In the modern world, women face many different threats of termination of pregnancy, even after such a long-awaited occurrence. One of the most common today is such a dangerous pathology as a shortened cervix, which a woman often finds out about while already carrying a baby under her heart. Why is such an anomaly dangerous, and what does “short cervix during pregnancy” mean? In this article we will try to figure this out.
Short neck during pregnancy: how to recognize
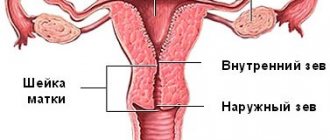
The cervix is its lower part, which is a kind of barrier between the organ itself and the external environment of the vagina . While carrying a baby, it performs two very significant functions:
- protects the fetus and amniotic fluid from various infections from the outside;
- holds the fetus in the uterus and prevents it from “breaking out” prematurely.
In order to fully support the considerable weight of the baby and not open prematurely, its length should be approximately one third of the length of the uterus itself (about 3-4 cm). However, there are cases when the cervix is too short, sometimes even less than 2 cm, which significantly complicates the process of normal pregnancy. In medical practice, this pathology is called isthmic-cervical insufficiency (ICI) and is one of the most common causes of miscarriages and the onset of premature labor.
It is extremely difficult to recognize this anomaly on your own, since there are no characteristic symptoms that clearly indicate its presence. Only a doctor can do this. We will consider diagnostic methods and symptoms of this pathology in more detail below.
Reviews
I haven't encountered this difficulty. My cervix was long (according to the norm) and closed. One friend had an ICN and a pessary fitted. Without limiting herself in anything: neither in sexual life, nor in physical activity, nor in emotional turmoil, she successfully reached the deadline for removing the pessary and gave birth to a healthy baby the next day. Provided that a week after installing the pessary, she went to sea by train for two days. A work colleague faced a different situation. From the very early stages after conception, she was in danger of miscarriage, bleeding, pain, and her cervix was missing the tip of a finger. She spent the entire first trimester in confinement, and when she returned to work (in the second trimester), the first ultrasound showed a sharp decrease in the length of the cervix. She was given a pessary and again admitted to the hospital. Strict bed rest, getting up only to go to the toilet, and constant obstetric supervision did not produce results. At 28 weeks, the cervix literally spread, pushing out the pessary, and contractions began. The child survived, but the first 5 years of his life were difficult to rehabilitate. My husband's second cousin experiences cervical shortening from pregnancy to pregnancy. She only had five of them. Despite the doctors’ warnings and persuasion to put in a pessary or get sutured, she does not take any active action. Surprisingly, all pregnancies end with the birth of healthy children almost at term. But this, of course, is an exception to the rule.
Shortening of the cervix during pregnancy is a common pathology in the practice of an obstetrician-gynecologist. A patient with such a diagnosis in history needs to visit the doctor on time with each new pregnancy, without neglecting examinations and ultrasound. If detected, you should carefully follow all medical recommendations, limit exercise, sports training, stress, and sexual contact.
Why is this diagnosis dangerous during pregnancy?
This feature is dangerous primarily because the shortened neck is not able to cope with the increasing load on it as the fetus grows , and therefore can open ahead of schedule, causing a miscarriage (up to 28 weeks), or birth before the due date. This situation is especially aggravated if the pregnant woman has polyhydramnios or the fetus is too large. Also, a shortened lower segment of the uterus can cause various infections to enter it, since it cannot serve as a full-fledged barrier protecting the baby.
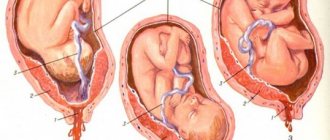
Unfortunately, this pathology also poses a danger during labor, as it can lead to excessive rapidity of labor. Thus, the opening of the lower part of the uterus occurs too quickly, while the remaining planes of the birth canal are not yet completely ready for the passage of the baby. This can provoke various complications: rupture of the soft birth canal (vagina, perineum, etc.), premature placental abruption, entry of amniotic fluid into the bloodstream, etc.
Preventive measures
Proper treatment of vaginitis and other inflammatory diseases of the genital organs will preserve the elasticity of the cervix. This applies equally to the period before pregnancy and to pregnant women.
