Cysts on the internal genital organs are often found in women of reproductive age. This neoplasm has different etymology and classification. Some types of lumps can dissolve spontaneously during menstruation and come out during menstruation. However, sometimes a benign tumor increases in size and provokes pain. If an ovarian cyst hurts, the nature of the discomfort will be different, as well as the reasons.
Sometimes a benign tumor increases in size and causes pain.
What's happened
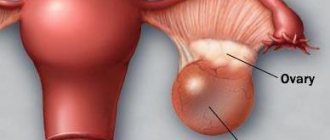
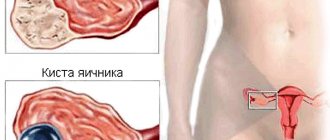
An ovarian cyst in a teenage girl is a benign capsule localized on the surface or inside the organ. The defect is filled with liquid contents and is surrounded by various walls.
The disease appears in women at any age, but in most cases the formation is diagnosed in a virgin between the ages of 12 and 15, when menstruation begins.
Unlike adults, girls have a small uterus, and the appendages in the pelvic area are located high. The dangerous group includes teenagers with irregular menstruation.
Often the pathological process develops when the organ is actively functioning, although sometimes the cyst occurs in newborn girls. Due to high physical activity in adolescence, the formation leg often becomes twisted, resulting in the first clinical signs of the disease.
Pain after physical therapy
Some women complain that the ovarian cyst hurts after physiotherapy. However, this is a very rare occurrence, because these procedures are aimed specifically at relieving pain.
The cyst may become painful after magnetic therapy if the patient went for the procedure without a preliminary histological examination. This often only makes the situation worse. When we are not talking about a follicular cyst, but about a real ovarian tumor, the pain will indicate the growth of the tumor.
Physiotherapy cannot be used as an independent type of treatment for cysts. Usually the patient is referred to them as part of rehabilitation. In general, physiotherapy aims to:
- prevention of adhesions;
- restoration of blood flow;
- normalization of endocrine function;
- restoration of hormonal levels.
Classification
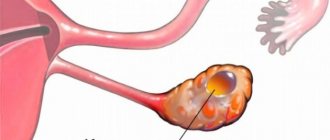
In most cases, the right ovary is affected. Ovarian neoplasms are divided into follicular defects, corpus luteum cysts and mucinous cavities.
The first type develops when fluid accumulates in unbursted follicles, the egg dies, as a result of which menstruation becomes prolonged and painful. Follicular formations often reach 10 cm in diameter.
Liquid contents with bloody impurities are formed in the corpus luteum. Such a cyst appears from hypothermia or excessive physical exertion.
It is extremely rare to diagnose a mucinous formation, characterized by copious mucous discharge. Sometimes specialists detect polycystic ovary syndrome in adolescents.
Causes
The frequent formation of benign lesions of the genital organs in girls is explained by the small size of the uterus and the high localization of the ovary. In addition, the following factors provoking the development of the disease should be highlighted:
- Having excess weight.
- Hormonal disorders.
- Constant nervous tension.
- Long-term use of hormonal drugs without a doctor's prescription.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Differences between cytology and colposcopy
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 6, 2021
Various pathologies of an infectious nature in the pelvic area, and the early onset of the menstrual cycle also significantly increases the likelihood of a cystic neoplasm.
In newborn girls, the disease appears due to a polluted environment, viral or bacterial diseases in the expectant mother during pregnancy. If a woman takes hormonal drugs, smokes or drinks alcohol during this period, then the risk of developing a benign cyst in the fetus is as high as possible.
Symptoms
Almost always, there are no pronounced symptoms of ovarian cysts in girls, so many teenagers do not even feel the presence of this formation. Because of this, the disease is most often diagnosed during a preventive ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs.
In rare cases, the tumor causes aching pain in the lower abdomen that precedes menstruation. At the same time, the size of the cystic cavity does not affect the severity of the symptoms.
Often large defects are asymptomatic, while small capsules with liquid can lead to serious complications. In an advanced situation, the menstrual cycle is disrupted, menstruation and urination bring severe pain, body temperature increases, the process of defecation becomes difficult, pain in the lower abdomen radiates to the lower limbs, lumbar or groin area, and increased fatigue occurs.
