Sometimes, during a routine ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, women are diagnosed with enlarged ovaries. As a rule, these changes do not have characteristic symptoms and do not always indicate the presence of a disease.
More often this occurs as a result of hormonal changes. In order not to miss the onset of the development of a serious pathology and to begin timely treatment, the exact causes of ovarian enlargement in women should be determined.
Is an ovarian cyst growing?
Women who are diagnosed with an ovarian cyst after diagnosis experience stress and have ambivalence about treatment methods for the disease. A cyst in the ovary in women is formed under the influence of various factors, which are identified by specialists during the examination.
The diameter of an ovarian cyst does not exceed 12 cm; on average, the size of the tumor in diameter reaches 4 cm. Experts cannot unambiguously determine the growth rate of the cyst, since this process is influenced by various factors. Medical observations have shown that in some women, tumor growth may stop for several years, after which the tumor begins to rapidly increase in size. In addition, the tumor may stop growing or rapidly increase in size.
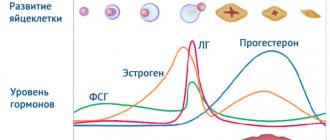
Experts associate the rapid growth of the tumor and the increase in symptoms with an increase in estrogen levels. However, a benign tumor with normal levels of female sex hormones may not cause any symptoms.
When treating patients, oncologists monitor how quickly the ovarian cyst grows and prescribe a set of therapeutic measures in accordance with the characteristics and rate of tumor development. Thus, a tumor size of more than 8 cm is one of the indications for surgical removal.
Expert opinion
Author:
Liliya Rashitovna Garayeva
Obstetrician-gynecologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences
An ovarian cyst is a fluid formation in the form of a bubble, due to which the size of the ovary can increase several times. Cysts are considered the most common formations; they develop over a long period of time, their size varies from a few millimeters to 20 centimeters or more.
There are many reasons for the formation of cysts, the most important among them are hormonal dysfunction, inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs, diseases of the endocrine system, abortion, including mini-abortion.
Some types of cysts resolve on their own, while others require complex hormonal and anti-inflammatory therapy. In some difficult cases, surgical intervention is prescribed.
The choice of treatment tactics depends on the nature of the tumor, the severity of the clinical picture, the age category of the patient, the need to preserve reproductive function, and the likelihood of a malignant process. Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital practice complex treatment of ovarian cysts in inpatient and outpatient settings.
What causes changes in ovarian volume?
The reasons why one ovary becomes larger may be the following:
- Appendicitis, while the right appendage increases, but the left ovary remains the same in diameter.
- Inflammation of the ovary, uterus or fallopian tubes.
- Ovulation, which is often accompanied by unilateral nagging pain, increased body temperature, and weakness.
- A single cyst (more than 3-5 cm in diameter) or multiple ovarian formations.
- PCOS.
- Cervical erosion. In this case, the microorganisms that provoked the development of pathology invade the ovarian tissue, resulting in the development of an inflammatory process.
- Malignant tumor of a paired organ.
Ovarian cyst: how to reduce swelling
Ovarian cysts of various sizes pose a danger to a woman’s reproductive health. In addition, a cyst on the left or right ovary can put pressure on internal organs. After examining a woman, oncologists select treatment methods aimed at eliminating the causes of the disease, its manifestations and possible consequences.
Some women believe that traditional medicine methods can reduce ovarian cysts, but this misconception leads to the progression of the disease and increased symptoms, since the woman does not receive the necessary treatment.
To stop tumor growth, conservative methods of therapy are used, the effect of which is aimed at normalizing hormonal levels. An important role in the treatment of ovarian cysts is played by exercise therapy and physiotherapeutic procedures that complement drug therapy.
However, if signs of compression of nearby organs by the tumor and other pathological symptoms appear, surgical removal of the tumor is performed. Ovarian cysts are removed using modern technologies without extensive trauma.
Symptoms, where to go
A gynecologist deals with ovarian diseases. After a conversation with the patient, collecting anamnesis, and an initial examination, he will prescribe additional studies. Taking tests and ultrasound diagnostics can take a lot of time, so you should seek help as early as possible.
It is not recommended to hope that everything will go away on its own if:
- pain in the abdomen, lower back;
- blood appears on days when there should not be menstruation;
- severe pain occurs during sexual intercourse;
- purulent discharge is present;
- painful urination occurs;
- there is discomfort in the genitourinary system.