Vitamins or hormone therapy prescribed by doctors can normalize the density of muscle tissue and the conduction of impulses, and will help the cervix in performing its main functions.
Excess weight of the woman herself and non-compliance with the diet during pregnancy put additional stress on the organs. It is important to monitor nutrition and weight dynamics during pregnancy.
If shortening is diagnosed, it is necessary to limit physical activity, heavy lifting, and bending. A woman should be able to lie down 2-3 times during the day and have a good night's rest.
When installing a pessary or applying sutures, the doctor will tell you about additional features of the regimen. Hospitalization will be required on the eve of the planned birth.
The diagnosis of “shortening of the cervix” made during pregnancy means a deviation of the diagnosed size from the norm. But it does not always indicate the threat of premature birth. It is possible to preserve the obturator function of the cervix if you follow the regimen and follow the doctor’s prescriptions.
Greetings, girls!
Have you heard of such a pathology as a short cervix? This violation is typical for a woman only during an “interesting situation.” Why does the cervix shorten during pregnancy?
We will answer this question, as well as many others related to the violation, today. I’ll say right away that you shouldn’t take this condition lightly.
Causes
There are several reasons why the lower segment of the uterus is shorter than normal:
- Congenital feature . So, this organ may have such a structure by nature and be a genetic feature.
- Hormonal changes. Due to hormonal changes in the pregnant woman’s body (usually from 11 to 27 weeks), active production of androgens begins, which can qualitatively affect the structure of the cervix: making it softer and shorter. Moreover, this does not affect the tone of the uterus in a pregnant woman.
- Various intrauterine interventions in the past . Previously performed abortions, scrapings and other manipulations, one way or another, could damage the cervix, leading to its deformation and shortening.
Threat to pregnancy
If the cervix shortens to 20-25 mm at less than 37 weeks, it can open under the weight of the fetus, causing premature termination of pregnancy and even rapid labor, threatening multiple ruptures of the cervix and vagina.
A condition when a pregnancy is in danger of being terminated due to the inability of the uterus to support the growing fetus is called isthmic-cervical insufficiency.
. Why this pathology occurs is indicated above.
Another danger for pregnancy with early shortening of the cervix is opening access to infections. The fetus at the stages of active growth is very vulnerable to pathogenic microflora, which can lead, if not to its death, then to developmental defects. A child may be born with both physical defects and a disorder of the central nervous system. Moreover, pregnancy can provoke a surge in pathogenic flora.
Symptoms
As a rule, a shortened neck does not “give” itself in any way either before or after conceiving a baby. Only in rare cases, pregnant women with this pathology may experience the following symptoms:
- watery or bloody vaginal discharge;
- slight aching pain in the lower abdomen;
- tingling pain inside the vagina.
If at least one of the above symptoms is present, a woman should immediately seek help from a doctor.
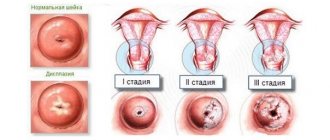
Norm and pathology
The uterus is the most important reproductive organ, consisting of the cervix, isthmus, fundus of the uterus and body; it is in it that the child is formed and grows. The cervix protects the fetus both mechanically and from the penetration of infections from the vagina. Normally, it has the shape of a cone with a length of 3 to 5 cm and a dense consistency. Its internal hollow part is called the cervical canal, in which a plug of mucus forms during pregnancy - it is this that creates protection against pathogens.
Shortening of the cervix during pregnancy to 2.5 cm or less is considered dangerous. This length is permissible only from 38 weeks, when the baby is full-term and the uterus is preparing for childbirth.
Diagnostics
Only a doctor can detect and make such a diagnosis for you . Usually, the fact that the lower part of the uterus is shorter than expected can be seen already during the first examination during registration (at 11 weeks). So, a doctor can diagnose such a pathology using:
- examination with a gynecological speculum;
- vaginal palpation;
- Ultrasound (considered the most reliable diagnostic method in this case).
