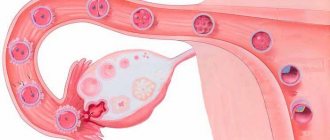
Adnexitis or salpingoophoritis is an infectious inflammation of the uterine appendages. The development of the disease begins with the infection entering the appendages, where, after settling on the mucous membrane of the fallopian tubes, an inflammatory process is formed, involving the epithelial (outer) walls of this organ.
Inflammation of the uterine appendages is a common ailment. Many women know firsthand about chronic inflammation of the appendages (adnexitis), experience pain for years, but ignore the disease and do not consult a gynecologist. Is adnexitis so harmless? We suggest you figure it out together.
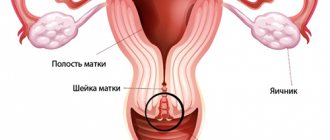
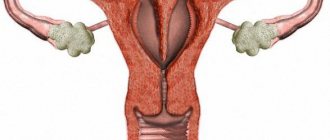
The uterine appendages include:
- ovaries - their isolated inflammation is called oophoritis,
- fallopian tubes - inflammatory changes in these structures are called salpingitis.
Classification of adnexitis:
- one-sided - left-sided or right-sided,
- bilateral - the disease develops simultaneously on both sides of the uterus, left and right.
By formation:
- primary - the infection reaches the fallopian tubes and ovaries on its own,
- secondary - the disease develops against the background of other infectious diseases, when pathological microorganisms spread to the uterine appendages from neighboring organs.
By type of flow:
- spicy,
- chronic.
Chronic adnexitis differs from acute adnexitis in less severe symptoms. However, curing this type of pathology is much more difficult.
Content
Definition and general information [edit]
Salpingoophoritis (adnexitis) is an infectious-inflammatory process of nonspecific or specific etiology in the fallopian tubes and ovaries. This is the most common pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
Oophoritis is almost always combined with salpingitis.
• Acute nonspecific (or specific) salpingoophoritis.
• Exacerbation of chronic nonspecific salpingoophoritis.
• Chronic nonspecific salpingoophoritis.
Etiology and pathogenesis[edit]
Nonspecific (nongonorrheal) salpingo-oophoritis is caused by pathogenic and opportunistic pathogens. Mixed infection is more common.
Initially, all signs of inflammation appear on the mucous membrane of the fallopian tubes (endosalpinx): hyperemia, microcirculation disorders, exudation, edema, cellular infiltration. The inflammation then spreads to the muscular lining of the fallopian tube. The tube thickens and lengthens, palpation becomes painful. Microorganisms, together with the contents of the tube, enter the abdominal cavity, affecting the serous cover of the tube and the surrounding peritoneum. Perisalpingitis and pelvioperitonitis occur. After ovulation, pathogens infect the granulosa membrane of the follicle and an inflammatory process develops in the ovary (oophoritis). When suppuration occurs, a tubo-ovarian formation occurs. An adhesive process develops very quickly in the ampullary region and the mouth of the fallopian tube due to thickening of the fimbriae and exudation. Exudate accumulates in the tube with the formation of hydrosalpinx. The adhesive process in the pelvis occurs as a result of the “gluing” of inflammatory fallopian tubes with the peritoneum of the retrouterine space, intestinal loops, and vermiform appendix (secondary appendicitis often develops).
Clinical manifestations[edit]
The first symptom of acute salpingoophoritis is severe pain in the lower abdomen, accompanied by an increase in body temperature to 38 ° C (sometimes with chills). Dysuria, bloating and dyspepsia are also possible. The patient's condition is usually of moderate severity, with weakness, headache, and loss of appetite.
With adequate treatment, acute inflammation ends in recovery. Sometimes the disease takes on the character of a subacute or chronic process with frequent exacerbations. During an exacerbation, the body temperature is low-grade or normal, and dull, aching pain in the lower abdomen and lower back is bothersome. Often complaints of dyspareunia and infertility.
Acute salpingitis and oophoritis: Diagnosis[edit]
In the anamnesis, attention is paid to complicated childbirth, abortion, intrauterine invasive manipulations, curettage, HSG (Hysterosalpingography), hysteroscopy, use of an IUD (intrauterine contraception), casual sexual intercourse, etc.
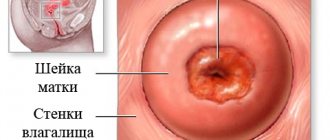
In acute inflammation, bimanual examination is always painful (especially in the area of the appendages), since the pelvic peritoneum is involved in the process (sometimes symptoms of peritoneal irritation are determined), the appendages are not clearly defined, the tissues in the projection of the appendages are swollen, with a pasty consistency. When examined using speculum, inflammatory endocervicitis and serous-purulent discharge from the external pharynx are often detected. In the chronic process, the appendages are also painful, but to a lesser extent, sclerosis and fibrosis of the fallopian tubes with the formation of an adhesive process limits their mobility, movements behind the cervix are painful.
