The cervix is normal
To understand whether the cervix has become lumpy or not, it is necessary to regularly conduct self-examination on different days of the cycle. During pregnancy, the surface and condition of the organ may change.
Normal state of the organ surface:
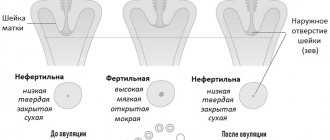
- during ovulation, the tissues of the organ soften and become loose and moist to the touch;
- immediately before menstruation, the cervix is hard and dry, drops low, in women who have given birth, the pharynx may be slightly open;
- during pregnancy, the cervix should be firm to the touch, located high from the vaginal opening by the end of the first trimester;
- softening of the cervix and its dilatation in pregnant women indicates the development of cervical insufficiency or the onset of labor.
The cervix of nulliparous women always feels smoother and harder to the touch; surface changes occur after childbirth or abortion and consist of scarring. It is scars that most often make the cervix lumpy to the touch.
Secret functions
- Like any liquid in our body, mucus has a bactericidal effect, preventing infection from entering the uterine cavity.
- At the initial and final stages of the menstrual cycle, the secretion inhibits the movement of sperm by increasing its viscosity and acidity, and in the middle of the cycle it becomes alkaline and liquid. Under such conditions, the survival and motility of sperm increases.
- After pregnancy, it thickens and forms a plug in the cervical canal, blocking the entrance to the uterine cavity. This occurs due to an increase in progesterone in the blood.
- Its condition can serve as a diagnostic sign of many diseases of the reproductive system.
The muscle layer is formed by smooth muscle tissue, which contains a lot of elastic fibers, due to which the cervical canal can stretch greatly. During childbirth, its clearance can reach ten centimeters. Smooth muscles are unique in that their contraction does not depend on our will. They are controlled by a special part of the nervous system, which is called the autonomic one. Thus, the width of the canal lumen is regulated by the nervous system. Depending on the circumstances, the lumen can be open or closed.
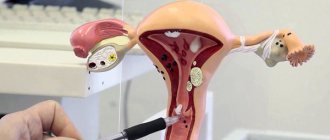
Anatomically, it is part of the uterus, which is located in the pelvis. Has a linear or cylindrical shape. The length normally ranges from three to four centimeters, but can shorten during pregnancy. Along its entire length it has two physiological narrowings - the internal and external pharynx. The external one is accessible to visual inspection, and by the opening of the canal one can judge whether the woman has given birth or not. In a young girl, the external opening will be in the shape of a point, but after childbirth it will be in the form of a slit-like opening. The external pharynx is not always accessible to visual inspection; the main thing is that it is visible on ultrasound.
Thus, the cervical canal plays a large role in protecting and communicating the uterus with the external environment, and is also actively involved in childbirth. Its existence ensures the unhindered passage of menstrual blood during menstruation. Any pathology of any of the layers will cause serious disturbances in the homeostasis of the entire reproductive system, therefore the diagnosis of pathologies of the cervical canal plays a very important role.
Causes of pathology
The cervix becomes bumpy to the touch in a number of gynecological pathologies, while the bumps may be painful or not cause discomfort upon palpation.
What diseases cause the cervix to become lumpy to the touch?
- Benign neoplasms of the nabothian glands in the form of cysts - the disease develops against the background of deteriorating patency of the glands, occurs without any special symptoms, and the cyst can be identified by touch, during ultrasound and vaginal examination in the speculum.
- Scars - appear after surgical interventions, difficult childbirth, injuries, mechanical damage during sexual intercourse. If the wound heals unevenly, the surface becomes bumpy to the touch.
- Ectopia is the most common pathology of the cervix; the mucous membrane becomes lumpy to the touch; often when an infection occurs, copious discharge appears, sometimes mixed with blood, and nagging pain in the lower abdomen. Various cauterization methods are used for treatment.
- Myoma - myomatous nodes appear in almost all women after 30 years, due to which the surface of the organ becomes lumpy. The neoplasm may be smooth and flat to the touch, located on a small stalk. Fibroids can cause infertility or miscarriage.
- Cervicitis is an inflammatory process localized in the vaginal part of the cervix, the disease is accompanied by copious cloudy discharge with a large amount of mucus, dull, aching pain in the lower abdomen, discomfort during sexual intercourse and the process of emptying the bladder and intestines.
- Papillomas often cause a bumpy surface of the cervical region. The etiological factor of the disease is human papillomaviruses. Genital warts must be removed.
Often, polyps that feel bumpy to the touch appear on the surface of the organ, which can bleed. These neoplasms are not considered benign due to their histological structure, but require observation, as they can cause precancerous changes in the cervix. Doctors insist on removing such elements.
Leukoplakia
Leukoplakia is keratinization of the cervical mucosa of varying degrees; the disease is not a fatal pathology, but there is a high probability of tissue degeneration into squamous cell carcinoma.
