Ignoring a disease such as chronic periadnexitis is quite dangerous, not only because of the serious risk of complications that threaten infertility. One of the likely consequences of the pathology is sepsis in case of possible accumulation of pus. Another is the further development of inflammation of the abdominal cavity, the ability of the pathology to cover a fairly large area. Periadnexitis appears as a complication of adnexitis. We are talking about a specific disease (a disease affecting the abdominal cavity), a complication after inflammatory processes in the appendages.
Normally, there should be no microorganisms at all in this part of the body. Therefore, there are no methods for natural control of their numbers. Violation of natural sterility leads to inflammation. The most common pathogens are gonococci, chlamydia, and streptococci. A separate problem is pathogenic microflora leading to tuberculosis. Periadnexitis in this case can be treated, but the nature of medical care will be quite specific.
Periadnexitis: left-sided, right-sided, bilateral
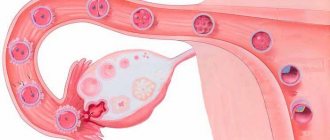
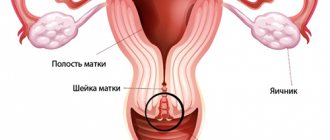
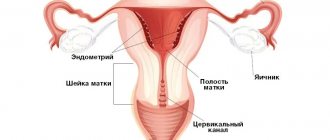
Periadnexitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum caused by inflammation of the uterine appendages.
Periadnexitis can be either unilateral (left-sided or right-sided) or bilateral. In a normal state, the uterine appendages do not contain microorganisms, but when pathogenic flora enters the appendages, inflammation develops, which causes periadnexitis.
The main causative agents of inflammatory processes are streptococci, gonococci, chlamydia, and tuberculosis microbacteria. Pathogenic microorganisms can enter the uterine appendages both through the genital route (for example, during unprotected intercourse with a chlamydia carrier) and from other areas of the body with blood and lymph.
Article navigation
Provoking factors
Adnexitis is characterized as inflammation that occurs when the genital organs are damaged by the activity of pathogenic microflora. The causative agent of the infectious process can be:
- streptococci;
- coli;
- Trichomonas;
- mycoplasma;
- chlamydia;
- Koch's sticks.
When performing unprotected sexual intercourse, pathogenic microorganisms easily penetrate into the cavity of the female body, where, once in favorable conditions for their life, they actively launch their reproduction processes. It is also worth noting that the development of the inflammatory process can occur against the background of an exacerbation of another pathological process, for example, appendicitis.
The presence of a contraceptive device in the uterine cavity ensures unhindered penetration of infection into the cavity of the fallopian tubes, against the background of which an inflammatory process with a purulent nature can form not only in the appendages, but also in the ovarian cavity. In medical practice, many cases have been registered when bilateral adnexitis begins to develop after surgical intervention is performed in the form of a curettage procedure or abortion. Also, provoking factors contributing to the development of infectious pathology may include:
- diseases of a chronic nature that develop in the cavity of organs located in the pelvic area;
- regular change of sexual partner;
- decreased level of the body's immune defense system;
- having sexual intercourse during the menstrual cycle;
- getting hypothermia.
It is important to know that in most cases, sperm can spread infectious microorganisms, so both partners should undergo treatment.
Treatment of periadnexitis
Treatment of periadnexitis involves eliminating the root cause – adnexitis. In case of an acute inflammatory process, the patient requires inpatient conditions and bed rest. To eliminate inflammation, the patient is prescribed antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. If there is a purulent process, laparoscopy is performed: accumulations of pus are removed, and antibacterial drugs are injected directly into the affected area. After the operation, the patient is prescribed painkillers.
In case of chronic periadnexitis, the patient is prescribed balneological procedures, paraffin baths and physiotherapeutic procedures.
For periadnexitis caused by the tuberculosis bacterium, treatment is carried out under special conditions.
There are many folk recipes for getting rid of adnexitis - they are used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. For acute adnexitis, they are ineffective and unsafe. In folk recipes, decoctions of herbs that have an anti-inflammatory effect are widely used.
