side. There may be some discomfort as the device moves through the intestine. If it is very strong, you need to warn your doctor.
- Transabdominal. The patient lies on her back, exposing the lower abdomen. A small amount of gel is poured onto this part of the body. It also lubricates the sensor. If an ultrasound shows a left ovarian cyst, the doctor will move the sensor from this side. Accordingly, if the tumor is located on the right side, all manipulations are performed on the right. If there is strong pressure on the abdomen, the patient will feel the urge to empty the bladder, but this will have to be ignored until the end of the procedure.
- Transvaginal. The woman undresses to the waist and, bending her knees, lies on her back. A condom soaked in gel is placed on the microsensor. The device is then inserted into the patient's vagina. This procedure is completely painless, however, uncomfortable.
All three types of diagnostics are also used for ultrasound after removal of an ovarian cyst.
After the ultrasound is completed, the woman can use a paper towel to remove the gel from the skin. When the doctor or his assistant prints out the image and study data, they will be given to the patient. After this, she can go to the attending gynecologist for further diagnosis.
Detection of cystic formations using ultrasound
Most often, an ovarian cyst on ultrasound is visible through the anterior abdominal wall. Using this safe diagnostic method, it is possible to assess its size, type and exact location.
There are no contraindications for performing ultrasound examination. It is performed on women of any age and in the presence of any disease.
When to do an ultrasound
If you feel unwell, you need to undergo a comprehensive medical examination. If discomfort is localized in the abdominal area, it is recommended to visit a gynecologist. The patient is sent for ultrasound diagnosis of ovarian cysts if she complains of:
- long delay of menstruation;
- increase in the volume of monthly discharge;
- painful desquamation (desquamation and separation of the uterine endometrium);
- acyclic blood secretion;
- regularly occurring, severe pain in the lower abdomen.
Such symptoms indicate the presence of a cystic formation on the body of the appendage. Its growth provokes reproductive dysfunction.
The main indication for an ultrasound examination is the detection of a round-shaped neoplasm in the projection of the ovary upon palpation. In this case, such diagnostics should be carried out regularly (1-2 times a month) in order to analyze its growth.
If the cyst was surgically removed, ultrasound is performed every 2-3 months for a year.
What kind of ultrasound is done for an ovarian cyst and the specifics of its implementation?
If there are benign and malignant neoplasms in the female abdominal area, there is a need for their visual analysis. Pelvic ultrasound for ovarian cysts can be transrectal, transabdominal and transvaginal:
Name of ultrasoundFeatures of the procedure
| Transrectal | It is highly informative. Involves inserting a sensor into the rectum. This study is carried out mainly in virgins. |
| Transabdominal | It is performed through the anterior wall of the peritoneum. For a small cyst, the method is ineffective |
| Transvaginal | The pelvic organs are viewed through the vagina. This research method is characterized by maximum information content. With its help, it is possible to view even small pathological processes on the appendages |
The standard duration of each of these manipulations is 5-10 minutes. During this time, the doctor will determine or deny the presence of an ovarian cyst on the body.
The information collected during the study is printed on a special form. It is interpreted by a gynecologist.
Data collected during an ultrasound are not an accurate diagnosis. It is diagnosed by a gynecologist based on the results of all tests.
Preparation for the procedure
First, a woman must determine the date of the onset of menstruation. Speaking about which day of the cycle to diagnose an ovarian cyst using ultrasound, experts note that the best time for this is 1-2 days after the completion of desquamation. That is, approximately 6-8 days of the cycle.
You need to go for this procedure with a referral from a gynecologist. Sometimes it prescribes a preliminary diagnosis. This is done with the aim of quickly orienting a specialist in the field of ultrasound examination, because, knowing about the suspicions of the patient’s attending physician, he will be able to quickly determine her pathology.
The patient should take with her:
- A disposable clean diaper.
- Shoe covers.
- A paper towel to remove gel from the body.
You must also have any identification document with you.