Ovarian cyst in a teenage girl (virgin): symptoms, causes, treatment, prognosis
During puberty, girls develop a menstrual cycle. As a result, it is during the current period that cystic formations of the ovaries are most often diagnosed.
The disease can occur for a long time without any clinical manifestations, but as it progresses, the pathological neoplasm can lead to serious complications.
Therefore, you need to know how to recognize and fix the problem in a timely manner.
Read more:
- Is pregnancy possible after an ovarian cyst?
Before planning a pregnancy, many women undergo examinations, and after being diagnosed with an ovarian cyst, doubts arise: is pregnancy possible after an ovarian cyst? All complications in op.
Why is an ovarian cyst dangerous?
The ovaries are the most important female organs of the reproductive system. They play an important role in conceiving a child because they contain eggs, which subsequently combine with male sperm.
How to remove an ovarian cyst
An ovarian cyst is a formation that is presented in the form of a bubble with liquid or semi-liquid state. This formation occurs in the structure of the ovary and increases its volume several times.
Space-occupying formations in the pelvis in childhood are rare. An ovarian cyst in a teenage girl is found in 1-4% of all gynecological pathologies of this age. But a full examination is necessary to exclude a malignant process.
The risk group for developing ovarian cysts includes girls with the following conditions:
- premature puberty;
- hormonal disorders;
- inflammatory diseases of the vulva and vagina with a recurrent course.
The incidence of neoplasm increases as puberty approaches. In girls aged 9-12 years, it is observed in 16.9% of cases, and up to 55% of the pathology occurs in girls aged 13-15 years. This indicates the stimulating role of the pituitary gland and sex hormones in the development of the cyst.
Malignant tumors in the pelvis are rare in adolescents. Ovarian cysts are often benign in origin, associated with follicular growth or the formation of the corpus luteum. After menarche, 1-2 years pass until a regular menstrual cycle is established.
If the egg is mature, a temporary endocrine gland is formed in the ovary - the corpus luteum. Her condition is negatively affected by:
- malnutrition;
- physical exercise;
- inflammatory diseases;
- stress;
- abortion.
Under their influence, a cyst is formed, which can resolve on its own.
At the age of 13, it is already possible to develop endometriosis. Its origin has not been precisely established, but it is noted that endometrial foci in atypical places may be a consequence of a violation of embryogenesis, the result of the introduction of menstrual blood.
A tumor gradually forms on the surface of the ovary, which has hormonal activity and itself responds to cyclic changes. The rejected endometrium does not come out, but accumulates under the capsule, forming a “chocolate cyst”.
A large group of benign ovarian tumors consists of cystadenomas. They develop from the germinal epithelium lining the surface of the organ. Histologically, it is serous and mucinous. It is impossible to differentiate a cyst from a functional formation before surgery.
Germ cell tumors account for half of all benign ovarian tumors. They consist of germinal tissues and are a consequence of improper embryogenesis. But in little girls they are rare, the frequency increases at 10 years.
Malignant tumors may have a cystic structure. They can be primary or metastatic and require careful diagnosis.
Clinical manifestations of ovarian cysts may be absent in 20% of cases; small neoplasms (up to 5 cm) develop asymptomatically. Sometimes the reason for visiting a doctor is the growth of the abdomen, which is especially alarming in a virgin.
There is no connection between the severity of symptoms and the size of the formation. Girls may complain of abdominal pain that bothers them constantly or on the eve of menstruation. Pain syndrome is more pronounced with endometrioid cysts.
Diagnostics
To detect the problem in a timely manner, you need to visit a gynecologist. During palpation of the pelvic area, the specialist will identify a painful lump. After this, it is important to undergo an ultrasound examination, which will accurately determine the shape, size, location and nature of the tumor.
If a malignant formation is suspected, then additional diagnostic methods are prescribed. After an ultrasound examination, the specialist prescribes watchful waiting or selects adequate therapy.