Symptoms of chronic periadnexitis
The chronic form of the disease can manifest itself in different ways. As a rule, it is characterized by a more blurred picture. Typically, women complain of pain in the lower abdomen, heavy periods, and periodic fever. Sometimes there is weakness, dizziness, loss of strength. If you have another disease and attempts to cure it, a weak tendency to improvement may be observed.
Sexual intercourse with chronic periadnexitis can result in a strong and acute attack of pain, which can only be relieved by taking sufficiently effective medications. It often becomes problematic to do gymnastics. Physical activity is difficult; when you suddenly try to straighten up or stand up, a strong feeling of heaviness appears. The menstrual cycle is disrupted, and the nature of the discharge can also periodically change.
Symptoms, causes and treatment of chronic periadnexitis
Chronic periadnexitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum that develops against the background of adnexitis, which has been going on for a long time and its symptoms cannot be completely and completely cured. After suffering from this most dangerous disease, approximately every fifth woman cannot become pregnant. Even if conception occurs, the presence of an inflammatory process in the uterus, appendages and peritoneum increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy tenfold.
General information
Often the disease leads to the development of many other negative consequences for the entire body. Firstly, there is a risk of pus accumulation and the development of sepsis. In addition, there is a tendency for periadnexitis to spread over a large area and for the inflammatory process to extend beyond the peritoneum. Many women experience disorders of the gastrointestinal tract or diseases of the urinary system. An adhesive process may also develop. As the exudate accumulates, it becomes thick and viscous. Strands are formed that change the location and functioning of organs. In addition, the appearance of adhesions is the main cause of pain in the pelvic area.
In most cases, patients are diagnosed with a chronic inflammatory process developing on the right side. Periadnexitis on the left is much less common. This is due to better blood supply to the right side of the pelvic cavity. However, the pathological process is not always one-sided. Without timely, effective treatment and properly selected medications, it affects the ovaries, fallopian tubes and peritoneum on both sides.
Causes of development and predisposing factors
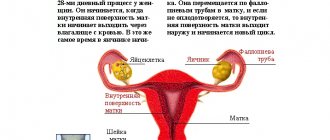
In healthy fallopian tubes and ovaries, sterile conditions are always maintained. Therefore, periadnexitis cannot develop without penetration of infection from adjacent areas (vagina or uterine cavity), or through blood and lymph from distant foci of chronic inflammation. When bacteria enter the mucous membrane of the fallopian tubes, the inflammatory process gradually spreads to the muscle layer, and then to the integumentary epithelium of the ovary, as well as to the peritoneum. During ovulation, pathogenic microflora affects the follicle or corpus luteum. Therefore, the infection begins to develop in the ovary.
It is worth noting that in a healthy body, the uterine appendages independently resist pathogenic microflora. For the development of infection, a woman must have certain predisposing factors. First of all, these will be:
Chronic adnexitis on the right
Doctors divide chronic adnexitis into subcategories depending on the location of the inflammation. Inflammation of the uterine appendages in accordance with this classification can be right-sided, left-sided and bilateral. We invite you to get acquainted with the features and signs of chronic adnexitis on the right.
Chronic right-sided adnexitis - what is it?
Chronic right-sided adnexitis is a prolonged inflammation of the paired uterine appendages (fallopian tube and ovary) on the right side. The pathology in many patients is accompanied by the active formation of adhesions, due to which the fallopian tube becomes obstructed and loses its functions. Against the background of chronic inflammation, purulent processes develop in the right ovary.
Signs of chronic adnexitis on the right
The main signs of chronic adnexitis on the right side:
- the menstrual cycle is disrupted;
- the abundance and duration of bleeding during menstruation increases;
- body temperature rises slightly;
- There is always a slight pain in the lower right abdomen.
A characteristic sign of chronic right-sided inflammation of the uterine appendages is alternating periods of attenuation and exacerbation of the pathology. Treatment is symptomatic. During remission, patients are recommended to undergo sanatorium treatment and physiotherapeutic procedures (mud therapy, UHF, magnetic therapy, suppositories).
