- Swelling in the affected area
- Increased temperature in the affected area
- Skin tingling
- Skin redness
- Redness of mucous membranes
Hyperemia is a condition caused by excessive filling of the capillaries with blood, which as a result causes the development of redness in a certain area.
Mostly skin hyperemia is noted, but any mucous membrane, any part of the body and any organ in the human body can be susceptible to this. This indicates that a person may have such phenomena as:
- conjunctival hyperemia;
- throat;
- cervix;
- vagina;
- stomach, etc.
It turns out that this phenomenon in itself is not a disease, but is a symptom of a particular disease. So, if a person has hyperemia of the pharynx, most likely, we are talking about a viral or bacterial pathology. The same can be said about redness of the cervix, vagina, stomach, throat, etc. That is, redness in the area of a particular organ is a consequence of the inflammatory process in it.
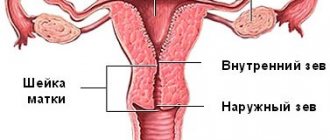
Chronic inflammation of the cervix: symptoms and treatment
Every woman wants to be healthy, but women's health in the genital area is perhaps the most vulnerable place.
According to statistics, various inflammatory processes in the cervix occur in every third woman of childbearing age. This is facilitated by various infections and a woman’s lack of attention to her health, and simply ignoring a routine medical examination, because often such inflammatory processes are asymptomatic and can only be detected during an examination by a doctor.
Inflammatory processes in the cervix can be triggered by various reasons and occur in different forms. But all such pathological processes are united by one name: “cervicitis”.
Causes of cervicitis
The causes of inflammation of the cervix can be very diverse. They lie in specific and nonspecific pathogens.
The most common causes of such inflammation are specific infections. These include : trichomonas, mycoplasma, syphilis, chlamydia, gonococci and herpes.
All these pathogens enter the female genital area directly during sexual intercourse.
Less common factors that provoke cervicitis are nonspecific conditionally pathogenic microflora.
These microflora include staphylococci, streptococci, fungi of the genus Candida, and E. coli. Such conditionally pathogenic microflora is present in the body of every woman; such organisms begin to actively develop only in favorable conditions for them, when the protective functions of the body are reduced.
Reasons that can cause pathological processes in the female genital area also include abortion, miscarriage, curettage, which can also injure the cervix and cause pathological changes in its mucous membrane.
The rarest factors that can provoke cervicitis include allergic reactions to latex, various spermicides and all kinds of intimate hygiene products. But such causes are very rare, and only in a very advanced stage can they cause cervicitis.
If detected untimely and at an advanced stage, such cervicitis can transform into chronic inflammation of the cervix. And it is already much less treatable.
Therefore, it is extremely important to carefully monitor your health, consult a doctor on time and undergo a medical examination even without any complaints in the sexual sphere.
What do you need to remember?
Based on information about the impact of pathology on the body, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- Cirvicitis is one of the most common gynecological diseases in women.
- Infections are the main cause of pathology.
- Severe symptoms allow you to consult a doctor in a timely manner.
- The main treatment is to eliminate the cause of inflammation.
- Cervicitis is dangerous for pregnant women.
- Prevention of sexually transmitted infections will help avoid illness.
Used Books
- Women's consultation. Management, Editor: Radzinsky V.E. 2009 Publisher: Geotar-Media.
- Infections in obstetrics and gynecology. Makarova O.V., Aleshkina V.A., Savchenko T.N. Moscow., Medpress-inform, 2007, 462 p.
- Clinical recommendations. Obstetrics and gynecology. Savelyeva G.M., Serov V.N., Sukhikh G.T. 2009 Publisher: Geotar-Media.
- Medicines used in obstetrics and gynecology /edited by V.N. Serova, G.T. Sukhikh / 2010, ed. 3, corrected and supplemented - M.: GEOTAR-Media.
- Infections in obstetrics and gynecology. Editors: Makarov O.V., Aleshkin V.A., Savchenko T.N., 2007, Publisher: MEDpress.
- Colposcopy. Prilepskaya V.N., Rogovskaya S.I., Mezhevitinova E.A. 2006 Publisher: MIA.
- Preventive examinations and cytological screening of the cervix. Polonskaya N.Yu., Yurasova I.V., Egorova O.V. 2008 Publishing.
Symptoms of cervicitis
Symptoms and signs of inflammation can be both pronounced and hidden.