Summing up
A short cervix during pregnancy is not an obstacle to bearing and giving birth to a healthy baby. At the twentieth week, when a deviation is detected, it is possible to take various measures and prolong the pregnancy until the period at which the baby will be considered full-term. The expectant mother is required to comply with all medical prescriptions and be determined to have a positive result, because excessive anxiety has a detrimental effect on pregnancy, and stress is of no use to either the mother or the child.
Read
Also:
- Menstruation after first sex: norm and pathology
- Anatomy of the uterus: location, structure and functions
- Late ovulation with a 28-day cycle - normal or pathological
- Periods in the first month of pregnancy - normal or pathological?
- Short cervix during pregnancy: diagnosis, treatment and prevention of pathology
- Endocervicosis – pathology of the cervix
Treatment
Fortunately, there are different treatment methods that are used when this pathology is detected:
- Taking hormonal drugs that can correct shortening if it was caused by hormonal imbalance. As a rule, if after 2-3 weeks the situation does not change, then more serious methods of treatment are used.
- Installation of a special gynecological pessary, which partially takes the load on itself and helps maintain the weight of the fetus and amniotic fluid.
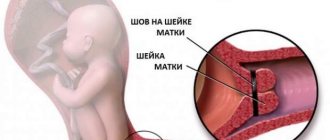
- Applying sutures to the cervix to prevent its premature dilatation. This operation is performed under anesthesia, no later than 28 weeks.
Papaverine (indications for use and beneficial properties)
As mentioned above, many women during pregnancy are associated with dilatation of the cervix in the second trimester, which leads to isthmic-cervical insufficiency or uterine hypertonicity. In order to prevent these types of pathologies, pregnant women are prescribed papaverine. Papaverine is a medicine that is produced in the form of suppositories or tablets.
This tool can cope with many problems. When muscle spasms occur, there is a need to eliminate them, which is possible with the help of progesterone. The lack of this hormone leads to uterine hypertonicity. Papaverine is also prescribed to increase this hormone. It helps relieve spasms and improve blood circulation in the reproductive organs.
This drug is not recommended for use in early pregnancy. The need for its use appears in the second and third trimester.
During this period of pregnancy, papaverine is used for abdominal pain and high blood pressure. However, it must be taken in combination with other medications. The drug helps relieve abdominal pain, prepare the cervix for childbirth, and also relieve pain during contractions.
Papaverine has a beneficial effect on the muscles of the uterus, relaxing them. The drug can also prevent the threat of miscarriage. The most important advantage of the medication is that it does not have a negative effect on the fetus.
Papaverine is prescribed in cases of threatened miscarriage and premature birth, as well as in the presence of uterine hypertonicity.
Girls and women who have kidney pathology and hypersensitivity to the substances contained in the drug are prohibited from taking the drug.
Papaverine is often prescribed before childbirth to significantly soften the cervix.
If there is a diagnosis of isthmic-cervical insufficiency, the use of papaverine is combined with magnesium sulfate. Usually these drugs are given on droppers. Medicines have a calming effect on the uterus. At the same time, it is necessary to give injections of papaverine to prevent the cervix from dilating even further.
It is recommended to use the drug in suppositories, as they are absorbed faster than tablets.
Video: 2nd trimester. Tonus, ultrasound, big gains
2nd trimester // TONUS/ Ultrasound/ BIG INCREASES
Video: ICN. My bedridden pregnancy
ICN. My bedridden pregnancy.
Video: my pregnancy 2nd trimester
My pregnancy is 2nd trimester. My doctor is a man
Prevention
Despite the fact that this pathology is diagnosed mainly after pregnancy, it is necessary to avoid situations that could cause it long before conception (unless, of course, this is a congenital feature of your body). To do this you should:
- regularly visit a gynecologist (at least once every 6 months) for timely detection of diseases of the reproductive system and their elimination in a non-surgical way;
- Carry out independent monitoring of your health and immediately consult a doctor if suspicious symptoms occur;
- choose the optimal means of contraception to avoid unplanned pregnancy and further abortions;
- Avoid casual sexual contact to protect yourself from various sexually transmitted infections.