Bacterioscopic and bacteriological examinations of discharge from the cervical canal, vagina and urethra are carried out to detect pathogens and determine their sensitivity to antibiotics.
Blood tests show nonspecific changes: in the acute process – leukocytosis, a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left, an increase in ESR, dysproteinemia with a predominance of globulin fractions, an increase in the content of C-reactive protein; in a chronic process - only an increase in ESR.
There are no clear ultrasound signs of salpingoophoritis. Sometimes you can visualize thickened fallopian tubes and suggest an adhesive process in the pelvis. With pelvioperitonitis, a small amount of fluid is found behind the uterus. Tumor-like tubo-ovarian formations can also be visualized. CT or MRI are sometimes used, especially in the differential diagnosis of ovarian tumors.
Differential diagnosis[edit]
Acute salpingoophoritis must be differentiated from acute surgical diseases (acute appendicitis, peritonitis, intestinal tumors, intestinal or renal colic). Laparoscopy allows for early topical diagnosis and selection of the correct treatment tactics.
Acute salpingitis and oophoritis: Treatment[edit]
During a chronic process or during the rehabilitation period after an acute process, physiotherapeutic methods are used: ultra-high frequency therapy (UHF therapy), magnetic therapy, electrophoresis with zinc, magnesium, hyaluronidase, etc., diadynamic currents, sanatorium treatment (radon baths and irrigation, thalassotherapy) .
Classification of salpingoophoritis
Salpingoophoritis has its own, albeit minor, classification
According to its course, this inflammatory disease of the appendages is divided into:
- Acute salpingoophoritis is a process that arose for the first time when the woman had never had such a process in her anamnesis.
At the same time, as it seems to many, simple salpingo-oophoritis, in which remission and exacerbation can alternate very often, is a fairly common cause of infertility, which is not always possible to cure even by the best and eminent specialists in the field of obstetrics and gynecology.
According to the localization of the pathological process, salpingoophoritis can be:
- One-sided, when inflammation affects only the right or left appendages.
- Bilateral, when the process develops both on the right and on the left.
There are also cases of inflammatory processes of these anatomical structures separately. In this case, we can talk about:
- Salpingitis is an inflammatory process involving the fallopian tube.
- Oophoritis, a process in which only the ovary becomes inflamed.
Due to the fact that such structures are anatomically closely interconnected, isolated forms of inflammation of them separately are quite rare, and often we are talking about a combined process in the form of inflammation of both the fallopian tube and the ovary.
Also, such a pathological process of the appendages can be divided relative to the flora that caused this pathology:
- Specific salpingoophoritis is a process caused, for example, by gonorrheal flora.
- Nonspecific adnexitis is a process caused by representatives of opportunistic and pathogenic flora. For example, it can be ureaplasma, mycoplasma and others.
Salpingo-oophoritis: uranium 10
One of the main systems by which salpingoophoritis is also classified is the international classification of diseases, hence the abbreviation “ICD”, or, more precisely, its tenth revision.
- Acute salpingitis, as well as oophoritis, are coded as N70.0.
- Chronic forms of this pathological process of the uterine appendages are coded as N70.1. Hydrosalpings also belongs to this section.
- Unspecified forms of inflammation of the appendages are classified as N70.9.
The etiological beginnings of such a process as inflammation (salpingoophoritis) of the female reproductive system.
In fact, there are currently quite a large number of reasons for the development of adnexitis. They can be associated with spontaneous onset due to the addition of pathogenic or opportunistic flora, or they can become a consequence of iatrogenicity, that is, the result of medical invasive interventions. These etiological factors include:
- Infections that are transmitted during sexual activity. As everyone now knows, unprotected sexual intercourse, that is, sex without a condom, is the cause of the transmission of dangerous infections such as human immunodeficiency virus, syphilis, and viral hepatitis. However, gonococci that cause gonorrhea, trichomonas that provoke trichomoniasis, chlamydia that manifest chlamydia, and so on can also be transmitted.
- Decreased immunity. These can be viral processes, and conditions after somatic pathologies caused by an inflammatory process, banal hypothermia, conditions after the use of drugs that reduce immunity (glucocorticoids), HIV.
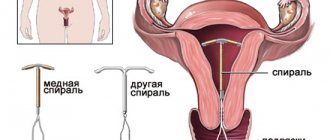
- Intrauterine contraceptives. This group includes the well-known spirals, which are installed directly into the uterine cavity.
- Surgical interventions that are introduced into the uterine cavity, for example, abortion by curettage of the uterine cavity, diagnostic curettage, hysteroscopy.
- The scourge of our time, the incidence of which is growing inexorably, appears to be tuberculosis, which can affect not only the respiratory system, as we all used to believe, but also the reproductive system, causing tuberculous salpingoophoritis, causing quite persistent infertility.
Adnexitis is a gynecological disease in women
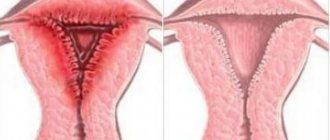
The gynecological disease Adnexitis is an inflammation of the uterine appendages caused by various infections, as shown in the photo.