Signs of uterine inflammation are as follows:
- Painful sensations in the lower abdomen. Such pains are predominantly aching and pulling in nature. They are similar to period pain. The severity of such pain depends on the individual characteristics of the female body, because everyone has a different pain threshold, and on the severity of the disease.
- Discharge mixed with pus or mucus. Such discharge can also be strong or barely noticeable.
- Pain when urinating.
- Discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse.
Such signs of the disease can be detected by the woman herself. When examined by a doctor, an experienced doctor will visually determine the following signs of inflammation of the uterus:
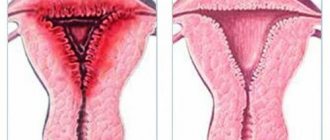
- Redness of the cervix.
- Loose cervix.
- Swelling of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal.
- Small ulcers and hemorrhages of the organ mucosa.
The severity of the symptoms of this disease also completely depends on the pathogen that provoked the disease. This is how the disease caused by gonococci develops most violently and clearly.
In this case, all of the above symptoms will be very pronounced, and it is simply unrealistic not to notice the pathological process in the female body.
There will be pain and discharge and hyperemia of the cervix . Gonococci are the cause of a loose cervix.
But if the disease is caused by chlamydia, then the symptoms will not be so pronounced: they will be weak, or the disease may be completely asymptomatic.
Trichomonas manifest themselves in the form of small ulcers and hemorrhages on the mucous membrane of the cervical canal.
If the pathology is caused by a herpetic virus, then upon examination a bright hyperemia of the cervix with many ulcers and hemorrhages of the mucous membrane is visualized.
Clinical picture
Since hyperemia of the skin of the face and mucous membranes is not a disease, the symptoms will depend on the location of the areas of redness, as well as the reasons that caused it.
General symptoms of this condition are manifested by the appearance of redness on the skin or mucous membranes. Other symptoms that may occur are:
- feeling of local temperature increase;
- feeling of tension in the area of redness;
- slight tingling;
- sometimes tissue swelling.
In addition, the symptoms of the pathological condition are complemented by the symptoms of the underlying disease that caused it. In particular, if a person has conjunctival hyperemia, he most likely has an inflammatory process, which is characterized by the following symptoms:
- lacrimation;
- pain in the eyes;
- discharge of mucus or pus.
Conjunctival hyperemia is often a symptom of conjunctivitis, as well as an allergic reaction or exposure to a mechanical irritant (sand, etc.) on the mucous membrane.
As mentioned above, an inflammatory process can also cause redness. Women experience hyperemia of the vaginal mucosa, but in this case they are worried not only about redness in the vaginal area, but also other symptoms, such as:
- itching;
- unpleasant odor;
- swelling of the labia;
- discharge of a different nature, different from the norm.
Mostly, hyperemia of the vaginal mucosa indicates the presence of a bacterial infection or STI. Therefore, such a woman should undergo a vaginal smear for microflora to identify the causative agent of the pathology.
Sometimes vaginal redness can be the result of an allergic reaction, for example to some medications or the latex used in condoms. Usually in this case, vaginal redness occurs immediately after using the allergic agent. Also, redness of the vagina can be a consequence of rough sexual intercourse - in this case, treatment is not required, only sexual abstinence for several days is indicated.
Redness of the cervix, which can be determined by a doctor during a gynecological examination, can be evidence of several pathologies. In particular, redness of the cervix occurs when erosion begins, as well as during inflammatory processes in this organ. If the doctor detects redness of the cervix during examination, taking a smear for culture and cytology is indicated. Additional research methods are also indicated to exclude or confirm the inflammatory process.
Additionally, redness of the cervix is a natural occurrence for women during pregnancy. In this case, there is no need to worry - the redness will go away on its own after delivery.
Diagnostic methods
This problem can be diagnosed only by examination by a doctor and after all the necessary tests and manipulations.
First, you will need to be examined by a gynecologist, who can often visually see this problem.
But in order for the treatment of such a disease to be as effective as possible, it is necessary first of all to identify the cause of the disease. After all, only after eliminating the cause is it possible to completely cure the disease.
After a visual examination using gynecological speculum, an experienced doctor will definitely prescribe additional tests: smear microscopy, bacterial culture, PCR.
A cytogram of inflammation will accurately show the causative agent of the disease , and accordingly the treatment will be more accurate. A cytogram refers to the taking and analysis of a scraping from the cervical canal.