Even if the pain is minor and decreases over time, in any case you need to contact a medical facility. The fact is that inflammatory processes and infection (if any) develop very quickly and there is a risk of serious complications.
Ovarian cysts and cystomas
An ovarian cyst, the tumor can be reduced using conservative methods, is a tumor-like formation. A distinctive feature of a cystoma is that it is a true tumor, the cells of which are dividing intensively. As the disease progresses, the cystoma can grow into neighboring organs and destroy their tissue. In addition, the tumor is capable of metastasis, however, the likelihood of its degeneration into oncology is low.
Cystomas quickly increase in size; formations of this type include: dermoid cyst, cystadenoma, endometrioid cyst. Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital Oncology Clinic have extensive experience in treating various types of tumors. Comprehensive programs designed for women include:
- taking medications of various spectrums of action;
- giving up bad habits and changing lifestyle;
- physiotherapeutic measures, physical therapy exercises;
- minimally invasive interventions if indicated.
Oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital are always ready to help women using their accumulated experience. At the diagnostic center of the Yusupov Hospital, patients have the opportunity to undergo an examination and receive its results as soon as possible.
Pregnancy
While maintaining the functionality of the ovaries, an increase in size does not affect conception. However, pregnancy itself can cause these changes. This happens as a result of hormonal changes.
When diagnosing an enlargement of the female organ during gestation, one can assume the presence of inflammatory processes that require treatment.
Any pathological processes in the pelvic organs require a comprehensive examination and therapeutic measures. Timely detection of diseases can prevent serious complications such as infertility and bleeding.
Ovarian enlargement is a common occurrence. This pathology is detected using ultrasound in a medical institution or by palpation if the organ is enlarged by 2 times or more. The ovary can enlarge not only in a young or mature woman, but also in adolescents 13-16 years old. Therefore, the topic under consideration is relevant for women and girls.
In this article we will tell you what to do if the ovary is enlarged, the causes of the pathology and we will determine the main signs of the disease.
Prevention of ovarian cysts
Ovarian cysts are a common gynecological problem, which, with timely diagnosis, can be solved using conservative methods. An ovarian cyst with blood flow or other varieties are formed under the influence of certain factors. Gynecologists recommend following the following recommendations to prevent the disease:
- regularly visit a gynecologist at least 2 times a year for timely detection of disorders and conditions that cause the development of cysts;
- use contraceptive methods prescribed by a gynecologist, taking into account individual characteristics;
- exclude serious physical activity, as well as limit sports during menstruation;
- prevent termination of pregnancy, as well as inflammatory processes in the genital organs;
- Avoid strict diets and excessive consumption of fatty foods.
When a patient contacts a patient for the purpose of preventing gynecological diseases, in particular ovarian cysts, oncologists conduct an examination and determine the current state of the body and the presence of disorders. After which specialists develop a comprehensive prevention program to prevent the pathological process.
Symptoms
Symptoms of ovarian enlargement begin to appear as the disease progresses, so in the early stages it is possible to detect changes only by ultrasound.
The clinical picture of ovarian enlargement is as follows:
- the patient is worried about constant fatigue;
- periodic nagging pains occur in the lower abdomen;
- pain in the lower back;
- pain and discomfort are felt during sexual intercourse;
- disruptions of menstruation (manifested by bleeding in the middle of the cycle);
- increased volume of daily vaginal discharge.
Important! The acute course of inflammatory processes can provoke an increase in temperature to high numbers. In such cases, you must immediately contact a medical facility.
Apoplexy
Apoplexy is a dangerous condition in gynecological practice, characterized by sudden rupture of the ovary and the development of bleeding into the abdominal cavity.
Treatment of ovarian cysts in Moscow
Many women who have been diagnosed with a benign ovarian tumor are asked the question: if an ovarian cyst develops, can it not be removed and the disease can be treated exclusively by conservative methods. Tumor reduction can occur under the influence of medications, but for large tumors they are ineffective.
One of the activities of the Yusupov Hospital is providing assistance to women with the development of ovarian tumors. Oncology clinic specialists improve their skills, attend congresses and seminars on modern approaches to the treatment of tumors, so women can entrust their health to highly qualified oncologists.