Preparatory measures depend on the type of ultrasound. For example, if a woman is having a transabdominal exam, she should fill her bladder first. This need is explained by the displacement of the intestines from the visual analysis zone. If this is not done, it will block the ovary affected by the cyst and the desired image will not be obtained.
Therefore, before performing a transabdominal ultrasound, the patient should drink at least 1.5 liters of mineral water, preferably without gas. This must be done 1 hour before the procedure.
If a woman is prescribed a transrectal examination of the ovaries, it is recommended to first do an enema to cleanse the intestines of feces.
You can undergo a transvaginal examination without prior preparation. However, hygiene measures will not be superfluous.
Carrying out gynecological diagnosis of cysts
This procedure is carried out in a special room equipped with diagnostic equipment. The method of conducting depends on the type of study:
- Transrectal. The sensor is lubricated with gel and inserted through the patient's anus. At the same time, she lies with her knees bent, on her side. There may be some discomfort as the device moves through the intestine. If it is very strong, you need to warn your doctor.
- Transabdominal. The patient lies on her back, exposing the lower abdomen. A small amount of gel is poured onto this part of the body. It also lubricates the sensor. If an ultrasound shows a left ovarian cyst, the doctor will move the sensor from this side. Accordingly, if the tumor is located on the right side, all manipulations are performed on the right. If there is strong pressure on the abdomen, the patient will feel the urge to empty the bladder, but this will have to be ignored until the end of the procedure.
- Transvaginal. The woman undresses to the waist and, bending her knees, lies on her back. A condom soaked in gel is placed on the microsensor. The device is then inserted into the patient's vagina. This procedure is completely painless, however, uncomfortable.
All three types of diagnostics are also used for ultrasound after removal of an ovarian cyst.
After the ultrasound is completed, the woman can use a paper towel to remove the gel from the skin. When the doctor or his assistant prints out the image and study data, they will be given to the patient. After this, she can go to the attending gynecologist for further diagnosis.
Normal abdominal organs on ultrasound
The parameters of the pelvic organs, indicating their normal performance, are determined by the woman’s age.
During menopause:
- in the second phase of the cycle the corpus luteum is not detected;
- follicles cannot be determined, since the number of their production is significantly reduced. There is no dominant follicle;
- the size of the appendages decreases.
During reproductive functioning:
- in the parenchyma of the appendages it is possible to view multiple follicles of different sizes (from 0.2 to 0.5 cm);
- after ovulation, the corpus luteum is clearly visible in the tissue surface of the ovary. Its size is from 0.5 to 2 cm;
- the dominant follicle is visible in the right ovary. It is 0.5-1 cm larger than the others;
- There is a small amount of fluid in the pelvic cavity.
What does an ovarian cyst look like on an ultrasound?
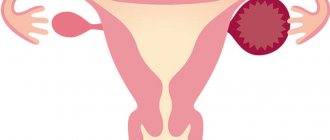
In gynecology, a cyst is a hollow tumor (usually benign) filled with fluid.
The main sign of an ovarian cyst on ultrasound is the formation of a hollow process on its body. It differs from a normal follicle in that it does not change at all throughout the cycle. In addition, such a tumor is larger in size.
In the ultrasound image, the ovarian cyst appears as a black spot, ranging in size from 3 to 20 cm.
Ultrasound diagnosis of cysts
Most of the processes on the body of the appendage are of benign origin. Before starting treatment, you need to determine the type of cyst.
Dermoid
They are one of the most common types of pathological processes on the body of the gonads. It can be not only benign, but also malignant. The second name for such a formation is teratoma. It occurs mainly in young women of childbearing age from 18 to 30 years.
On ultrasound, MRI and CT it appears bilateral or single-chamber. In 60% of cases, teratomas contain calcium in their structure. Inside they are filled with fatty fluid, which is produced by the sebaceous gland.
The presence of a teratoma on the ovaries can be visually determined by echogenic stripes.
Hemorrhagic
This formation is a blood clot. Its structure is single-chamber, hypoechoic. Inclusions can be different, for example, with fibrin threads.