Exacerbation of chronic right-sided adnexitis in its external manifestations is very similar to an acute inflammatory process. The woman experiences pain in the lower abdomen, increasing weakness, constant fatigue and irritability, a low-grade fever (37-37.5 °C), and serous or purulent discharge from the vagina may appear.
The most common symptoms of the disease
When periadnexitis becomes chronic, its manifestations will not be constant, but periodic.
Outside periods of exacerbation they are practically absent. The appearance of uncomfortable symptoms can be triggered by cyclical changes that occur before menstruation, as well as strong emotional or physical stress. The most common complaints of patients include: Another feature that chronic periadnexitis has is the occurrence of acute pain after sexual intercourse. Only strong painkillers can alleviate the condition in such a situation. In addition, pain or a feeling of heaviness may also occur during physical activity. Most often this happens when a woman suddenly stands up or straightens up.
It must be taken into account that depending on the type of disease, patients may have different localization of pain. For example, if periadnexitis develops on the right side, it is in this area that discomfort will occur. Outside the period of exacerbation, periodic pain is aching and of unclear localization.
With bilateral inflammation, discomfort occurs in the groin area on both sides, and then is projected onto the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity. If, in addition to periadnexitis, there are foci of infection or concomitant diseases in the body, they also have a significant impact on the clinical picture and symptoms.
Chronic left adnexitis
Chronic left-sided adnexitis - what is it?
What are the reasons for the development of chronic adnexitis on the left, what kind of pathology is it and can it be avoided? Such questions are often asked in the gynecologist's office. Chronic inflammation always develops against the background of an acute infection that is not detected in a timely manner. Rarely, but there are still cases when adnexitis initially becomes chronic, develops slowly and asymptomatically. The chronic form of the disease is characterized by periods of exacerbations and remissions. Exacerbation of chronic left-sided adnexitis can be recognized by high body temperature and increased pain inside the abdomen.
The inflammatory process in the fallopian tube and ovary located on the left leads to the appearance of adhesions and the proliferation of connective tissue. Because of this, the tube becomes obstructed and the woman develops partial infertility. The ovary also loses its functions. If the disease progresses further, then the egg on the left simply will not be able to come out and become available for fertilization. This is manifested by menstrual irregularities, heavy or, conversely, scanty bleeding.
Symptoms of left-sided chronic adnexitis:
- mild throbbing pain in the lower abdomen (they do not cause much discomfort to the patient);
- painful sensations also appear during sexual intercourse (the woman tries to prevent the sensation of pain, therefore she avoids sexual intimacy with her partner);
- when walking fast or having a bowel movement, discomfort occurs;
- body temperature increases (the symptom is observed only in some women, its appearance depends on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body);
- acute pain in the abdomen, which is projected to the sacral area (they appear in the form of attacks, short-term, disappear quickly);
- the volume of bloody discharge from the vagina increases, and the time of its appearance does not correspond to the phase of the menstrual cycle;
- general malaise and fatigue, the occurrence of depression.
The main danger of chronic left-sided adnexitis is the weak severity of its symptoms. Many women ignore the alarming signals of their body and consult a doctor only when the time for successful treatment has passed. Another serious problem is that due to chronic adnexitis, adhesions form on the left, which may be the cause of the symptoms described above. Every woman can prevent such unfavorable consequences of inflammation in the ovaries and uterine appendages. She should carefully monitor her health and pay attention in time to the signs that are characteristic of left-sided adnexitis.
Diagnostic measures
An appointment with a specialist always begins with a conversation. The doctor needs to clarify when and why the infection entered the body. During the conversation, it often turns out that the woman had an abortion or medical and diagnostic procedures. The specialist is also interested in whether the pain occurs on the right or left side, and what its nature is.