The causes of the development of the disease have not been fully identified, but the main provoking factors are considered to be hormonal imbalance, infections and injuries, deficiency of retinol in the body, and bad habits. Most often, the disease is diagnosed in women with irregular cycles and malfunctions of the immune and endocrine systems.
How to determine leukoplakia by touch:
- The verrucous or warty form may be lumpy on palpation. At the initial stage, there are no signs, this disease does not manifest itself with clear clinical symptoms. This variety is caused by the human papillomavirus with a high risk of carcinogenesis. During examination, the gynecologist notes the presence of small gray spots that rise slightly above the surface of the mucosa.
- A simple type of leukoplakia is difficult to determine on your own - the surface of the cervix does not become bumpy to the touch, this type is considered the least dangerous in terms of degeneration and is formed at the site of trauma to the mucous membrane.
Possible additional symptoms are itching, burning, copious discharge, sometimes with blood. For treatment, cryotherapy, radio wave method, laser cauterization are used, and antiviral and anti-inflammatory drugs are additionally prescribed.
Cervical cancer
Malignant neoplasms of the cervix are one of the most dangerous diseases, in which the organ becomes lumpy to the touch. Self-examination can help in diagnosis, but is not fundamental.
What does the cervix feel like when you have cancer?
- malignant neoplasms have a lumpy structure, unclear contours, benign tumors feel smoother to the touch and have a regular shape;
- during the examination, you can determine the structure of the formation by touch - during oncological processes it becomes partially or completely soft and immobile;
- It is advisable to record how the lesion is located - in cancer, the formation is closely connected to nearby tissues.
The presence of an oncological process is indicated by an increase in the inguinal and axillary lymph nodes, swelling of the lower extremities.
To eliminate a malignant tumor, conservative treatment methods are rarely used; most often, the tumor is removed surgically, after which the woman is prescribed a course of chemotherapy.
Treatment of pathology and prevention of premature birth
In order to restore the normal functioning of the reproductive system, the expectant mother must undergo a full course of treatment. The choice of treatment method depends entirely on the degree of reduction and height of the cervix, and is prescribed exclusively by the treating gynecologist. In this case, in no case should you self-medicate, since in this case it can have the most dire consequences for the expectant mother. Surgical correction of the uterine cervix is used.
To eliminate this pathology, several treatment methods are used:
- Use of medications, including hormonal drugs.
- Pessary - this technique involves placing a special rubber ring on the cervix, which helps reduce the load and is worn until the moment of birth.
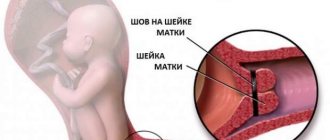
- A suture placed on the cervix - this procedure is called cerclage and helps to avoid premature labor of the reproductive organs.
During the treatment process, a pregnant woman must strictly adhere to a few simple rules: try to maintain bed rest, limiting herself from excessive physical exertion. In the most severe cases, treatment is carried out in a hospital setting - and most often the therapy is accompanied by the installation of an obstetric pessary.
In the most dangerous cases, when the width of the cervix is less than 20 mm, cervical cerclage is recommended - this procedure involves the application of special sutures that protect the reproductive organ from premature termination of pregnancy. Cerclage is not used if the gestational age exceeds 27-28 weeks. The sutures are removed immediately before birth.
Future mothers should be especially careful about their sex life. A weak uterus in pregnant women requires complete abstinence from any sexual activity throughout all trimesters of pregnancy. Each orgasm is accompanied by the fact that the reproductive organ actively contracts, which can pose a serious threat to the successful bearing of a child. Therefore, in such cases, it is recommended to strictly observe sexual rest throughout the entire period of pregnancy.
Every woman preparing to become a mother should be extremely careful about her health. Do not think that a reduction in the cervix can become an obstacle to bearing a healthy and active baby. Timely seeking medical help will help you give birth to a child, regardless of the length and size of the uterine cervix.
Video: Cervix during the onset of labor
Beginning of labor - dilatation of the cervix
Precautionary measures
Since the reasons for changes in the surface structure of the cervix are different, self-medication becomes dangerous. An annual examination by a gynecologist and independent palpation help to identify pathology in a timely manner.
Basic diagnostic methods:
- smear for cytology - allows you to identify the presence of oncological processes;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs - helps to detect concomitant pathology of the gynecological tract;
- hysteroscopy and separate curettage - the method is intended for diagnosing polyps, which often make the surface of the cervix lumpy;
- detailed examination for STIs using the PCR method including all types of HPV, as well as a tank. seeding of the separated cervical canal.
Anatomical features
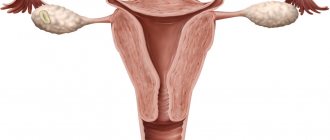
The cervix is the lower section of the uterus, which is the connecting link between the cavity and the vagina. Inside it is the cervical canal, which is the only way to communicate with the environment and the internal genital organs.
Since it is through the cervical tissue that infection can occur, it has a special defense mechanism. There are two pharynxes: the external one, which opens into the vaginal cavity, which is accessible to the doctor for examination, and the internal one, located at the junction with the uterine cavity. These structures are primarily needed not only to protect organs from viruses and pathogenic bacteria, but also for normal pregnancy.