The wall thickness of such a neoplasm is variable. It often has blood vessels arranged in a circular pattern.
Most often, their presence provokes severe pain. But there have been cases when a pathological process on the body of the hemorrhagic type of ovary was discovered by chance, and its presence was not accompanied by discomfort.
Follicular
On ultrasound it looks like a single-chamber hypoechoic formation of a round shape. Its walls are very thin, and its contour is smooth and clear.
Source: https://TvoiYaichniki.ru/diagnostika/kista-na-uzi
Normal abdominal organs on ultrasound
The parameters of the pelvic organs, indicating their normal performance, are determined by the woman’s age.
During menopause:
- in the second phase of the cycle the corpus luteum is not detected;
- follicles cannot be determined, since the number of their production is significantly reduced. There is no dominant follicle;
- the size of the appendages decreases.
During reproductive functioning:
- in the parenchyma of the appendages it is possible to view multiple follicles of different sizes (from 0.2 to 0.5 cm);
- after ovulation, the corpus luteum is clearly visible in the tissue surface of the ovary. Its size is from 0.5 to 2 cm;
- the dominant follicle is visible in the right ovary. It is 0.5-1 cm larger than the others;
- There is a small amount of fluid in the pelvic cavity.
The conclusion indicates the size of the organs, location, contours, characteristics of the follicles, as well as the changes detected. Healthy ovaries are located on the side and behind the uterus, have an uneven surface due to follicles, clear contours, and may vary slightly in size.
Normal indicators:
- length: 20–37 mm;
- width: 18–30 mm;
- thickness: 16–22 mm.
The number of follicles depends on the day of the menstrual cycle. From the 5th day of the cycle they begin to grow. By the middle of the cycle, the dominant (main) follicle reaches its maximum size. After this, ovulation occurs, and a corpus luteum forms in place of the burst follicle. It gradually decreases if pregnancy does not occur.
Normal characteristics of follicles depending on the day of the menstrual cycle:
- Days 5–7: 5–10 follicles with a diameter of 2–6 mm;
- 8–10 days: 1 dominant follicle with a diameter of 12–15 mm and 5–9 follicles up to 10 mm;
- 11–14 days: 1 dominant follicle with a diameter of 16–20 mm, ovulation;
- 15–18 days: corpus luteum with a diameter of 15–20 mm;
- 19–23 days: corpus luteum up to 25–27 mm;
- 24–27 days: the corpus luteum regresses to 10–15 mm;
- menstrual days: no corpus luteum.
Ultrasound picture of ovarian pathology
Ultrasound examination can identify the following types of pathological formations of the appendages:
- Functional cysts: luteal and follicular, as well as their variety - hemorrhagic;
- Organic cysts: paraovarian, dermoid, serous;
- Ovarian endometriosis;
- Polycystic ovary syndrome;
- True gonadal tumors: benign and malignant.
According to the classification, polycystic ovary syndrome does not relate to gonadal cysts and tumors, but is usually considered together with this pathology in terms of differential diagnosis.
In the description of the ultrasound, the doctor always indicates:
- Size of formation (diameter);
- Localization of the identified pathology;
- The presence of concomitant changes in other pelvic organs.
Let's take a closer look at the ultrasound picture for each pathology.
Ultrasound helps to indirectly determine the type of cyst; the final diagnosis is made by histological examination.
Follicular cyst
On ultrasound it looks like a hypoechoic single-chamber oval or round formation with thin walls. The contour is clear and smooth, inclusions are not detected. The contents of the cavity are anechoic. The size of the formation is usually no more than 12 cm. Normal ovarian tissue can be seen behind.
With Doppler ultrasound, blood flow inside and around the cavity is not determined. The photo below shows a follicular cyst:
In rare cases, a follicular ovarian cyst is detected in the fetus. This formation persists throughout intrauterine development and usually regresses spontaneously in the first months after the birth of the child. The photo shows this pathology:
Corpus luteum cyst
Defined as a hypoechoic round or oval formation with a thick wall. The contour of the cavity is clear and even, no inclusions are detected. Sizes – from 3 to 8 cm.