If you do find out that you have such a problem while you are already pregnant, the following recommendations will be useful to you:
- avoid physical activity, long walking and rest more often;
- wear a special bandage for pregnant women, which, one way or another, reduces the load on the body;
- Avoid sexual intercourse during pregnancy.
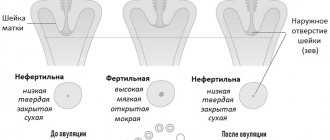
Changes in cervical length depending on gestational age
During the period from conception to childbirth, the cervix changes not only in its color, but also in length and consistency. Before conception, this part of the woman’s reproductive system is closed and has a dense consistency. Clots of mucus can be traced in the cervical canal; they contribute to the faster passage of sperm to the egg.
After conception and during the formation of the embryo, the cervical canal becomes softer, the pink color changes to bluish. This is due to the acceleration of blood supply to the uterus.
Then, until the 28th week, the cervix gradually increases in size. After this, the cervix begins to shrink. And just before birth, its size is less than 25 cm.
Thus, the normal dimensions of the cervix are:
- at 20-24 weeks – 4.0-4.5 cm;
- at 25-28 weeks – 3.5-4.0 cm;
- at 29, 30 and 31 weeks – the size of the cervix begins to decrease to 3.5 cm;
- at 35-39 weeks – 3.0-1.5.
The note! Depending on the individual characteristics of the pregnant woman’s body, norms may vary.
Short cervix at 20 weeks of pregnancy
At the 20th week, fetal development accelerates and the uterine fundus increases. It is during this period that mothers feel the movements of their baby, the fetus increases significantly in size and begins to put pressure on the navel muscles. If there is a short cervix with the condition of its constant increase during this period, there is a threat of fetal loss.
Recommendations:
- visit the gynecological office in a timely manner;
- consult a doctor;
- exclude any physical and psychological stress.
Short cervix at 30 weeks
During this period, as a rule, women go on maternity leave. This is the optimal period, based on the fact that a woman at this stage has a fairly large belly, the pressure on the uterine os increases even more (especially in case of multiple or polyhydramnios pregnancy).
Recommendations:
- limit or exclude the factor of visiting work;
- limit emotional or physical stress;
- visit a doctor in a timely manner;
- provide the most comfortable and favorable environment for the pregnant woman.
Short cervix from 32 weeks
As a rule, the last ultrasound is performed this week. After this procedure, the doctor assesses the risks of progression of premature birth. Of course, from this week all the efforts of doctors and families should be directed towards the birth of a healthy child in the optimal time.
Recommendations:
- preventive hospitalization (at risks of premature pregnancy);
- minimum anxiety and physical activity;
- get as much rest as possible;
- creating comfortable conditions for the birth of a child.
The note! In most cases, the pathology of a short cervix is accompanied by increased uterine tone. This factor causes a high risk of premature birth and spontaneous abortion.
Cervix before natural birth
A few weeks before birth, changes occur in the cervix that will help the baby to be born at the right time. The third and fourth weeks before the onset of labor pass with the uterus tilted back. Before labor begins, the uterus must be positioned exactly in the center of the pelvis. The readiness of the birth canal is manifested by strong softening and elasticity of the tissues of the cervix; one or two fingers of the doctor pass inside. In those who give birth for the first and second time, the cervix sharply shortens and smoothes to 1 cm. Afterwards, clots of mucus come out, and the uterus begins to open. Full dilatation is slow and ranges from 10 to 12 centimeters, which is enough for the baby to pass through the birth canal. Once dilation is complete, contractions will begin.
What to do?
It is important to note that if a woman has a short cervix before pregnancy, she should regularly visit her gynecologist. This is necessary in order to monitor the condition of this organ. Quite often, shortening of the uterus leads to the development of many dangerous pathologies.
However, in most cases, this pathological condition is determined only during pregnancy. It is identified by a gynecologist during an examination of the expectant mother on a chair. If abnormalities are detected, the doctor should refer the woman for an additional transvaginal ultrasound examination.