Next, a gynecological examination is performed. Palpation in the chronic form of the disease practically does not cause pain in the appendage area. However, when periadnexitis develops, the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries partially lose mobility. After the examination, the doctor prescribes a set of examinations:
Features of treatment
To cure chronic periadnexitis, simply eliminating the infection is not enough. Therapy for the disease should also eliminate the consequences of a long-term inflammatory process. Therefore, the patient is selected drugs that:
Conservative treatment, on the recommendation of a doctor, can be supplemented with massage, balneological procedures, and mud therapy. Also, chronic inflammation can be quickly eliminated by procedures using alternating magnetic and diadynamic current, ultrasound. The main purpose of prescribing these treatment methods for periadnexitis is to improve blood microcirculation in the pelvic organs. To complement the basic treatment, a specialist may recommend vaginal irrigation and the use of medicated tampons.
In some cases, chronic inflammatory disease requires surgical treatment. For example, with diffuse inflammation of the abdominal cavity, lack of expected results after drug treatment, or with rupture of the pyosalpinx. If the pathological process progresses and the ovaries or fallopian tubes become deformed, their removal is required. Sometimes in advanced cases it is impossible to do without removing the uterus.
Main symptoms and treatment for chronic adnexitis
Modern women have to deal with many gynecological diseases.
This fact is explained by unfavorable environmental conditions, constant stress, and physical activity. Untimely or incorrect treatment can lead to serious complications, including infertility. One of the most common and, by the way, very young diseases is chronic adnexitis. As with some other female ailments, chronic adnexitis often causes exacerbations, accompanied by very unpleasant symptoms. Signs of the disease significantly worsen the quality of life of representatives of the fair half of humanity, which affects the performance and, of course, the psychological state of patients.
How to cure chronic adnexitis? This question is asked by a considerable number of women who have had to experience all the “delights” of this unpleasant disease. To answer it, you should first of all find out what kind of disease it is and what its main manifestations are.
Symptoms
If a specialist suspects his patient has right-sided adnexitis, the symptoms and treatment of the pathological condition are determined by him individually.
Right-sided adnexitis in women is accompanied by such manifestations.
- Pain in the area where the fallopian tubes, ovaries, and sacrum are located (intensifies with bowel movements, heavy physical exertion, during sex and urination).
- High temperature (up to 39°C).
- Fatigue and general weakness.
- Menstrual irregularities (heavy or scanty periods).
The symptoms of right-sided adnexitis are taken into account by the doctor when drawing up a treatment plan.
Confirming the diagnosis of adnexitis using ultrasound is very simple.
Chronic adnexitis - what is it?
Adnexitis is a disease of the female genital organs.
In other words, this is the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the uterine appendages, or more precisely, in the ovaries and fallopian tubes. Most often, this disease becomes bilateral in nature and is accompanied by the accumulation of purulent fluid in the lumens of the appendages. Unfortunately, many women, when unpleasant symptoms occur, for some reason do not rush to see a doctor for help. Even such a symptom as severe pain in the lower abdomen is simply ignored, and most women prefer to cope with the manifestation of the disease on their own. However, such actions do not lead to anything good in the end. Taking any painkiller, a woman is at great risk of soon going to the doctor with a more serious problem of reproductive function.
Moreover, after a certain period of time, the chronic stage of the disease may begin, namely chronic adnexitis. It follows that the drug for the treatment of chronic adnexitis should be prescribed exclusively by a qualified specialist.
Acute right-sided adnexitis
Acute right-sided adnexitis is characterized by inflammation of the uterine appendages (ovaries, fallopian tubes) on the right. Against the background of the pathology, the patient experiences severe pain in the right lower abdomen, which can “respond” to the sacrum. Increased pain occurs at the time of defecation, intense physical activity, sexual intercourse or urination. Active inflammation leads to a sharp increase in body temperature to 38-39 °C. An indirect sign of right-sided adnexitis can be called fatigue and constant weakness. The disease is a consequence of infectious agents entering a woman’s body (chlamydia, staphylococci, mycoplasmas, streptococci, enterococci).
The preceding condition to the acute phase of uterine inflammation is subacute right-sided adnexitis. The symptoms are the same for both conditions. True, subacute inflammation is not so severe, and a woman may not pay attention to the first signs of a serious illness. An untimely visit to the doctor can cause the disease to enter the chronic phase, the treatment of which will be lengthy.