In this case, the contents of the canal mucosa are taken and examined in detail.
The cytogram will accurately show the contents of the taken smear, detect pathogenic microflora, determine the presence or absence of inflammatory secretions, cancer cells, show the number of leukocytes, erythrocytes and other blood cells (if any), and even accurately show the correspondence of the epithelium to the age characteristics of the woman.
You should prepare for the cytogram. To do this, it is necessary not to do any douching for 2-3 days, not to use suppositories, creams, or suppositories. A few days before the scheduled test, you should abstain from sexual intercourse. Also, a few days before the study, you must stop taking hormonal contraceptives.
It is best to conduct this study in the middle of the cycle, on days 14-15.
Prevention
Let's consider preventive measures:
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules.
- Refusal of promiscuity, use of barrier methods of contraception.
- Regular visits to the gynecologist - twice a year.
- If possible, avoid mechanical influences: abortions, installation of spirals.
- Strengthening the immune system.
Inflammation of the cervical canal is a common but solvable problem. Timely effective treatment will allow you to get rid of the disease and avoid consequences.
Treatment of cervicitis
To know how to treat cervical inflammation , it is necessary to accurately determine the causative agent of the disease. Depending on the cause of cervicitis, treatment consists of taking antibacterial or antiviral drugs.
If the disease is caused by infections , then treatment with sumamed, monomycin, maxaquin, erythromycin and other antibacterial drugs would be advisable.
If the disease is caused by fungi of the genus Candida, then antibacterial therapy is not prescribed at all; it would be appropriate to take antifungal drugs such as Diflucan and its analogues.
Very often, with this disease, doctors prescribe suppositories for cervical inflammation called terzhinan. This is a complex preparation of local action. Chlorophyllipt, silver nitrate, and dimexide are also used for topical use. The vagina is treated with such solutions.
The most difficult to treat are inflammatory processes of viral etiology. Typically, such problems are caused by the genital herpes virus. Such treatment will be the longest and will require the use of antiviral drugs, immunostimulating agents and the use of immunoglobulin.
Types of infection
Cervicitis has several varieties.
Let's talk about each of them.
Spicy
This type of disease is characterized by rapid development. Infectious and inflammatory processes are pronounced, in addition, almost all the symptoms of the disease can often be present at the same time.
Chronic
It can occur against the background of other inflammatory diseases or develop from untreated acute cervicitis.
Typically, chronic cervicitis is accompanied by scanty mucopurulent or simply mucous discharge, and slight swelling of the cervical tissue.
In the case of a prolonged course of the chronic stage of cervicitis, the cervix begins to thicken, and erosion often occurs.
Purulent
Based on the name, it is clear that in this case the inflammation is accompanied by copious mucopurulent discharge.
The cause of their occurrence may be male urethritis caused by sexually transmitted diseases. Most often, this type of cervicitis occurs when the patient has gonorrhea.
Atrophic
With atrophic cervicitis, inflammation is accompanied by thinning of the cervical tissue. In the case of advanced forms of atrophy of various parts of the genital tract, urination disorders are often observed, so in addition to the gynecologist, it is imperative to visit a urologist. Most often, this type of disease develops from a chronic form.
Viral
Caused by diseases of viral etiology (human papillomavirus or genital herpes). Its treatment, as a rule, is complex and quite difficult: the woman is prescribed antiviral drugs, immunomodulators, and irrigation of the uterine cavity with special compounds is also necessary.
Bacterial
With bacterial cervicitis, a strong inflammatory reaction is not observed, although there is still a disturbance in the vaginal microflora. It can be caused by a bacterial infection - colpitis, gonorrhea, vaginosis, etc.
Cystic
The most unpleasant type of cervicitis. Its cause is considered to be a combination of several infections (streptococci, staphylococci, trichomonas, chlamydia, etc.). The result of this “bouquet” of diseases is the proliferation of columnar epithelium on the surface of the uterus and its complete overgrowing with cysts.
According to experts, in this case the cervix is an unpleasant sight, because it is almost completely covered with countless cysts. It is often combined with erosions.
Nonspecific cervicitis
This species is not associated with any sexually transmitted infections. Most often occurs in the presence of bacterial vaginosis. Nonspecific cervicitis occurs, usually in young women, and is characterized by fairly copious purulent discharge. Moreover, as in other cases, inflammation begins due to a violation of the natural microflora of the vagina.
What is it, what is it dangerous?