The inside of the cervical canal is lined with epithelial glandular cells capable of producing mucus. By the appearance of the cervix, by its color and surface, as well as by the consistency of the mucus, the doctor can assume the presence of some pathology.
Examination of the cervix is also of great importance during pregnancy and labor.
Prevention
Many women experience a lumpy surface of the cervix. With timely treatment, tuberosity can be eliminated quickly, minimizing the development of complications and frequent relapses.
Preventive measures:
- eliminate chaotic sex life to minimize the risk of contracting dangerous infections;
- be careful about prescribing and taking oral contraceptives, which can disrupt hormonal balance and lead to the growth of polyps;
- Perform annual PAP and HPV tests to detect changes;
- use vaccination to prevent HPV infections;
- after a difficult birth accompanied by ruptures, be observed by a gynecologist. As a rule, scar deformities must be excised;
- If pathological discharge, pain and discomfort appear, as well as if lumpiness is detected, consult a doctor.
Abortions and numerous curettages are one of the reasons for the appearance of scars. Protected sexual intercourse will help avoid unwanted pregnancy and infections that can cause changes in the condition of the mucous membrane.
Normally, the cervical part of the uterus should be smooth; if its surface becomes bumpy to the touch, self-medication should be excluded. A change in the condition of the surface of an organ can be caused by banal scars or dangerous pathologies.
Guest, thank you very much for your answer! I wish you good health and more. Tell us, if possible, in more detail about your symptoms. Have you had cervical deformity, enlarged anterior-posterior wall and microhematuria? Even after the first bleeding during PA, one smart uzologist told me to demand a referral to the RDV. But my gynecologist said that this can provoke the growth of fibroid nodes. ((((Now, of course, I will do it. True, we only do the usual RDV, without optical control. Or look for a hystero? Girls, did the oncogynecologist tell you before receiving the test results about any suspicions? What do they even say in such cases? I wish everyone health and only good news!
Location of the uterine cervix
Where is the cervix located and how does its position change during pregnancy? After successful conception, it deviates slightly posteriorly, becoming a kind of part of the posterior wall of the vagina. The location at the bottom allows you to tightly hold the fetus, preventing the possibility of spontaneous abortion.
When examining the reproductive organs, the doctor must determine the height of the cervix. This is a very important indicator, because changes in the height of the cervix can be quite a serious cause for concern, indicating that the tone of the uterus is noticeably increasing.
This condition can be dangerous for the normal bearing of a child and cause fetal rejection. With increased tone, experts most often recommend treatment in a hospital setting.
In most cases, prematurely terminated pregnancy is the result of isthmic-cervical insufficiency, ICI - that is, a pathologically short uterine cervix. This pathology can develop for various reasons:
- Hormonal disorders in the female body, in particular – insufficient production of progesterone.
- Various injuries to the uterus during previous births, abortions or surgical interventions.
- Heavy uterine bleeding, which led to pathological changes in the structure of the reproductive organ.
- Infectious and inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs.
- Individual anatomical features of the female reproductive system.
Any deviation from the norm regarding the position and size of the cervix is an alarming sign that can warn of possible risks for the successful bearing of a child.
This is the protection of the uterus and the transport system of the embryo.
Thanks to its ability to change size and shape in response to hormonal changes, the cervix is a kind of “acrobat” of the female body. It has two main functions. When you are not pregnant, it protects you by keeping bacteria, pool water, tampons, and sex toys out of your uterus. If you decide to have a child, it is through this channel that sperm move in search of an egg, and during pregnancy it helps the baby stay in the uterus and not be born prematurely.
“Star” of viruses: how to avoid getting the flu and the whole truth about vaccines
Methods for examining the reproductive system
Today, various diagnostic measures are used to study the female reproductive system during pregnancy, allowing the size and location of the cervix to be determined with maximum accuracy.
For this purpose, two main methods are used, which are considered the most informative:
- Gynecological examination - The doctor may examine the cervix, assessing its size, length and density, as well as height and degree of dilatation.
- Ultrasound examination – also called cervicometry. With its help, the doctor examines the degree of maturity of the cervix and the level of its dilatation.
One of the main methods is palpation - during a gynecological examination, doctors carefully measure the length and consistency of the uterine cervix, and where exactly its external os is located. In a normal, healthy state, the cervix is dense, hard, the width of the external pharynx does not exceed the volume of the tip of the finger.
These diagnostic measures are recommended to be carried out regularly, starting from 19-21 weeks of pregnancy. This is necessary for constant monitoring of changes in the female reproductive system.
Ultrasound examination in the vast majority of cases is carried out in a transabdominal way - that is, measurement using a sensor that a specialist moves over the belly of the expectant mother. If necessary, for example, if there is a suspicion of a shortened cervix, an additional ultrasound examination may be prescribed, which is performed using the transvaginal method. In this case, control is carried out using a sensor inserted directly into the vaginal cavity.