Types of chronic adnexitis and its symptoms
Probably the most dangerous symptom of chronic adnexitis is the “non-manifestation” of the disease in the initial stages. A woman can be sick, but have no idea about it. Only an exacerbation of the disease or a woman’s desire to become a mother can notify her of the presence of this disease.
Types of chronic adnexitis
Considering the fact that the initial stage of chronic adnexitis often does not manifest itself at all, and any symptom is perceived by a woman as a short-term phenomenon, all female representatives are recommended to undergo a medical examination at least once a year.
This will help avoid serious health problems such as ectopic pregnancy or infertility. It is worth taking into account that with chronic adnexitis, the clinical picture is quite ambiguous , and each symptom can mislead a woman. Therefore, the manifestation of any sign is a mandatory reason to consult a doctor.
Symptoms of chronic adnexitis
Treatment of left-sided adnexitis
Left-sided adnexitis: treatment of acute and chronic forms of the disease
Therapy of acute forms of adnexitis is carried out using the following drugs:
- anti-inflammatory;
- painkillers;
- antimicrobial and antibacterial.
Basically, the fight against acute adnexitis is carried out using antibacterial drugs from the following list:
- tetracycline;
- ampicillin;
- metronidazole;
- gentamicin;
- ofloxacin;
- erythromycin.
To eliminate acute inflammation in left-sided adnexitis, doctors most often use antibiotics that have a long half-life. If the disease is complicated by purulent processes, the course of therapy includes antibacterial drugs of different groups (for example, penicillins and aminoglycosides). Medicines can be taken orally or intravenously. At the initial stage of therapy, antibiotics are injected into a vein, and subsequently replaced by tablets with a similar effect.
Answering the question “how to treat chronic left-sided adnexitis,” gynecologists draw patients’ attention to the fact that against the background of constant inflammation, adhesions can form, which only complicate the treatment process. The adhesive process develops in the advanced stage of chronic adnexitis and provokes obstruction of the uterine tubes.
Quite often, girls and women have problems related to the reproductive organs. One of the common diseases, which is diagnosed mainly in representatives of the fair half of humanity aged 20 to 30 years, is adnexitis, which can be left-sided or right-sided.
Exacerbation and consequences
If a woman feels that the pain intensifies during sexual intercourse, then this is nothing more than an exacerbation of adnexitis. In addition to the main signs characteristic of the disease, a woman is also accompanied by such a symptom as increased pain during menstruation .
You cannot hesitate in such a situation and the help of a qualified doctor is necessary. The specialist, having studied the patient’s condition, prescribes effective and competent treatment for exacerbation of chronic adnexitis. If a woman nevertheless continues to ignore her painful condition and does not begin to treat the developing pathology, then the inflammation, in simple words, will “move” from the appendages to other pelvic organs. As a result, the patient may experience complications such as:
Not treating the disease and not engaging in medical intervention leads to more serious consequences, which can only be dealt with by a surgical procedure aimed at removing some of the uterine appendages.
Acute left-sided adnexitis
Acute left-sided adnexitis is active inflammation of the uterine appendages on the left side. Its characteristic features:
- fever, chills;
- intoxication of the body;
- a slight increase in temperature (in some patients this symptom is absent);
- weakness and malaise;
- disturbances in the functioning of other internal organs and systems of the female body.
If the acute pathological process with left-sided adnexitis is severe (with the formation of a tubo-ovarian abscess, rupture of the ovary or fallopian tube, the development of inflammation in the peritoneum), then upon palpation the doctor detects protective muscle tension of the peritoneal walls on the left. Due to the long-term lack of treatment for acute left-sided adnexitis, the disease becomes chronic.
Adhesive periadnexitis
Adhesive periadnexitis is a very unpleasant and very dangerous disease for a woman’s health. Firstly, an infection can get into the ovarian tissue, and purulent contents often accumulate in these female organs. Secondly, many internal organs malfunction.
Possible complications of chronic adnexitis
Quite often, periadnexitis becomes chronic as a result of improper or interrupted treatment. Ultimately, this leads to the fact that chronic periadnexitis requires surgical intervention to remove the pus accumulated in the pelvic organs. The consequences may be the most unexpected and most disastrous, so the disease will not tolerate self-treatment.