With Doppler ultrasound, a distinctive sign of a luteal cyst is observed - the appearance of a “ring of fire” around the cavity (parietal blood flow). This is clearly demonstrated in the photo below:
Hemorrhagic cyst
The cavity filled with blood is presented as a hypoechoic single-chamber structure with various inclusions: fine suspension or fibrin threads. The wall thickness is determined by the initial pathology. With Doppler ultrasound, blood flow in the lumen of the cavity is not detected, as can be seen in the following photo:
Decoding normal results
One ovary in a woman is always slightly larger than the other - this is due to the peculiarities of their work. The dominant organ is large due to the constant production of eggs, the second in most cases is responsible only for the production of hormones. Therefore, identifying different sizes of appendages should not frighten the patient.
Normal ovarian size on ultrasound in adult women:
- length – 20-37 mm;
- width – 18-30 mm;
- thickness – 16-22 mm;
- volume – 4-10 cubic meters. cm.
Minor deviations can be considered normal. If the appendages are excessively large, their inflammation, the presence of neoplasms and other pathologies are diagnosed. Small ovaries are not the norm - such organs most often have low functionality, cause infertility or signal the onset of menopause.
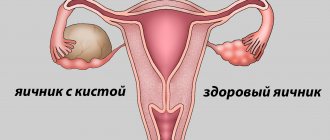
What does an ovarian cyst look like on an ultrasound?
In gynecology, a cyst is a hollow tumor (usually benign) filled with fluid.
The main sign of an ovarian cyst on ultrasound is the formation of a hollow process on its body. It differs from a normal follicle in that it does not change at all throughout the cycle. In addition, such a tumor is larger in size.
In the ultrasound image, the ovarian cyst appears as a black spot, ranging in size from 3 to 20 cm.
A simple cyst is a formation with thin walls. An increase in the echo signal is observed behind it. There is no dense content inside a simple cavity. No blood flow is observed. Often, functional formations are identified that appear in patients of childbearing age or during menopause.
Sometimes women are diagnosed with simple cysts, which in fact act as either paratubular tumors or cystadenomas. Malignant tumors are extremely rare in practice, especially when it comes to single-chamber tumors. Simple functional inclusions formed against the background of hormonal abnormalities are often identified.
Simple cysts up to 30 mm in size that occur in women of childbearing age are normal and do not pose a danger. If the size of the formation after menopause is up to 70 mm, then most likely it is benign. Foreign inclusions with a diameter of 70 mm or more are difficult to analyze on ultrasound, so an MRI is performed.
Follicular neoplasm
The diameter does not exceed 10 cm. It has a surface without protrusions, a thin wall, and filling with a watery consistency. Ultrasound reveals tissue of an unchanged appendage. Often the follicular cavity is single-chamber and is asymptomatic. Women with simple formations measuring 5 cm or more undergo a dynamic ultrasound.
In the study, the follicular cavity is defined as a thin-walled single-chamber inclusion, behind which an amplified acoustic signal can be traced. When bleeding into the formation, a diffuse hyperechoic suspension is detected. The ovarian parenchyma is visible along the periphery. A characteristic sign of follicularity on ultrasound is the absence of blood flow inside the cavity.
Has dimensions up to 40-50 mm. Sometimes hemorrhage occurs into the cavity. On ultrasound, a luteal tumor is determined by the “ring of fire” - numerous blood vessels piercing the wall. There is no blood supply inside the formation. The risk of its occurrence increases with the use of drugs that stimulate ovulation.
Hemorrhagic inclusion
Such a neoplasm of the appendage forms after hemorrhage into the luteal body or into a follicular cyst. In this case, an acute pain syndrome occurs in the lower abdomen, but sometimes an asymptomatic course of the pathology is observed. When the cavity ruptures, blood accumulates in the area of the reproductive organ and appendages.