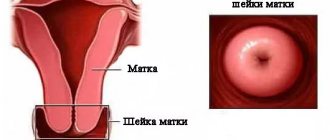
Hyperemia of the cervix (on the mucous membrane) is a pathological redness. It can be caused by two reasons (one of the following):
- too much blood “flows” into the arterial vessels (the so-called active form of the pathology);
- in the venous vessels the blood “stagnates” (passive form).
Hyperemia is traditionally divided into:
- Local - the cervix is hyperemic only in a separate area.
- Generally, not only the cervix changes color, but also the vagina.
Hyperemia can be chronic or acute. Periods of exacerbation and remission are typical for chronic pathology. For acute hyperemia, short periods of very intense redness of the cervix are common.
Why does the cervix turn red?
Redness on the cervix may occur when:
- the body becomes infected with some kind of infection;
- mechanical injuries occur. You don't have to fall on your stomach to get them. Injuries may appear after examination by a gynecologist or after sex. Such “traumatic” redness usually does not pose any danger and does not require any treatment. After just a few days it disappears on its own;
- pathological lengthening (elongation) or prolapse (prolapse) of the uterus occurs;
- problems with the heart and blood circulation arise;
- blood vessels are compressed by the neoplasm;
- varicose veins appeared in the pelvic area;
- the pelvic organs are overcooled. This often happens when a woman sits on something cold for a long time;
- the body is overheated. Pathology can, for example, appear if a woman works in any industry in extremely hot conditions;
- the lungs or bronchi “stutter”. If there are problems with these respiratory organs, the level of hemoglobin also usually increases;
- increased blood pressure;
- allergic reaction to hygiene products or any medications;
- hormonal changes occur. That is why hyperemia is typical for pregnant women, maturing teenage girls, as well as women who are about to menstruate or menopause;
- not everything is in order with the blood-forming organs;
- constipation appears. Usually such constipation goes along with intra-abdominal hypertension and congestion in the veins.
Preventive measures
To prevent the cervical mucosa from turning red, a woman should:
- try not to expose your genitals to sudden temperature changes;
- Stop using any hygiene products that contain potential allergens. We are talking primarily about odorous substances and alcohol;
- wear loose underwear made of natural fabric;
- wash regularly;
- do not forget about charging;
- eat more vegetables to prevent constipation;
- stop eating fatty, salty and spicy foods. You will also have to exclude alcohol, coffee, strongly brewed tea and sweets;
Hyperemia of the uterine cervix often does not manifest itself or has vague symptoms. That is why, in order to detect it in time, you need to be checked annually by a gynecologist.
Hyperemia may not seem like a serious problem. However, if this “frivolous” problem is not dealt with, it can lead to serious illnesses. Therefore, at the first signs of it, you should urgently go to the doctor.
Hyperemia is not a separate disease, but is considered only a symptom. This pathological process can indicate the development of serious diseases, as well as be a temporary physiological or borderline phenomenon, which does not cause harm to health.
When there is redness of the mucous membrane of the cervical uterus, objective symptoms are often not observed, so it is important to visit a gynecologist once or twice a year. Cervical hyperemia occurs in pregnant women and can occur as a result of injury, infection, circulatory disorders, uterine prolapse and elongation, and can also be a sign of heart and lung diseases. Therefore, it is important to promptly identify the cause and begin treatment.
What diseases does it most often indicate?
Most often, hyperemia indicates the following diseases:
- Cervicitis (inflammatory processes in the cervix). This disease is usually caused by various pathogens that are transmitted during sex. Pathology can also develop as a result of mechanical damage to the vagina, hormonal disorders and the death of natural vaginal microflora. There are two types of cervicitis: exocervicitis (inflammation of the outer parts of the cervix) and endocervicitis (inflammation in the cervical canal). Treatment of cervicitis cannot be delayed, otherwise there is a high risk that the red cervix will begin to erode, shift and increase in size.
- Dysplasia. Redness can also be a sign of the onset of dysplasia - a serious disease that, without proper treatment, can harm not only the cervix, but also all the main female reproductive organs.
- Gonorrhea. Transmitted during sexual contact. In addition to a red neck, the disease is characterized by an unpleasant-smelling yellow vaginal discharge. Gonorrhea is dangerous. If left untreated, it affects the entire uterus, not just the cervix.