What to do
Parents need to pay attention to the health of their child. To protect against a cystic defect, you need to normalize your daily routine, avoid hypothermia, stressful situations, and increased physical activity. Bad habits in an expectant mother can cause illness in a newborn girl, so you should stop smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
The same applies to long-term use of hormonal drugs without a doctor’s prescription, and frequent visits to the solarium. Ovarian cysts can lead to serious consequences during adolescence, so it is important to immediately consult a doctor if alarming symptoms appear.
In addition, annual visits to the gynecologist and an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs will allow timely diagnosis of the disease and protect the reproductive system.
In the absence of symptoms and complications, the doctor prescribes only observation. Otherwise, conservative therapy or surgical resection of the cavity is used.
Forecast
The prognosis in the absence of a complicated course is favorable. With the help of adequate treatment, you can completely get rid of cystic formation and protect yourself from dangerous consequences. Sometimes the tumor goes away on its own. To prevent relapse, a teenage girl should avoid nervous strain and increased physical activity.
Any hormonal or anti-inflammatory drugs should be used only as prescribed by a specialist. During pregnancy, the expectant mother is obliged to eliminate bad habits and completely cure infectious pathologies.
Ovarian cysts are common in girls. Almost always, a timely visit to a doctor allows you to eliminate a benign cavity. If the situation is neglected, dangerous complications develop, so it is important to get rid of the problem at the initial stage.
Treatment
Follicular formation is prone to spontaneous resorption during the menstrual cycle. Treatment is used only when the formation is actively increasing. Medications are selected depending on the girl’s age, body characteristics, and the presence of chronic pathologies.
With the help of special hormonal agents, it is possible to eliminate the formation, improve the functionality of the affected ovary, and preserve the reproductive system. To stop the progression of the disease, contraceptive medications are sometimes prescribed.
Treatment lasts three months. During therapy, you need to stay in bed, avoid excessive physical activity, and take vitamin supplements. For severe pain, anti-inflammatory drugs are used.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Echosigns of adenomyosis
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 4, 2021
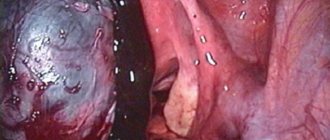
If the leg of the defect is torsed, laparoscopy is performed, preserving reproductive function. The essence of such an operation is to eliminate only the pathological formation, while healthy tissue structures and the organ itself remain unharmed.
If complications arise, an oophorectomy is performed, when the cavity is excised along with the ovary. It is extremely rare to perform adnexectomy, in which the appendages are completely removed.
Ovarian cyst in a teenage girl: symptoms and treatment at 14, 15 and 16 years old
An ovarian cyst can occur in a teenage girl for various reasons. Most often this is due to hormonal changes in the body and the onset of the menstrual cycle. In most cases, the pathology is detected at the age of 12–15 years during puberty. But there are situations when a neoplasm occurs in newborns.
In most cases, ovarian pathology is detected at the age of 12–15 years during puberty.
Provoking factors
Cystic tumors are a dense capsule with liquid contents. Most often they are localized on the right ovary. Due to the insufficient development of the gonads, disturbances in their activity occur, which provokes the appearance of a cyst. There are reasons that increase the risk of formation:
Past inflammatory processes, infectious diseases, and stress can have an effect.
- endocrine disorders;
- overweight, as well as obesity of any stage;
- neoplasms appear due to the early onset of menstruation;
- if hormonal stimulation of the ovaries was carried out or hormones were prescribed to treat any diseases, the risk of cysts increases;
- inflammatory processes and infectious diseases;
- long-term cooling;
- stress;
- bad habits;
- hereditary predisposition.
The causes of ovarian cysts in newborn girls have not yet been sufficiently studied.
Types of cystic formations
There is a classification according to which a cyst on the ovary in a teenage girl can be one of the following types:
- follicular. The appearance process is associated with ovulation. During a standard menstrual cycle, the follicle does not rupture for any reason. It fills with fluid and eventually degenerates into a cyst. With this type, the thickening reaches 10 cm in diameter. Menstruation becomes longer and more painful;
- Corpus luteum cyst. Most often associated with immaturity of the reproductive organs. Due to the rapid maturation of eggs, the corpus luteum grows greatly. The cyst is filled with fluid and blood clots. In most cases, development can be triggered by prolonged cooling, excessive exercise, or the use of certain drugs; The cyst is filled with fluid with blood clots.