On ultrasound it appears as a single-chamber formation with a hyperechoic suspension. Fibrin threads are transformed into an openwork mesh. Sometimes such extraneous inclusion looks dense. There is no blood flow inside it, but it can be traced along the periphery.
Formations with a size of 50 mm or more, formed during childbearing age, are subject to dynamic observation. Large tumors in patients in early menopause and 5 years after the last menstruation are regularly examined using magnetic resonance imaging.
This type of ovarian cyst is formed from ovarian tissue or has a different etiology.
Nonfunctional neoplasms include:
- A paraovarian cyst, which is defined by ultrasound as an inclusion up to 15-20 cm in size, has a round shape and the contents have a liquid consistency. Unlike others, it does not have a leg. If the paraovarian inclusion is large, then when separated by a sensor from the paired organ, it looks like a bladder.
- Inclusive formation of irregular shape, single or multi-chamber. The internal contents are anechoic; when hemorrhage occurs, fibrin impurities appear.
- foreign inclusion up to 10-15 cm in diameter is filled with chocolate-colored contents inside. Seals are visible on the smooth inner surface. There may be several areas of endometriosis on ultrasound.
Endometrioma appears as a round formation with a double contour and a uniform hypoechoic structure, resembling opaque glass. Dense inclusions are not observed. The capsule consists of 30% hypoechoic foci. There is no internal blood flow.
Mature teratoma. Click to enlarge
- in 85% of cases it is formed on one ovary and has dimensions from a pinhead to 20 cm, and an oval or circle shape. On ultrasound examination, in 90% of cases it is determined to be single-chamber. The formation has a hypoechoic structure and hyperechoic internal inclusions.
Thus, each ovarian cyst is characterized by features that differentiate it from other similar formations by ultrasound. Large foreign inclusions require dynamic monitoring.
Most ovarian cysts are benign. With familial forms of ovarian or breast cancer, the risk of malignant pathology increases. Ectopic pregnancy, hydrosalpinx, tubo-ovarian abscess can be mistakenly regarded as an ovarian cyst.
What does an ovarian cyst represent on an ultrasound and what can it be confused with during the study?
What an ovarian cyst looks like on an ultrasound is a fairly relevant topic, since cystic formations have become a common pathology in women and teenage girls.
A cyst is a benign neoplasm that contains fluid; its treatment often requires surgical methods. Often this formation develops asymptomatically, so the woman is not aware of its existence and discovers it only during a routine examination or treatment of another disease. Ultrasound examination is usually prescribed to diagnose a pathological formation.
Indications for ultrasound
Ultrasound examination is a common diagnostic method during preventive visits to the gynecologist. Indications for ultrasound are:
- irregularity or absence of menstruation;
- pain of various types in the lower abdomen;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse, especially in the ovarian area;
- menstruation, which is accompanied by pain;
- disturbance in the intensity of vaginal discharge;
- infertility;
- inflammation of the appendages;
- pregnancy planning, IVF;
- abuse of bad habits;
- overweight;
- preventive diagnostics of the genital organs.
On what day of the cycle should I do an ultrasound?
Not all women know on what day of menstruation an ultrasound of an ovarian cyst can be done. This procedure is carried out only at the end of menstruation. There is no point in conducting a study during the procedure, since the presence of blood distorts the results, and the doctor may not make an accurate diagnosis.
If a woman does not know when to do an ultrasound, it is better to contact a medical institution for consultation. The gynecologist will explain that the diagnosis is prescribed at the beginning of the cycle - the procedure is not carried out at the end of menstruation, since the endometrium is actively growing. Day 5-10 of the cycle is considered optimal.
Preparing for an ultrasound
Before the study, the girl must adhere to a special diet for three days; drinking water without gas is allowed. Transvaginal ultrasound requires only an empty bladder.
Transabdominal ultrasound requires a full bladder. Therefore, before the procedure, a woman needs to drink as much liquid as possible, preferably non-carbonated. When a woman feels the first urge to go to the toilet, an ultrasound examination should be performed. Compliance with all doctor’s recommendations guarantees maximum reliability of diagnostic results.