Causes of the disease
The causes of adnexitis have been studied for a very long time by many luminaries of medicine, but almost all of them came to the conclusion that in most cases this disease appears due to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms onto the mucous membrane of the female genital organs. Among the main causative agents of the disease are:
In addition, there is an additional list of real causes and factors that provoke the development of the described pathology. This:
Treatment of chronic adnexitis
If the treatment of acute adnexitis is carried out necessarily in a hospital, then with chronic adnexitis the first step is to find out the cause of the disease. It follows that the treatment of chronic adnexitis requires the use of the following types of therapy:
Treatment of the disease should begin only after a comprehensive medical examination. The specialist must refer the patient to undergo certain tests and only after that a particular drug is prescribed.
Antibiotics for chronic adnexitis are prescribed strictly by a doctor and are included in therapy when acute adnexitis becomes chronic. It should be noted that any drug prescribed by a doctor should not be skipped, since such actions can lead to unsafe complications and an increase in treatment time. To achieve a quick and positive result, the treatment regimen for adnexitis must be strictly controlled by both the doctor and the patient himself.
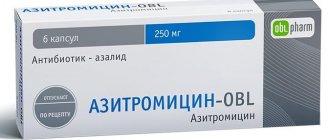
An antibiotic is the main drug used by the patient during the treatment of chronic adnexitis. The following medications are used:
In most cases, the antibiotic is administered intravenously and always in a hospital setting. After the patient feels relief, the doctor prescribes medications in the form of tablets. During illness, it is very important for a woman to support her body by taking vitamin complexes.
Using candles won't hurt either . This drug helps reduce pathogenic microflora to a minimum and relieve the inflammatory process. The main advantage of this remedy is the lightning-fast reach of foci of inflammation.
In addition to drug therapy, the patient needs to undergo physiotherapeutic procedures that reduce existing inflammation and stop the development of adhesions. This procedure also eliminates such an unpleasant symptom of chronic adnexitis as pain. You should not refuse such an effective event as taking therapeutic mud baths.
Basic principles of therapy
In most cases, treatment of bilateral inflammation of the appendages is carried out in a hospital setting under the supervision of qualified specialists. But, if salpingoophoritis was diagnosed at the initial stage of its development, then a course of treatment can be carried out at home.
After the patient has completed the full course of diagnostic measures, the doctor prescribes the most effective treatment regimen with antiviral and antibiotic drugs for 10-14 days. Among the antibiotics, depending on the type of infection, penicillins are prescribed - Bicillin-5, macrolides - Azithromycin, Erythromycin, tetracyclines - Tetracycline, fluoroquinolones - Oflaxacin. Self-medication in the development of such a pathology can result in disastrous consequences, so the elimination of the disease should be done under the guidance of the attending physician.
In the process of suppressing infectious microorganisms, the vital activity of which can lead to irreparable impairment of the functionality of the reproductive organs of the female body, one should not forget about strengthening the immune defenses. Therefore, the complex of therapeutic treatment must necessarily include taking immunostimulating drugs, vitamin complexes and probiotics.
As an addition to the main therapy, the following techniques may be prescribed:
- electrophoresis, or vibration massage;
- treatment in a sanatorium-resort area;
- gynecological massage sessions;
- regular ultrasound diagnostics.
Preventive actions
Every woman is simply obliged to carefully monitor her women's health, so that later she does not have to ask the painful question of how to treat chronic adnexitis. It is very important to consult a gynecologist at the first news of the disease. The acute stage of the disease detected in time is treated much faster and will prevent the development of the chronic stage .
If a woman does receive a diagnosis of “chronic adnexitis,” she should:
A patient who follows these simple, but very important and necessary rules, experiences a stable remission of the disease.
Chronic adnexitis is not a death sentence, but if you do not follow doctors’ recommendations or self-medicate, you can end up with very serious complications , which will be very, very difficult to get rid of. Therefore, a visit to the doctor and timely treatment is the first step towards a healthy and pain-free life.
Source