In addition, when treating ovarian cysts, the main goal of oncologists is to preserve the patient’s reproductive function, therefore, when treating tumors, minimally invasive techniques are used with a minimal rehabilitation period.
You can seek advice from an oncologist at the Yusupov Hospital. The medical institution guarantees confidentiality and protects clients’ personal data. Appointments are made by specialists by calling the Yusupov Hospital.
Diagnosis of epididymal enlargement
It is quite difficult to determine by palpation that one ovary is enlarged due to a small cyst. For this purpose, it is best to use ultrasound. Early stages of cancer are not diagnosed by palpation, but are clearly detected when the tumor has grown into the tissue.
Palpation allows only to suspect pathology. For a more detailed diagnosis, you need to see a doctor and undergo an ultrasound examination, as well as take a vaginal smear, blood tests for hormones, and be screened for STDs. It is recommended to do an ultrasound of the thyroid gland. This will allow us to assess the functioning of this body.
In most cases, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. Hospitalization is required if two ovaries are significantly enlarged. A comprehensive study allows you to find the reason why the appendages have become larger, as well as prescribe adequate therapy. In addition to medications, physiotherapy is sometimes used, which has a beneficial effect on the condition of the entire reproductive system. However, it cannot be used if a woman has cancer.
How to treat
It all depends on what caused the enlargement of the ovaries. When the doctor determines the true cause, he selects the appropriate therapy. Most often, gynecologists restore a woman’s health in the following ways:
- return of hormonal levels to normal;
- improvement or restoration of metabolism;
- restoration of the menstrual cycle;
- restoration of reproductive function.
For treatment to be effective, the patient will be advised to lead a healthy lifestyle. In addition, you should stick to a diet: low-calorie and healthy foods will help improve metabolism and reduce excess weight. But you need to take into account an important point: you cannot bring the body to stress, the transition to dietary nutrition should be slow. It is recommended to talk with your doctor about choosing a diet.
If necessary, your doctor may prescribe hormonal medications to balance female and male hormones.
If treatment with diets and medications is useless, the primary cause of the disease has been identified and eliminated, and the ovaries are still enlarged, then the doctor may suggest contacting a surgeon. Using laparoscopy, the surgeon will restore the ovarian tissue, after which the organ will return to normal.
The answers given above were why the ovaries enlarge. There may actually be many reasons. A competent gynecologist, after a thorough examination, based on the results of tests and ultrasound, can refer you to other specialists for advice. Until the cause is determined, ovarian shrinkage is unlikely. Exceptions may include stress and lifestyle changes. In case of serious pathologies, the doctor will explain what to do and how to treat. In addition, it is recommended to do a control ultrasound every year or more often (at the insistence of the attending physician).
Misconceptions and fears
Often, the busy, busy life rhythm of a modern woman does not give her time to take care of herself and her health. Sometimes patients diagnose and treat themselves. Which leads to the disease becoming chronic or incurable.
It is impossible to examine yourself and feel for a cyst or any pathology on the ovaries. Only a qualified gynecologist can do this. If you suspect an ovarian tumor, do not be afraid of surgery. Some types of cysts can be treated with conservative medications. But if surgery is recommended, there is no time to delay. Because we can talk about preserving life. Modern surgery makes the operation less traumatic and gentle. Removing the ovaries in our time does not deprive a woman of reproductive function. It is possible to conceive and carry a child through in vitro fertilization.
Please note: The main thing is not to neglect basic examinations by a gynecologist, lead a healthy lifestyle and follow doctors’ recommendations. Early diagnosis of the disease provides a chance for complete recovery and preservation of all body functions.
We recommend you learn: Ovarian hypofunction, what is it?
Detection of pathology
A preliminary diagnosis can be made based on an analysis of symptoms. For this purpose, anamnesis is collected. Information about any inflammatory diseases of the reproductive sphere, the presence of abortions in the past, the characteristics of labor, the patient’s well-being, etc. is valuable.
The main diagnostic methods are:
- examination on a gynecological chair,
- clinical blood test (inflammation is indicated by a high level of leukocytes),
- Ultrasound,
- examination of a smear from the genital tract,
- blood test for hormones,
- hysterosalpingoscopy,
- diagnostic laparoscopy.