How is it carried out?
There are three methods of performing ultrasound:
- transvaginal - a special sensor is inserted into the vagina. It is considered the most reliable research method, which allows you to visually assess any deviations;
- transrectal - prescribed to girls who have not yet begun to be sexually active. The sensor is inserted into the intestine through the anus;
- transabdominal - a conventional study, the sensor is moved along the surface of the abdomen. Diagnostics makes it possible to detect large tumors.
What does a cyst look like on ultrasound?
During the examination, the doctor can see cystic neoplasms of different etiologies, which are divided into two types:
- functional;
- pathological
Functional education
| Follicular cyst | One of the most common pathologies. During ovulation, the follicle releases a mature egg containing fluid, resulting in the formation of a tumor. It is distinguished by an oval or round shape, has an expressive contour and thin walls. Grows no more than 10 cm - requires urgent medical intervention. For small sizes (no more than 3 cm), only observation of the neoplasm is necessary. |
| Corpus luteum cyst | If the corpus luteum remains in the ovarian tissues after menstruation, a tumor forms in it. This tumor tends to resolve on its own, sometimes requiring surgical intervention. Quite often it is mistaken for an ectopic pregnancy. It grows up to 5 cm and has thick walls. |
| Hemorrhagic cyst | It is a complicated functional neoplasm. The inside is filled with blood. As the blood vessels grow, they stretch and burst. A common pathology among women after 35 years. |
Non-functional
| Endometrioid cyst | It is a striped neoplasm on the ovary, contains inside the blood that was not released during menstruation, the membrane consists of endometrial tissue. For therapy, they resort exclusively to surgical methods, after which the woman needs to undergo a long course of hormonal treatment. The neoplasm is distinguished by dense walls of 2-8 mm, which may contain small round cavities. |
| Dermoid cyst | It is an oval formation formed from embryonic cells. To avoid malignancy into a malignant tumor, surgical therapy is resorted to. Can grow up to 20 cm. |
| Ovarian cystadenoma | It is divided into 2 types - papillary and simple serous cystadenoma. In the first case, there are small bulges on the walls on the inside. This is their only difference. Single-chamber neoplasm requires surgical treatment. |
Can an ultrasound be wrong?
Can an ultrasound be wrong about an ovarian cyst? Yes, a neoplasm can be confused with pregnancy. Often, in the results of studies, a woman is diagnosed with a cyst, but when preparing for treatment it turns out that there is no tumor.
The cyst can be confused if the girl did not follow the preparatory measures before the ultrasound examination, for example, she underwent diagnostics during her period. The tumor may be incorrectly differentiated.
Cystic formation is usually benign in nature. Treatment of the tumor depends on various factors. The most effective way is surgical therapy. Ultrasound is one of the most common and reliable methods for detecting tumors.
Source: https://kistaoff.ru/yaichniki/na-uzi
Decoding the results
The condition of the organs is determined by several parameters that are recorded on the diagnostic sheet. Using some values, you can independently decipher the results of an ultrasound scan of the uterus and ovaries, and the presence of any abnormalities in their functioning.
Location
Normally, the ovaries are located on both sides of the uterus, on the side walls of the pelvis. They may be slightly shifted relative to the uterus - with a slight change this is not considered a deviation. In most cases, the norm of location is determined individually - for some women it may differ slightly from the established standards. This is explained by the anatomical features of the internal organs.
Dimensions
It is most convenient to determine the size of the appendage in the first days after the end of menstruation. At this time, dominant follicles and the corpus luteum are still absent, which simplifies the specialist’s work. The obtained values must be compared with the size standards described above.
Fabric structure
When examined by a doctor, the number of ripening follicles and the size of the corpus luteum are determined. These parameters depend on the day of the menstrual cycle and its total duration. The general structure of the organs should be homogeneous. If echo signs of a cyst of the right or left ovary are detected, its size and cause of origin are determined. If it is difficult to make a diagnosis, some formations are additionally examined by biopsy.