Often the etiology of the disease is the effect of streptococci, staphylococci or E. coli on the woman’s genitals.
Inflammation of the appendages may also occur if infectious agents enter. This type of infection is transmitted sexually by species such as gonococci, which causes gonorrheal adnexitis. A rare cause of inflammation can be a tuberculous process that spreads through the vessels of a woman’s body.
It is most common in women aged 20-45 years. The female disease Adnexitis is considered dangerous, since if not treated on time, it leads to more serious health consequences and ultimately provokes infertility or ectopic pregnancy. But even when pregnancy occurs, newborn babies in the first half of the year often suffer from Thrush or Candidiasis.
Salpingoophoritis: symptoms, treatment
Inflamed fallopian tube, ovary: salpingoophoritis and its clinical picture.
The main symptoms of inflammation of the appendages include the following nuances of the health of the female body:
- Hyperthermic reaction. This term refers to an increase in body temperature. It can be as low as low-grade fever, increase slightly to 38 degrees, or it can manifest as massive hyperthermic syndrome with increases in readings up to 40 degrees. It all depends on the extent and prevalence of the process, as well as on its neglect, that is, how timely or untimely qualified medical care was provided.
- One of the most common symptoms of inflammation “female style” is pain. With adnexitis, which has sluggish characteristics, this symptom may be the only one by which one can suspect the presence of a pathological process in the gynecological area. The pain can be localized either on the right or left, or have a bilateral location. Its intensity can also vary from minor discomfort to severe pain that disrupts the woman’s condition.
- The presence of discharge of varying intensity. Since the uterine appendages and the reproductive organ itself are closely interconnected, infection from the tube can easily enter the uterus, and inflammation of the uterine mucosa can also develop, as a result of which there may be discharge with an unpleasant odor, yellow, greenish in color.
- General weakness, which is characterized by intoxication in the body from the functioning and waste product of pathogenic flora, which caused such inflammation of the female appendages.
However, even the presence of some symptoms that are characteristic of adnexitis does not at all mean the presence of this particular pathological condition, since such symptoms can occur in many processes, including those that require immediate surgical intervention. Only doctors can differentiate the symptoms and make the correct diagnosis, so if any complaints appear, you should not make a diagnosis and treat it yourself, but turn to specialists who will do everything for you.
Causes
Symptoms and causes of Adnexitis in women may vary depending on the infection that caused the inflammatory process, as well as the conditions for the development of pathogenic microflora. In medicine, there are several risk factors that can contribute to the development of pathology:
All of these factors contribute to another common condition in women: thrush. which may occur against the background of Adnexitis. Treatment of thrush is carried out on an outpatient basis; you can choose effective anti-thrush tablets for women. who can cope with the disease even in 1 day.
Often, the development of salpingoophoritis is associated with concomitant problems, such as ARVI, herpes, influenza, or appears as a result of indiscriminate use of hormonal drugs.
Sodium thiosulfate is used to cleanse the body; you can read reviews from doctors here.
Psychosomatics plays an important role, that is, experts believe that internal psychological factors are the cause of the development of the disease. A woman to some extent feels flawed or cannot understand how to behave with a man and thereby realize her feminine qualities. As a result, she invents a disease for herself on a psychological level. Then chronic Adnexitis is treated not only with medications, but also with regular visits to a psychologist.
Prevention of salpingoophoritis
Prevention of salpingoophoritis is the main direction that should be used to prevent not only the inflammatory process of the fallopian tubes and ovaries, but also to prevent the development of complications of such a process, which can literally ruin the entire future life of a representative of the fair sex. Such consequences include infertility, which, unfortunately, can be provoked by what some women consider to be a harmless condition such as salpingoophoritis.
Complications of salpingoophoritis
Adnexitis is a rather dangerous pathological process, neglect of attention to which can lead to quite serious complications of salpingoophoritis.
The woman should be hospitalized in the gynecological department, where doctors will prescribe competent antibiotic therapy, anti-inflammatory treatment, resorptional and antihistamine therapy. Nursing care for salpingoophoritis in a hospital setting will ensure timely and qualified administration of both intramuscular and intravenous injections, as well as intravenous infusions, which are so necessary for the treatment of the inflammatory process of the appendages.
Diagnostics and diagnosis
Establishing a diagnosis of salpingoophoritis in some cases can be a very difficult task, since at an early stage of development, the symptoms are the same as those of colpitis, endometriosis, hydrosalpinx or metroendometritis. Therefore, differential diagnosis is used to help recognize or eliminate concern. A complete blood and urine test is performed, an ultrasound and an MRI are prescribed.
A smear of more than 100 leukocytes indicates that a woman has an inflammatory process in her body. To confirm, the doctor can use an ultrasound scanner to check for echo signs of pathology.
Based on the protocol of the examinations, the doctor makes a conclusion and establishes a diagnosis.