Maintaining a daily routine
Doctors recommend that expectant mothers strictly monitor what they do during the day. The daily routine is very important. In order to normalize the tone of the uterus, you should definitely get enough sleep regularly. Sleep should be at least 8-9 hours a day.
To prevent the cervix from further shrinking, the expectant mother should monitor her excessive emotions. Severe anxiety or worry over trifles leads to disruption of nervous activity and spastic contraction of smooth muscles. This condition can only increase the shortening of the cervix.
Optimal physical activity helps the expectant mother maintain the tone of the female genital muscles. To normalize it, yoga classes for pregnant women or regular walks in the fresh air are suitable. Also, to prevent the worsening of this pathology, doctors prohibit the expectant mother from lifting weights.
Normalizing excess body weight is a very important condition for maintaining the health of the female genital organs. During pregnancy, the expectant mother already gains weight. This is due to the baby growing in her tummy, as well as the entire mass of all the placental membranes. Too much weight can lead to compression of the reproductive organs, which also causes shortening of the cervix.
In some cases, doctors may recommend that women suffering from this pathology wear a special bandage. It helps to fix certain parts of the spine, and also somewhat reduces the likelihood of premature birth.
It is recommended to wear such bandages, as a rule, 4.5-5 months before giving birth. The obstetrician-gynecologist prescribes the wearing of these orthopedic devices after a clinical examination.
Shortening the cervix is not a contraindication for sexual intercourse. Only in certain acute pathologies can doctors recommend that women limit their sexual activity. As a rule, such recommendations are given to expectant mothers in the last stages of their pregnancy.
Gynecological treatment
If, against the background of a short cervix, a woman has developed isthmic-cervical insufficiency, then she will require special treatment methods. In this case, doctors usually apply sutures that fix the os of the uterus. They will be removed only immediately before childbirth.
Some of the methods are surgical and are performed in an operating room. As a rule, in this case, mandatory intervention of an anesthesiologist is required.
Another method of treating isthmic-cervical insufficiency caused by a too short cervix is the application of an obstetric pessary. This special device is inserted into the cervical canal and fixes the pharynx from the inside. An obstetrician-gynecologist installs an obstetric pessary.
This procedure is invasive and therefore requires mandatory preparation. It is better that it is performed only by an experienced and qualified doctor. After installing an obstetric pessary, doctors limit physical activity and recommend that expectant mothers get plenty of rest.
Drug therapy
In some situations, doctors may recommend hormonal treatment to the expectant mother. This is possible in cases where pathological changes in a woman occur against the background of existing dishormonal disorders. In such a situation, doctors prescribe medications that compensate for the lack of specific female hormones.
"Utrozhestan" is one of the medications prescribed to correct the problems that have arisen. Gynecologists can prescribe this drug at various periods of pregnancy. For up to 12 weeks, taking Utrozhestan promotes the attachment of the fetus to the wall of the uterus, as well as the beginning of its intrauterine development.
Taking this drug also significantly reduces the risk of spontaneous miscarriage. By the later weeks of pregnancy, the increase in progesterone in the blood decreases slightly. This physiological reaction is necessary for the expulsion of the fetus from the mother's womb. In this case, taking Utrozhestan may lead to a worsening of the final stage of pregnancy.
This drug can be prescribed in the form of capsules or various suppositories. In most cases, it is taken three times a day. Dosages are selected individually, taking into account the patient’s weight, the presence of concomitant diseases, as well as the nature of the pregnancy.
Expectant mothers should remember that any hormonal medications must be prescribed by a doctor. Self-use of such drugs can lead to the development of quite dangerous conditions for the fetus and her own health.
A short cervix is not at all a contraindication for planning pregnancy. With such a physiological feature, a woman can become a mother more than once. For the normal course of pregnancy, only timely monitoring of the baby’s condition while he is in the mother’s tummy is required.
It is better to determine the shortening of the cervix before conceiving the baby. The only exception is if this pathology occurs in a pregnant woman directly during pregnancy. Timely diagnosis of this condition can reduce the significant risk of developing various diseases in both the pregnant woman and her baby.
Gynecologist Lyudmila Shupenyuk will talk about how long the cervix should be during pregnancy in the next video.