- mucinous. This type resembles a follicular neoplasm on the ovary. The difference is the excess accumulation of mucus. If the process is started, both ovaries are affected, which eventually leads to polycystic disease.
Polycystic disease in adolescents
This is a dangerous type of lump that affects both ovaries. Bilateral neoplasms can be caused by hormonal imbalances, infectious processes and other disturbances in the functioning of internal organs. Due to the complicated course, the process can cause infertility.
Due to the complicated course of the process, it can cause infertility.
The presence of polycystic ovary syndrome can be determined by the following signs:
- menstruation is inconsistent;
- in the intervals between cycles, spotting may appear;
- oiliness of the skin increases, acne forms;
- metabolism slows down, resulting in weight gain;
- hairs on the body begin to grow in large quantities;
- a slight, intermittent pain is felt in both ovaries (sometimes the lower back also hurts);
- the temperature rises.
Symptoms of ovarian pathology in adolescents
In most situations, it is difficult to determine the presence of an ovarian cyst in a teenager, since it rarely manifests itself.
Only complicated forms and large sizes of a benign tumor lead to the appearance of symptoms. This is primarily irregular menstruation.
However, in adolescence, cycles are often disrupted due to the immaturity of the reproductive system. Therefore, this is rarely paid attention to.
Another possible symptom is the appearance of spotting between periods. If there is twisting of the cyst stalk, its spontaneous rupture or other complications, the signs become more obvious:
Depending on the cause, the pain varies in intensity.
- abdominal pain. Depending on the cause that caused it, there are varying degrees of intensity. Sometimes the pain syndrome spreads to the anus;
- the urge to urinate increases, but at the same time there is a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- constipation or, conversely, diarrhea may occur;
- nausea or vomiting appears;
- general health worsens (even to the point of fainting);
- the temperature rises.
If these symptoms are present, urgent care and hospitalization are required.
What are the consequences of not receiving treatment for ovarian cysts?
In adolescence, the problem cannot be ignored, as this is fraught with the development of dangerous complications. The most common include:
- increase in cyst size. If it reaches a large diameter, it begins to put pressure on other internal organs and causes severe discomfort;
- suppuration of the contents, development of the inflammatory process;
- cases of cyst torsion occur. Presented with symptoms such as sharp paroxysmal pain, fever, vomiting, etc.;
- spontaneous rupture of membranes. When contents enter the abdominal cavity, inflammation develops and intoxication occurs; Due to rupture of the cyst membranes, inflammation is possible.
- in rare cases, the neoplasm may degenerate into a malignant tumor;
- the risk of adhesions increases, which threatens infertility;
- in the most advanced cases, removal of the ovary on which the cyst is located will be required.
Diagnosis of ovarian cysts
If the lump can already be felt with a finger, the gynecologist will be able to identify it during a routine examination. In the absence of complications or inflammation, the girl will not feel pain when pressing on the walls of the tumor. Pain syndrome is characteristic of complicated processes.
If the lump can already be felt with a finger, the gynecologist will be able to identify it during a routine examination.
To clarify the diagnosis and determine the exact size and location of the tumor, the doctor will prescribe an ultrasound, as well as additional blood and urine tests. After the examination, treatment methods for ovarian cysts are selected.
Treatment methods
The treatments given to teenage girls are usually different from those given to adult women. This is due to immaturity and instability of the reproductive system.
The doctor may take a wait-and-see approach and watch to see if the tumor in the ovary changes in size.
There are often cases when it resolves spontaneously after several menstrual cycles.
If this does not happen, hormonal therapy is usually used. Drugs are selected individually. In some cases, surgery to remove an ovarian cyst may be required.
Drug therapy
Most often, medications are prescribed when there are disruptions in the menstrual cycle. They are also required when the tumor on the ovary increases in size. The list of medications includes oral contraceptives that contain female hormones. To restore the proper functioning of internal organs, three months of use are usually sufficient.
Most often, medications are prescribed when there are disruptions in the menstrual cycle.
In each case, medications must be prescribed individually. The patient’s weight, height, age, and the results of hormone tests are taken into account.