- Urogenital (genitourinary) chlamydia. The disease is transmitted sexually. Its causative agent is one of the types of chlamydia (C. trachomatis). This type of chlamydia is very common and is more common than gonorrhea. This disease is dangerous, although it often does not have pronounced symptoms. It can lead to infertility, as well as cause inflammatory processes in the uterine appendages (adnexitis) and inflammation of the vaginal mucosa (vaginitis).
- Urogenital mycoplasmosis. The disease is caused by the pathogen Mycoplasma. It is transmitted during sex. The disease has no obvious symptoms.
- Urogenital trichomoniasis. The disease is caused by Trichomonas parasites, which are transmitted during sex. In addition to cervical hyperemia, urogenital trichomoniasis is characterized by smelly leucorrhoea with a foamy consistency.
- Bacterial vaginosis. The main reason for the development of the disease is the replacement of lactobacilli (representatives of natural microflora) by harmful microorganisms. The disease is characterized by leucorrhoea that smells like fish, as well as discomfort during sexual intercourse.
- Candidiasis. The causative agent of the disease is a fungus of the Candida family. The main cause of candidiasis is problems with the immune system. The main symptoms of the pathology are whitish discharge with a curd-like consistency, as well as pain during urination.
Diseases that develop into cancer
Location of affected areas
Outgrowths and normal tissue at the same level
In addition to elevations, there are areas affected by erosion
The outgrowths are layered on top of each other, forming elevations
- The appearance of simple leukoplakia can be caused by hormonal disorders, organ injuries, infections;
- With atypia (precancerous disease) occurs when growths are layered.
Treatment: simple leukoplakia, once detected, cannot be treated. However, a cancer test is performed once a year. If atypical cells are detected, the area is cauterized using the radio wave method.
- Condyloma. Warty growths caused by HPV. The risk of transformation into cancer is accompanied by a large spread among the population. However, only high-risk types of HPV can lead to cancer.
There are two types of condylomas: flat, pointed.
Treatment: removal of growths using a laser.
The cellular structure is disrupted in the lower layer of the epithelium;
They arise as a result of regression and long-term therapy with anti-inflammatory drugs.
High layers of tissue are damaged;
In 1 out of 5 cases it becomes severe.
Deep layers of tissue are affected;
The cellular structure does not differ from cancer, however, changes occur only in the mucosa.
Treatment: biopsy, staging and histological studies. For moderate severity, laser coagulation is used, for severe cases, conization of the organ is used.
General symptoms of hyperemia
Despite the fact that hyperemia is not a separate disease, it still has some typical symptoms. This:
- tachycardia and high blood pressure;
- non-menstrual bleeding;
- distension and pain in the vagina and perineal area.
Active arterial and passive venous forms of hyperemia have their own special manifestations. For arterial redness typical:
- dilated arteries and severe redness in the area where the blood has rushed;
- pulsation caused by dilated arteries and accelerated blood flow in the area of redness;
- increased lymphatic blood flow.
Venous hyperemia is characterized by:
- blue-violet or purple color of the mucous membrane of the cervix;
- edematous processes in the mucous membrane;
- burning, itching and other unpleasant sensations in the area of redness.
Diagnostics
As mentioned above, redness of the cervix is a symptom of various pathologies, and not a separate disease. Therefore, in order to detect the causes that caused hyperemia, a comprehensive diagnosis will be required.
The doctor begins it with a general examination and review of the medical history. He may then refer the patient to:
- Ultrasound, which includes Doppler ultrasound. This study helps check whether the patient has tumors that can compress the vessels and cause hyperemia;
- computed tomography. With this study, tumors and other causes of venous (passive) hyperemia can be detected;
- electrocardiography with dynamic blood pressure measurement;
- colposcopy;
- blood test for hormones and hemoglobin.
Research will help determine what kind of redness it is and investigate its cause.
Treatment options
Treatment for hyperemia depends on the specific disease that caused it. The woman will need:
- use pharmaceuticals to heal wounds if redness is caused by mechanical injuries to the uterus;
- use antihistamines if the cause of the pathology is an allergic reaction;
- get rid of erosions or varicose veins if the cervix is hyperemic precisely because of these diseases;
- take antifungal, antiviral or antibacterial medications if the redness is caused by infections;
- treat lung or heart diseases if hyperemia is caused by increased hemoglobin;
- take antihistamines (Suprastin, Claritin) or drugs that improve blood microcirculation (Persantin, Curantil) if the pathology is caused by swelling.