Only in this case can you achieve a good result and not cause harm. While undergoing treatment, you should visit your doctor regularly to monitor any changes that occur. It is also necessary to avoid physical activity.
Surgery
Surgical intervention for the presence of a cyst in teenage girls is very rarely prescribed. Doctors resort to it only in situations where there is a threat to the life or health of the patient. If there is an inflammatory process, additional antibiotics may be required, after which surgery may be prescribed.
Surgery for adolescents is prescribed in rare cases.
The procedure is carried out in cases where suppuration of the contents has occurred, there is torsion of the pedicle of the ovarian tumor, or spontaneous rupture of the capsule walls has occurred.
If surgical intervention is required, the cavity is removed along with its contents using standard excision or laparoscopy. In rare situations, it will be necessary to remove not only the cyst, but the ovary on which it is located.
Traditional methods of therapy
Any folk remedies that you plan to use to improve your condition must be agreed with your doctor. Gynecologists are against the use of such drugs in teenage girls, since their body reacts sensitively to any intervention.
Peony tincture is diluted in water and drunk twice a day.
If the attending physician approves the use of traditional methods, then to slow down the growth of the cyst, you can use the usual peony tincture. 1 tsp. The product is diluted in a glass of water and drunk twice a day. The course lasts 10 days.
A combination of honey and viburnum juice gives a good effect. They are mixed in equal proportions and consumed 1 - 2 tablespoons daily for a month.
Preventive measures
If the development of a neoplasm on the ovary is associated with hormonal imbalances, it is difficult to prevent the development of a cyst. However, there are general recommendations that will reduce the risk of compaction:
- Regular examinations by a gynecologist are required. Scheduled visits to the doctor will allow you to identify the tumor at an early stage; Regular examinations with a gynecologist are required.
- During adolescence, it is important to provide the child with a stable emotional state. Parents should ensure that the girl does not experience stress and try to protect her from possible negativity;
- it is necessary to monitor any changes in well-being. When inflammatory processes are detected, they must be eliminated;
- During adolescence, physical activity should be present, but overload should be avoided. Due to hormonal changes, a large load is placed on the body and there is no need for unnecessary activity;
- Avoid taking hormonal medications. Use them only as prescribed by your doctor;
- Parents need to monitor whether the child has bad habits. In adolescence, they can lead to irreparable consequences.
A cyst on the ovary can be dangerous to a girl’s health during adolescence. Most often, the tumor resolves spontaneously, but sometimes leads to the development of complications.
If the problem is ignored, adhesions may form over time, causing infertility in the patient. To treat a benign tumor, hormonal therapy and, less commonly, surgery are prescribed.
In rare cases, it may be necessary to remove not only the capsule, but also the ovary itself.
Source: https://kistateka.ru/yaichniki/u-devochki-podrostka
Complications
If an ovarian cyst is left untreated during adolescence, there is a high probability of developing serious complications, some of which can even be fatal. In advanced cases, suppuration of the neoplasm occurs, as a result of which the liquid contents change their structure and volume.
Sometimes adhesions appear, leading to infertility. The most common consequence of a cystic defect is pedicle torsion. This condition causes nausea with vomiting and severe pain in the lower abdomen in the sick teenager, which is not relieved by analgesics.
When the formation ruptures, peritonitis develops, accompanied by acute pain in the appendages, fever, and loss of consciousness. Malignant degeneration of the pathological process occurs extremely rarely.
During malignancy, the formation intensively increases, as a result of which it compresses neighboring organs. In addition to the lack of timely treatment, complications are caused by damage to the reproductive system, excessive physical exertion, and sexual intercourse at an early age.
Pain during menstruation
The overall cycle is assessed based on how the tumor behaves during menstruation. Usually a woman feels pain before the arrival of planned blood secretion. During menstruation, the discomfort only intensifies. The stomach begins to ache and pull.
Active sex often makes the discomfort permanent and provokes torsion of the leg or rupture of the ovary itself. During menstruation, the cyst puts pressure on the paired gland. If its size is large, the patient feels discomfort in the intestines and bladder.
After menstruation, the tumor sometimes disappears on its own and is no longer visible on ultrasound.